Distributed dynamic event-based finite-time dissipative synchronization control for semi-Markov switched fuzzy cyber-physical systems against random packet losses
Xiru Wu(伍錫如), Yuchong Zhang(張煜翀), Tiantian Zhang(張畑畑), and Binlei Zhang(張斌磊)
School of Electronic Engineering and Automation,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
Keywords: cyber-physical systems, finite-time synchronization, distributed dynamic event-triggered mechanism,random packet losses
1.Introduction
Cyber-physical systems (CPSs), as the complex systems integrating computation, networks communication and control,[1,2]have been investigated intensively due to their frequent applications in network coordination and physical resources, such as network power schedules, multi-agent control and remote estimation.[3-5]It is worth noting that reliability has become the increasingly critical network-induced issue in the control of real CPSs.In Refs.[6,7], the sliding mode control approach was deployed for CPSs with malicious attacks to guarantee security and reliability.In particular, bandwidth limitation is becoming a serious problem due to the physical properties of network interaction, which generates inevitable information packet losses.Nevertheless,current research rarely refers to the effect of random packet losses in CPSs, aside from the interconnected multi-systems with complex structure.
The Takagi-Sugeno (T-S) fuzzy model has been used to handle complex nonlinear systems due to its remarkable competence in accurate approximation.[8-10]Reference [11] built the model of partially coupled complex networks via a collection of IF-THEN rules and fuzzy membership functions.To solve the immeasurable state problem, Ref.[12] also developed an adaptive fuzzy observer using IF-THEN fuzzy rules.The T-S fuzzy model was applied in the resilient controller design of CPSs to deal with input saturation and cyberattack in Ref.[13].In reality, abrupt changes in system structure may lead to unexpected mode variation and system instability,such that Markov switched parameters are introduced to organize the T-S fuzzy system model.[14,15]In Ref.[14], a finite-time asynchronous state estimation scheme was raised for Markov jump T-S fuzzy systems.As reported in Ref.[16],the transition probability matrix is considered to be time-varying because the sojourn time obeys arbitrary probability distributions.In view of this, semi-Markov switched T-S fuzzy systems have more relaxed constraint compared with conventional ones.[17,18]For instance,in Ref.[17],Zhanget al.concerned the stabilization issue of uncertain T-S fuzzy systems under a semi-Markov chain.Therefore, it is meaningful to further explore the effective control theory in T-S fuzzy CPSs(TSFCPSs)subject to semi-Markov switched modes.
In the study of system stability control, most of the existing results focused on Lyapunov stability within an infinite time interval, but some realistic scenes require finitetime control performance.The authors in Ref.[19] applied a power integrator technique combined with a backstepping method to achieve finite-time stability control.Such a theory has been imported to finite-time synchronization (FTS)and, simultaneously, it should also be emphasized that consideration of system properties in the achievement of FTS is necessary.[20,21]As the description of the immanent relationship between storage functions and supply rates,dissipativity performance can reflect the internal stability and has been regarded as a more powerful tool in system control than passivity andH∞theory.[22]With regard to a class of Markovian jump inertial neural networks,Songet al.derived the less conservative criterion of FTS with a dissipative index in Ref.[23].As reported in Ref.[24],the global dissipativity based on the Filippov solution was developed to ensure the FTS of memristorbased neural networks.However, the dissipative problem of FTS control for TSFCPSs has not attracted adequate attention.
To cope with the limited communication resources, an event-triggered mechanism (ETM) was proposed to reduce frequent data transmission and overmuch consumption.[25-28]By this means, the updated data of the control input are released only when a prespecified trigger condition is satisfied.In Ref.[29], based on adaptive ETM, the authors proposed a quantized method for the distributed estimation of semi-Markov switched sensor networks.With the event-based control technique, the stability problem of linear systems suffering packet losses was solved in Ref.[30].In recent literature,a class of dynamic ETM was designed by setting an internal iterative variable in the triggering condition, which possesses lower triggering frequency than conventional ETM.[31-33]As shown in Ref.[33],the authors proposed aH∞filtering strategy for a T-S fuzzy system based on dynamic ETM, which contributed to reduction of the consumption.Although the dynamic ETM has shown superiority, some redundant data will be transmitted if subsystems share a unified triggering condition, which promotes the motivation for extending related studies under the distributed framework.[34-36]Besides,the process of packet dropout is depicted by a stochastic sequence following the continuous Bernoulli distribution in previous studies like Refs.[37-39],but this method is unsuitable for a non-uniform sampling situation where triggering instants fail to be transmitted.Therefore, there is the need to establish a realistic framework to analyze a distributed dynamic ETM(DDETM)influenced by random packet losses in semi-Markov switched TSFCPSs.
According to the aforementioned analysis, this paper aims to investigate the strictly dissipative FTS issue of semi-Markov switched TSFCPSs with packet dropouts under a distributed dynamic event-based pinning control scheme.The main contributions are summarized as follows:
1) To investigate the finite-time synchronization strategy within the framework of CPSs with interconnected multisystems, a T-S fuzzy model-based distributed control construction is developed.In contrast to the network models in Refs.[21,42],the presented system considers parameters subject to a semi-Markov chain and a communication process restrained by packet loss simultaneously.
2)The pinning strategy and DDETM are jointly proposed to improve the transmission schedule of desired controller signals.Unlike the approaches in Refs.[25-27],a dynamic variable related to synchronization errors is introduced to design the triggering condition,which results in a lower information update frequency.Additionally,aiming to handle the stochastic data loss sequence that does not satisfy Bernoulli distribution, an equivalent prediction model distinguished from Refs.[37-39]is provided to transform the triggering instant.
3) Based on augmented terms with respect to delays,a mode-dependent Lyapunov-Krasovskii functional (LKF) is constructed to guarantee the FTS accompanied by the desired dissipative performance.Compared with the sum-term estimation methods in Refs.[11,27,31,43],an extended reciprocally convex matrix inequality(ERCMI)is combined with a delayproduct-type double sum term to derive a tighter result with less conservatism.
The rest of this paper is arranged as follows: Section 2 describes the preliminaries and builds the problem model.In Section 3,synchronization and dissipativity analysis of closedloop TSFCPSs proceed via strict mathematical derivations.Section 4 provides two examples to verify the theoretical results.Section 5 gives the conclusions.
