Kinesin-microtubule interaction reveals the mechanism of kinesin-1 for discriminating the binding site on microtubule
Yi-Zhao Geng(耿軼釗), Li-Ai Lu(魯麗愛(ài)), Ning Jia(賈寧), Bing-Bing Zhang(張冰冰), and Qing Ji(紀(jì)青),?
1School of Science,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
2Institute of Biophysics,Hebei University of Technology,Tianjin 300401,China
Keywords: kinesin,tubulin,microtubule,molecular dynamics simulation
1.Introduction
Kinesin is a molecular-motor superfamily which has 14 subfamilies and takes microtubule as the“walking”track.[1-3]Kinesin-1 (also called conventional kinesin) is the founding member and the model protein of kinesin superfamily.[4,5]It is an ATP-powered dimeric motor protein responsible for organelle transportation in neural cells.[6,7]The microtubulebinding site and the nucleotide-binding site of kinesin-1 both locate in the motor domain.Two identical motor domains of kinesin-1 dimer switch their positions on the microtubule surface to walk processively in a hand-over-hand manner.[8-10]This processive walking requires that the kinesin-microtubule interactions switch between the strong binding and the weak binding state, i.e., to be strong enough for kinesin-1 to stand firmly on microtubule in the noisy cytoplasmic environment and to be weak enough to detach from microtubule and walk ahead.[11,12]The strength differences of kinesin-microtubule interaction is coupled to the different nucleotide-binding states of the motor domain.[13-17]Experiments have revealed that kinesin-1 in the nucleotide-free (apo) and ATP-binding state binds strongly to the microtubule and that in the ADPbinding state it binds weakly to or even detaches from the microtubule.[18-22]The different binding strengths of kinesin-1 in the different states originate from the variations of the nucleotide-binding state dependent kinesin-microtubule interactions.
Microtubule not only provides the walking track for kinesin-1 but also modulates its mechanochemical cycle.Microtubule has four aspects of effects on the function of kinesin-1.Firstly, microtubule provides the track for kinesin-1.The strong kinesin-microtubule interaction effectively avoids the premature detachment of kinesin-1 from microtubule.Secondly, microtubule catalyzes the ATPase of kinesin-1.It is proved that kinesin-1 binding to the microtubule greatly increases the rate of ATP hydrolysis and the rate of ADP release.[23-25]Thirdly, microtubule provides the mechanical support for kinesin-1’s force-generation step.The groove betweenα-tubulin andβ-tubulin is the anchor site for kinesin-1’s switch-II helix (theα4 helix) during the motor-domain rotation induced by ATP binding, which is a key step of the force-generation process of kinesin-1.[26-28]Finally, the coupling between the kinesin-microtubule interaction and the nucleotide-binding states of the motor domain provides the basis of the gating of kinesin-1’s mechanochemical cycle.[29-32]All these functions of microtubule must be achieved through the kinesin-microtubule interaction.To fully understand the controlling mechanism of microtubule to the functions of kinesin-1, the interactions between the motor domain of kinesin-1 in different nucleotide-binding states and the tubulin should be clarified.
Interactions between the kinesin’s motor domain and the microtubule lattice have attracted experimental and theoretical researches for decades.Researches of microtubule decorated with kinesin showed that kinesin binds to theβ-subunit of tubulin.[33,34]Early negative-stain electron microscopy experiments identified that kinesin contacts with both theαtubulin andβ-tubulin.[35-37]By comparing the x-ray structures and the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) images,Marxet al.[38]concluded that kinesin binds mainly to theβtubulin and theα4 helix of the motor domain locates on the intradimer interface betweenα- andβ-tubulins.By mutating different residues of kinesin-1 in the kinesin-microtubule interface, Klumppet al.[39-42]found a group of residues participating in the kinesin-microtubule interaction.Sindelaret al.[43-45]also found some key secondary structures in contact with microtubule,especially L8,L11 and L12,by using cryoelectron microscopy.Through molecular dynamics(MD)simulations,Aproduet al.[46]showed that the interacting strength between tubulin and motor domain in ADP-binding state is half the strength in the apo/ATP-binding state.Mutation and MD simulation researches showed that mutations of several positively charged residues of kinesin-1 dramatically weaken the interactions between motor domain and tubulin.[47-50]Wanget al.[51,52]obtained the first high-resolution structures of kinesin-tubulin complex in kinesin’s ATP-binding and apo states.These structures provided massive information about the interactions between kinesin-1 and theα-βgroove.The modeling in this work is based on these x-ray structures.From the above-mentioned studies,it can be concluded that the binding site of kinesin on the microtubule surface is between theα- andβ-tubulins within a protofilament and the kinesinmicrotubule interaction is dominated by electrostatic interactions.
When binding to the microtubule surface, the motor domain of kinesin-1 always docks to the groove betweenαtubulin andβ-tubulin and theβ-tubulin locates ahead of theαtubulin in the plus direction of microtubule(Fig.1(a)).[33,34,38]We call this groove theα-βgroove and the groove betweenβtubulin andα-tubulin is called theβ-αgroove.The molecular mechanism for how kinesin-1 discriminates these two sites and recognizes the correct binding site is still a question.For kinesin-3, Nittaet al.found that a pair of charged residues in L7 might play an important role in the discrimination ofα/β-tubulin.[53]When the motor domain of kinesin-3 binds to theα-βgroove,this pair of residues form matched interaction with a pair of oppositely charged residues onβ-tubulin,while,due to the sequence difference betweenα-andβ-tubulins,the matched interaction would be lost if the motor domain binds to theβ-αgroove of microtubule.This work provided a reasonable clue for the understanding of theα/β-tubulin discrimination mechanism of kinesin.However,the pair of residues in L7 of kinesin-3 is not conserved in kinesin-1.Therefore, a thorough understanding of theα/β-tubulin-discrimination mechanism of kinesin-1 needs a systematic analysis of the kinesinmicrotubule interactions.
