Multi-layer phenomena in petawatt laserdriven acceleration of heavy ions
Wanqing SU (蘇琬晴),Xiguang CAO (曹喜光),Chunwang MA (馬春旺),Yuting WANG (王玉廷) and Guoqiang ZHANG (張國強(qiáng))
1 College of Physics,Henan Normal University,Xinxiang 453007,People’s Republic of China
2 Shanghai Advanced Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 201210,People’s Republic of China
3 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shanghai 201800,People’s Republic of China
4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,People’s Republic of China
5 Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology,Henan Academy of Science,Zhengzhou 450046,People’s Republic of China
Abstract Laser-accelerated high-flux-intensity heavy-ion beams are important for new types of accelerators.A particle-in-cell program (Smilei) is employed to simulate the entire process of Station of Extreme Light (SEL) 100 PW laser-accelerated heavy particles using different nanoscale short targets with a thickness of 100 nm Cr,Fe,Ag,Ta,Au,Pb,Th and U,as well as 200 nm thick Al and Ca.An obvious stratification is observed in the simulation.The layering phenomenon is a hybrid acceleration mechanism reflecting target normal sheath acceleration and radiation pressure acceleration,and this phenomenon is understood from the simulated energy spectrum,ionization and spatial electric field distribution.According to the stratification,it is suggested that high-quality heavy-ion beams could be expected for fusion reactions to synthesize superheavy nuclei.Two plasma clusters in the stratification are observed simultaneously,which suggest new techniques for plasma experiments as well as thinner metal targets in the precision machining process.
Keywords: petawatt laser-plasma interaction,laser-driven heavy-ion accelerator for synthesizing superheavy nuclei,particle-in-cell,multi-layer phenomena,target fabrication
1.Introduction
The laser-plasma accelerator (LPA) is a new type of particle accelerator for future scientific research with three advantages over traditional particle accelerators: (1) its acceleration gradient is four orders of magnitude larger; (2) its pulse duration is three orders of magnitude shorter; (3) its transverse divergence is three orders of magnitude lower [1].Meanwhile,the potential applications of LPAs also lie in their compact size [2,3],low cost,simplicity and higher particle energies [4].With the generation of ultra-intense ultra-short lasers,research on laser-driven heavy-ion sources might lead to significant advances in the development of heavy-ion-driven inertial fusion [5],heavy-ion neoplasm therapy [6],generation of high-energy-density states in matter [7,8],cutting-edge research on quark-gluon plasma for heavy-ion collisions [9,10],the study of exotic nuclear structures [11] and material modification [12].Moreover,since the synthesis of superheavy element 118 (oganesson)in 2006,researchers are on an increasingly difficult voyage to explore heavier nuclei,and the new heavy-ion accelerator with a promising high-temperature and high-density plasma environment could provide new experimental opportunities[13,14].
Experiments on particle acceleration by ultra-intense and ultra-short lasers are able to produce electron and ion beams;the acceleration of heavy ions to produce high-intensity heavy-ion beams remains to be explored.Simulated by a twodimensional (2D) particle-in-cell (PIC) code ELMIS [15],composite targets were shown be able to produce ion beams with an energy spread as low as 2% and Fe24+with energy up to 36 MeV/u at laser intensities of 1022W/cm2[16].Simulated results using a 2D PIC code KLAP2D [17,18]showed that a laser of 1 .1×1021W/cm2can turn out a singleenergy Fe24+beam with a peak energy of 100 MeV/u [19],and 2D PIC simulations with the EPOCH code [20] showed an acceleration ability with Au up to 1.2 GeV,which has been confirmed in experiments [21].