Notations Throughout the paper,Rnand Rn×mrepresent then-dimensional Euclidean space and the set of alln×mdimensional real matrices; Z+denotes the set of all positive integers;l2[0,∞) means the space of square-summable infinite vector functions over [0,∞); vecn{·}is the symbol of the column vector, includingnblocks; diag{·}means a block-diagonal matrix;?refers to the Kronecker product;cmax(R) (cmin(R)) represents the maximum eigenvalue (minimum eigenvalue) of the matrixR; Pr{·}andE{·}represent the probability of event occurrence and mathematical expectation,respectively;Sym{P}=PT+P;and?denotes the symmetric term of a symmetric matrix.In addition, the matrixQ >0(Q <0)meansQis a positive-definite matrix(negativedefinite matrix).
2.Problem formulation and preliminaries
Consider a class of semi-Markovian switched discretetime complex networks withNcoupled nodes as the CPSs,which can be described by the following T-S fuzzy rules:
Plant rulem: Ifκ1(k)isGm1,κ2(k)isGm2,...,andκp(k)isGmp,then

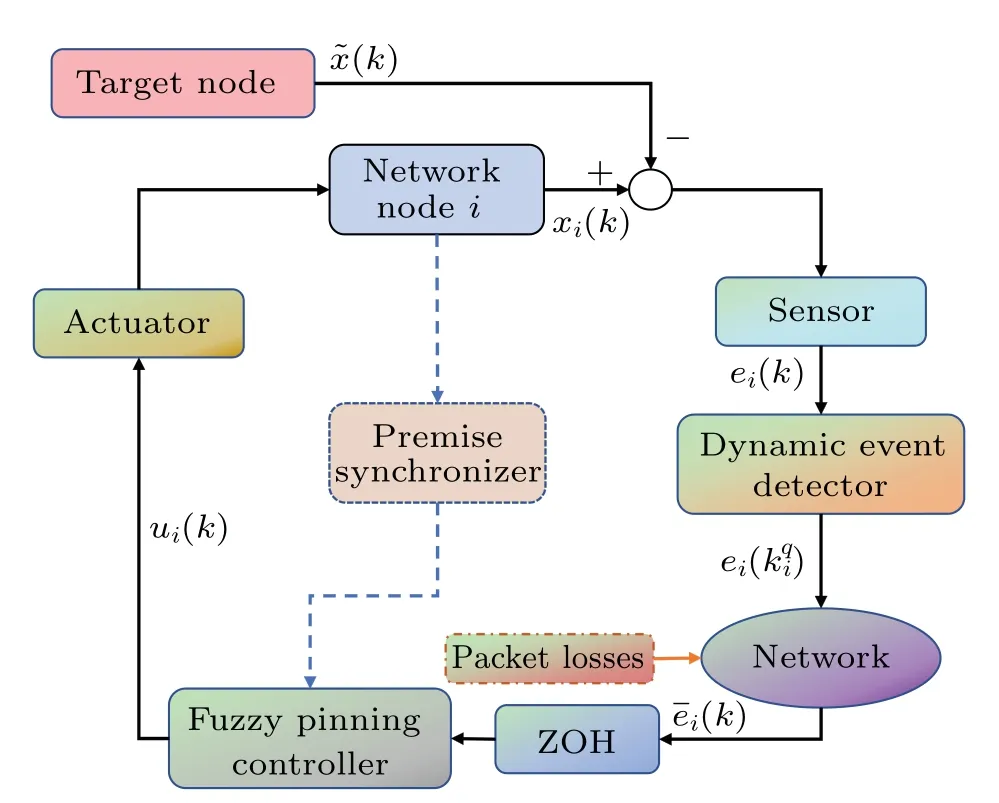
Fig.1.A block diagram of the control procedure in node i.
Asψst(k)is time-varying with incomplete measuring information,it can be expressed by the following new form:
forμ? ≥0.Based on Refs.[16,18,22],ψ?stis limited by the following boundary conditions:
Via the weighted average fuzzy blending method, the global TSFCPSs model with respect to subsystem (1) is described as
where ?mrepresents the simplification of the normalized membership function ?m(κ(k))satisfying
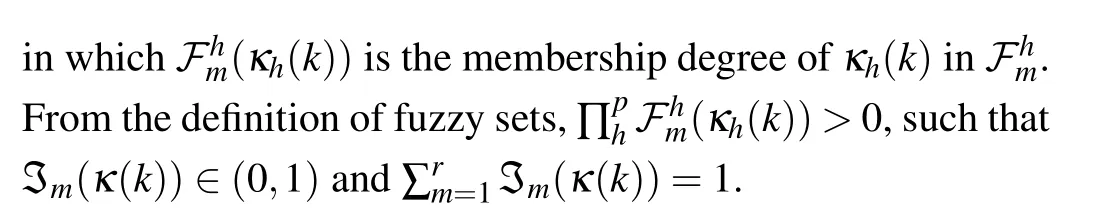
The model of the target node in TSFCPSs is given as
where ?x(k)∈Rn, ?y(k)∈Ryare vectors on behalf of the target state and corresponding control output, respectively.The initial state of ?x(k)is set as ?ν(s)fors ∈{-ˉσ,-ˉσ+1,...,0}.
We defineei(k)=xi(k)-?x(k)andeyi=yi(k)-?y(k),such that we obtain the synchronization error system of TSFCPSs as below:

To compensate the lost data caused by packet losses,the estimated error is introduced to the controller design.Combined with the parallel distribution control(PDC)technology,the fuzzy pinning controller can be given by the following rules:
Controller rulev: Ifκ1(k) isGv1,κ2(k) isGv1,..., andκp(k)isGvp,then
where ˉei(k) is the estimated control input andis theith control gain matrix under the fuzzy rulev.Besides,φiis the pinning parameter, whereφi=1 means theith node is controlled,otherwiseφi=0.
The distributed event generator functionQ(·,·) is regulated as follows:

Here, ?ρiis a given positive parameter,andΓi(k)represents theith internal dynamic variable,which is described as
withΓi(0)=≥0 and the given constantηi ∈(0,1).
Remark 1 Compared with the traditional ETMs,shown in Refs.[25-27],restricted by a static-coefficient-related triggering threshold, the adopted DDETM is established under a time-varying constraint condition,where the dynamic variableΓi(k) is influenced by the real-time system errorsei(k) andεi(k).It is obvious from Eq.(8)that the triggering mechanism will reduce to the static ETM in Ref.[27]if parameter ?ρigoes to infinity.Therefore, the DDETM can flexibly regulate the distributed controller performance by changing parametersδiand ?ρi.It easily observes that the value ofδiincreases together with the decrease of the triggering rate, while the triggering rate increases with the growth of ?ρi.