To investigate the interactions between kinesin-1 and microtubule and the discrimination mechanism of the different binding site of kinesin-1, we performed various MD simulations and obtained the stable complex structures of the motor domain (in the apo, ATP-binding and ADP-binding state)and tubulin (α-βgroove andβ-αgroove).The statistical analysis of the simulation trajectories reveals the details of the interactions between kinesin-1 and microtubule lattice in kinesin’s different nucleotide-binding states.The motor domain of kinesin-1 preferentially binds to theα-βgroove of the microtubule lattice due to the stronger binding strength between motor domain andα-βgroove than that between motor domain andβ-αgroove.When binding to theα-βgroove,the motor domain in the apo and ATP-binding state binds strongly to the tubulin and binds loosely to the tubulin in the ADPbinding state.Based on these findings and the analysis of the sequences and structures of the C-terminal tails of theα-andβ-tubulins, we propose a two-step discrimination mechanism of kinesin-1 to recognize the proper binding site on microtubule.
2.Methods
The structures of the motor domain of human kinesin-1 (4HNA,[52]4LNU[51]and 1BG2[54]) and microtubule lattice (3J6F[55]) are used for modeling.Here, 4HNA and 4LNU are the motor domain-tubulin-complex structures in the ATP-binding and apo state, respectively; 1BG2 is the monomer structure of kinesin-1’s motor domain in the ADPbinding state without tubulin.Because the tubulin structures of 4HNA and 4LNU are in the curved conformation,[51,52]which is different from the conformation of tubulin in the microtubule lattice, we modified the position ofβ-tubulin of 4HNA and 4LNU by taking the structure of microtubule lattice (3J6F) as the reference.Because the curved-to-straight transition of tubulin shows limited changes in the tubulinkinesin interface,[52]this modification did not cause the structural clash between the motor domain andβ-tubulin.The ADP-AlF-4of 4HNA was replaced with ATP molecule by keeping the adenosine rings of these two molecules coincided.The designed ankyrin repeat proteins(DARPin)of 4HNA and 4LNU were used to stabilize the tubulin structure for crystallization and were deleted in our models.The coordinate water molecules and Mg2+were maintained.Because the complex structure of the motor domain and tubulin in kinesin-1’s ADPbinding state is still not available,1BG2 was manually placed at 5 °A above the tubulin to freely search the binding site on tubulin through MD simulations.The same strategy was used in the simulations of motor domain binds to theβ-αgroove of tubulin.The structure ofβ-αtubulin was extracted from the 3J6F.
The constructed six motor domain-tubulin complexes were buried in an explicit water sphere as the initial conformations for MD simulations.The radius of the water sphere is set to 70 °A to maintain~12 °A margin to avoid the boundary effect.TIP3P model[56]was used to model the water molecules.Na+and Cl-were added to the system to ensure an ionic concentration of 150 mM and zero net charge.Each model contains~150000 atoms.Since each model has only oneα-tubulin and oneβ-tubulin, to mimic a stable microtubule conformation,a group of atoms in tubulin(Cαatoms of E168,L227,V353 inα-tubulin and Cαatoms of T168,L227,T353 inβ-tubulin) were harmonically fixed.The selection of the fixed atom is to keep the relative positions of different subdomains of tubulin.
The software used for modeling is VMD (version 1.9.3).[57]The MD simulations were performed by using NAMD(version 2.12)[58]with force field CHARMM36[59-62]at the constant temperature of 310 K.The integration time step is 2 fs.The non-bonded Coulomb and van der Waals interactions were calculated with a cutoff using a switch function starting at a distance of 13 °A and reaching zero at 15 °A.Before the simulation run, the protein-water systems were minimized in 30000 steps by using conjugate-gradient method.The simulation time of each model was 200 ns and each model was simulated twice.The accumulated simulation time was 2.4μs.The criteria of hydrogen bond and salt bridge is as follows: The distance between the acceptor atom and the hydrogen atom of a hydrogen bond is less than 3 °A.The distances of the center atoms(Cζof arginine,Nζof lysine,Cγof aspartic acid and Cδof glutamic acid)of two charged groups are less than 8 °A.
The binding free energies between motor domain and two different grooves were calculated by using the molecular mechanics/generalized Born surface area (MM/GBSA) method based on the simulation trajectories(50 ns-200 ns).The software used for the MM/GBSA calculation is MolAICal.[63]The figures were produced by using VMD, Discovery studio 3.5 visualizer and Origin 8.5.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Interactions between the motor domain of kinesin-1 and the α-β groove of tubulin
Under the normal condition,the motor domain of kinesin-1 binds to the groove between theα-andβ-tubulins(theα-βgroove, Fig.1(a)).To identify the interacting residues of the motor domain and theα-βgroove in the different nucleotidebinding states of kinesin-1,the motor domain-tubulin complex structures were evolved 200 ns using MD simulations.
