Alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist treatment in a rat model of Huntington’s disease and involvement of heme oxygenase-1
Laura Foucault-Fruchard , Claire Tronel Sylvie Bodard Zuhal Gulhan Julie Busson Sylvie Chalon Daniel Antier
1 UMR 1253, iBrain, Université de Tours, Inserm, Tours, France
2 CHRU de Tours, H?pital Bretonneau, Tours, France
Introduction
Epidemiological studies have shown that smokers have a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases than non-smokers.These effects seem to be related to the activation of nicotinic receptors by nicotine, which is a nonselective agonist of alpha 7 nicotinic receptor (α7nAChR) (Gotti and Clementi, 2004; O’Reilly et al., 2005; Thacker et al., 2007). Several studies have reported the beneficial effects of α7nAChR activation on neuronal survival and neuroinflammation in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases (Medeiros et al., 2014; Sérrière et al., 2015). These homopentameric ligand-gated cation channel receptors are widely expressed on neurons and non-neuronal cells (microglia, astroglia,oligodendrocytes and endothelial cells) (Bertrand et al.,2015). In peripheral macrophages, cholinergic anti-in fl ammatory mechanisms through stimulation of α7nAChR are well documented (Egea et al., 2015; Han et al., 2017). Shytle et al. (2004) reported that both activated microglia and macrophages can mediate the inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) release.Accordingly, it was hypothesized that the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP) identified in the periphery has a brain counterpart in the central nervous system (CNS)that could regulate microglial activation.
Referring to the CNS, it has been previously stated that α7nAChR stimulation was associated with the activation of the Jak2/PI3K/AKT cascade, which promotes translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) to the nucleus (Parada et al., 2010). By analogy with the mechanism observed in periphery, Nrf2 activation could promote the overexpression of phase II antioxidant enzymes such as heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). The end products of HO-1 activity are known for their ability to reduce the inflammatory response (Egea et al., 2015). To date, there is little evidence related to the participation of this CAP in the brain. Additional experiments are necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
We have recently shown that repeated administrations of a potent agonist of α7nAChR, PHA 543613, decreased microglial activation in a dose-dependent manner and significantly improved neuronal survival in anin vivoneuroinflammatory excitotoxic rat model (Foucault-Fruchard et al., 2017). PHA 543613, also known as [N-(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]-Oct-3-yl-furo [2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide hydrochloride], is characterized by rapid brain penetration(Acker et al., 2008). Published data about this compound provide additional support for the hypothesis that it represents a potential drug in the management of neurodegenerative diseases. This agonist was shown to improve cognitive function in a model of Schizophrenia (Wishka et al., 2006). It has also demonstrated neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in different intracerebral haemorrhage models and in neurodegenerative rodent models such as models of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases (Kraキ et al., 2012, 2013, 2017; Sadigh-Eteghad et al., 2015; Sérrière et al., 2015). Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to assess the participation of HO-1 in the modulation of neuronal loss and neuroinflammation mediated by α7nAChR activation in a rat model of brain excitotoxicity. The model of acute neuroinflammation chosen, admitted as an animal model mimicking the early-stage Huntington’s disease, is obtained by unilateral striatal injection of quinolinic acid(QA). QA is an agonist of glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors with excitotoxic properties. This heterocyclic amino acid increases the expression of various enzymes (proteases, lipases, and endonucleases) that leads to neuronal death (Schwarcz and Kohler, 1983; Estrada Sanchez et al., 2008). Dysfunction of neuronal activity related to the QA injection induces a pro-inflammatory environment leading to the activation of surrounding microglial cells (Estrada Sanchez et al., 2008).
Material and Methods
Animals
Experiments were conducted on 10-week-old normotensive male Wistar rats (n= 12) (Janvier Labs, Le Genest-Saint-Isle,France), housed in a temperature (21 ± 1°C)- and humidity-controlled (55 ± 5%) environment in a 12-hour light/dark cycle (food and waterad libitum). All procedures were carried out according to the European Community Council Directive 2010/63/EU for laboratory animal care and the experimental procedure was approved by the Regional Ethical Committee (Authorization N°2015022011523044).
