Dynamic stabilization of atomic ionization in a high-frequency laser field with different initial angular momenta
Di-Yu Zhang(張頔玉) Yue Qiao(喬月) Wen-Di Lan(藍(lán)文迪) Jun Wang(王俊)Fu-Ming Guo(郭福明) Yu-Jun Yang(楊玉軍) and Da-Jun Ding(丁大軍)
1Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy(Jilin University),Changchun 130012,China
Keywords: stabilization of atomic ionization,atomic initial states
1. Introduction
With the development of ultrafast laser technology, the amplitude of a laser electric field has reached the Coulomb field intensity that is felt by electrons in atoms. Many nonlinear phenomena can be observed for an atom irradiated by a strong laser pulse, such as high-order harmonic generation,[1–9]above-threshold ionization,[10–15]nonsequential double ionization,[16,17]etc. The basis of these phenomena is the ionization of the bound-state electrons in the atoms,which interact with the driving laser.
When the single-photon energy of the driving laser is smaller than the ionization energy of the atomic initial state, the ionization mechanism transitions from multiphoton ionization[18]to tunneling ionization[19]and even abovebarrier ionization,[20]as the intensity of the driving laser increases, and the corresponding ionization probability will increase gradually. When the single-photon energy of the driving laser is greater than the ionization energy of the atomic initial state,the ionization stabilization phenomenon could be observed[21–25]particularly in a high-frequency laser field. In this case, the atomic ionization probability increases with the driving laser in the lower-intensity region. By contrast,when the laser intensity reaches a certain value, the atomic ionization probability will decrease as the laser intensity further increases. This ionization stabilization phenomenon was first discovered by Gersten[26]and Gavrila[27,28]when they investigated the strong-field ionization of a hydrogen atom in laser fields, and explained within the Floquet theory based on the Kramers–Henneberger(K–H)transformation.[29,30]Using the K–H transformation, the interaction between the laser field and the atom can be regarded as a time-dependent potential function. In a high frequency laser electric field, the movement of electrons can be represented by the lower eigenstates of the time dependent potential. In general,the laser pulse has an envelope;thus,using the multimode Floquet theory for investigating the stabilization is necessary. Recently,Guoet al.theoretically studied the ionization of an atom under ionization stabilization conditions and found the multipeak structures of the obtained photoelectron spectra,which were assigned to the interference between the ionized electrons from the rising and falling parts of the laser electric field.[31]
Most of the atomic ionization stabilization phenomena were investigated in linearly polarized (LP) laser fields,and only a few studies have been conducted on the atomic ionization stabilization caused by circularly polarized laser fields.[23,32–34]Atomic or molecular photoionization may exhibit some new features caused by circularly polarized laser fields,which are absent in the case of linear polarization. Pont and Gavrila[28]found that the ionization stabilization phenomenon of a hydrogen atom can also occur when the laser field is circularly polarized. Liang[32]theoretically investigated the dynamic interference of a hydrogen atom in an intense circularly and LP high-frequency XUV pulses. The dependence of ionization stabilization on laser polarization was studied theoretically[33,34]and experimentally[35]for atoms with a magnetic quantum number of zero. Another notable feature is the dependence of the strong-field ionization rate on the sign of the magnetic quantum number with regard to the rotation direction of the applied laser field.[36]Recently, the ionization of an atom with different initial angular momenta in an infrared laser field was investigated.[37]The result indicated that in the same driving laser pulse,remarkable differences in the ionization probability of atoms with different initial angular momenta could be observed because of the nonadiabatic effect.
With the rapid development of advance free-electron lasers,[38]particularly the polarization-controlled free-electron laser,[39]the intense high-frequency light interaction with atoms/molecules has attracted considerable attention as these free-electron laser sources have provided a powerful tool for atomic and molecular physics to extend the nonlinear interaction region.In the present work,we studied the effect of initial states with different angular momenta on the atomic ionization stabilization in such intense high-frequency laser fields.In addition, we calculated the ionization of an atom with different initial orbital angular momenta in the high-frequency laser field using the numerical solution of the time-dependent Schr¨odinger equation. The results showed that the atomic ionization stabilization occurs in the linearly and circularly polarized laser pulses, but the characteristics of the ionization stabilization are different for laser pulses with different polarizations and for atoms with a certain initial state angular momentum. Thus,we calculated the evolution of time-dependent wave packets to explain this phenomenon. Unless otherwise stated,atomic units are used throughout this paper.