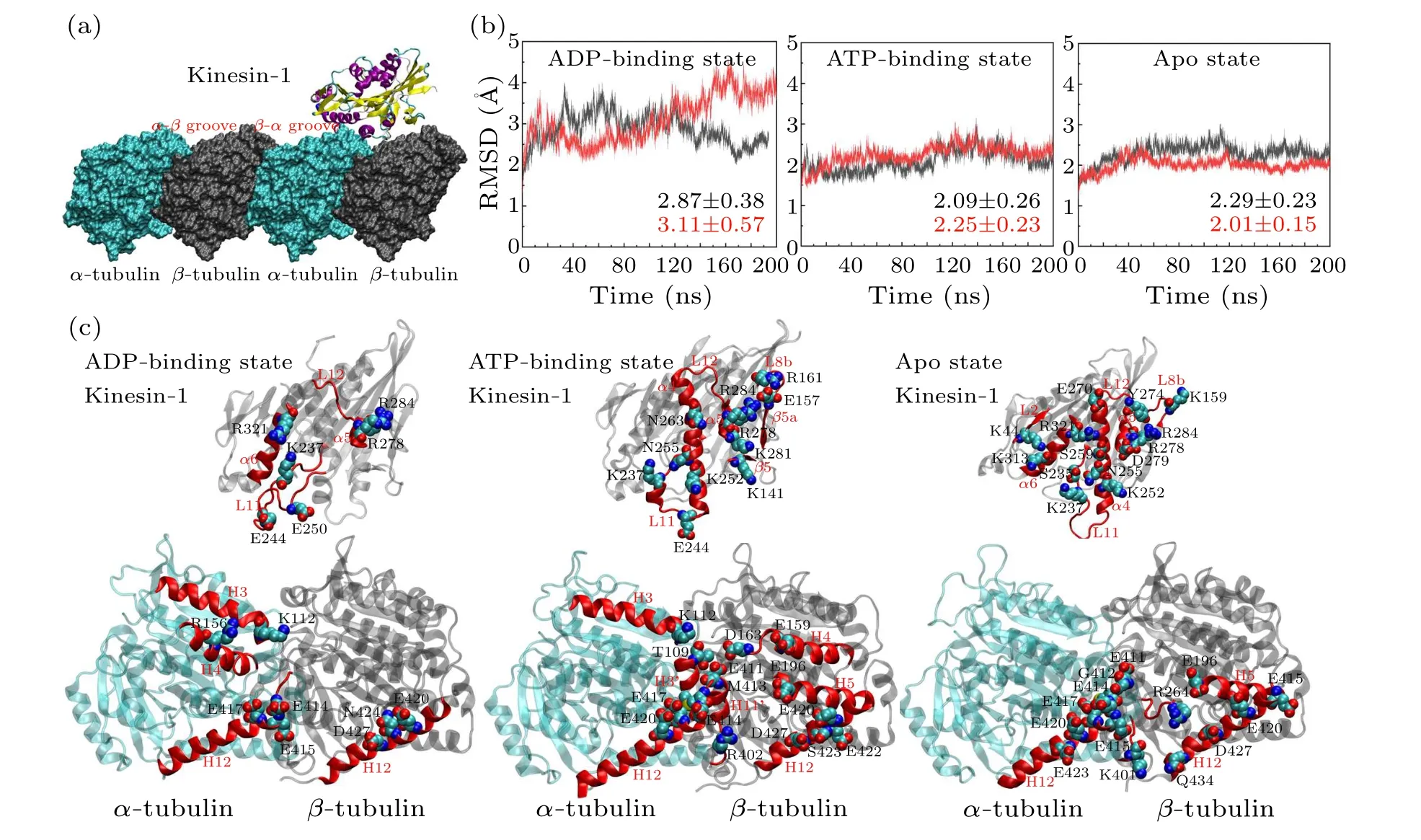
Fig.1.Interactions between the motor domain of kinesin-1 and the α-β groove of microtubule.(a)The binding site of kinesin-1 on microtubule lattice.The groove between the α-tubulin and the β-tubulin is the α-β groove and that between the β-tubulin and the αtubulin is the β-α groove.The motor domain of kinesin-1 binds to the α-β groove.(b)The RMSDs of the six simulation trajectories in different nucleotide-binding states.Each model is simulated twice.The averaged values of the RMSDs are calculated.The RMSDs of the model in ADP-binding state show higher RMSD and fluctuation compared with the models in other nucleotide-binding states.(c)The key interacting residues in motor domain(top)and α-β groove(bottom).The motor domain and tubulins are placed to show the kinesin-microtubule interface.The motor domain shows the bottom view of the interface and the tubulins show the top view of the interface.The interacting residues are different in the three nucleotide-binding states.The secondary structures participate in the kinesin-microtubule interaction are highlighted in red.The interacting residues are shown in VDW mode.The hydrogen atoms of these residues are eliminated.