Excitotoxic neuroinflammation model mimicking early-stage Huntington’s disease
Rats were anesthetized with isoflurane (4% for induction and 2% for maintenance, gas anesthetizing box, AerraneTM,Baxter, France) and placed in a stereotaxic David Kopf apparatus (Phymep, Paris, France) to be lesioned in the right striatum with QA (150 nmol, 2 μL, Sigma Aldrich, Lyon,France) at the following stereotaxic coordinates according to the Atlas of Paxinos and Watson (Paxinos and Watson,2008): anterior-posterior (AP): +0.7 mm; medial-lateral(ML): –3 mm; dorsal-ventral (DV): –5.5 mm from bregma.
PHA 543613 injection
Western blot assay
On day 4, the rats were killed by decapitation and both ipsilateral and contralateral striata were dissected from brain tissue. These hemispheres were homogenized with lysis buffer and supplemented with sodium fluoride (NaF), phenylmethane sulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails (Couturier et al., 2012). Lysates were centrifuged at 15,000 ×gfor 15 minutes at 4°C. The resulting supernatants were collected to measure the quantity of total protein using the Bradford method. After denaturation(100°C, 5 minutes), beta mercaptoethanol and bromophenol blue were added to 30 μg of samples. Proteins were separated on a SDS gel electrophoresis (40 minutes, 200 V) and were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Biorad,Marnes-la-Coquette, France). The blots were blocked for 3 hours at room temperature with 5% (v/v) nonfat dried milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween 20 and then incubated with primary antibodies anti-HO-1 (1:300, rabbit antibody, ab68477, Abcam, Paris, France) or anti-α7nAChR(1:200, rabbit antibody, ab10096, Abcam, Paris, France) in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C. Membranes were incubated with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary polyclonal antibody at room temperature (1:7500, goat antibody, 111-033-144, Jackson Immunoresearch, West Grove,PA, USA) for 2 hours. Mouse polyclonal antibody against β-actin was used as housekeeping protein (Sigma Aldrich,Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France). Immunoreactive proteins were exposed to the enhanced chemiluminescence western blotting detection system and the signals were captured using the Gbox system and the GeneSys image capture soft-ware (Syngene, Ozyme, Saint Quentin en Yvelines, France).The densitometry relative difference between HO-1/α7nAChR and β-actin was analyzed with ImageJ software(National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA).The expression levels of HO-1 and α7nAChR proteins in all rats were quantified independently of each other on the same nitrocellulose membrane. Each protein was quantified in all rats (n= 12) under the same condition and at the same time.
Statistical analysis
Results were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software v.5,San Diego, California, USA and expressed as the mean ±SEM(Standard error of the mean). Comparisons between groups were performed using the Mann-WhitneyUtest and comparisons between ipsilateral and contralateral striata were conducted using the Wilcoxon one-tailed test. The level of significance wasP< 0.05.
Results
Effect of PHA 543613 treatment on HO-1 expression in the striatum

Figure 1 Effects of PHA 543613 treatment on HO-1 expression in the striatum of rats using western blot assay
HO-1 expression was evaluated in ipsilateral and contralateral striata in the QA-vehicle (n= 6) and QA-PHA (n=6) groups. The results are illustrated in Figure 1. Western blot assay results revealed that HO-1 protein expression was significantly decreased in both groups (P< 0.05), and there was a significant difference in the decrease of HO-1 protein expression between the ipsilateral and contralateral striata in each group (HO-1/β-actin ratio in the QA-vehicle group:0.69 ± 0.13 in the contralateral striatumvs. 0.37 ± 0.09 in the ipsilateral striatum; HO-1/β-actin ratio in the QA-PHA group: 1.20 ± 0.20 in the contralateral striatumvs. 0.91 ± 0.18 in the ipsilateral striatum;P= 0.03). However, HO-1 expression in the ipsilateral striatum of rats in the QA-PHA group was significantly higher than in the QA-vehicle group (+146%;P= 0.02). HO-1 expression level in the contralateral striatum was also higher in the QA-PHA group than in the QA-vehicle group (+74%, not statistically significant).
Effect of PHA 543613 on α7nAChR expression in the striatum
Quantification of α7nAChR expression was performed on ipsilateral and contralateral striata in the QA-vehicle (n= 6)and QA-PHA (n= 6) groups. The results are illustrated in Figure 2. The overall level of α7nAChR in the contralateral and ipsilateral striata was determined using western blotting(QA-vehicle group: 0.60 ± 0.05 in the contralateral striatumvs. 0.60 ± 0.09 in the ipsilateral striatum; QA-PHA group:0.50 ± 0.01 in the contralateral striatumvs. 0.52 ± 0.06 in the ipsilateral striatum). No significant difference was observed between the animals (P> 0.05).