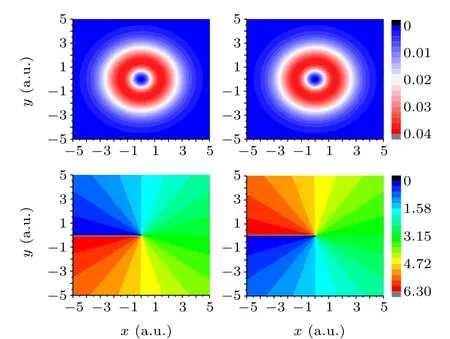
Fig.1. (a)Electronic density of the initial state with m=-1. (b)The phase of the initial state with m=-1. (c)The electronic density of the initial state with m=+1. (d)The phase of the initial state with m=+1.
2. Theory and models
In investigating atomic ionization in a strong laser electric field,calculating the time-dependent electronic wave function of the atom irradiated by the laser pulse is necessary. Therefore,we must solve the time-dependent Schr¨odinger equation of the bound electron in the laser field
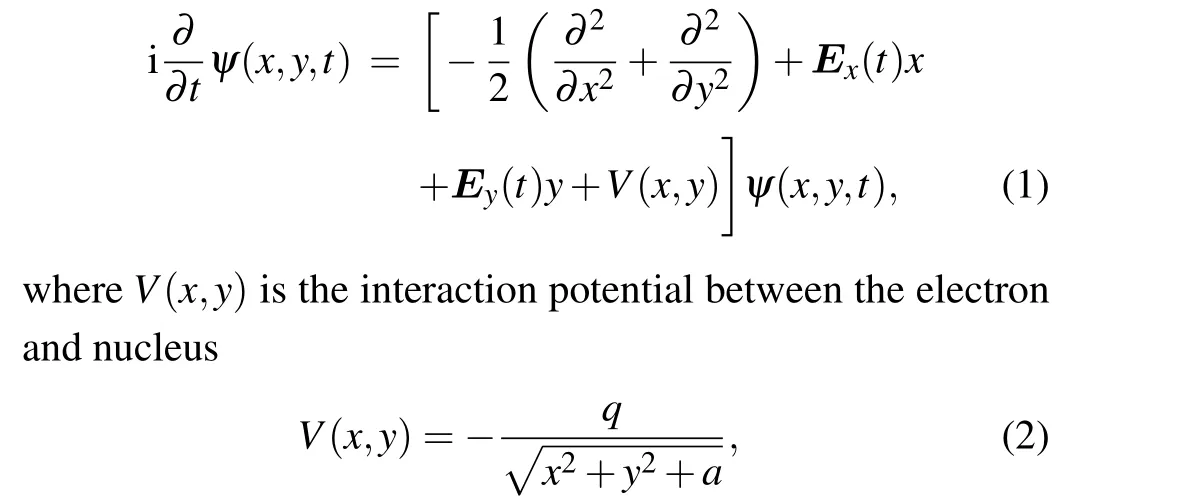
whereqandaare the soft-core parameters. In this paper,three initial states with the same energy (-0.579, the ground state energy of the argon atom) were selected, and the magnetic quantum numbers were 0(a=0.3893,q=1.0)and±1(a=1.0,q=2.0715).Ex(t)andEy(t)are thexandycomponents of the laser field,respectively. When the driving laser pulse is LP,the following equation is calculated:
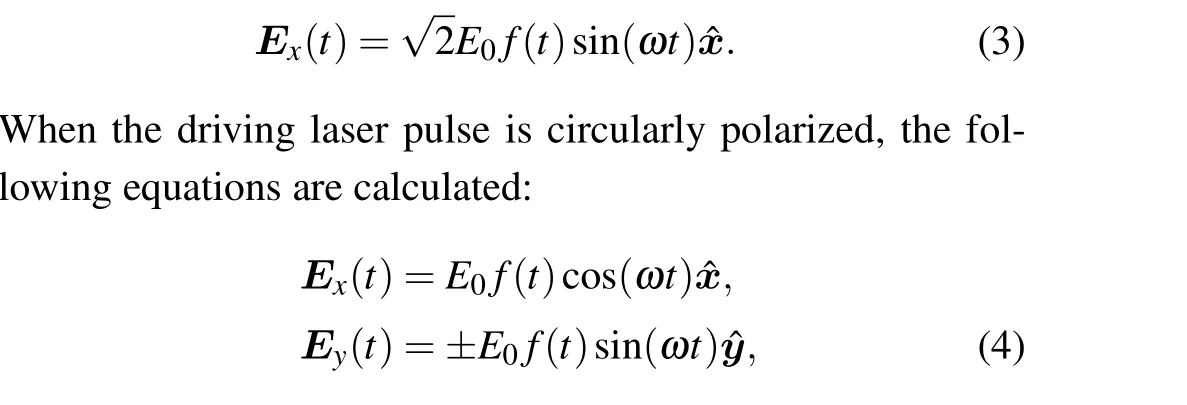
where “+” and “-” correspond to the left-handed and righthanded circularly polarized laser fields, respectively.E0andωare the electric field peak amplitude and center frequency of the laser pulse, respectively. The laser pulse envelopef(t)=sin(πt/nT)2was used,n=10,ω=1 andT=2π/ωis the optical cycle of the pulse. The time-dependent equation has no analytical solution; one can solve it through a numerical scheme. In this work, the finite element discrete variable representation[40]method was used to calculate the time-dependent wave function of the system. The range of the computational grid in thexandydirections was-200 to 200,and 1400 elements with four points in each element were adopted in the calculation. The Lanczos method was used as the time propagation scheme.[41]The dimension of the Hamiltonian matrixhin the Krylov subspace was 5×5,and the time step of the calculation was 0.1. In the case of the maximum intensity of driving laser pulses, we checked the convergence of ionization stabilization by changing the spatial boundary,time interval,and laser intensity. Relative errors of the calculation results with different parameters in the two cases were less than 10-3,which confirmed the reliability of our numerical simulation
