微納米多孔不銹鋼表面高效吸附活性生物大分子
余占江 陳永強(qiáng) 楊曉達(dá),*
(1北京大學(xué)藥學(xué)院化學(xué)生物學(xué)系,天然和仿生藥物國家重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室,北京100191;2樂普(北京)醫(yī)療器械股份有限公司,北京100022)
1 Introduction
In the efforts for discovery of novel biomaterials in medical devices and implants,improving the biocompatibility and mechanical performance has always been the two primary issues.The next generation of biomaterials has been proposed to be smart or biomimetic materials.A key challenge in designing smart biomaterials is to modify material surface with functional biological or synthetic molecules/nanoparticals to mimic the extracellular matrix(ECM)of natural tissue.1
Among biopolymers,alloys,and ceramics,stainless steel(AISI 316L)is one of the most prominent available commercial materials for medical devices,2-4e.g.,cardiovascular stents,bone,and dental implants.The 316 L stainless steel exhibits long-standing performance and good biocompatibility,2which make stainless steel implants safe and efficient treatment option over the much more expensive anecdotal superior titanium alloys.5
One major limitation for stainless steel is the lack of chemically active groups on the metal surface for covalently immobilization of functional molecules.A great deal of efforts have been made to engineer the metal surface with a variety of organic and inorganic coatings,for instance,heparin hydrogel,6carbohydrates,7polydopamine,8,9poly(ethylene glycol)and various hydrophilic polymers,10-12peptides and peptide nanofiber,13-16polyelectrolyte micelles,17alkanethiol layers,18doped diamond-like carbon,19sputtered TiN/TiO2,20,21hydroxylapatite,22hydrothermal calcium nanocomposites,23and S-phase layers,24etc.On these bases,antibodies,vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF),VE-cadherin,thrombin inhibitor,and liposomes were covalently attached to the surface of metal implants.These works improved greatly the cytocompatibility of the materials,for instance,the pro-healing approach immobilized antibodies capturing endothelial progenitor cells(EPC)from circulation on the blood contact surface of the stents;25the stents were shown to significantly reduce the thrombosis by facilitating stent endothelialization.26,27However,the use of synthetic polymer matrixes was suggested negative for in-stent restenosis by some studies.25,28
Surface modification at the nanoscale was suggested to promote protein adsorption and cell adhesion.12,29-31Grafting the surface roughness and topography by electrochemical erosion29or ultrafast laser irradiation32has been investigated to improve cytocompatibility.A functionalized TiO2nanonodule-in-micropit smart titanium surfaces was shown to enhance osteoblast proliferation and differentiation while the micropitted surface actually inhibited osteoblast growth.20Comparing with mirror-polished stainless steel surfaces,nanostructured surfaces showed better adhesion and differentiation for osteoblastic cells.29It was found that cells responsed to surface energy and three dimensional(3D)patterns.31The 40-75 nm nanopores on 316L stainless steel enhanced fibroblast cell proliferation and signal transduction while~200 nm nanopore surfaces greatly attenuated.30However,the effects of micro/nano surface on adsorption of functional biological molecules for smart biomaterial have so far not been well investigated.
It has long been recognized that stainless steel surface can irreversibly adsorb proteins33-35but far less effective for functional protein immobilization than some noble metals,e.g.,gold that is most frequently used for immobilization of biomolecules.36,37Providing that micro/nano-structured surface of stainless steel can effectively adsorb active biomacromolecules,a novel polymer-free smart metal platform for developing new biomaterials,e.g.,stents,would be achieved.For this purpose,the present work investigated adsorption of antibodies and enzymes on micro/nanoporous 316L stainless steel in comparison with smooth and gold-coating stainless steel surfaces.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
316L stainless steel plates and stents were from Lepu Medical Technology Co.,Ltd.(Beijing).Mouse monoclonal antibody against human CD34 was from Biolegend(USA),FITC-labeled goat anti-mouse monoclonal antibody(FITC-IgG)and horseradish peroxidase conjugated goat anti-mouse immunoglobulins(HRP-IgG)from BD Biosciences(USA).4?,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole(DAPI,the purity≥99%),RPIM 1640,4?,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole,diaminobenzidine(DAB,the purity ≥99%)and tetramethylbenzidine(TMB,the purity≥99%)from Amresco(USA),L929 fibroblast and CD34 positive KG-1a cells were from American Type Culture Collection(ATCC,USA).Horse radish peroxidase(HRP,EC.1.11.1.7)and all other reagents of analytical grade were from Sigma-Aldrich(USA).
2.2 Preparation of 316L stainless steel surface
The polished 316L stainless steel plates(1.0 cm×1.0 cm)were cleansed with 20%hydrochloride acid for 10 h at room temperature and 75%ethanol for 15 min at 100 kHz ultrasonicator,the plates were dried in a stream of filtrated air.To produce a porous surface,the plates were acid-etched with 10%hydrochloride acid for 10 min in the assistance of 0.2 A,500 Hz electric current.For gold coating,the plates were either sputter-coated with gold or incubated with 5%H2AuCl4solution for 17 h at 37°C.All the treated metal plates were cleaned finally by 75%ethanol as described above.Then the products were observed and analyzed with a S-4800 scanning electron microscope(SEM,Hitachi,Japan).