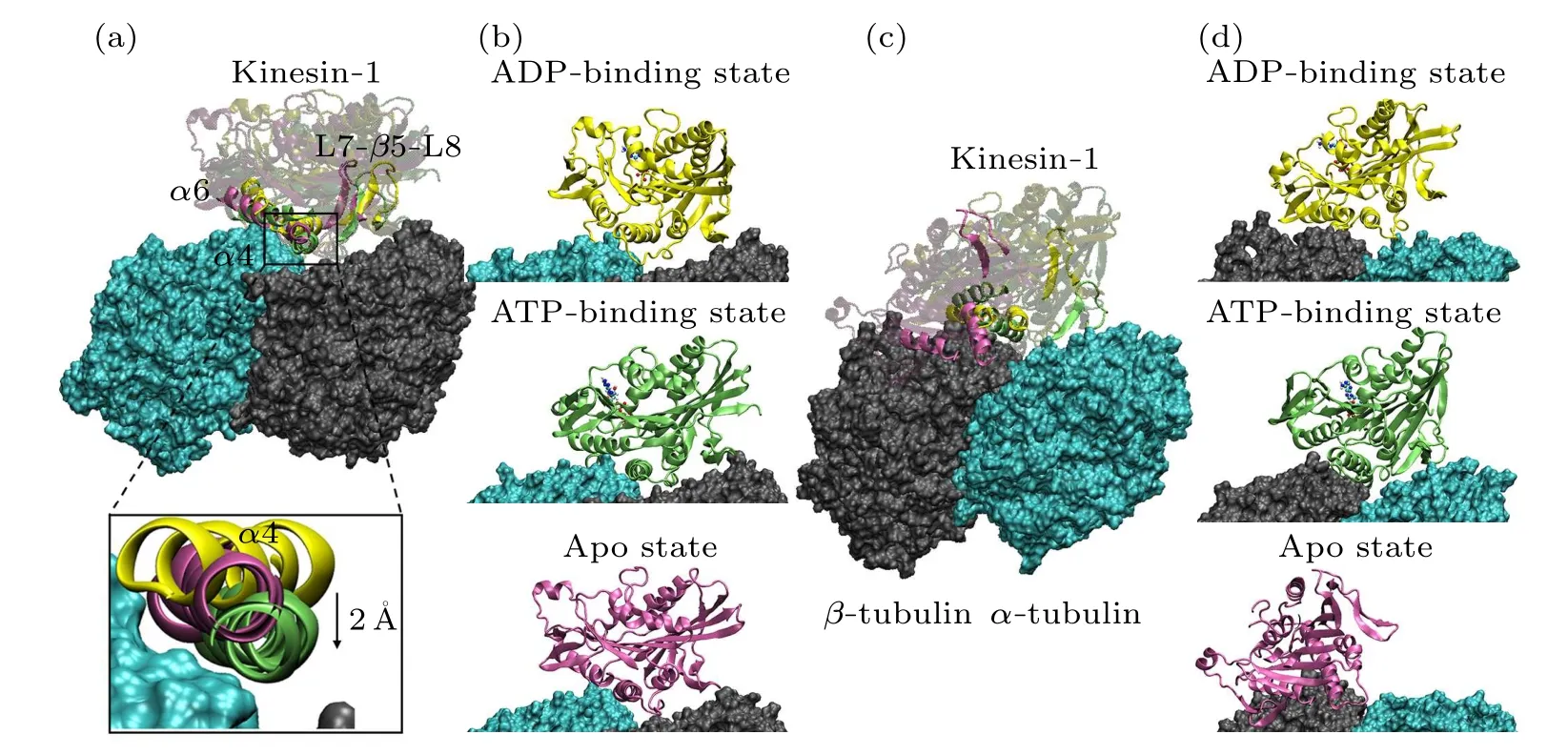
Fig.2.Conformations of the motor domain-tubulin complexes after 200 ns MD simulation.(a) and (b) The superimposed structure (a)and the respective structures (b) of motor domains in different nucleotide-binding states binding to the α-β groove.The tubulins are shown in the surface mode and the motor domains are shown in the new cartoon mode with different colors(ADP-binding state in yellow;ATP-binding state in green;apo state in purple).The ADP and ATP molecules are explicitly shown.In(a),the secondary structures(α4,α6 and L7-β5-L8)of the contact surface of motor domain are highlighted.The positions of three α4 helices are explicitly shown.Relative to the orientation of α4 in the ATP-binding(green)and apo(purple)states,the α4 of motor domain in ADP-binding state(yellow)rotates~40°.The α4 of motor domain in ATP-binding state enters deeper into the α-β groove.(c)and(d)The superimposed structure(c)and the respective structures(d)of motor domain in different nucleotide-binding states binding to the β-α groove.
Figure 2 shows the stable microtubule-binding conformations of the motor domain of kinesin-1 in different nucleotidebinding states.The binding position of the motor domain in the ATP-binding state and that in the apo state are similar.Though the motor domain in the ADP-binding state binds to the same site on theα-βgroove, it rotates~40°compared with the binding conformations of the other two states(measured through the longitudinal direction of theα4 helix)[Fig.2(a)].This is consistent with the experimental results in the literature[20,22]that the motor domain in the ADP-binding state loosely binds to the microtubule.The root-mean-square deviations (RMSDs) of the six trajectories also confirm this conclusion[Fig.1(b)].The RMSDs of the two ADP-bindingstate simulation trajectories show larger values and deviations,which demonstrate that the motor domain in ADP-binding state unstably binds to theα-βgroove.
All the six simulations reach equilibrium after 50 ns relaxation run[Fig.1(b)]and the statistical analysis is performed based on the 50-200 ns trajectories.To give the statistical description of the kinesin-microtubule interactions, the occupancy rate of each hydrogen bond and salt bridge is calculated(defined as the percentage of the bonding time in the 50-200 ns equilibrium trajectory).Based on the calculated occupancy rate, we identify the significant interacting residues in different nucleotide-binding states(both the occupancy rates of the two trajectories in each nucleotide-binding state are larger than 40%, see Table 1 and Fig.1(c)).From Table 1, the kinesinmicrotubule interactions are dominated by the electrostatic interactions.Though the interacting residues are different in different nucleotide-binding states of the motor domain, the microtubule-binding residues of kinesin-1 mainly concentrate in the L7-β5-L8 domain, L11 loop,α4 helix, L12 loop,α5 helix andα6 helix[Fig.1(c)].Since the motor domain binds to theα-βgroove of the microtubule, it interacts with both theα- andβ-tubulins.The interacting residues onα-tubulin mainly locate in H3 helix,H11 helix,H11'-H12 loop and H12 helix and those onβ-tubulin mainly locate in H5-S6 loop and H12 helix.