By projecting the time-dependent wave functionψ(x,y,t)at the end of the laser pulse on the eigenstate wave function,the probability of the atom with different eigenstates under the action of the laser field can be obtained. Using the eigenstate projectionci(t)=〈ψi(x,y)|ψ(x,y,t)〉where the eigenenergy is less than 0,the ionization probability of the atom is obtained by
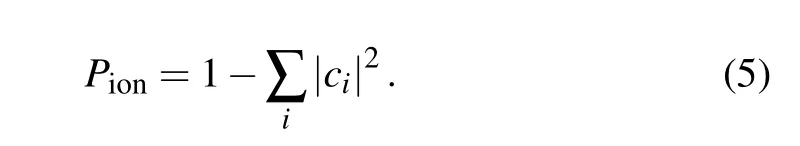
In the calculation, the solution of each eigenstate of the system was obtained from the transformation of the equation into a one-dimensional problem using the scheme of the variable separation in polar coordinates.[42]
We presented the electron density distribution and phase of the initial state wave function with a magnetic quantum number of±1 calculated from the scheme shown in Fig.1.For them=-1 andm=+1 state, the spatial distribution of the electron density is the same,but their phases are opposite. For them=-1 state, the phase gradually increases in the clockwise direction[as shown in Fig.1(b)]and the electron rotates clockwise. For them=+1 state,its phase gradually increases in the counterclockwise direction[as shown in Fig.1(d)]and the electron rotates counterclockwise.
3. Results and discussion
This work aimed to explore the ionization stabilization of atoms with different orbital angular momenta irradiated by a high-frequency laser field. After obtaining the initial state of the system,we calculated the ionization probability that varies with the laser intensity of the atomic initial state and the orbital angular momentumm=-1 irradiated by left-handed circularly polarized (LCP), LP, and right handed circularly polarized(RCP)laser pulses. For the same laser intensity,the energies of the laser pulse with different polarizations are the same.The ionization probability varying with the peak amplitude of the electric field is presented in Fig.2. In the calculation,the range of the peak amplitude of the laser electric was from 0.1 to 3.0. As shown in Fig.2, the ionization probabilities of the atom irradiated by different polarized lasers increase rapidly in the low-laser-intensity region with the increase in laser pulse intensity. By contrast,when the pulse intensity reaches a certain value,the ionization probability does not continuously increase. Beyond this laser intensity, the ionization probability of the atom decreases with the increase in pulse intensity.