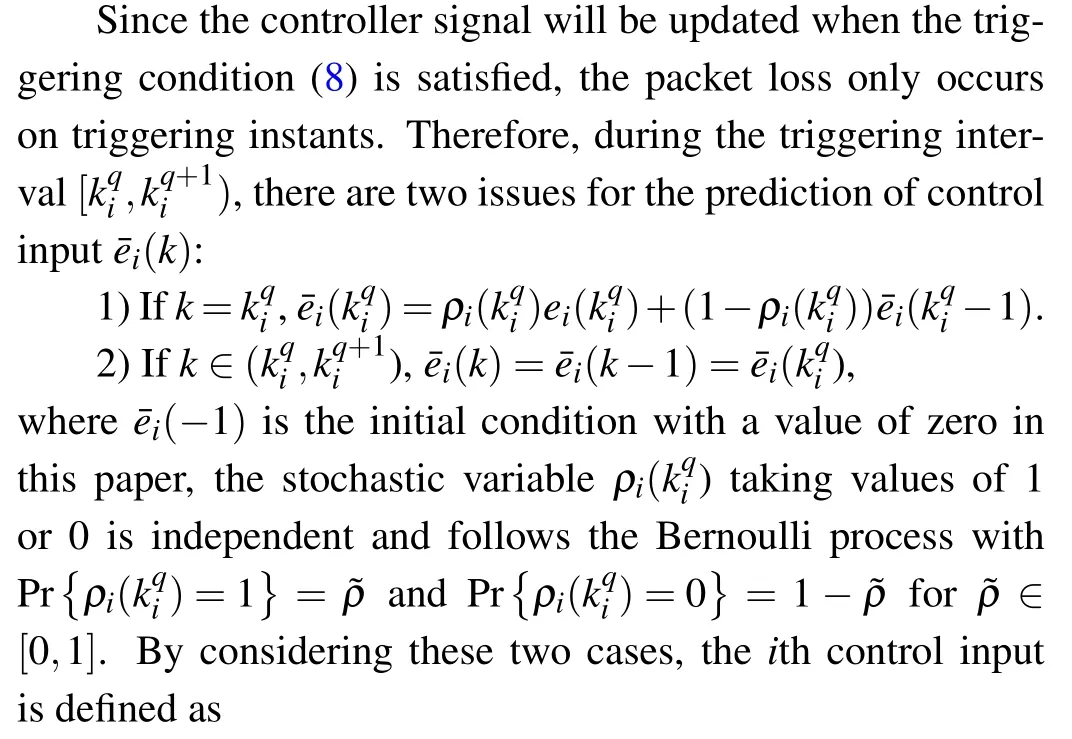

The controller dynamics can be obtained by computingei(k)in the interval offor the availability ofTherefore, controller (12) can share the same premise variablesκi(k)with system(1).
Remark 2 Combined with the packet dropout behavior,the controller limited by the event-triggered condition will receive a relatively less feasible data packet from the sensor.It is worth noting that triggering instants are non-uniform sequences,such that the continuous Bernoulli distribution model in Refs.[8,29,38] cannot be directly employed to describe the event-based controller.By constructing a new sequence{χ(k)}k∈Z+in regard to variable, the circumstance of triggered data transmission will be captured adequately.

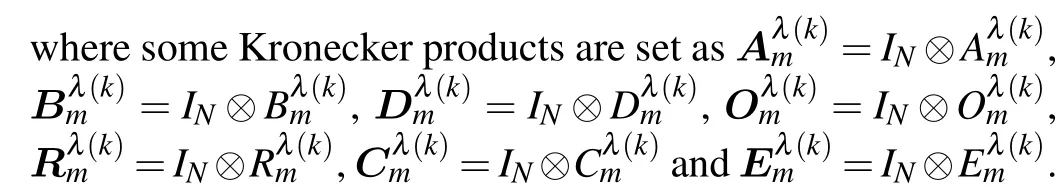
Figure 2 demonstrates the operation framework of the closed-loop system, where the DDETM is proposed to manage the signal transmission.Moreover,a compensation mechanism is employed in the control input to guarantee the reliability.
Before conducting further analysis,some essential definitions,assumptions and lemmas are listed.
Definition 1[20]There is a matrixQ, a given constant ?ωand two positive scalarsε1,ε2withε1<ε2.The error system (13) is said to be mean-square finite-time bounded with respect to(ε1,ε2,X,T, ?ω)if the following condition is insured for?k ∈{1,2,...,T}:
Definition 2[22]Given a fixed scalarγ >0,the real matricesΥ1=ΥT1≤0,Υ2andΥ3=, system (1) with disturbanceω(k)∈l2[0,∞) can achieve the strictly (Υ1,Υ2,Υ3)-γdissipative FTS with respect to(?1,?2,X,T, ?ω,γ)if error system(13)satisfies the condition of Definition 1 and the following inequation for allT ≥0:
where the energy supply rateJ(ey(k),ω(k))is denoted as
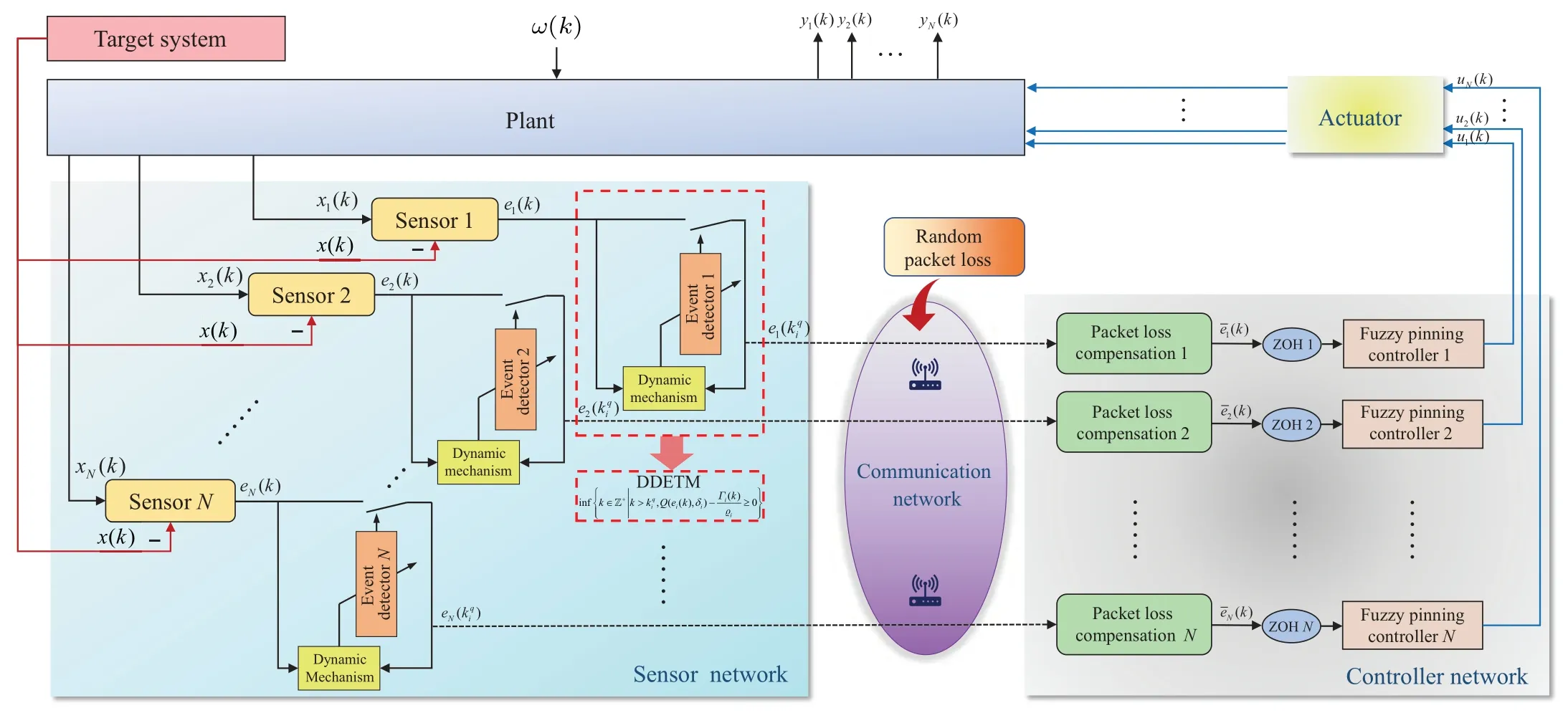
Fig.2.The framework of detailed signal transmission in the whole closed-loop CPSs.
Assumption 1 The initial value of the error system should conform to the following condition:
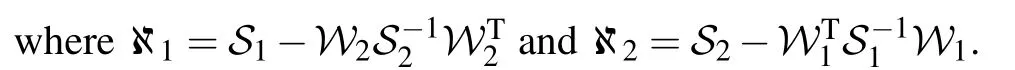
Lemma 3[41]For a positive matrixQand positive integerν1<ν2, any discrete-time variableχ(k)∈Rncan satisfy the following inequality:
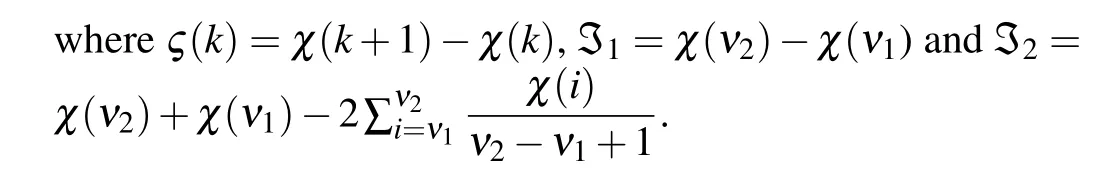
3.Main results
In this section,the finite-time strictly dissipative synchronization conditions are discussed and the desired controller is designed under the DDETM.
3.1.Finite-time boundness analysis
The finite-time boundness of synchronization errors will be analyzed firstly in the following theorem.Consider the semi-Markov switched error system (13) affected by random packet losses.

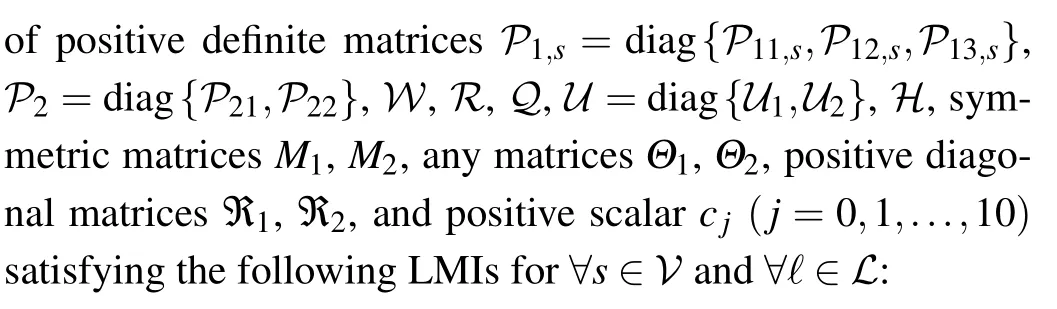
where

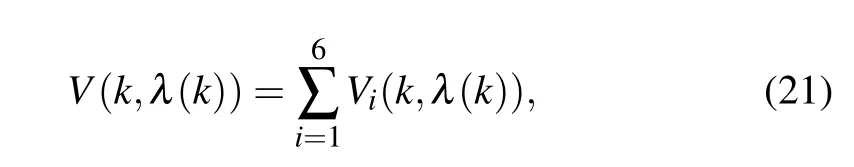
where
where
Define ΔV(k,λ(k)) =V(k+1,λ(k+1))-ξV(k,λ(k)), we can obtainE{ΔV(k,λ(k))}along the trajectories of the error system(13),and it follows that
Using Lemma 3,we can obtain
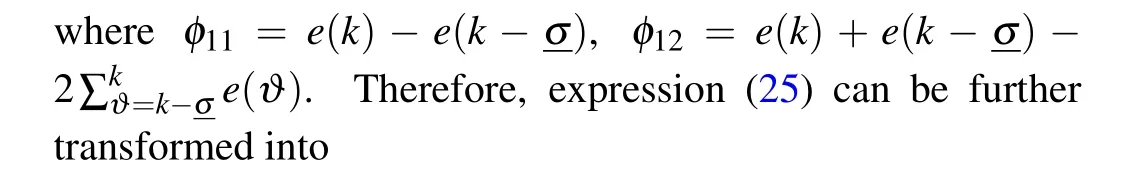
Then,
To estimate the bound ofE{ΔV5(k,λ(k))},the following zero-value equations are presented for any symmetric matricesM1andM2:
With the combination of Eqs.(30) and (31), it follows from Jensen’s inequality theory that
where the delay-dependent termΠ3,[σ(k)]is described as
Relying on the inequality(17)in Lemma 2,Π3,[σ(k)]can be further bounded as follows:

Notice that activation functions satisfy the Lipschitz continuity in(A2),and one has the following inequations:
whereA1,A2,B1andB2are defined in Eq.(20).Moreover,based on the event-triggered constraint condition (8), we can derive that for any positive constant ˉh,
Repeating the process from inequations (21)-(35), we easily get
where
andis stated in Eq.(20).From the convex combination technique and(A1),we have the following inference:
Then,with the help of the Schur complement theory,the constraint<0 will hold for≤σ(k)≤if inequation(18)is satisfied,such that
Hence, we can further conduct the following iterative operation with regard to finite timek:
wherecmax(H)is the maximum eigenvalue of matrixH.The value ofV(0,λ(0))is estimated as
With the combination of inequations(42)and(43),we have
Due to the conditionP11,s ≥c11Xin Eq.(19),it exists as
such that the following inequation holds:
The finite-time boundness of the error system (13) can be eventually derived.This completes the proof.