2.3 Adsorption of anti-CD34 antibodies or HRP on metal surface
The metal plates were incubated for 30 min at 37°C with antihuman CD34 monoclonal antibody(0-200 μg·mL-1)or HRP(0-0.5 mg·mL-1)in 0.1 mmol·L-1of carbonate sodium buffer,pH 9.6.Then the plates were washed three times with 10 mmol·L-1phosphate buffered saline(PBS,pH 7.4)containing 0.2%Tween-20.
To investigate the effect of surfactant on protein adsorption,the cleaned plates were pre-incubated with 0.5%-5%Tween-20 before incubation with 200 μg·mL-1of monoclonal antibody against human CD34 or 0.5 mg·mL-1of HRP as described above.
2.4 Analysis of protein adsorption on metal surface
For analysis of the amount of HRP adsorbed on the metal surface,38the treated plate was put into a 12-well cultural plate and then 0.8 mL of colorization solution containing 0.1 mmol·L-1of tetramethylbenzidine(TMB)was added and incubated for 15 min at 37°C.The reaction was terminated with 0.5 mL of 1 mol·L-1H2SO4and the absorbance at 450 nm was measured with a microplate reader(ASCENT,Labsystems Oy,Finland).
For analysis of the amount of anti-CD34 antibodies on the metal surface with an ELISA assay,the plates were first blocked with 10%bovine serum albumin(BSA)in 10 mmol·L-1phosphate buffered saline(pH 7.4)for 24 h at 4°C,then incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody(BD Biosciences,USA)diluted(1:500)in 10 mmol·L-1PBS,pH 7.4 for 1 h at 37°C.After three-times washing,colorization with TMB substrate was conducted as described above.
2.5 Wettability assessment
For comparison of the wettability,the contact angles for metal plates were measured with an optical contact angle instrument(DSA100,Kruss Inc.,Germany).
2.6 In vitro cell capturing activity of anti-CD34 antibodies-coated 316L stainless steel stents
To determine the specific activity of antibody coated on stainless steel surface,the in vitro cell capturing activity of micro/nanoporous stents with or without antibody coating were incubated at 37 °C with cell suspension(1×106mL-1,either CD34+KG-1a cells or fibroblast L929 cells)for 1 h.These cells were previously stained with 50 μg·mL-1DAPI fluorescent dye as described in literature.39After rinsing three times with PBS,the stents were photographed and analyzed on a Fluorescence Microscope equipped with an image analyzing program(BX41,OLYMPUS,Japan).
2.7 Statistical analysis
All results were expressed as mean±standard error of each sample.Each experiment was repeated independently three times.One-way ANOVA was conducted using an OriginTM8.0 program(Microcal,USA)for data comparison.A value of p<0.05 was considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 SEM observation on 316L stainless steel surface
The surface of various 316L stainless steel plates were observed under a microscopy(Fig.1).Although sputter-gold plates showed yellow color,these plates exhibited a similar shining smooth surface to that of polished metal plate(Fig.1(A,B)).Chemically deposited-gold plates(Fig.1(C))showed a tarnished but plainer surface with a lightly golden color when compared with the sputter-gold plates.In contrast,the porous plates by anodization treatment(Fig.1(D))showed a rough surface.When taking a closer look on SEM(Fig.2),the plates showed a microtexture that is full of irregular pores with an average size of(400±160)nm.The surface roughness was estimated and the contour arithmetic mean deviations(Ra)were 0.007,0.005,0.013,and 0.033 μm for polished stainless steel plate,sputter-gold plate,chemically deposited-gold plate and porous plate,respectively.
3.2 Protein adsorption on surface of metal plates
For assessment of protein adsorption,an enzyme(HRP)and a mouse monoclonal antibody against human CD34 were used as the representative of functional biological macromolecules.The physical data of HRP and antibody are listed in Table 1.
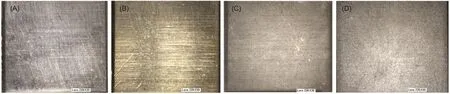
Fig.1 Microscopic images(30×)of surfaces of polished stainless steel plate(A),sputter-gold plate(B),chemically deposited-gold plate(C),and porous plate by anodization treatment(D)
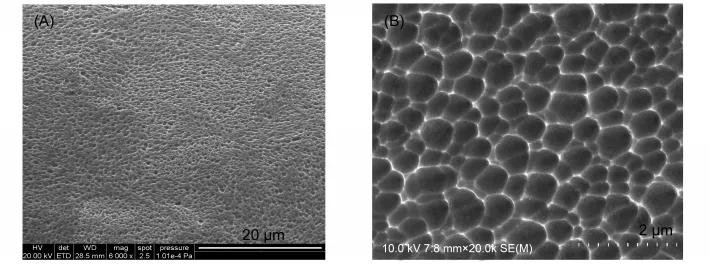
Fig.2 Scanning electron microscope(SEM)images of the surface of porous stainless steel plate by anodization treatment
Adsorption of HRP on various stainless steel plates were shown in Fig.3(A).The amount of HRP,expressed as enzymatic activity,increased with enzyme concentrations in solution.Polished plates and gold-coated plates exhibited similar extents of enzyme adsorption while porous plate adsorbed most amount of HRP than the other three plates.