Simulations suggest enhancement of the quality of heavyion beams from LPAs,giving stronger beam intensity and smaller divergence.The Station of Extreme Light (SEL),one of the end stations of the hard x-ray free electron laser system “SHINE” that is under construction in Shanghai,China,will provide high-intensity lasers up to 100 PW[22-24].In this work,using parameters of a SEL 100PW laser system,a 2D 3V (three-velocity) PIC code Smilei is employed to simulate the laser acceleration of ten types of metal targets,and the yields of ions and related properties are discussed.In section 2,a brief description of Smilei and the simulation parameters is presented.In section 3,available information about ions in the Smilei simulations is presented,including the ion spatial distribution,energy spectrum,ionization and spatial electric field distribution.In section 4,ion-beam parameters are further illustrated and discussed.The conclusions of this work are presented in section 5.
2.Model description
Smilei is a PIC code co-developed by high-performance computing specialists and physicists.In Smilei,particles satisfying Vlasov's equation are ionized in the electromagnetic field and gradually form a self-consistent dynamical system [25-27].The main theoretical formulae are
wheresdenotes a given species consisting of particles with chargeqsand massms,x and p denote the position and momentum of a phase-space element,fs(x,p,t) is the distribution function of the plasma,is the relativistic Lorentz factor,cis the speed of light in a vacuum,and ?0,μ0,ρ and J are the vacuum permittivity and permeability and charge and current densities,respectively.
As an open-source,user-friendly,multi-purpose PIC code,Smilei has been applied to a wide range of physicsrelated studies from relativistic laser-plasma interaction to astrophysics [28].The Smilei program can simulate the dynamics effectively,which includes the primary acceleration mechanisms of laser-target interaction of target normal sheath acceleration (TNSA) [29-34],break-out afterburner[35-43] and radiation pressure acceleration (RPA) [44].The RPA mechanism is also classified as laser-piston [45],holeboring [46,47],light-sail [48,49] and phase-stable acceleration [50].The basic steps in a Smilei simulation include the initialization of time,space and electromagnetic fields,the loading of particles,time step,space step and input parameters,and then obtaining information about particles by loop conformity calculation according to conservation laws and ion ionization theory of ions.
Both Smilei and EPOCH,which is extracted from the paper of Wanget al,simulate a laser (a0=80) hitting an Au target ( 150 nm) [21],as shown in figure 1(a).The tendencies of all Au ion energy spectra are approximately same.The ions are accelerated by the ultra-intense laser and then form a beam.To improve the beam quality,a short target can be considered to produce a high-intensity,low-divergence beam.
The simulation parameters are set as follows.A circularly polarized Gaussian laser with wavelength λ=1μm,peak intensityI=1023W/cm2,which corresponds to a normalized laser amplitude ofa0≈190 and full-width-athalf-maximum (FWHM) of 7.5 fs,and focal spot size of 5μm is set in this 2D PIC simulation.The size of the space is 6λ×10λ with even partition mesh grids of 600×1000,while the time step is equal to 22 as .The heavy-ion metal target is located atx0=1μm,and every cell contains 49 metal ions with an initial charge of 1+and 49 electrons at the metal target position; the density of the metal target is the same as the corresponding density of the metallic solid.The simulated targets are 10 metals of length 4μm and a thickness of 100 nm (Al and Ca) or 200 nm (Cr,Fe,Ag,Ta,Au,Pb,Th and U).
3.Simulation results
3.1.Multi-layer phenomenon of Th target
The PIC simulation can obtain the phase space data for every ion that moves forward under the propulsion of the ultraintense laser.Figures 1(b),(d) and (f) depict the spatial distributions of ions for Th targets of thickness 50 nm,100 nm and 500 nm at 120 fs with dimensionless areal densities σ=(ne×d)/(ncr×λ)≈ 1.52,3.04 and 15.18,respectively (neis the electron density,ncris the critical density anddis the thickness of target).It can be found that,as the target thickness increases,there are obvious differences in the spatial distribution of ions.The specific manifestation is that ions in the thinnest target move forward collectively,ions in a thinner target move forward but gradually split into two layers and ions in a thick target only move forward partially.