Discussion
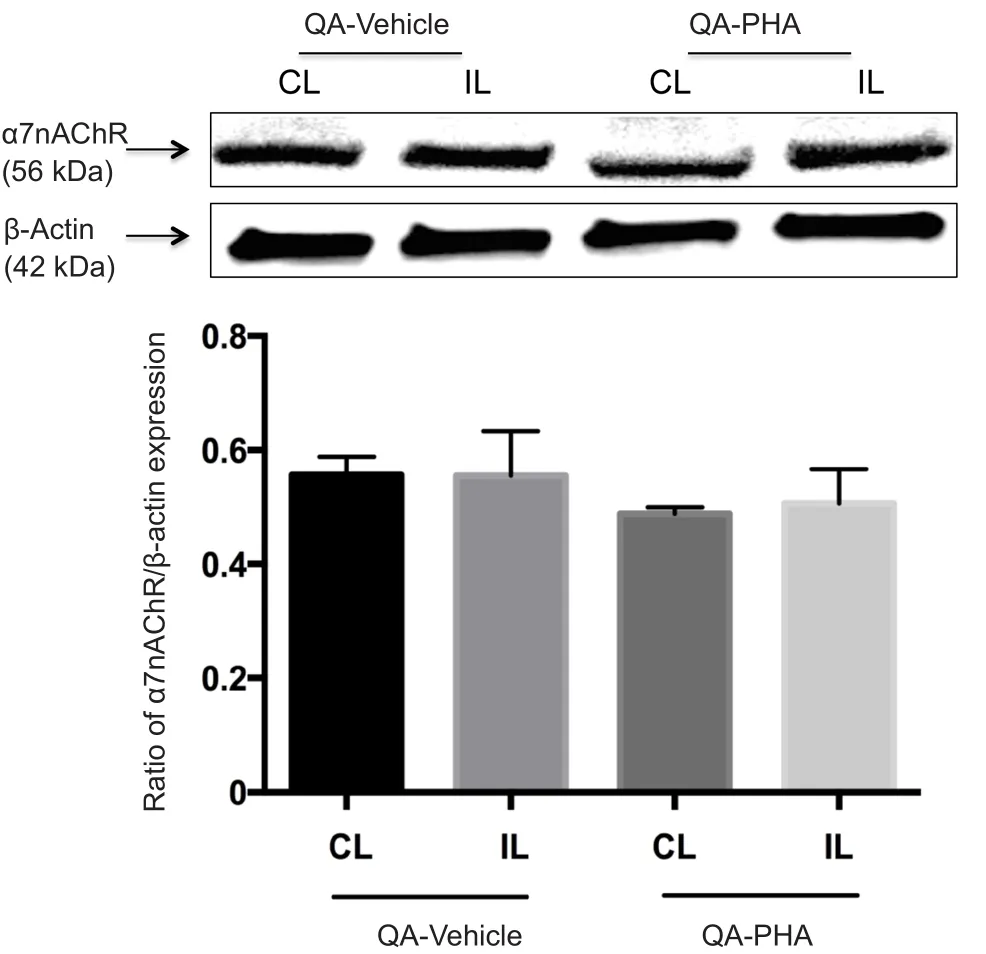
Figure 2 Effect of PHA 543613 on α7nAChR expression in the striatum of rats using western blot assay
PHA 543613 has already demonstrated neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects in rodent models of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases (Krafft et al., 2012, 2013, 2017; Sadigh-Eteghad et al., 2015; Sérrière et al., 2015). We have recently highlighted that PHA 543613 decreased microglial activation with a dose effect and improved neuronal survival in a rat model of Huntington’s disease and we recently confirmed the agonist properties of PHA 543613 on α7nAChR expression in neuron and astrocyte cultures (Foucault-Fruchard et al., 2017).However, the pathways activated following the stimulation of α7nAChR in the brain are poorly understood. The present study aimed to add knowledge about the expression of a key component of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway,HO-1, after repeated administrations of α7nAChR agonist.HO-1 end products generated from heme degradation may modulate inflammation. First, carbon monoxide (CO)released from HO activity may modulate apoptotic, proliferative, and inflammatory cellular programs. CO can downregulate the production of pro-inflammatory mediators(interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor, inducible nitric oxide synthase…) and upregulate the anti-inflammatory cytokines(interleukin-1, interleukin-10…)viathe mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. CO can also stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species, which can downregulate pro-inflammatory transcription (transforming growth factor-β, Egr-1…). Bilirubin, another product of heme degradation, may also exert anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effects. However, the degree of HO-1 activation should be regulated because a third end product of HO-1,Fe2+may be deleterious in the case of excess activation (Ryter et al., 2015).