For antibody(monoclonal anti-CD34 antibodies)adsorption(Fig.3(B)),polished stainless steel plates hardly adsorb antibodies.Chemically deposited-gold plates adsorbed a few with increase of antibody concentration in solution.The sputter-gold plates could most effectively adsorb antibody in a concentration-dependent manner.The porous plates exhibited a similar capacity of antibody adsorption as the sputter-gold plate,however,with a saturation concentration.The maximal amount of antibody adsorption on porous plates was calculated to be ~1200 ng·cm-2according to a calibration method described previously.38
3.3 Effect of surfactant on protein adsorption
As shown in Fig.4,pretreatment of metal plates by surfactant Tween-20 could significantly reduce antibody adsorption almost by half;Herein,the porous plates exhibited a similar effect with the sputter-gold plates.However,Tween-20 did not affect adsorption of HRP on both metal surfaces.
3.4 Wettability of metal plates upon protein adsorption
Surface wettability was thought to be one important factor tuning cell adhesion and protein adsorption31,40,41and also closely related with the adsorbed amount of proteins.42The results of water contact angles of the plates before and after protein adsorption were shown in Fig.4.It is noted that porous treatment and gold coating barely reduced the contact angles.However,adsorption of protein can significantly increase the wettability of the metal surface.Although on the porous plate,protein adsorption produced the best wetness surface,nevertheless,the difference between the plates was far less than that between the protein species.This indicated that change of surface wettability for metal plates is more dependent on the adsorbed protein.
3.5 Cell capture capacity of antibodies adsorbed tomicro/nanoporous 316L stainless steel stents
In smart biomaterials,antibodies are used to selectively attach target cells(e.g.,stem cell or progenitor cells)to form mimetic tissue on the implants in situ.To test the efficiency and the selectivity of the antibodies immobilized,we tested the cellcapture capacity of porous metal stents coated with anti-CD34 mouse monoclonal antibodies.The results are shown