The difference in ionization probabilities of atoms irradiated by the laser pulse with different polarizations is also presented in Fig.2.In the RCP laser field,the atom has the largest ionization probability. WhenE0=1.0, the atomic ionization probability is close to 1,and then,as the laser intensity further increases,the ionization probability gradually changes and finally exhibits weakly decreasing behavior. In the LP laser field, the atomic ionization probability is less than the atom irradiated by an RCP laser. When we increase the laser intensity toE0=1.0, its ionization probability reaches the largest value,and then,as the laser intensity further increases,the ionization probability gradually decreases. For the LCP laser,the atomic ionization probability is the smallest of the three polarized laser pulses. As the laser intensity increases, the ionization probability increases at a low rate. When we continuously increase the intensity toE0=2.3, the ionization probability reaches its maximum. However, when the laser intensity is further increased, the ionization probability decreases rapidly. Therefore, the ionization stabilization phenomenon occurs when the polarization of the driving laser pulse is linearly or circularly polarized, either left or right handed. The ionization probability of the atom is determined by the driving laser intensity and amplitude of the transition between the initial state and continuous state. Given the difference in coupling intensities for different initial and continuous states,the laser intensities required for the appearance of ionization stabilization are different; that is, the stronger the coupling is,the smaller is the laser intensity required for the appearance of such a phenomenon.
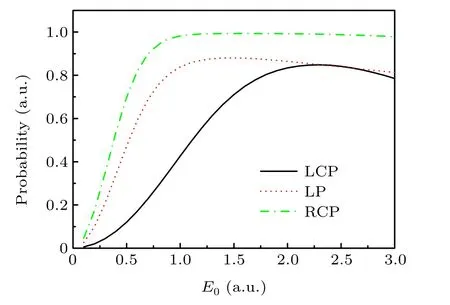
Fig. 2. Dependence of the atomic (the initial state of the atom is m=-1)ionization probability with the peak amplitude of the driving laser pulse with the right-handed circular (green dash-dotted line), linear (red dotted line),and left-handed circular(black solid line)polarizations.
In addition, the ionization behavior of the atom irradiated by different polarized laser pulses is investigated to comprehensively understand the difference. Using the eigenfunctions of the atom obtained by numerically solving the time-independent Schr¨odinger equation, one can calculate the transition matrix elements〈ψconti.(x,y)|x+iy|ψini.(x,y)〉,〈ψconti.(x,y)|x|ψini.(x,y)〉, and〈ψconti.(x,y)|x-iy|ψini.(x,y)〉(from the initial states to the continuum states). For the atomic initial state withm=-1, the corresponding transition matrix elements are shown in Fig. 3. As the energy of the final state increases, the intensity of the transition matrix elements initially increases and then decreases. For the atomic initial state withm=-1, the transition matrix element〈ψconti.(x,y)|x-iy|ψini.(x,y)〉is the largest,followed by〈ψconti.(x,y)|x|ψini.(x,y)〉and〈ψconti.(x,y)|x+iy|ψini.(x,y)〉.The intensity variations in transition matrix elements are consistent with the values of the ionization of atomic ionization irradiated by the LCP,LP and RCP.Therefore,the distinction among the ionization probabilities of the atom irradiated by different driving laser pulses can be well understood.