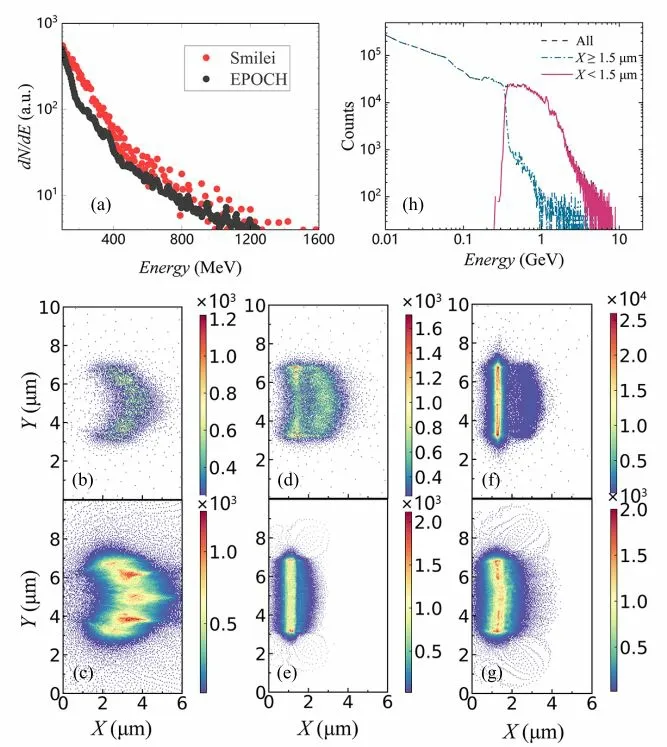
Figure 1.(a) The ion energy spectrum simulated by Smilei and EPOCH,which is extracted from the paper of Wang et al [21] for an a0=80 laser on a 150-nm thick Au target.Ion spatial distributions simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser on a Th target at 120 fs.The target thickness is 50 nm ,100 nm (which shows stratification) and 500 nm in (b),(d) and (f),respectively.Ion spatial distributions simulated by Smilei for a laser with I=1023 W/cm2 and FWHM =15 fs ,I=1022 W/cm2 and FWHM =7.5 fs ,and I=1022 W/cm2 and FWHM =20 fs on a Th target of thickness 100 nm at 120 fs in (c),(e) and (g),respectively.(h) The front and back layer ion energy spectra and charge distribution simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser on a 100 nm thick Th target at 60 fs.See section 4 for beam parameters.
As a further comparison,the laser is given three different sets of parameters.Figures 1(c),(e) and (g) show the spatial distributions of ions for Th targets of thickness 100 nm at 120 fs ,with a laser peak intensityI=1023W/cm2and FWHM of 15 fs ,a laser peak intensityI=1022W/cm2and FWHM of 7.5 fs,and a laser peak intensityI=1022W/cm2and FWHM of 20 fs,respectively.Th ions are given a greater acceleration by the laser with a larger FWHM and laser peak intensity.However,there is no distinct stratification in any of the three simulations described above.
Collectively,the major acceleration mechanism of the thinnest target is RPA and that of the thickest target is obviously TNSA.The thinner target shows a hybrid acceleration mechanism,comprising contains RPA and TNSA [51].When the thickness of the Th target is 100 nm,the major acceleration mechanism for higher-energy lasers is RPA,whereas that for lower-energy lasers is TNSA.This is distinct from the conventional RPA or TNSA mechanism and is a highly intriguing new phenomenon that allows us to gain an in-deepth understanding of abnormal behaviors in the laser-accelerated heavy-ion process.
The front and back layer energy spectra of Th ions are shown in figure 1(h); these are analyzed simulating a 100 nm Th target.The first peak is located atE=0,which overlaps with the energy spectrum of the latter Th ions(X<1.5μm ).The second peak appears nearE=1 GeV,which overlaps with the energy spectrum of the former Th ions (X≥1.5μm).We conclude that both form the final energy spectrum of Th ions and may induce the double-layer plasma of the metal target.