in Fig.5 and Fig.6.For CD34 negative L929 fibroblast cells,bare porous metal surface caught a few cells(~9844 cells·cm-2);while the antibody-coated metal surface held a little more(~11593 cells·cm-2),probably due to better wettability after antibody coating.For CD34 positive KG-1a cells,bare porous metal surface caught much fewer amount(~3929 cells·cm-2)than L929 cells.This is conceivable because fibroblasts usually have higher adhesive capacity.Remarkably,the antibody-coated metal surface caught almost ten folds of cells(~36256 cells·cm-2).These results indicated the antibody can remain high efficiency and specificity on the micro/nanoporous sur-face of stainless steel.

Table 1 Physical data of tested proteins
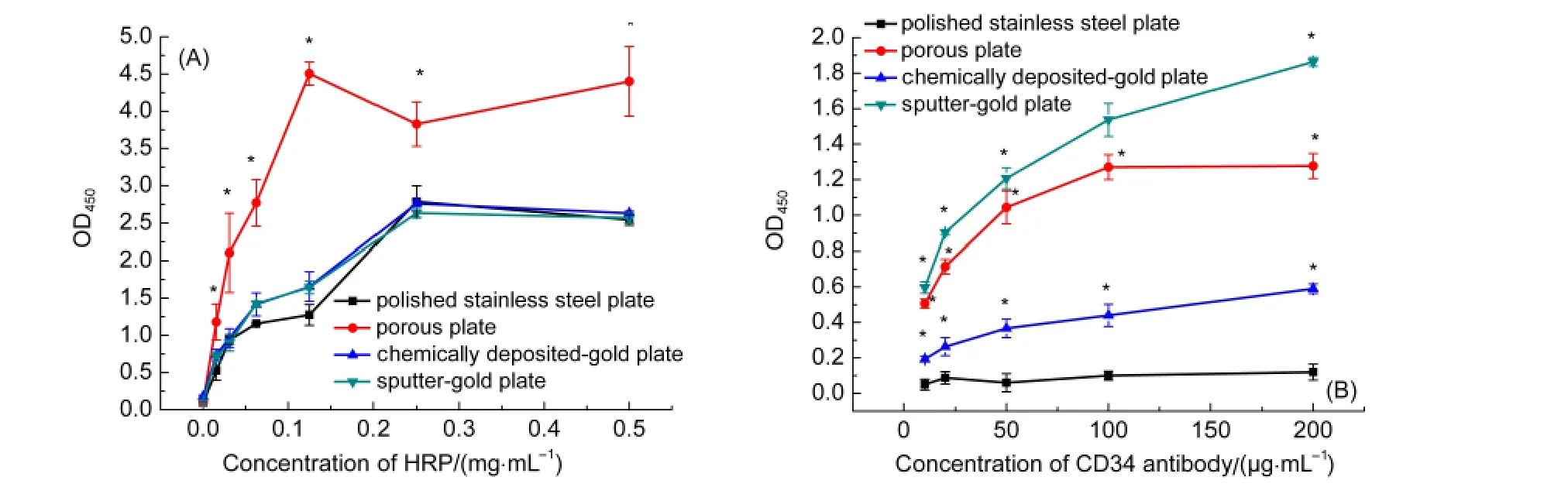
Fig.3 Adsorption curves for HRP(A)and mouse monoclonal antibodies against CD34(B)on 316Lstainless steel plates variously treated as described above
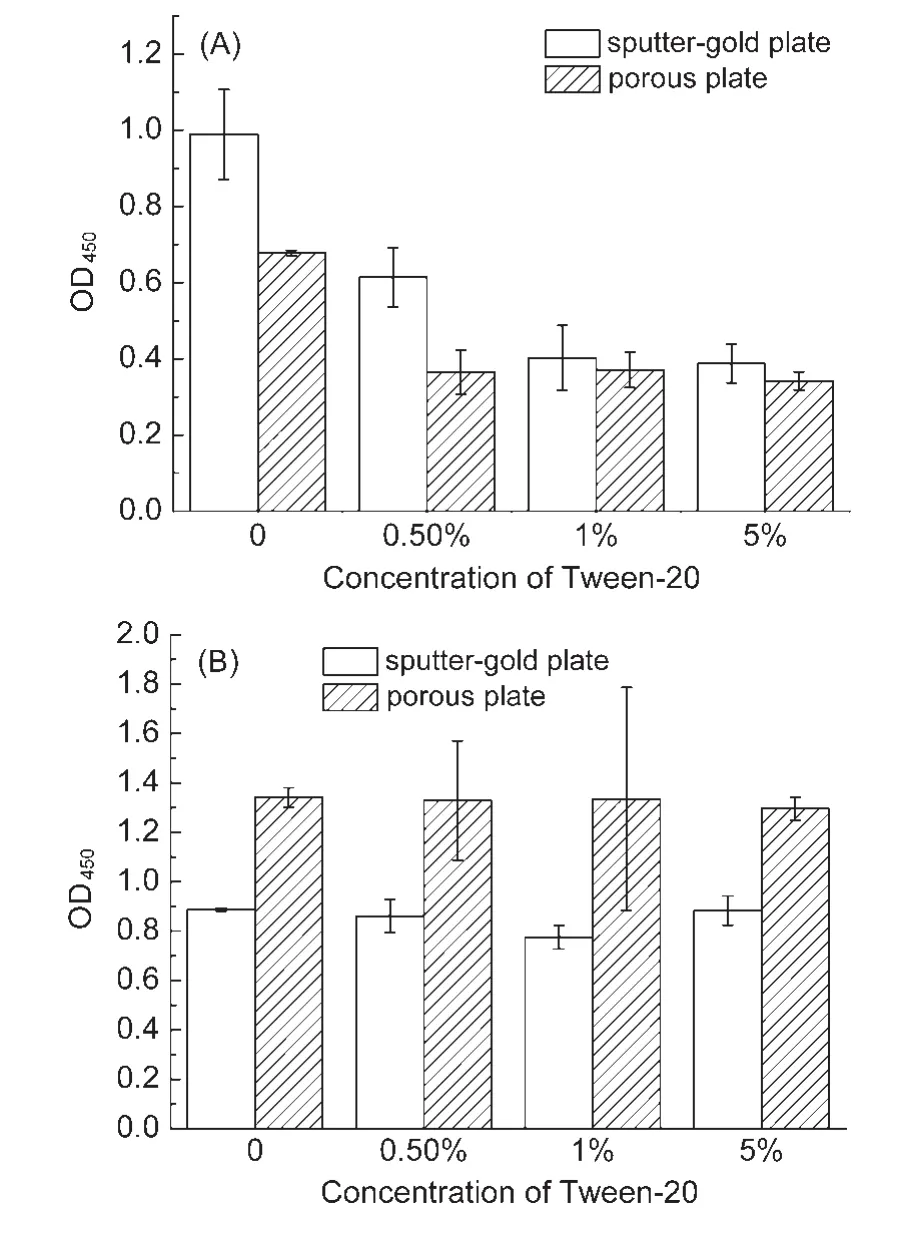
Fig.4 Effect of surfactant on antibody(A)and horse radish peroxidase(B)adsorption on porous and sputter-gold stainless steel plates
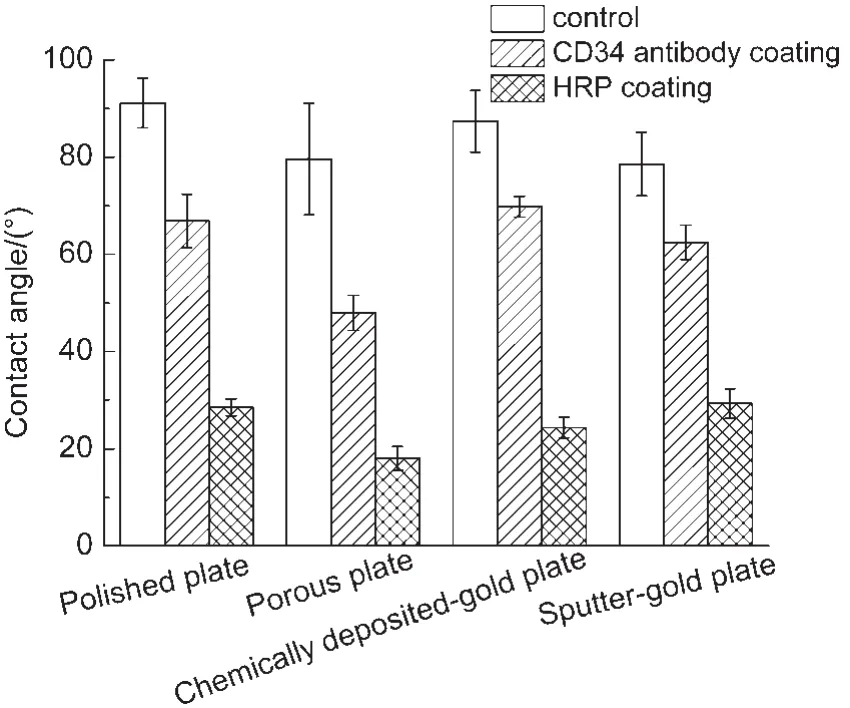
Fig.5 Contact angles of various 316Lstainless steel plates before and after adsorption of proteins(HRPor mouse monoclonal antibodies)
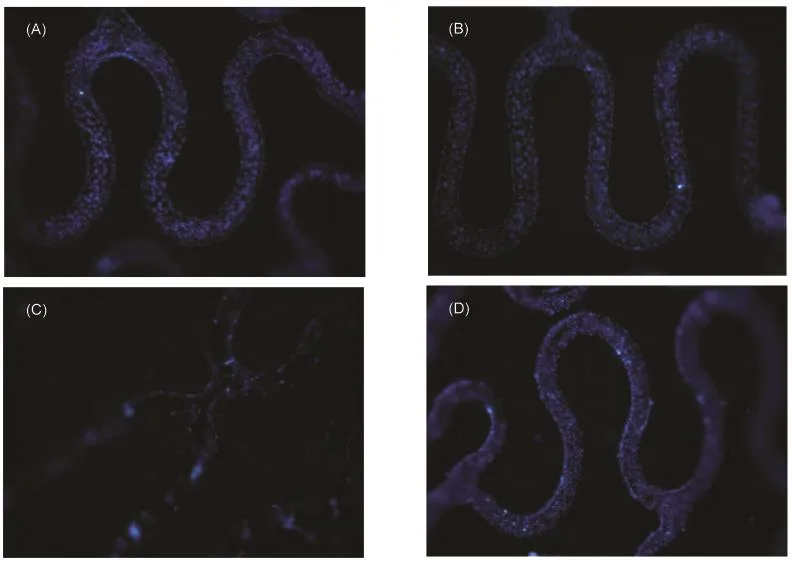
Fig.6 Fluorescence microscopic images(40×)of CD34 positive or negative cells adhesive to micro/nanoporous 316Lstainless steel stents
4 Discussion
For effective immobilization of functional biological molecules on surface of biomaterials,the amount of biomolecules,the stability of immobilization,and the residue activity are the key concerns.Therefore,most methods use covalent bonds to attach biomolecules10,43,44and in this way modification of metal surface with organic polymers or inorganic particles with active groups(e.g.,―OH,―CHO,―COOH,―NH2,etc.)would be necessary.
In the present work,we tested the efficiency of direct physical adsorption of antibodies and enzymes on stainless steel surface by making use of micro/nano structures with an aim to develop novel smart metal implant,e.g.,prohealing stents.The experimental results indicate that the stainless steel with micro/nano texture can high-efficiently adsorb biomacromolecules with desired biological activity.