In our study, we observed a significant decrease of HO-1 expression in ipsilateral striatum compared with contralateral striatum in both groups (–86% and –33% in the QA-vehicle and QA-PHA groups respectively). Tasset et al. (2010)performed anin vitrostudy and demonstrated that QA exerted a pro-oxidant effect and decreased Nrf2 expression on rat striatal slices. Consequently, it is possible to speculate that this phenomenon is associated with a decrease of transcription of anti-oxidant genes such as HO-1. Colin-Gonzales et al. (2013) also investigated the effects of QA infused intrastriatally on HO-1 expression in rats. Contrary to our experimentation, they observed an increase in a time-dependent manner at 1, 3, 5 and 7 days post QA lesion compared with control animals. However, it is important to highlight that the experimental procedure was different from ours.The dose of QA used (240 nmol) was higher than in our surgical lesion technique, and the stereotaxic coordinates were different (AP: +0.5 mm; ML: 2.6 mm from bregma;DV: 4.5 mm from dura). In addition, HO-1 expression was only quantified in the ipsilateral striatum of QA and control animals lesioned with isotonic saline solution.
In the present study, we revealed for the first time that repeated administrations of the α7nAChR agonist, PHA 543613, significantly increased HO-1 expression in the ipsilateral striatum of the QA-PHA group compared with QA-vehicle. Increased HO-1 expression was also observed in the contralateral striatum. Several studies have already highlighted a correlation between HO-1 expression and HO-1 activity in the CNS (Colín-González et al., 2013; Lin et al.,2017). The ipsilateral side represents the region of interest in our QA lesion model. These observations correspond to a protective action of HO-1 activation as described previously(Suttner and Dennery, 1999). The dual behavior, protective(formation of anti-oxidant compounds) or toxic (production of Fe2+), of this enzyme is widely reported and the protein expression level depends on the neuroinflammation model and drug exposure methods (Colín-González et al., 2013;Tronel et al., 2013). Increased HO-1 expression, 10 times higher than the basal value, seems to be toxic whereas 2-fold to 10-fold increase in HO-1 expression seems to be protective (1.7-fold and 2.4-fold increases in HO-1 expression in ipsilateral striatum relative to contralateral striatum in the QA-vehicle and QA-PHA groups respectively) (Suttner and Dennery, 1999). After activation, the α7nAChR theoretically undergoes rapid desensitization to limit the influx of Ca2+into the cell which can lead to excitotoxicity. A compensating mechanism characterized by an increased number of α7nAChR binding sites in several brain regions, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, can be initiated (Christensen et al.,2010). However, 4-day treatment with PHA 543613 did not lead to a significant modification of α7nAChR expression.This finding suggests that HO-1 expression is not associated with an increase of α7nAChR density.
Increased HO-1 expression in our study seems to underlie the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects associated with α7nAChR activation observed under excitotoxic conditions. Other studies have supported the correlation between the neuroprotective effects and the induction of HO-1 expression in neurodegenerative models (Parada et al., 2014; Buendia et al., 2015). Taken together, these observations reinforce the hypothesis that the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway identified in the periphery has a brain counterpart in the CNS. However, other signaling pathways such as Nrf2 (i.e., activator protein 1, nuclear factor kappa B or hypoxia inducible factor-1) can regulate HO-1 expression(Alam and Cook, 2003; Ferrándiz and Devesa, 2008) and further investigations have to be performed to confirm our hypothesis.
Author contributions:LFF contributed to the conception, design,definition of the intellectual content, literature retrieval, experimental studies, data acquisition and analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation and editing and was the guarantor of the paper. CT contributed to the conception, design, definition of intellectual content, experimental studies, and manuscript review. SB, ZG and JB contributed to the experimentation. SC and DA contributed to the conception, design,and definition of the intellectual content, and manuscript review. They contributed equally to this work and approved the final version of this paper for publication.
Conflicts of interest:The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Financial support:This work was supported by the Région Centre-Val de Loire (2014 00094049 – AP 2014-850) and the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n°278850 (INMiND). The funding bodies played no role in the study design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the paper, and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Research ethics:All procedures were carried out according the European Community Council Directive 2010/63/EU for laboratory animal care and the experimental procedure was approved by the Regional Ethical Committee (Authorization N°2015022011523044).