Remark 4 In the finite-time boundness analysis of the closed-loop error system, an augmented mode-dependent LKF, containing vectors?1(k),?2(k) and?3(k), is constructed and inspired by Ref.[23].Differing from the common LKF that is only formed by error or state vectors, the augmented terms observe more information of delays through more sum-terms.Specifically, the improved delay-producttype terms inV1(k,λ(k))andV6(k,λ(k))further consider the change rate ofσ(k)and develop the results in Ref.[41].Moreover, the proposed>0 in Eq.(19) provides a more relaxed range for the stability criterion.
Remark 5 In Refs.[11,27,31], some inequality techniques, such as Abel lemma, Wirtinger-based inequality and Jensen’s inequality,were introduced to handle the single sumterm or simple double sum-term.However,the delay-producttype double sum term inV6(k,λ(k)) will contribute to more nonlinearities and uncertainty.To obtain more accurate estimation, the ERCMI is raised by not introducing additional decision variables or adding the dimension of LMIs, in order to further reduce the conservatism.
3.2.Finite-time strict dissipativity analysis
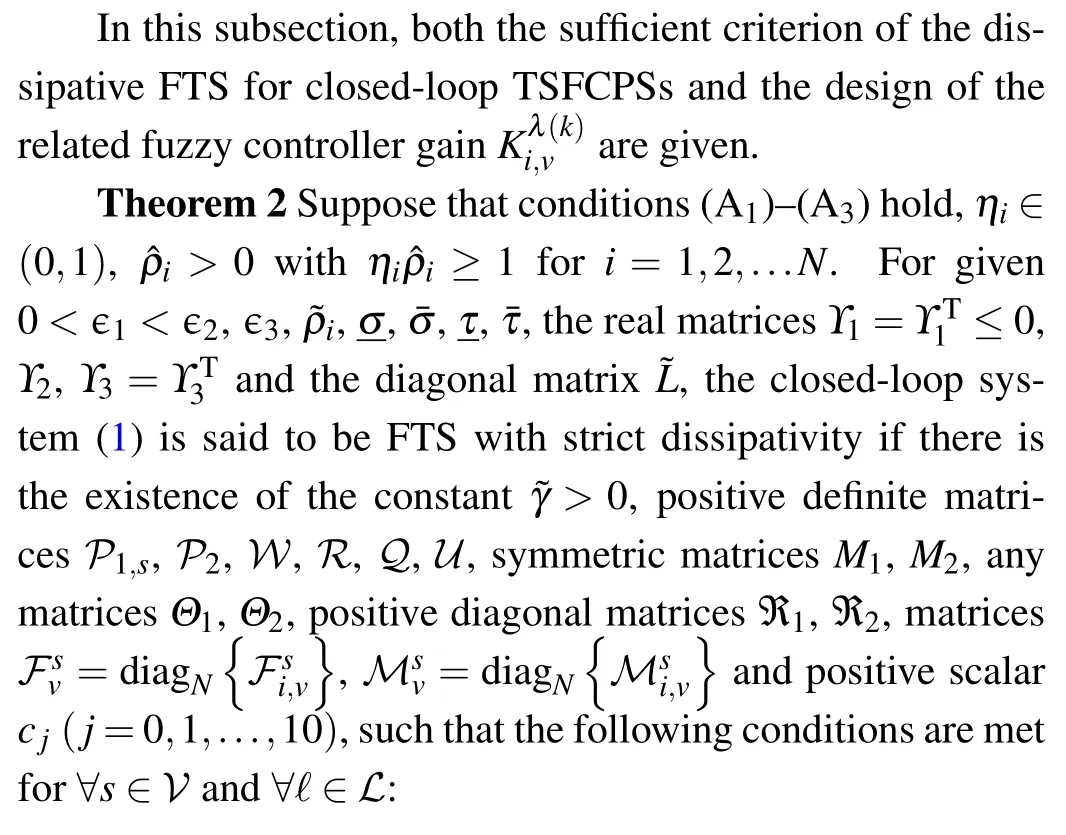
where
and other parameters are defined in Eq.(20).Moreover, the controller gain matrix is described as
Proof Considering the LKF candidate constructed in Theorem 1.For any invertible matrixFsv, one has the following zero-value equation:
As the controller is greatly impacted by the pinning parameterφi,we can further obtain the following inequation:
To study the strictly dissipative performance of the synchronization error system,an object function is constructed as follows:
Similar to Eq.(38),it derives from Eqs.(49)-(51)that

Recalling Eq.(40)and the application of the Schur complement, we can getE{ΔV(k,λ(k))-G(k)} ≤0, which is equivalent to
Based on the iterative operation within the time interval[0,k]in Eq.(42),it derives the following inequation under the zeroinitial condition:
With the premises ofE{V(k,λ(k))}>0,it is easily concluded that
Obviously, the closed-loop TSFCPSs can satisfy finite-time strictly (Υ1,Υ2,Υ3)-γ-dissipative performance in the right of Definition 2.The proof is accomplished.
Remark 6 In terms of the dissipativeness definition and results of Theorem 1,a new framework is established to analyze the finite-time dissipative synchronization of the closedloop system,in order to obtain the sufficient condition in Theorem 2.By utilizing the LMI technique, controller gain matrices under various modes can be calculated.Notice that the number of modes and nodes affects complexity; therefore, a tradeoff between computational burden and conservation is necessary in real application.