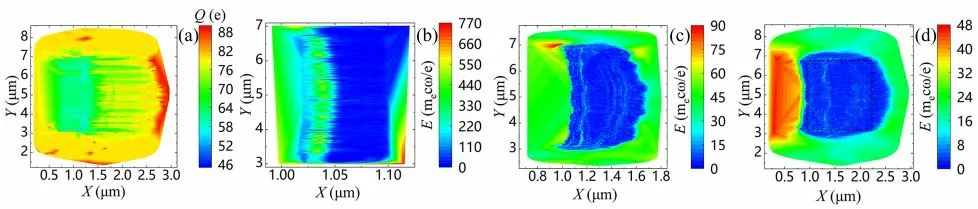
Figure 2.(a) The charge distribution simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser on a Th target of thickness of 100 nm at 60 fs.Electric field intensity distributions simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser on a Th target of thickness of 100 nm at (b) 20 fs ,(c)40 fs and (d) 60 fs.
The ionization rate of heavy ions is determined by the Ammosov-Delone-Krainov equation for each electron ionized in the electromagnetic field.Ionization occurs cumulatively as time increases,with ionization energy being converted into kinetic energy,and a new self-consistent dynamical system is formed.For this simulation,the ultraintense laser accelerates and ionizes Th ions,then new plasma images are constantly iterating and eventually Th ions that are fully ionized may obtain the maximum energy.For the 100-nm thick Th target,the charge distribution of Th ions at 60 fs is shown in figure 2(a).The minimum ionization state of Th ions is 46+,and these are mainly distributed in the position of the initial target.The maximum ionization state of Th ions reaches 89+,and these are mostly scattered in the end of the plasma cluster.Moreover,there are higher ionization states of Th ions spreading over the edge of the plasma cluster,and ions in intermediate ionization states are sporadically located around the target.The above discussion indicates that the approximate location of ions can be inferred from the degree of ionization.For instance,the smaller the charge state of the ion,the closer its position is to the target,while the larger the charge state of the ion,the further its position is from the target.
The ions are influenced by the Lorentz force,and their motions inversely change the collective electromagnetic field,so the tendency of ion movement can also be visible from the evolution of the spatial electric field.For the same selection of a 100-nm thick Th target,the evolution of its spatial electric field intensity is shown in figures 2(b)-(d),where ω=1 is the reference frequency.The electric field intensity at both ends ofx-space is higher than that at the center position at 20 fs,as shown in figure 2(b).The electric field intensity at the edge ofx-yspace is larger than that in the middle,and the strength of the electric field increases from the center to the outside at 40 fs,as shown in figure 2(c).Figure 2(d) shows the distribution at 60 fs,which is similar to figure 2(c); however,the electric field intensity at the middle position presents a weak-strong-weak image,which may be the physical reason for the phenomenon of the layering of Th ions.
The layering phenomenon demonstrates a three-stage evolution based on the results for the energy spectrum,ion ionization and electric field [52].
(1) The super-intense laser strikes the surface of the dense target; this is called surface layer interaction.
(2) The laser interacts with the plasma,which includes an ionization reaction.The front layer moves forward quickly,while the back layer moves slowly.
(3) Stratification is generated.Two cluster plasmas move forward together.
3.2.Multi-layer phenomena of metal targets
Based on the pictures of the spatial distribution of the thinner nanometer-thick Th target,the stratifications are also seen in simulations of other metal targets.In the simulations for Al and Ca targets of thickness 200 nm,and Cr,Fe,Ag,Ta,Au,Pb,Th and U targets of thickness 100 nm at 60 fs,as shown in figures 3(a)-(j),distinct layering phenomena in spatial distributions can be seen.The delamination of metal targets with different target thicknesses is very distinctive due to the differences in atomic number,density,ionization properties,etc [53-55].Thicker targets containing lighter nuclei show delamination,while targets containing heavier nuclei are relatively harder to accelerate.Besides,the spatial distributions of targets with the same target thickness and different nuclei also differ from each other.Further discussion on this can be found below.