Data sharing statement:Datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Plagiarism check:Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review:Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Acker BA, Jacobsen EJ, Rogers BN, Wishka DG, Reitz SC, Piotrowski DW, Myers JK, Wolfe ML, Groppi VE, Thornburgh BA, Tinholt PM, Walters RR, Olson BA, Fitzgerald L, Staton BA, Raub TJ,Krause M, Li KS, Hoffmann WE, Hajos M, et al. (2008) Discovery of N-[(3R,5R)-1-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide as an agonist of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: in vitro and in vivo activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:3611-3615.
Alam J, Cook JL (2003) Transcriptional regulation of the heme oxygenase-1 gene via the stress response pathway. Curr Pharm Des 9:2499-2511.
Bertrand D, Lee CH, Flood D, Marger F, Donnelly-Roberts D (2015)Therapeutic potential of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Pharmacol Rev 67:1025-1073.
Buendia I, Egea J, Parada E, Navarro E, León R, Rodríguez-Franco MI,López MG (2015) The melatonin-N,N-dibenzyl(N-methyl)amine hybrid ITH91/IQM157 affords neuroprotection in an in vitro Alzheimer’s model via hemo-oxygenase-1 induction. ACS Chem. Neurosci 6:288-296.
Christensen DZ, Mikkelsen JD, Hansen HH, Thomsen MS (2010)Repeated administration of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor(nAChR) agonists, but not positive allosteric modulators, increases alpha7 nAChR levels in the brain. J Neurochem 114:1205-1216.
Colín-González AL, Orozco-Ibarra M, Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Rangel-López E, Santamaría A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, Barrera-Oviedo D,Maldonado PD (2013) Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) upregulation delays morphological and oxidative damage induced in an excitotoxic/pro-oxidant model in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 231:91-101.
Couturier J, Paccalin M, Lafay-Chebassier C, Chalon S, Ingrand I,Pinguet J, Pontcharraud R, Guillard O, Fauconneau B, Page G(2012) Pharmacological inhibition of PKR in APPswePS1dE9 mice transiently prevents inflammation at 12 months of age but increases Aβ42 levels in the late stages of the Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:344-360.
Egea J, Buendia I, Parada E, Navarro E, León R, Lopez MG (2015)Anti-inflammatory role of microglial alpha7 nAChRs and its role in neuroprotection. Biochem Pharmacol 97:463-472.
Estrada Sánchez AM, Mejía-Toiber J, Massieu L (2008) Excitotoxic neuronal death and the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Arch Med Res 39:265-276.
Ferrandiz ML, Devesa I (2008) Inducers of heme oxygenase-1. Curr Pharm Des 14:473-486.
Foucault-Fruchard L, Doméné A, Page G, Windsor M, Emond P, Rodrigues N, Doll, F, Damont A, Buron F, Routier S, Chalon S, Antier D (2017) Neuroprotective effect of the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor agonist PHA 543613 in an in vivo excitotoxic adult rat model. Neuroscience 356:52-63.
Gotti C, Clementi F (2004) Neuronal nicotinic receptors: from structure to pathology. Prog Neurobiol 74:363-396.
Han B, Li X, Hao J (2017) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway:An innovative treatment strategy for neurological diseases. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 77:358-368.
Kraキ PR, Altay O, Rolland WB, Duris K, Lekic T, Tang J, Zhang JH(2012) α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonism confers neuroprotection through GSK-3β inhibition in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 43:844-850.
Krafft PR, Caner B, Klebe D, Rolland WB, Tang J, Zhang JH (2013)PHA-543613 preserves blood-brain barrier integrity after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Stroke J Cereb Circ 44:1743-1747.
Kraキ PR, McBride D, Rolland WB, Lekic T, Flores JJ, Zhang JH (2017)α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor stimulation attenuates neuroinflammation through JAK2-STAT3 activation in murine models of intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomed Res Int 2017:8134653.
Lin CC, Yang CC, Chen YW, Hsiao LD, Yang CM (2017) Arachidonic Acid Induces ARE/Nrf2-Dependent Heme Oxygenase-1 Transcription in Rat BrainAstrocytes. Mol Neurobiol doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0590-7.