The following corollary is formulated for the Markov switched CPSs absent from the T-S fuzzy model:
where
and other notations are given by Eq.(48).If LMIs are feasible,the controller gain is calculated asFurthermore, we can also derive the condition of finite-timeH∞synchronization for CPSs when settingΥ1=-1,Υ2=0 andΥ3=γ2+γ.
4.Numerical simulations
In this section,numerical examples and simulation results are presented to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed theories.
Example 1 Consider the following dynamic equation of the gearing connected single-link robot arm as the target model of CPSs:[25,38]
whereq(t)and ˙q(t)denote the arm angle position and angular velocity.Given parameterL=0.5,g=9.81,D=2.Here,Mλ(k)andJλ(k)are mode-dependent withM1= 1,J1= 1,M2=5,J2=5,M3=10 andJ3=10.
Setxi1(t)=qi(t) andxi2(t)= ˙qi(t) for CPSs containing six nodes,and Eq.(57)can be discretized by the first-order Euler approximation method with the sampling period Δt=0.1 s.Referring to Ref.[38],the CPSs are constructed by a T-S fuzzy model with the following membership functions:
wherexi1(k)∈(-π,π),β=10-2/π.System parameters subject to two fuzzy rules and three modes are selected as
Fuzzy rule 1 Ifxi1(k)is 0 rad,then
The retarded coefficient is set as?=0.9.

Fig.3.The physical structure of the gearing connected single-link robot arm and coupled topological relation under three switched modes.
As shown in Fig.3, CPSs can change topology relations among three modes, and the corresponding elements in the transition probability matrix satisfy
WhenL=2,the values ofare given as

Assume that nodes 1, 2 and 6 are the controller, some parameters are supposed as ?L=diag{I,I,0,0,0,I},ξ=1.02,?1=10,?2=50,T=50, ?ρ1= ?ρ2= ?ρ6=0.15,η1=η2=0.6,η6=0.5, ?ρ1= ?ρ2= ?ρ6=25,δ1=δ2=δ6=0.4 and ?ω=1.8.The dissipativity-related matrices are set asΥ1=-0.4I,Υ2=IandΥ3=4I.By solving the LMIs proposed in Theorem 2,controller gains and the maximum dissipative levelγare deduced.Table 1 gives the allowable maximum dissipative levelγfor different ˉσandδi, where a larger ˉσresults in the decrease in dissipative levelγand a smallerδiwill improve the dissipative performance.
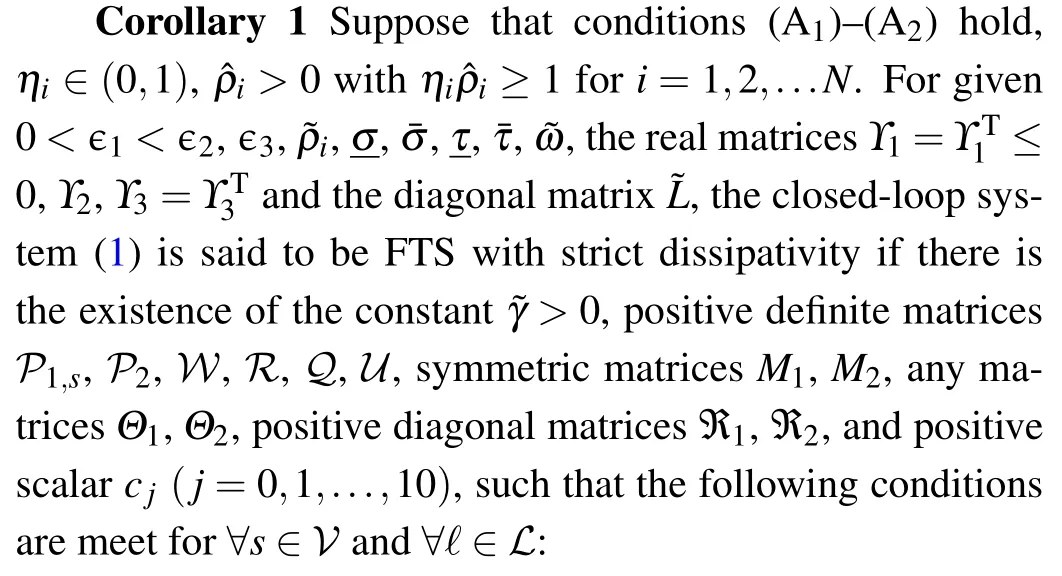
Randomly choose the initial values of CPSs within the range of[-π,π], and let ?x(k)=[-3,2]fork ∈[-5.0]Z.Figure 4 reveals the evolution of synchronization errors under random 200 realizations, which proves that the designed control method can ensure error convergence.As shown in Fig.5,the states of CPSs subject to packet losses track the state of the target node in finite timeT.As Remark 3 said,the PDC method is used and the curves of the controller states and their triggering instants are depicted in Figs.6(a)and 6(b).The update frequency of the control signals is reduced efficiently.