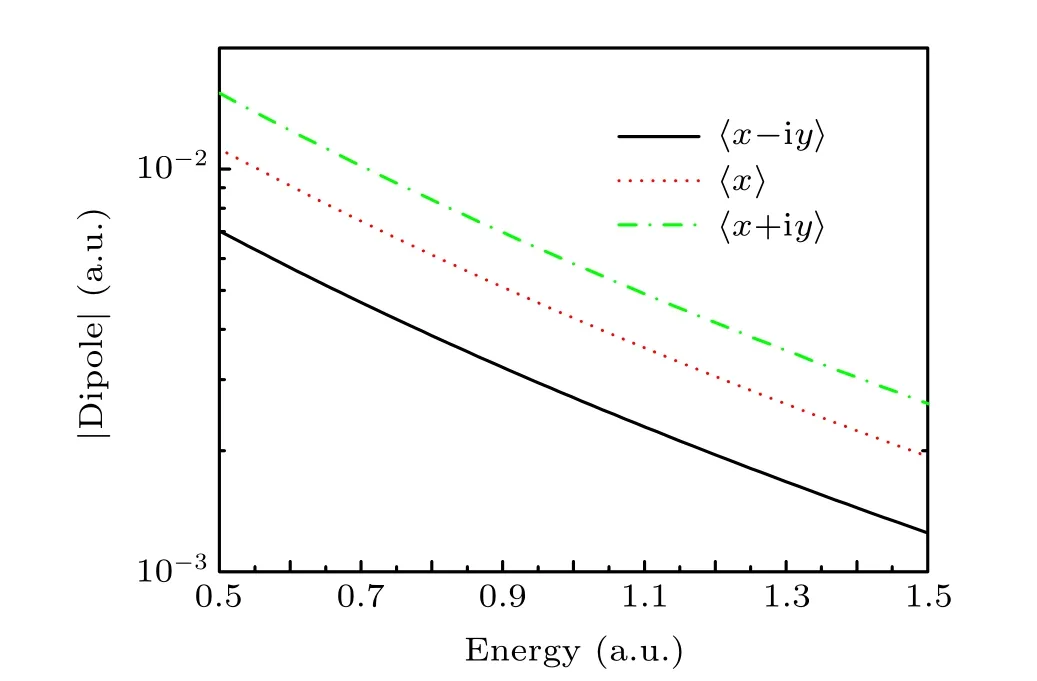
Fig.3. Transition matrix elements from the initial states m=-1 to the continuum state of the atom.
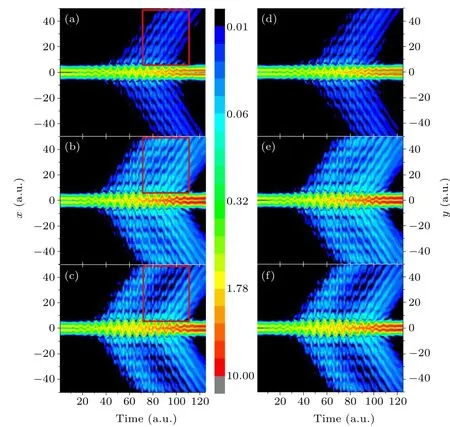
Fig.4. Evolution of the time-dependent probability density of the initial state of m=-1 in the left-handed circular polarization field: the pictures at the left show the x direction: (a)E0 =1.5, (b)E0 =2.3, and(c)E0 =2.7. The pictures at the right show the y direction: (d)E0=1.5,(e)E0=2.3,and(f)E0=2.7.
We calculated the time evolution of the electron density distribution for the initial statem=-1 irradiated by the lefthanded circular polarization laser pulse with different intensities to explain the ionization stabilization of the atom. The result is shown in Fig.4.The peak amplitude of the laser electric feild is as follows:in thexdirection(a)E0=1.5,(b)E0=2.3,and(c)E0=2.7,in theydirection,(d)E0=1.5,(e)E0=2.3,and(f)E0=2.7. When the laser intensity is low,there is low,no ionization occurs at the rising and falling parts of the laser pulse.Ionization primarily occurs at the peak of the laser pulse envelope [Figs. 4(a) and 4(d)]. As the peak amplitude of the laser electric feild increases toE0=2.3, the variation of the electron density distribution with time is similar to the case ofE0=1.5. WhenE0=2.3, ionization occurs in more optical cycles, and as the peak of the laser field increases, the ionization probability increases accordingly[Figs.4(b)and 4(e)].When the peak amplitude of the driving laser electric field increases toE0=2.7,a different situation occurs.The ionization near the laser pulse envelope peak of the laser field[Figs.4(c)and 4(f)]weakens. The differences in the electron density distribution for the three intensities are presented in the red box of the Fig. 4. This phenomenon is consistent with the previous observation under one-dimensional conditions.[43]Given the circular polarization of the driving laser pulse, ionization weakening can be observed in thexandydirections.