First,the micro/nanoporous stainless steel surface adsorbed high amount of proteins(Fig.3),which is close to(for antibodies)or even more(for HRP)than those attached to sputter-gold surface.Gold can form coordination bond with―SH of proteins or adsorb protein via strong van der Waals interactions.36Gold surface is well-known in biomedical and bioanalytical applications for immobilization of protein or even protein particles.37Herein,the protein adsorption capacity of the porous stainless steel surface is shown to be at least comparable with the gold surface that is much more expensive.
The reasons for high protein adsorption capacity for the porous stainless steel surface may lie on the followings:(i)the porous plates exhibited much rougher surface.The surface roughness is one key factor for molecular adsorption because the rough surface has bigger external surface area and pocket effect supports more protein loading.45,46In fact,the amount of HRP adsorption was by and large with the surface roughness(Fig.3(A));(ii)formation of protein multilayers by surface-induced aggregation as observed previously on stainless steel microparticles;34,47(iii)the monoclonal antibody showed different adsorption profile from that of HRP.The molecular size of monoclonal antibody(~15 nm)is larger than that of HRP(~6 nm);however,considering the pore size(~400 nm)of the metal plate,this size difference is too small to explain the adsorption profile.The mechanism of interaction between protein molecules with porous surface is worthwhile to be investigated further.
Second,the protein attached on the porous stainless steel surface is stable.The experimental results showed that adsorption treatment with 10%BSA or 0.2%Tween-20 solution could not remove the enzymes/antibodies from the metal plate,which agrees with that stainless steel-protein interaction is strong48and protein adsorption to stainless steel could be irreversible.34,47While pre-treatment with Tween-20 buffer could reduce antibody adsorption by half(Fig.4(A))but had no effects on HRP adsorption,possibly because of the interaction between the antibody and surfactant.