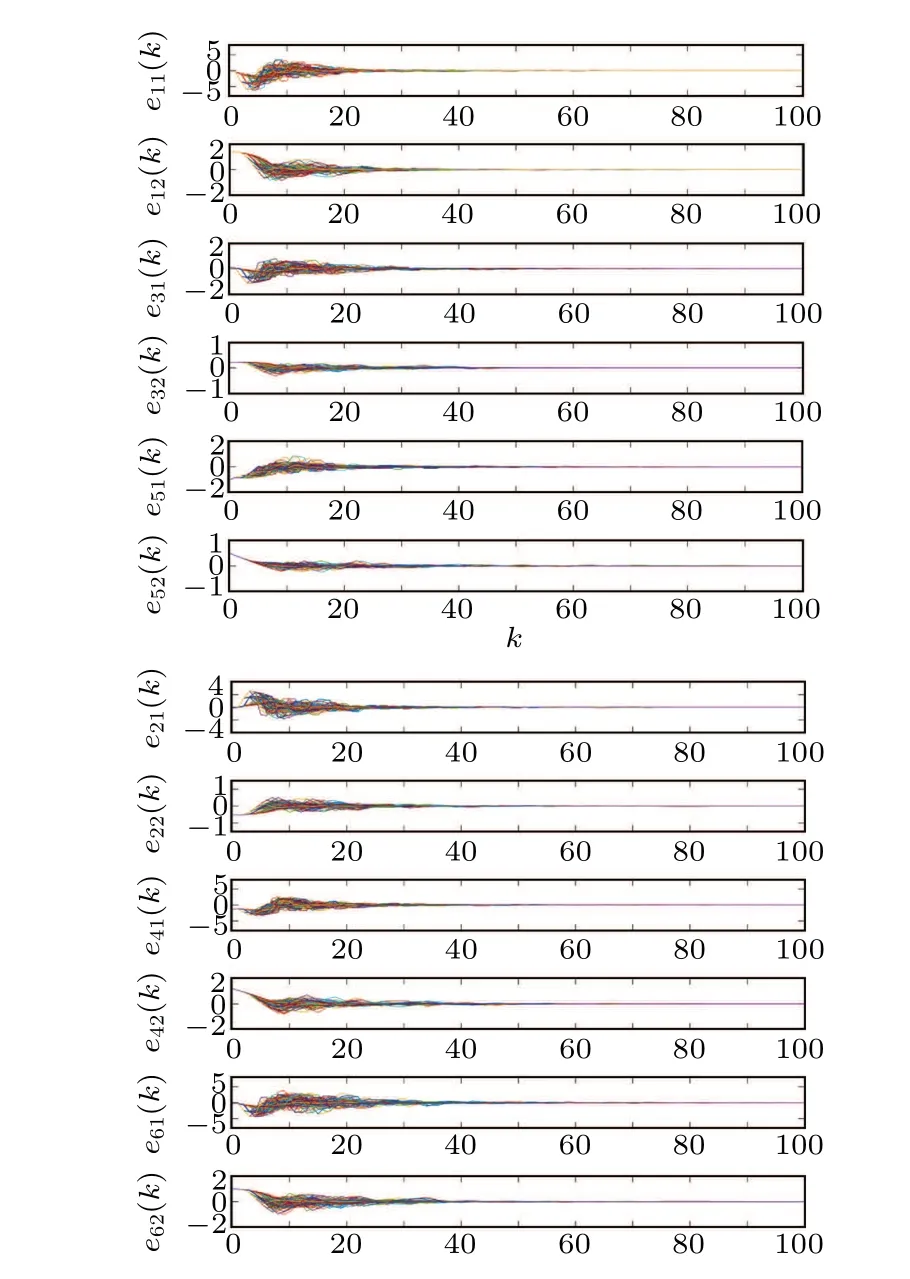
Fig.4.The response of the synchronization errors in closed-loop CPSs under 200 realizations.
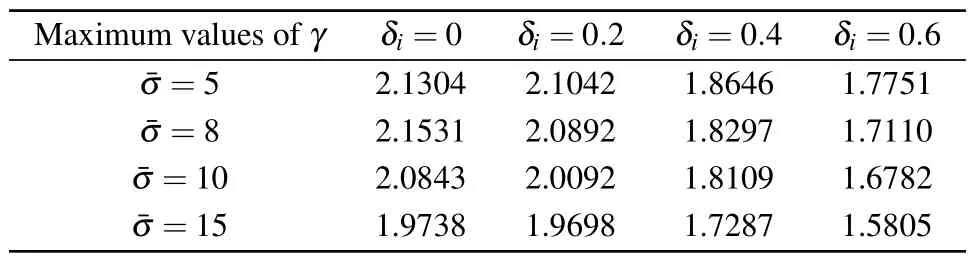
Table 1.The allowable maximum dissipative level γ for various ˉσ and δi.
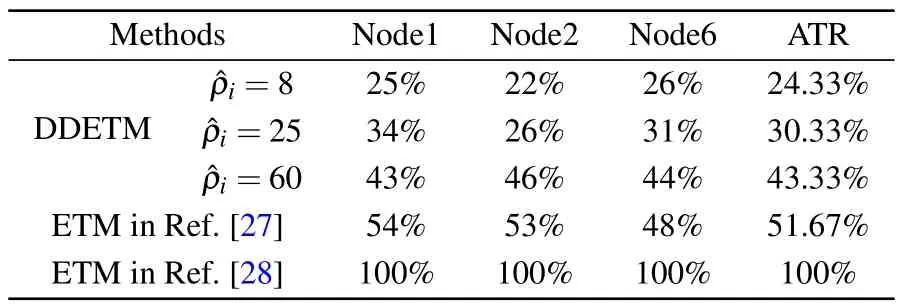
Table 2.A comparison of TR under various methods.
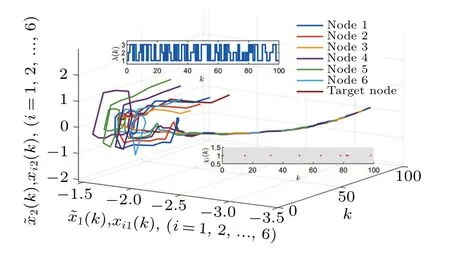
Fig.5.States of the closed-loop CPSs under packet losses and switched system modes.
To indicate the advantage, Table 2 compares the triggering rate (TR) of three pinned nodes under various triggering mechanisms in Refs.[27,28]and this paper.Clearly,the average TR(ATR)of our used DDETM is significantly lower than techniques in others.Moreover, we observe ATR rises with the growth of ?ρi.
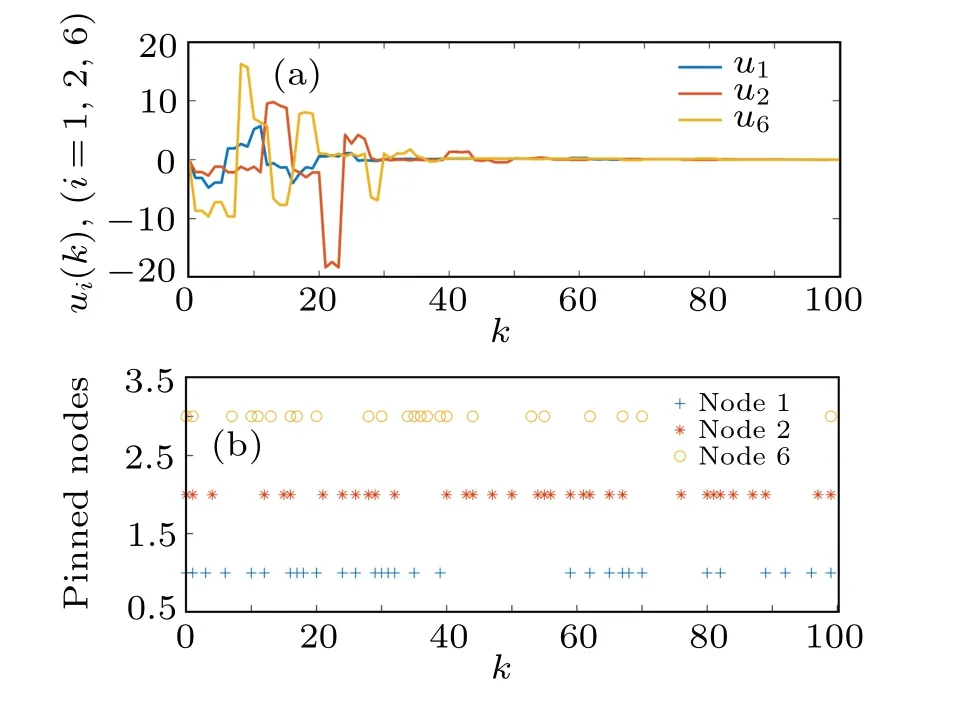
Fig.6.(a)The curves of controller signals.(b)The triggering instants of controllers 1,2 and 6.