Therefore,we investigated the ionization variation of the atom with the initial statem=+1 irradiated by the same laser pulse. For the linear polarization driving laser pulse,the variation of the atomic ionization probabilities with the initial statem=±1 is the same as the change of the incident laser intensity. However,for the circularly polarized driving laser pulse,the ionization probabilities are opposite to the change of the incident laser intensity for atoms with the initial statem=-1 andm=+1. When the initial state ism=-1,the ionization variation of the atom in the LCP laser field is the same as the initial statem=+1 in the RCP laser field,but when the initial state ism=-1,the ionization variation in the RCP laser field is the same as the initial state ofm=+1 in the LCP laser field.
We further analyzed the angular distribution of the ionized electron to understand this initial-state dependency on ionization. Given the polar coordinates (x=ρcos(θ),y=ρsin(θ)) the wave function is expressed asψ(ρ,θ) =φ(ρ)ξ(θ),and the time-independent Schr¨odinger equation of the radial and angular parts of the eigenfunction is calculated as follows:

In calculating atomic ionization, one must project the final wave function on the continuous eigenstate wave function.For two-dimensional calculation, obtaining the eigenstate wave function of the system in the Cartesian coordinate is difficult.Thus, eigen equations must be adopted in polar coordinate[Eqs. (6) and (7)]. This scheme can decompose the calculation of two-dimensional eigenstates into two one-dimensional eigenstate problems. For a givenλ, all radial eigenstates can be obtained easily. Using these eigenstates, the probability of the continuous states can be calculated quickly. By solving this equation,the angular part of the eigenfunction can be given asξ(θ)=eimθ,m=0,±1,±2,..., and the radial part of the eigenfunction can be given asφ(ρ). Finally,the corresponding wave function is obtained asΦ(ρ,θ)m=φ(ρ)eimθ.Using the circularly polarized laser,the generation of the ionized electron from an atom should satisfy not only the conservation of energy but also the conservation of angular momentum. The variation of the population of the ionized electron with the driving laser intensity form= 0,m >0, andm <0, is presented in Fig. 6. For the initialm=-1 state,when the driving circular polarized laser pulse is left-handed[Fig.5(a)]and right-handed[Fig.5(b)],the probability distribution of the ionized electrons is different whenmis different.For the left-handed case,when the magnetic quantum number is +1, the angular momentum of the ionized electron should be distributed inm=0. For the right-handed case, its magnetic quantum number is-1, and the angular momentum of the ionized electron should be-2. Therefore, the primary population of the electron is distributed in the eigenstates ofm <0. Using this theory, the ionization of ionized electrons from them=-1 state irradiated by an RCP laser is the same as that from them=+1 state irradiated by an LCP laser.

Fig. 5. Population of the ionized electron generated from the m=-1 state varies with the peak amplitude of the driving laser pulse whose polarization is left-handed circular (a) and right-handed circular (b). The population includes the total population(cyan solid line)). The population with magnetic quantum number m is less than zero (black solid line), equal to zero (red dotted line),and greater than zero(green dash dotted line).
The difference in the ionization stabilization from the atom with different initial states can also be understood qualitatively using their corresponding dipole transition amplitude.The formulation of the KH state contributes to the ionization stabilization of the atom irradiated by the driving laser. For the ionization stabilization laser intensity, the main contribution of the ionization comes from the rising edge and falling edge of the laser pulse. When the amplitude of the transition dipole between the initial state and continuous states is larger,the probability of the ionization is larger; thus, the ionization stabilization feature is not evident. When the amplitude of the transition dipole is small, the role of the laser intensity becomes more important, thus, the ionization stabilization feature becomes pronounced. The momentum distribution of the photoelectron emission spectra[31,44]of different atoms during ionization stabilization in light intensity was calculated to analyze the effect of the ionization stabilization of atoms on different orbital angular momenta(Fig.6).