The key binding residues on the motor domain of kinesin-1 are Lys237 in the L11 loop, Arg278 in the L12 loop and Arg284 in theα5.These residues contact with the same sites on the tubulin in all the six simulation trajectories.The Glu414,Glu417 and Glu420 in theα-tubulin constitute a negatively charged binding pocket for the binding of the motor domain.This is a key binding site on the microtubule since the Lys237 of the motor domain enters this pocket in all the three nucleotide-binding states.The Arg278 and Arg284 are the key residues of the motor domain to contact with theβtubulin.The Arg278 enters a binding pocket consisting of the Glu196, Glu420, Ser423, Asn424 and Asp427 of theβtubulin.The Arg284 forms a stable salt bridge with the Glu420 of theβ-tubulin in all the six simulation trajectories.These three key binding sites determine the binding position of the motor domain of the kinesin-1 on theα-βgroove of microtubule.The interactions between Lys237 andα-tubulin identified by MD simulations also exist in the crystal structures of kinesin-tubulin complex in the ATP-binding state (4HNA)and apo state(4LNU)(Figs.S2 and S3 in the supporting material).The interactions between Arg278 and theβ-tubulin exist in the crystal structure in ATP-binding state but absent in the apo-state structure.The key interaction between Arg284 and Glu420 ofβ-tubulin is absent in both the crystal structures.The distances of the atoms in the key interactions are shown in Figs.S2 and S3.More than half of the interactions shown in the crystal structures are maintained in the MD simulations.Because the slightly curved tubulin is straightened in the modeling, some interactions between motor domain and tubulin are adjusted to the straight conformation of tubulin.
Though the L11 loop,α4 helix, L12 loop andα5 helix contact with the tubulin in all the nucleotide-binding states,except for the Lys237, Arg278 and Arg284, other binding residues present the nucleotide-binding state dependent variations due to the different conformations of the motor domain in different nucleotide-binding states.From Fig.2(a), when binding to the tubulin, the motor domain in the apo state and the ATP-binding state locate in the same position with theα4 helix of the motor domain in the ATP-binding state enters deeper into theα-βgroove(~2 °A).ATP molecule binds into the motor domain in the apo state will induce a rotation of the motor domain except for theα4 helix.[12,25,44]This conformational change also influences the kinesin-microtubule interaction.Theα6 helix of the motor domain in ATP-binding state has an upward rotation.[12,25]The conformational change ofα6 helix destroys the two salt bridges formed betweenα6(Lys313 and Arg321) andα-tubulin (Glu420 and Glu415).The ATP binding induced motor-domain rotation also weakens the binding of L7-β5-L8 domain to theβ-tubulin.
The ATP hydrolysis andγ-phosphate release induce further conformational changes of the motor domain from the ATP-binding state to the ADP-binding state.[12]It is proved that the ADP-binding-state motor domain can only loosely bind to the tubulin.[20,22]The MD simulations show that, except for the three key residues(Lys237,Arg278 and Arg284),nearly all the contacts between ADP-binding-state motor domain and tubulin are destroyed (Table 1).It is reasonable to speculate that the binding strength of the motor domain in the ADP-binding state to tubulin is the weakest in the three models.The key interactions between ADP-binding-state motor domain and tubulin include seven salt bridges and one hydrogen bond (Table 1).As a contrast, there are twelve salt bridges and six hydrogen bonds in the apo state and thirteen salt bridges and six hydrogen bonds in the ATP-binding state.We also calculated the binding free energy of the motor domain to the tubulin (Table 2).The binding free energy between ADP-binding-state motor domain and tubulin(theα-βgroove)is~-33.98±0.03 kcal/mol.The binding free energies of other two states are similar(~-75.71±0.03 kcal/mol in the ATP-binding state and~-86.97±0.05 kcal/mol in the apo state).The binding free energy between motor domain in ADP-binding state andα-βtubulin is about half of that in other two nucleotide-binding states.By using umbrella sampling simulations,the changes in potential of mean force (PMF) of pulling the motor domain of kinesin-1 away fromα-βgroove are calculated in Ref.[64].The maximum change of PMF of motor domain in ADP-binding state away from theα-βgroove with conformational change is~17.7kBT(~11 kcal/mol) and that in apo state is~46kBT(~28 kcal/mol).The ratios of binding energy in the motor domain’s ADP-binding state to that in the apo state obtained from two different methods are consistent.
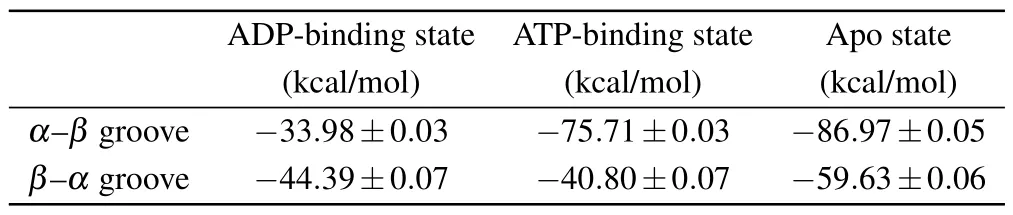
Table 2.The binding free energy of motor domain of kinesin-1 to the two grooves.
3.2.The β-α groove is not a favorable binding site for the motor domain of kinesin-1
When kinesin-1 searching for their binding site on microtubule or walking along the microtubule lattice, the motor domain binds to theα-βgroove of the microtubule, not the adjacentβ-αgroove.There must be a mechanism that the motor domain of kinesin-1 can discriminate these two sites.
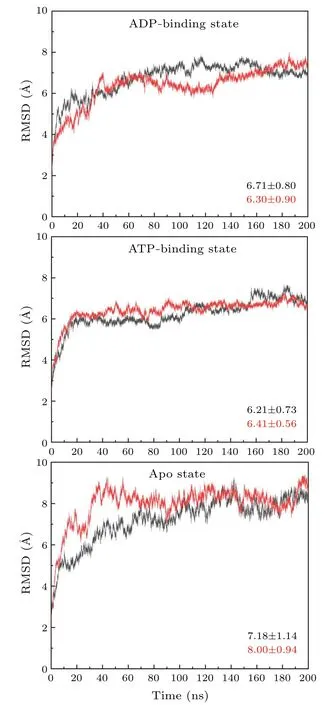
Fig.3.The RMSDs of the simulation trajectories of motor domain docking to the β-α groove.Each model is simulated twice and the averaged values of the RMSDs are calculated.