Medeiros R, Castello NA, Cheng D, Kitazawa M, Baglietto-Vargas D, Green KN, Esbenshade TA, Bitner RS, Decker MW, LaFerla FM (2014) α7 Nicotinic receptor agonist enhances cognition in aged 3xTg-AD mice with robust plaques and tangles. Am J Pathol 184:520-529.
O’Reilly EJ, McCullough ML, Chao A, Jane Henley S, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Ascherio A (2005) Smokeless tobacco use and the risk of Parkinson’s disease mortality. Mov Disord 20:1383-1384.
Parada E, Egea J, Romero A, del Barrio L, García AG, López MG (2010)Poststress treatment with PNU282987 can rescue SH-SY5Y cells undergoing apoptosis via α7 nicotinic receptors linked to a Jak2/Akt/HO-1 signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 49:1815-1821.
Parada E, Buendia I, León R, Negredo P, Romero A, Cuadrado A,López MG, Egea J (2014) Neuroprotective effect of melatonin against ischemia is partially mediated by alpha-7 nicotinic receptor modulation and HO-1 overexpression. J Pineal Res 56:204-212.
Paxinos G, Watson C (2008) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates:Compact. 6thed. Academic Press/Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Ryter SW, Choi AM (2016) Targetingheme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide for therapeutic modulation of inflammation. Transl Res 167:7-34.
Sérrière S, Doméné A, Vercouillie J, Mothes C, Bodard S, Rodrigues N, Guilloteau D, Routier S, Page G, Chalon S (2015) Assessment of the protection of dopaminergic neurons by an α7 nicotinic receptor agonist, pha 543613 using [18F]lbt-999 in a Parkinson’s disease rat model. Front Med 2:61.
Sadigh-Eteghad S, Talebi M, Mahmoudi J, Babri S, Shanehbandi D(2015) Effect of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation on beta-amyloid induced recognition memory impairment. Possible role of neurovascular function. Acta Cir Bras 30:736-742.
Schwarcz R, K?hler C (1983) Differential vulnerability of central neurons of the rat to quinolinic acid. Neurosci Lett 38:85-90.
Shytle RD, Mori T, Townsend K, Vendrame M, Sun N, Zeng J, Ehrhart J, Silver AA, Sanberg PR, Tan J (2004) Cholinergic modulation of microglial activation by alpha 7 nicotinic receptors. J Neurochem 89:337-343.
Suttner DM, Dennery PA (1999) Reversal of HO-1 related cytoprotection with increased expression is due to reactive iron. FASEB J 13:1800-1809.
Tasset I, Pérez-De La Cruz V, Elinos-Calderón D, Carrillo-Mora P, González-Herrera IG, Luna-López A, Konigsberg M, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Maldonado PD, Ali SF, Túnez I, Santamaría A (2010)Protective effect of tert-butylhydroquinone on the quinolinic-acid-induced toxicity in rat striatal slices: role of the Nrf2-antioxidant response element pathway. Neurosignals 18:24-31.
Thacker EL, O’Reilly EJ, Weisskopf MG, Chen H, Schwarzschild MA,McCullough ML, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Ascherio A (2007) Temporal relationship between cigarette smoking and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 68:764-768.
Tronel C, Rochefort GY, Arlicot N, Bodard S, Chalon S, Antier D (2013)Oxidative stress is related to the deleterious effects of heme oxygenase-1 in an in vivo neuroinflammatoryrat model. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:264935.
Wishka DG, Walker DP, Yates KM, Reitz SC, Jia S, Myers JK, Olson KL, Jacobsen EJ, Wolfe ML, Groppi VE, Hanchar AJ, Thornburgh BA, Cortes-Burgos LA, Wong EH, Staton BA, Raub TJ, Higdon NR, Wall TM, Hurst RS, Walters RR, et al. (2006) Discovery of N-[(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide, an agonist of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, for the potential treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: synthesis and structure--activity relationship. J Med Chem 49:4425-4436.
 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2018年4期
中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2018年4期
- 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Use of curcumin in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
- Compound of icariin, astragalus, and puerarin mitigates iron overload in the cerebral cortex of Alzheimer’s disease mice
- Structural neural connectivity of the vestibular nuclei in the human brain: a diffusion tensor imaging study
- Intracerebroventricularly-administered 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion and brain-derived neurotrophic factor affect catecholaminergic nerve terminals and neurogenesis in the hippocampus, striatum and substantia nigra
- Induced dural lymphangiogenesis facilities soluble amyloid-beta clearance from brain in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
- Brain remodeling after chronic median nerve compression in a rat model