Since the energy spectra of ions obtained from a single simulation of the above metal targets fluctuate obviously,we set different random number seeds in 10 simulations for each metal target and made an average to obtain the final energy of the ion.After the aforementioned procedure,the energy spectra reflecting the real ion energies were generated with more distinct trends.
The energy spectra of metal ions with various targets of different thicknesses at 60 fs are displayed in figure 3.When the target thickness is 200 nm,the width of the Ca ion energy spectrum is larger than that of Al ions,as shown in figure 3(k).Their dimensionless areal densities are 12.04 and 4.61,respectively.Other metal targets (100 nm,Cr and Fe ions with the narrowest energy spectra) have almost the same energy distribution,meanwhile the maximum energy of Pb and Th ions with the widest energy spectra can reach 9-10 GeV.Their dimensionless areal densities are 8.32,8.46,3.30 and 3.04,respectively.The energy distributions of Ag,Ta,Au and U ions are similar to each other,and their energy spectra are in the middle of the range compared with other metal ions,as shown in figure 3(l).Their dimensionless areal densities are 5.87,5.55,5.90 and 4.83,respectively.In addition,there are two peaks in all the energy spectra,with the energy spectra of Cr and Fe ions having the most pronounced peaks.
4.Discussion
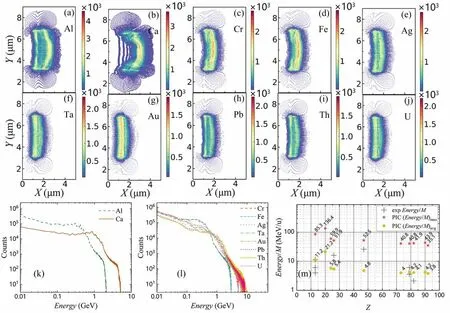
Figure 3.Ion spatial distributions simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser on different metal targets: (a),(b) Al and Ca targets of thickness 200 nm at 60 fs ; (c)-(j) Cr,Fe,Ag,Ta,Au,Pb,Th and U targets,respectively,with a thickness of 100 nm at 60 fs.Ion energy spectra simulated by Smilei for SEL 100 PW laser on different metal targets: (k) Al and Ca targets with a thickness of 200 nm at 60 fs; (l)Cr,Fe,Ag,Ta,Au,Pb,Th and U targets with a thickness of 100 nm at 60 fs.(m) Energy distribution diagrams for different metal ions were simulated as above and obtained experimentally,as detailed in section 4.
When it comes to the energy of these ions,there have already been some experiments conducted to measure ion energy.The average and maximum energies of these simulations,with experimental energies,are displayed in figure 3(m).The experimental energies of Al are 4 MeV/u,6.1 MeV/u and 11.5 MeV/u,respectively,in a laser-driven ion acceleration experiment by Neelyet alwith a 1019W/cm2laser and 100 nm Al target [56] and by Palaniyappanet alwith 2×1020W/cm2and 8×1020W/cm2lasers and 110 nm and 250 nm Al targets [57].The experimental energy of Au is 3.6 MeV/u in the laser-driven ion acceleration experiment by Wanget alwith a 1022W/cm2laser and 150 nm Au target [21].The experimental energy of Pb is 2.1 MeV/u in the laser-driven ion acceleration experiment by Clarket alwith a 5×1019W/cm2laser and 2 mm Pb target [58].As the laser intensity increases,a higher ion energy was recorded for a nanometer metal target.The experimental energies of Fe,Ag and Au were 16.1 MeV/u,26 MeV/u and 6.1 MeV/u,respectively,and three of these are higher than the average energy of simulations and come from composite targets [21,59,60].