Docking of the motor domain to microtubule is dominated by two factors, i.e., the geometric shape and the nonbonded interactions.Since theα-βgroove and theβ-αgroove have similar surface shape, it thus seems that the section of theα-βgroove should originate from the differences of the non-bonded interactions between the motor domain and the two sites of microtubule.
Based on the above considerations,we investigate the interactions between the motor domain of kinesin-1 and theβ-αgroove of microtubule.The RMSDs of the six trajectories are significantly larger than that of the simulations of motor domain binding to theα-βgroove, which indicate larger conformational changes of the protein when the motor domain binding to theβ-αgroove of microtubule(Fig.3).All of the simulations reach equilibrium after~50 ns simulation run.Thus, the statistical analysis of the interactions between the motor domain and theβ-αgroove is based on the 50-200 ns trajectories.
The sequence analysis of the amino acids on the kinesintubulin interface shows~40%identity between theα-tubulin and theβ-tubulin [Fig.4(a)].The two tubulins swap their positions when the motor domain binds to the two different sites.The amino-acid sequence differences of theα-tubulin and theβ-tubulin, thus may affect the motor domain-tubulin interactions because of the loss of the matched residues.The comparison of the key interactions(Table 1)and the sequence analysis[Fig.4(a)]shows that the sequence differences on the 112, 159, 163, 422, 423 and 427 sites ofα-tubulin andβtubulin eliminate the key interactions when the motor domain binds to theβ-αgroove.Lys112 inα-tubulin is a typical interaction site with kinesin-1 since it forms salt bridges with Glu244 and Glu250 in the motor domain when docking to theα-βgroove.If the motor domain docks to theβ-αgroove,it would face the Ala112 at this position inβ-tubulin and the salt bridges would be lost.The similar situations occur at the positions 159,423 and 427 of tubulin.The sequence differences at positions 163 and 422 in tubulin are even more important.At these two positions, the interacting sites in theα-tubulin are two negatively charged residues (Asp163 and Glu422),which form salt bridges with two positively charged residues in kinesin-1 (Lys252 and Arg161) when the motor domain docking to theα-βgroove.The residues inβ-tubulin at these two positions are two positively charged residues(Lys163 and Arg422) which would form repulsive contact with the two positively charged residues in the motor domain if it docks to theβ-αgroove.These sequence differences ofα-tubulin andβ-tubulin can modify the binding pattern of the motor domain because the motor domain-tubulin interaction network is changed.
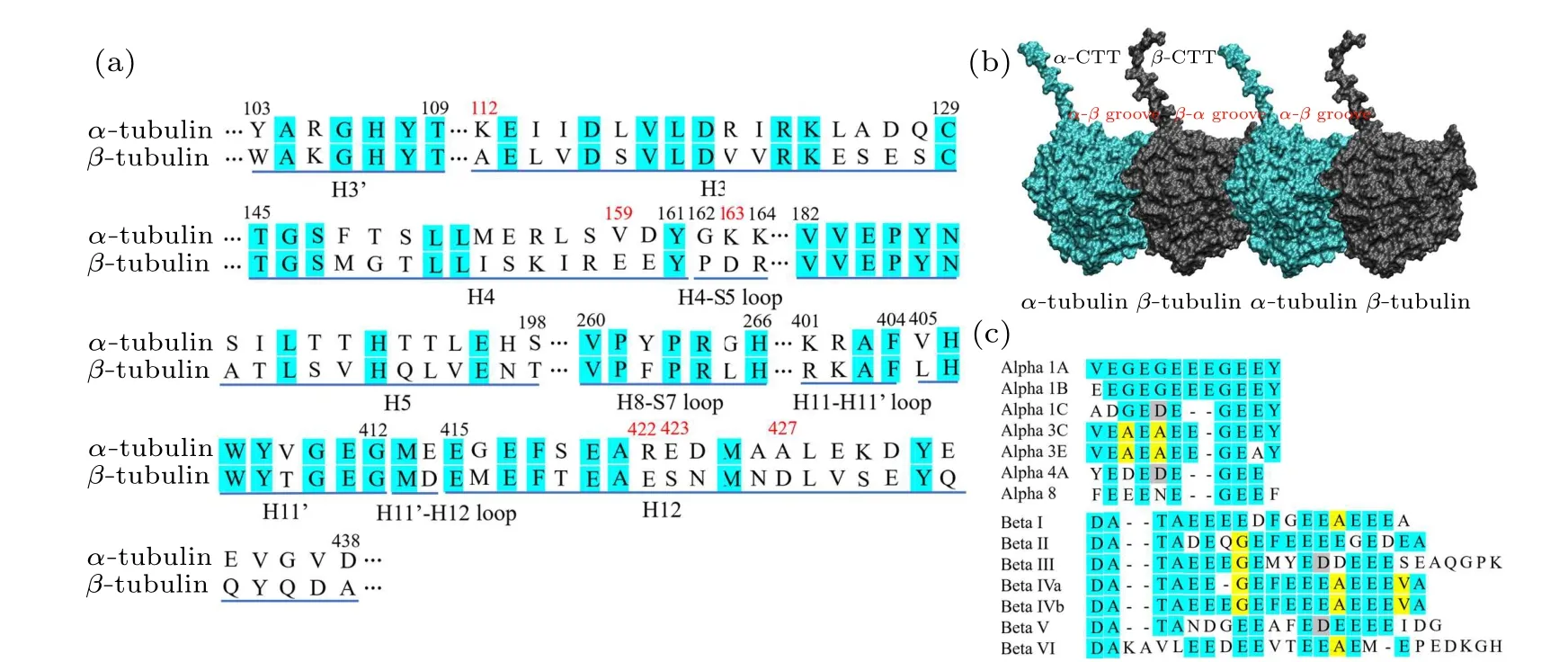
Fig.4.Sequence alignments of the kinesin-contacting structures of α-and β-tubulins and the positions of tubulin’s C-terminal tails.(a)Sequence alignments of the kinesin-contacting structures of α-tubulin and β-tubulin.The identity of the sequences is ~40%.H represents helix and S represents strand.The loop is labeled by the two structures it connect to.Two adjacent helices separated by a short loop have the same number and a single quotation mark is added to distinguish them.(b)The positions of the C-terminal tails of α-tubulin and β-tubulin.The α-CTT locates on the β-α groove and the β-CTT locates on the α-β groove.(c) The sequence alignments of the C-terminal tails of α-tubulins and β-tubulins.The lengths of the α-CTTs is shorter than that of the β-CTTs.