Example 2 For Corollary 1,consider the Markov doublemode-switched CPSs,including five subsystems where the parameter matrices are provided in Table 3.

Based on LMIs given in Eq.(55), we can calculate the feasible controller gains as follows:
and the allowable maximum dissipative levelγ=2.5261.
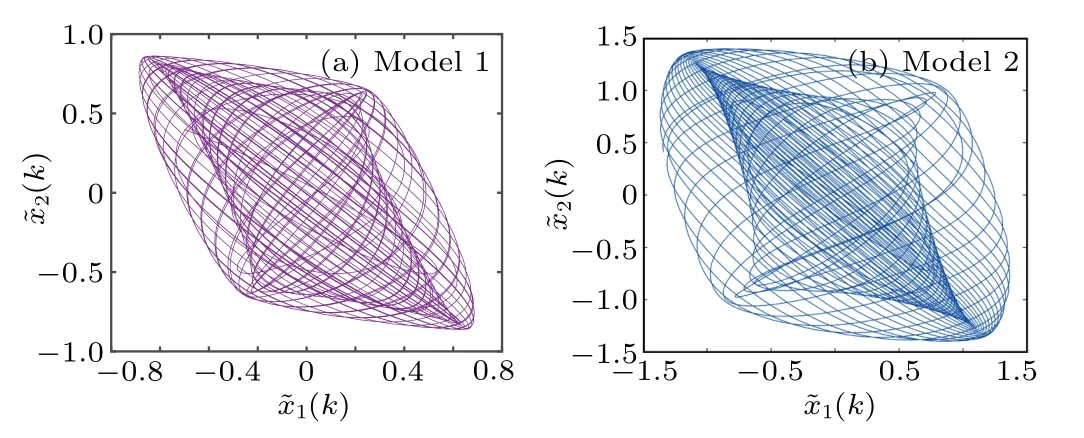
Fig.7.The phase diagram of ?x(k)for two switched modes.

Table 3.System parameter matrices for each mode.
Assumed initial values of nodes in the interval [-3,3],simulation results of closed-loop errors and states are exhibited in Fig.8, where FTS can be realized for CPSs suffering from random packet losses.Controller signals are shown in Fig.9 and the curves are step-like;this indicates that transmission only occurs at triggering sampling instants.Figure 10(a)gives the variation tendency of three dynamic variablesΓi(k)fori=1,2,5, which vary together with the synchronization errors.The triggering performance of each node is displayed in Fig.10(b).
In the following, the control performance for the situation of different parameter values will be discussed.As listed in Table 4,we compare the TR when the value ofδiis set from 0 to 0.8.It is obvious that ATR decreases with the decline ofδimonotonically,as described in Remark 1.Although a lower TR saves more computation resources,control ability may be affected because of receiving less available data.

Fig.10.(a)The evolutions of the dynamic variable Γi(k)for i=1,2,5.(b)The triggering instants of controllers 1,2 and 5.
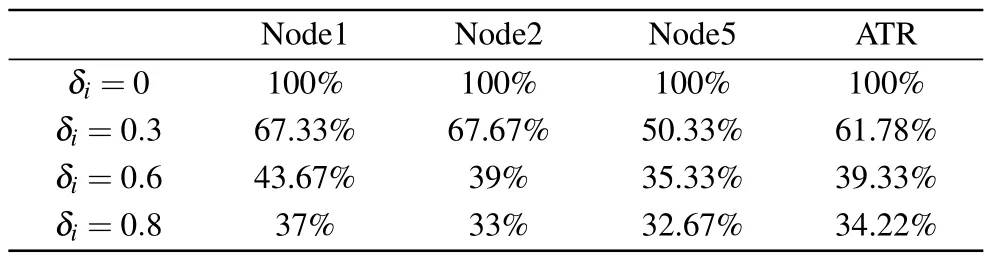
Table 4.A comparison of TRs under different values of δi.
5.Conclusions
In this paper, the problem of finite-time dissipative synchronization control for TSFCPSs subject to semi-Markov switched parameters and packet losses has been addressed by applying the DDETM.Aiming to build the model of signals affected by random packet dropouts transmitting to the controller, combined with a compensation strategy, an equivalent prediction model is introduced to process the Bernoulli distributed time sequence.Based on an augmented modedependent LKF and ERCMI technique, the criterion of FTS with strictly dissipative performance has been deduced in terms of LMIs, which further solves the control gain matrices.The theoretical effectiveness and superiority are proved by two examples.In the future,the event-based control strategy will be extended to CPSs with more realistic problems,such as cyber-attack and sensor faults.
Acknowledgements
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.62263005),Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.2020GXNSFDA238029), Laboratory of AI and Information Processing (Hechi University),Education Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (Grant No.2022GXZDSY004), Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (Grant No.YCSW2023298),and Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education (Grant Nos.2022YCXS149 and 2022YCXS155).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Corrigendum to“Reactive oxygen species in plasma against E.coli cells survival rate”
- Dynamic decision and its complex dynamics analysis of low-carbon supply chain considering risk-aversion under carbon tax policy
- Fully relativistic many-body perturbation energies,transition properties,and lifetimes of lithium-like iron Fe XXIV
- Measurement of the relative neutron sensitivity curve of a LaBr3(Ce)scintillator based on the CSNS Back-n white neutron source
- Kinesin-microtubule interaction reveals the mechanism of kinesin-1 for discriminating the binding site on microtubule
- Multilevel optoelectronic hybrid memory based on N-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 film with low resistance drift and ultrafast speed