According to the spatial distribution and ionization of heavy ions,a 2D target ( 4μm×0.1 or 0.2μm) can be extended to a 3D target ( 4μm×4μm×0.1 or 0.2μm),and the corresponding ion beam intensity can be obtained from equation (6),
wherelis the length of the chosen space in thex-direction,Nis the number of ions,vis the average velocity of ions,is the average charge number of ions in the chosen space andeis the unit electric charge.The expression for the divergence of the ion beam in 2D space can be described by equation (7)
The region of the ion beam isX∈[1.5μm,6μm] andY∈[3μm,7μm] .The conversion efficiency η can be obtained fromEions/Elaser,whereEionsis the energy of all ions andElaser≈ 212 J is the energy of the laser presented above.The beam intensity,divergence and laser-to-ion energy conversion efficiency of all metal ions can be obtained from the above equations and compared with the respective results of simulations at 60 fs; these are listed in table 1.
Compared with the beam intensity of 1.8 mA obtained by Dubenkovet alfor Ta ions accelerated by a 10 J/μs CO2laser in 1996 [12],this result is about five to six orders of magnitude higher.While compared with the beam intensity of 1.4 MA obtained by Wanget alfor Fe ions simulated with a linearly polarized laser intensityI0=1.1×1021W/cm2and an 800-nm thick target in 2014 [19],this result is of the same order of magnitude.The stronger laser and the thinner metaltarget separately cause the beam intensity in this simulation to be larger than both the above.In some way they also reflect the variability of results from different acceleration mechanisms.Here the target is small and pure metal,and the conversion efficiency is thereby relatively low compared with the efficiency of 30% calculated by Domanskiet alfor a 100 nm Pb target with a 20 nm pre-plasma layer at the front irradiated by a 1023W/cm2laser (corresponding to laser energy of 270 J ,pulse duration 30 fs and focal spot 3μm ) [55],8% calculated by Petrovet alfor a 20 nm Au target with a 5 nm contaminant layer on the back irradiated by a 3×1021W/cm2laser [53] and 15% - 19% experimentally acquired by Badziaket alfor a 3μm Au target with a 5μm CH ablator at the front irradiated by a 200 J laser [61].Furthermore,the parameters controlling the stratification are not only the target thickness but also the laser parameters,of which the main factor is the laser energy,including the FWHM and focal spot size,which should be comparable to the length of the target.In other words,stronger lasers might be able to stratify thicker targets when the parameters of both the laser and the target are appropriate.
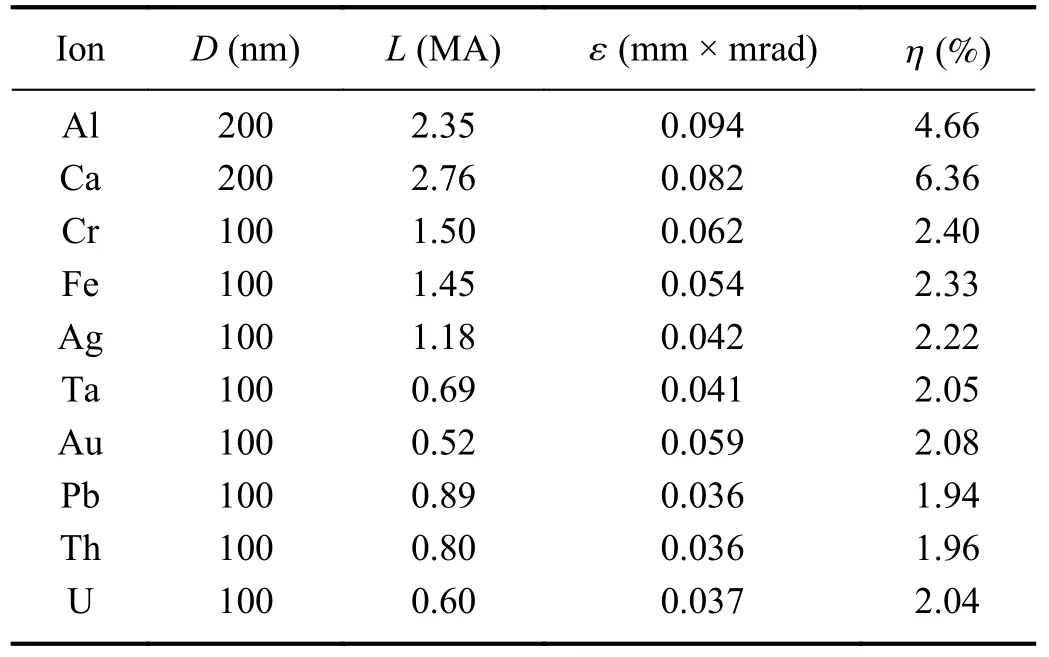
Table 1.Target thicknesses (D),intensities (L) and divergences ( ε)of the ion beams,and laser-to-ion energy conversion efficiencies ( η)simulated by Smilei for the SEL 100 PW laser.