The interactions between the motor domain and theβαgroove are shown in Table 3.Consistent with the above analysis that the amino-acid-sequence differences ofα-tubulin andβ-tubulin affect the matched interactions between motor domain and tubulin when binding to theβ-αgroove, the amount of the key interactions is dramatically reduced when kinesin-1 is docked to theβ-αgroove.There are only 5 salt bridges in the apo state,4 salt bridges in the ADP-binding state and 5 salt bridges and 1 hydrogen bond in the ATP-binding state(Table 3).Accordingly,the binding positions of the motor domain on theβ-αgroove have significant changes from that of the kinesin binds to theα-βgroove [Figs.2(c) and 2(d)].The binding free energy between the motor domain of kinesin-1 and theβ-αgroove (~-44.39 kcal/mol in the ADP-binding state,~-40.80 kcal/mol in the ATP-binding state and~-59.63 kcal/mol in the apo state)are weaker than that between the motor domain in strong microtubule-binding states(ATP-binding and apo state)and theα-βgroove.These results indicate that theβ-αgroove is not a proper kinesinbinding site.
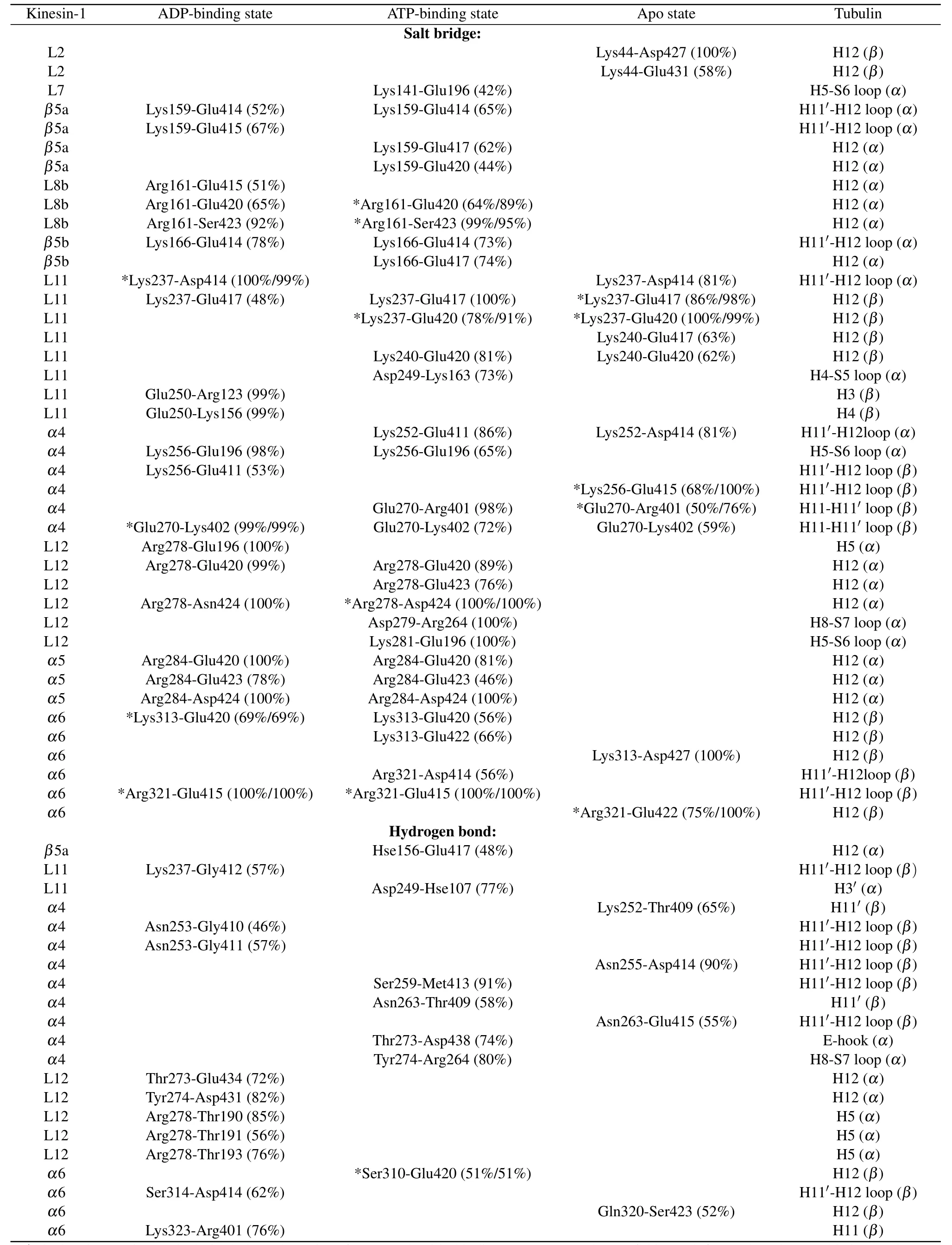
Table 3.Interactions between motor domain of kinesin-1 and β-α groove of microtubule.