The wettability of the stainless steel has been proposed to be a predominant mechanism governing both protein adsorption and cell adhesion.40,41As shown in Fig.5,there was a great reduce of water contact angles upon antibody or HRP adsorption,indicating significant reduce of surface Gibbs free energy and suggesting a highly spontaneous and strong adsorption of antibody/HRP protein onto the surface like fibrinogen.49Several points are worthwhile to note here:(1)the wettability of HRP coated surfaces are much higher than that of antibody-coated surface,indicating that the wettability of protein-modified metal surface is primarily dependent on the properties of the protein rather than the nature of metal.Similar adsorption behavior of proteins at stainless steel-liquid interfaces has been observed previously;33(2)although the surface of gold-modified plates adsorbed more proteins than the stainless steel plates,however,the wettability of gold surface is apparently less.Since surface wettability is correlated to the transition of surface cytocompatibility from cell-phobic to cell-philic,31,41this result may suggest that the protein-engineered stainless steel surface could be better than gold for medical implants;(3)for the same type of metal surfaces,higher amount of protein adsorption gave higher wettability,which is consistent with previous observation.42
Third,many works have shown that due to the strong surface interaction,adsorption of protein(e.g.,fibrinogen and BSA)on 316L stainless steel could result in partial unfolding of proteins and significant changes in the secondary structure that occur predominantly within the first minute of adsorption.46,49This raises a question of whether the proteins directly on the metal surface can keep their biological activity and specificity.
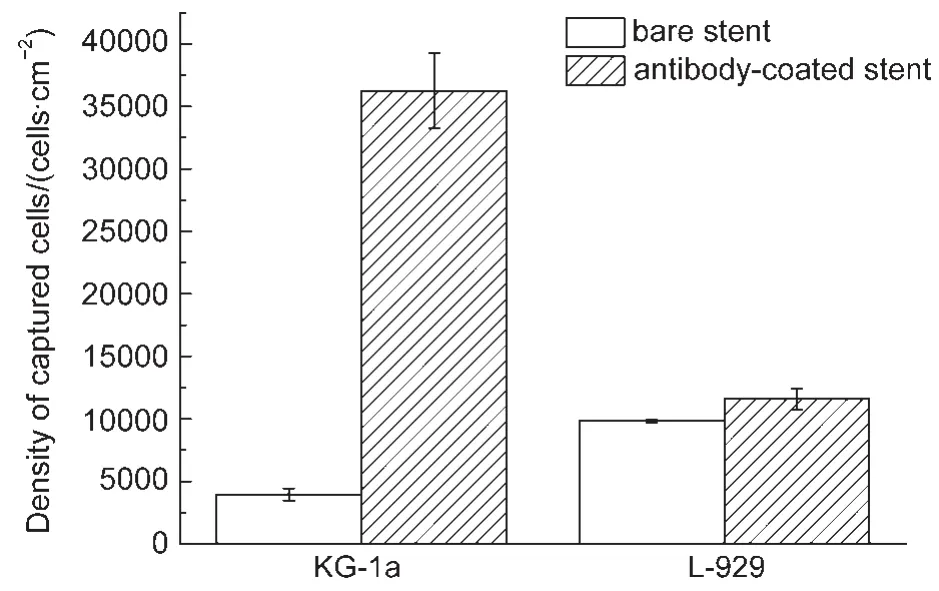
Fig.7 Quantatification of adhesion of CD34 positive(KG-1a)or negative(L-929)cells to bare or antibody-coated micro/nanoporous 316Lstainless steel stents
Fortunately,we observed that both HRP enzyme and antibodies retained high activity on the porous metal surface.Especially,as shown in Figs.6 and 7,stainless steel stents with micro/nanoporous surface coated with an anti-CD34 antibody can capture the target cells with both high efficiency and high specificity,which shall allow the development of novel polymer-free and economic smart biomaterials with stainless steel by direct protein adsorption on micro/nanoporous surface.
The reasons for antibodies and HRP to keep their specific activity remain further investigated.However,several possibilities may include:(1)unlike fibrinogen and BSA,HRP and antibodies are rigid global proteins and thus resist to conformational change;(2)the surface pocket of the porous metal may accommodate the enzyme/antibody molecules in favorable states similarly to the case of protease on microporous zeolite MCM-22;45(3)the proteins may form multilayers on the metal surface.Then the proteins in the upper layers may be less influenced by surface forces and then keep a full activity.Nonetheless,in the future studies,systematic exploration to the roles of 3D micro/nano morphology of metal surface on immobilization of a variety of biological macromolecules and the effects on their structure and biological functions are envisaged.
5 Conclusions
In summary,the present work investigated adsorption of two important functional biomolecules,i.e.,monoclonal antibodies and HRP enzymes,on micro/nanoporous 316L stainless steel in comparison with smooth and gold-coating stainless steel surfaces.Our results indicate that antibodies and enzymes can be loaded firmly on the micro/nanoporous surface in a large amount and these proteins retained high biological activity.In addition,the porous metal surface coated with functional protein exhibited much enhanced wettability,indicating a better cytocompatibility.The current work suggested novel polymerfree and economic smart biomaterials with stainless steel for biomedical applications.