The LPA,as a new type of accelerator,might become a unique experimental approach for exploring nucleosynthesis,such as superheavy nuclei.The maximum energy of the Th ion beam above is about 43.9 MeV/u,which is up to 7.5 - 6.1 MeV/u of the multinucleon transfer reaction with the Texas A&M University (TAMU) Cyclotron [62].A LPA with a 100 mA class Au+ion source has been well designed[63],and the low divergence of the primary ion beam may greatly simplify the design of the experimental setup.Additionally,a LPA might be used to separate highly ionized heavy ions with different charge states in order to further improve the beam quality and produce a pure beam of highflux-intensity heavy ions in future [55].
In addition,a thinner target can be prepared when the front layer is peeled off,and there is no doubt that a short metal target is key to this manufacturing process.We can then splice into one piece of large and ultra-thin foil or put a coat on the surface of the material directly,such as active colloidal particles.
5.Conclusion
In conclusion,we used the PIC program Smilei to simulate the SEL 100 PW ultra-intense ultra-short laser hitting an easy-to-manufacture and accelerated metal target.Stratification is seen,and the motion,energy and charge of metal heavy ions in an electric field are discussed as well.Ion energies can reach an order of magnitude of 10 GeV,the ion beam intensity is about 1 MA and the divergence is about 0.05 mm×mradin this simulation.Unique scenarios in the RPA and TNSA hybrid acceleration mechanisms are the intriguing layering phenomena,which can provide a new solution to laser selection and the type and size of metal targets with heavy nuclei in future experiments.This process can be applied to study LPAs for heavy-ion beams,laser manufacturing of thinner metal targets and heavy-ion fusion reactions in a plasma environment.The better performance of the target is likely to be used in the future research,such as heat resistance and no ready generation of other compounds like oxides,carbides or nitrides [36].However,the layering phenomenon still has to be confirmed and investigated by probing ion motion trajectories or energy spectra in experiments.It is innovative to optimize the heavy-ion beam generated by a LPA.If better conditions for heavy-ion nuclear reactions can be achieved using a high-power laser source,new superheavy nuclei can be explored or the chart of nuclides may be enlarged [64,65].
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to X.Q.Yan at Peking University,H.W.Wang at Shanghai Advanced Research Institute,Chinese Academy of Sciences and J.Pu,K.X.Cheng,Y.F.Guo and C.Y.Qiao at Henan Normal University for fruitful discussion.Cao and Su are grateful for support from the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No.XDB34030000),the National Key R & D Program of China (No.2022YFA1602404),National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.U1832129) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No.2017309).Ma,Su and Wang thank the Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province of China (No.21IRTSTHN011).
 Plasma Science and Technology2024年2期
Plasma Science and Technology2024年2期
- Plasma Science and Technology的其它文章
- Detection of Al,Mg,Ca,and Zn in copper slag by LIBS combined with calibration curve and PLSR methods
- Experimental study on the effect of H2O and O2 on the degradation of SF6 by pulsed dielectric barrier discharge
- Phase field model for electric-thermal coupled discharge breakdown of polyimide nanocomposites under high frequency electrical stress
- Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure positive pulsating corona discharge in degradation of textile dye Reactive Blue 19 enhanced by Bi2O3 catalyst
- Airfoil friction drag reduction based on grid-type and super-dense array plasma actuators
- Characteristics of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy of liquid slag