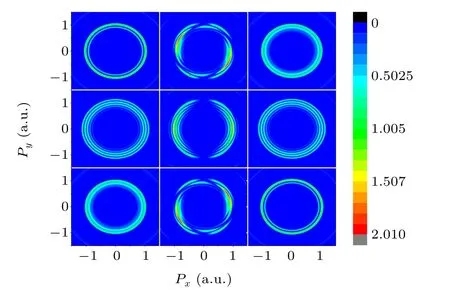
Fig. 6. Photoelectron emission spectra of different initial states in the feild strength of ionization stabilization region. For the initial state m=-1: (a)left-handedcircular polarization andE0 =3.0, (b) linearpolarization and E0 =2.5 (c)right-handedcircular polarization and E0 =2.5. For the initial state m=0: (d) left-handed circular polarization and E0=2.5, and(e) linear polarization and E0 =2.5 For the initial state m=+1: (f)right-hand circular polarization and E0=2.5,(g)left-hand circular polarization and E0 =2.5, (h) linear polarization and E0 =2.5, (i) right-handed circular polarization and E0=3.0.
Figures 6(a)–6(c)show the momentum distribution of the photoelectron emission spectra of the initialm=-1 state driven by LCP, LP, and RCP lasers. Figures 6(d)–6(f) and 6(g)–6(i) are photoelectron momentum distributions of the atom withm=0 state andm=+1 state driven by three lasers,which show a great distinction among different orbital angular momenta. A multiring structure can be observed in the photoelectron momentum distribution of different orbital angular momenta. However, different orbital angular momenta show different characteristics. When the atom is driven by the laser electric field in them= 0 state, a clear multiring structure can be observed. The strength of each ring is close.For the atom in the initial state ofm=-1, the number of rings in the photoelectron emission spectrum is significantly reduced. Notably,when the driving light is LP,the photoelectron emission spectra of the atom whose magnetic quantum number ism=-1 exhibit a multiring vortex structure, and the photoelectron emission spectra with different orbital angular momenta rotate in opposite directions. On the basis of the above mentioned analysis, the photoelectron emission spectrum can reflect the characteristics of the atom in different orbital angular momenta and driving lasers,which is convenient to observe the high-frequency ionization stabilization during experiments. Figures 6(b),6(e),and 6(h)show the photoelectron momentum distributions of the atom irradiated by laser pulses whose intensities are in the ionization stabilization region. Given the dynamic interference, the momentum distribution of the photoelectron emission exhibits strip structures.The driving laser is LP; thus, when the initial-state angular momentum of the atom is 0,the angular momentum distribution is primarily concentrated in the laser polarization direction. When the initial-state angular momenta of the atom are±1, the direction of the maximum value in the photoelectron emission spectrum is changed because of the distribution of the ionized electron during ionization. For weak laser intensities,no dynamic interference strip is observed in the spectrum,but the angular change of the maximum value of the momentum distribution can still be observed.
4. Conclusion
We theoretically investigated the ionization of atoms with different initial orbital angular momenta in a high-frequency laser field. The ionization stabilization phenomena were observed for atoms with different orbital angular momenta.When the laser field vector and motion of the electron rotated in opposite directions,the ionization stabilization of the atom was evident. Our results showed that the features of ionization stabilization are related to the atomic orbital angular momenta and polarization of the laser field. The finding of this work may be observed in future experiments using the free-electron laser.
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China(Grant No.2019YFA0307700),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12074145, 11627807, 11774175, 11534004, 11774129,11604119, and 11975012), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (Grant No.30916011207).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Design of vertical diamond Schottky barrier diode with junction terminal extension structure by using the n-Ga2O3/p-diamond heterojunction
- Multiple modes of perpendicular magnetization switching scheme in single spin–orbit torque device
- Evolution of the high-field-side radiation belts during the neon seeding plasma discharge in EAST tokamak
- Phase-matched second-harmonic generation in hybrid polymer-LN waveguides
- Circular dichroism spectra of α-lactose molecular measured by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy
- Recombination-induced voltage-dependent photocurrent collection loss in CdTe thin film solar cell