(1) Holzapfel,B.M.;Reichert,J.C.;Schantz,J.T.;Gbureck,U.;Rackwitz,L.;Noth,U.;Jakob,F.;Rudert,M.;Groll,J.;Hutmacher,D.W.Adv.Drug Deliv.Rev.2013,65,581.doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.009
(2) Nagarajan,S.;Mohana,M.;Sudhagar,P.;Raman,V.;Nishimura,T.;Kim,S.;Kang,Y.S.;Rajendran,N.ACS Appl.Mater.Interfaces 2012,4,5134.
(3)Abdel-Fattah,T.M.;Loftis,D.;Mahapatro,A.J.Biomed.Nanotechnol.2011,7,794.doi:10.1166/jbn.2011.1346
(4) Hayes,J.S.;Richards,R.G.Expert.Rev.Med.Devices 2010,7,843.doi:10.1586/erd.10.53
(5)Weckbach,S.;Losacco,J.T.;Hahnhaussen,J.;Gebhard,F.;Stahel,P.F.Unfallchirurg 2012,115,75.doi:10.1007/s00113-011-2145-0
(6)Joung,Y.K.;You,S.S.;Park,K.M.;Go,D.H.;Park,K.D.Colloids Surf.B:Biointerfaces 2012,99,102.doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.10.047
(7) Slaney,A.M.;Wright,V.A.;Meloncelli,P.J.;Harris,K.D.;West,L.J.;Lowary,T.L.;Buriak,J.M.ACS Appl.Mater.Interfaces 2011,3,1601.doi:10.1021/am200158y
(8) Lionetto,S.;Little,A.;Moriceau,G.;Heymann,D.;Decurtins,M.;Plecko,M.;Filgueira,L.;Cadosch,D.J.Biomed.Mater.Res.A 2013,101,991.
(9)Yang,Z.;Tu,Q.;Zhu,Y.;Luo,R.;Li,X.;Xie,Y.;Maitz,M.F.;Wang,J.;Huang,N.Adv.Healthc.Mater.2012,1,548.doi:10.1002/adhm.201200073
(10)Kang,C.K.;Lim,W.H.;Kyeong,S.;Choe,W.S.;Kim,H.S.;Jun,B.H.;Lee,Y.S.Colloids Surf.B:Biointerfaces 2013,102,744.doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.09.008
(11) Caro,A.;Humblot,V.;Methivier,C.;Minier,M.;Salmain,M.;Pradier,C.M.J.Phys.Chem.B 2009,113,2101.doi:10.1021/jp805284s
(12)Kang,C.K.;Lee,Y.S.J.Mater.Sci.Mater.Med.2007,18,1389.doi:10.1007/s10856-006-0079-9
(13) Ceylan,H.;Tekinay,A.B.;Guler,M.O.Biomaterials 2011,32,8797.doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.018
(14) Davis,E.M.;Li,D.Y.;Irvin,R.T.Biomaterials 2011,32,5311.doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.04.027
(15) Ignatova,M.;Voccia,S.;Gabriel,S.;Gilbert,B.;Cossement,D.;Jerome,R.;Jerome,C.Langmuir 2009,25,891.doi:10.1021/la802472e
(16)Imamura,K.;Kawasaki,Y.;Awadzu,T.;Sakiyama,T.;Nakanishi,K.J.Colloid Interface Sci.2003,267,294.doi:10.1016/S0021-9797(03)00700-8
(17) Falentin-Daudre,C.;Faure,E.;Svaldo-Lanero,T.;Farina,F.;Jerome,C.;Van De Weerdt,C.;Martial,J.;Duwez,A.S.;Detrembleur,C.Langmuir 2012,28,7233.doi:10.1021/la3003965
(18) Harvey,J.;Bergdahl,A.;Dadafarin,H.;Ling,L.;Davis,E.C.;Omanovic,S.Biotechnol.Lett.2012,34,1159.doi:10.1007/s10529-012-0885-8
(19) Secker,T.J.;Herve,R.;Zhao,Q.;Borisenko,K.B.;Abel,E.W.;Keevil,C.W.Biofouling 2012,28,563.doi:10.1080/08927014.2012.698387
(20) Horia,N.;Iwasaa,F.;Uenoa,T.;Takeuchib,K.;Tsukimuraa,N.;Yamadaa,M.;Hattorib,M.;Yamamotoc,A.;Ogawaa,T.Dental Materials 2010,26,275.doi:10.1016/j.dental.2009.11.077
(21)Subramanian,B.;Ananthakumar,R.;Kobayashi,A.;Jayachandran,M.J.Mater.Sci.Mater.Med.2012,23,329.doi:10.1007/s10856-011-4500-7
(22) Subramanian,B.;Dhandapani,P.;Maruthamuthu,S.;Jayachandran,M.J.Biomater.Appl.2012,26,687.doi:10.1177/0885328210377534
(23)Valanezahad,A.;Ishikawa,K.;Tsuru,K.;Maruta,M.;Matsuya,S.Dent.Mater.J.2011,30,749.doi:10.4012/dmj.2010-153
(24) Buhagiar,J.;Bell,T.;Sammons,R.;Dong,H.J.Mater.Sci.Mater.Med.2011,22,1269.
(25)Wendel,H.P.;Avci-Adali,M.;Ziemer,G.Int.J.Cardiol.2010,145,115.doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.06.020
(26) Granada,J.F.;Inami,S.;Aboodi,M.S.;Tellez,A.;Milewski,K.;Wallace-Bradley,D.;Parker,S.;Rowland,S.;Nakazawa,G.;Vorpahl,M.;Kolodgie,F.D.;Kaluza,G.L.;Leon,M.B.;Virmani,R.Circ.Cardiovasc.Interv.2010,3,257.doi:10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.109.919936
(27) McGuigan,A.P.;Sefton,M.V.Biomaterials 2007,28,2547.doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.01.039
(28) Rossi,M.L.;Zavalloni,D.;Gasparini,G.L.;Mango,R.;Belli,G.;Presbitero,P.Int.J.Cardiol.2010,141,e20.
(29) Le Guehennec,L.;Martin,F.;Lopez-Heredia,M.A.;Louarn,G.;Amouriq,Y.;Cousty,J.;Layrolle,P.Nanomedicine 2008,3,61.doi:10.2217/17435889.3.1.61
(30) Pan,H.A.;Liang,J.Y.;Hung,Y.C.;Lee,C.H.;Chiou,J.C.;Huang,G.S.Biomaterials 2013,34,841.doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.078
(31) Ranellaa,A.;Barberogloua,M.;Bakogiannia,S.;Fotakisa,C.;Stratakisa,E.Acta Biomaterialia 2010,6,2711.doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2010.01.016
(32) Nayak,B.K.;Gupta,M.C.Optics and Lasers in Engineering 2010,48,940.doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2010.04.010
(33) Fukuzaki,S.;Urano,H.;Nagata,K.J.Ferment.Bioeng.1995,80,6.doi:10.1016/0922-338X(95)98168-K
(34) Bee,J.S.;Chiu,D.;Sawicki,S.;Stevenson,J.L.;Chatterjee,K.;Freund,E.;Carpenter,J.F.;Randolph,T.W.J.Pharm.Sci.2009,98,3218.
(35)Sakiyama,T.;Aya,A.;Embutsu,M.;Imamura,K.;Nakanishi,K.J.Biosci.Bioeng.2006,101,434.doi:10.1263/jbb.101.434
(36)Hagiwara,T.;Sakiyama,T.;Watanabe,H.Langmuir 2009,25,226.
(37) He,C.X.;Yuan,A.P.;Zhang,Q.L.;Ren,X.Z.;Li,C.H.;Liu,J.H.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2012,28,2721.[何傳新,袁安朋,張黔玲,任祥忠,李翠華,劉劍洪.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2012,28,2721.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB201207191
(38)Zhang,F.;Guo,W.;Yu,Z.;Wang,Y.C.Chin.J.Pharm.Anal.2011,31,862.
(39) Berry,J.L.;Santamarina,A.;Moore,J.E.,Jr.;Roychowdhury,S.;Routh,W.D.Ann.Biomed.Eng.2000,28,386.doi:10.1114/1.276
(40) Hao,L.;Lawrence,J.Proc.Inst.Mech.Eng.H 2006,220,47.doi:10.1243/095441105X68999
(41) Mikulewicz,M.;Chojnacka,K.Biol.Trace.Elem.Res.2011,142,865.doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8798-7
(42) Matsumura,H.;Saburi,M.Colloids Surf.B:Biointerfaces 2006,47,146.doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2005.12.004
(43) Mourtas,S.;Kastellorizios,M.;Klepetsanis,P.;Farsari,E.;Amanatides,E.;Mataras,D.;Pistillo,B.R.;Favia,P.;Sardella,E.;d?Agostino,R.;Antimisiaris,S.G.Colloids Surf.B:Biointerfaces 2011,84,214.doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.01.002
(44) Muller,R.;Abke,J.;Schnell,E.;Macionczyk,F.;Gbureck,U.;Mehrl,R.;Ruszczak,Z.;Kujat,R.;Englert,C.;Nerlich,M.;Angele,P.Biomaterials 2005,26,6962.doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.05.013
(45)Liu,P.;Xing,G.W.;Li,X.W.;Ye,Y.H.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2010,26,1113.[劉 平,邢國文,李宣文,葉蘊(yùn)華.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2010,26,1113.]doi:10.3866/PKU.WHXB20100448
(46) Omanovic,S.;Roscoe,S.G.J.Colloid Interface Sci.2000,227,452.doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.6913
(47) Bee,J.S.;Davis,M.;Freund,E.;Carpenter,J.F.;Randolph,T.W.Biotechnol.Bioeng.2010,105,121.doi:10.1002/bit.v105:1
(48) Hedberg,Y.S.;Killian,M.S.;Blomberg,E.;Virtanen,S.;Schmuki,P.;Odnevall Wallinder,I.Langmuir 2012,28,16306.doi:10.1021/la3039279
(49)Desroches,M.J.;Omanovic,S.Phys.Chem.Chem.Phys.2008,10,2502.doi:10.1039/b719371h