3.3.The two-step mechanism of kinesin-1 for discriminating the α-β groove and β-α groove
As shown in the above sections, the binding of kinesin-1’s motor domain to theα-βgroove is much more favorable than binding to theβ-αgroove.However,when searching for the binding site on microtubule,the motor domain of kinesin-1 is firstly captured by the C-terminal tails (CTTs) of tubulin (Fig.4(b)).The CTT is negatively charged and highly flexible.[65]Because most of the amino acids of both the CTTs ofα-tubulin andβ-tubulin are glutamic acids,the CTT is also called E-hook.[66]CTT is not conserved and has nearly all of the posttranslational sites of microtubule.[67-69]The different posttranslational modifications of the CTT control the binding of various microtubule-associated proteins.[68]It has shown that the modifications of the CTT can affect the affinity and velocity of kinesin.[70]The differences between theα-tubulin’s CTT (α-CTT) and theβ-tubulin’s CTT (β-CTT) may also contribute to the discrimination of theα-βgroove and theβ-αgroove.
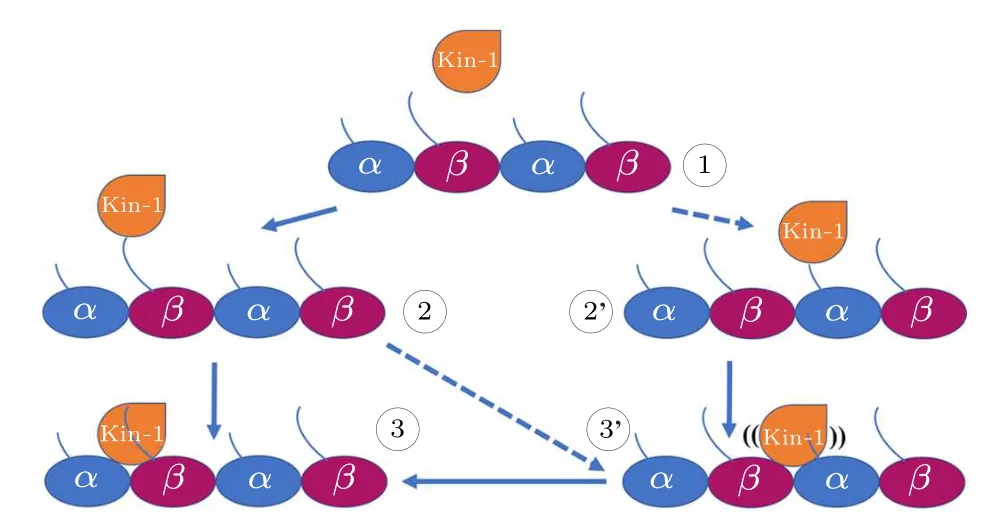
Fig.5.The proposed two-step mechanism of kinesin-1 for discriminating the α-β groove and the β-α groove.When searching for the binding position on microtubule (1), the motor domain of kinesin-1 prefers to bind to the C-terminal tails of β-tubulin (the β-CTT) since the β-CTT is longer than the α-CTT (2).Because the β-CTT locates on the α-β groove,it is easier for the motor domain to bind to the α-β groove(3).However,motor domain can also be captured by the α-CTT(2')and bind to the β-α groove(3').In this situation,the motor domain can not bind stably to the β-α groove.The motor domain can detach from the β-α groove and continue to search for the proper binding site.The processes of 1 to 2' and 2 to 3' is less frequently happened.
The lengths of theα- andβ-tubulin tails are different.Theα-CTTs contain 10-12 residues and theβ-CTTs contain 16-22 residues [Fig.4(c)].This produces a length variation(~2 nm)between theα-CTT and theβ-CTT(fully extended).The longerβ-CTT also has larger amounts of negative charges over theα-CTT.Considering the construction of the microtubule, theβ-CTT locates in theα-βgroove while theα-CTT locates in theβ-αgroove(Fig.4(b)).Due to the electrostatic repulsion between the adjacent CTTs and the repulsion between the negative charges within the same CTT,the CTT, though highly flexible, has a preferential orientation away from the microtubule surface and assumes mainly an extended conformation.[71,72]When the motor domain of kinesin-1 gets close to the microtubule,its positively charged microtubule binding site tends to firstly attracted by theβ-CTTs since they are longer in length and stronger in negativity.Because theβ-CTT locates on theα-βgroove,it is easier for the motor domain to get close to the region above theα-βgroove.Therefore, the longβ-CTT facilitates the binding of kinesin-1 to theα-βgroove.When searching for the binding site on microtubule, the motor domain of kinesin-1 may also bind to theβ-αgroove.However,it cannot bind stably to theβ-αgroove of microtubule because the different amino-acid sequences ofα-andβ-tubulins limit the interactions between motor domain andβ-αgroove.The motor domain,thus,can detach from theβ-αgroove and continue to search for the proper binding site(Fig.5).When walking on the microtubule lattice, the selection of the binding site of kinesin-1 is exclusive.Kinesin-1 forms a dimeric structure and walks along a single protofilament of microtubule.One of the motor domain binds stably to theα-βgroove,the other motor domain cannot bind to the adjacentβ-αgroove due to the structural clash (Fig.6).Theα-βgroove is the binding site of most of the kinesin-family members.Considering the conservation of kinesin’s motor domain,the proposed two-step discrimination mechanism may also apply to other family members of kinesin.
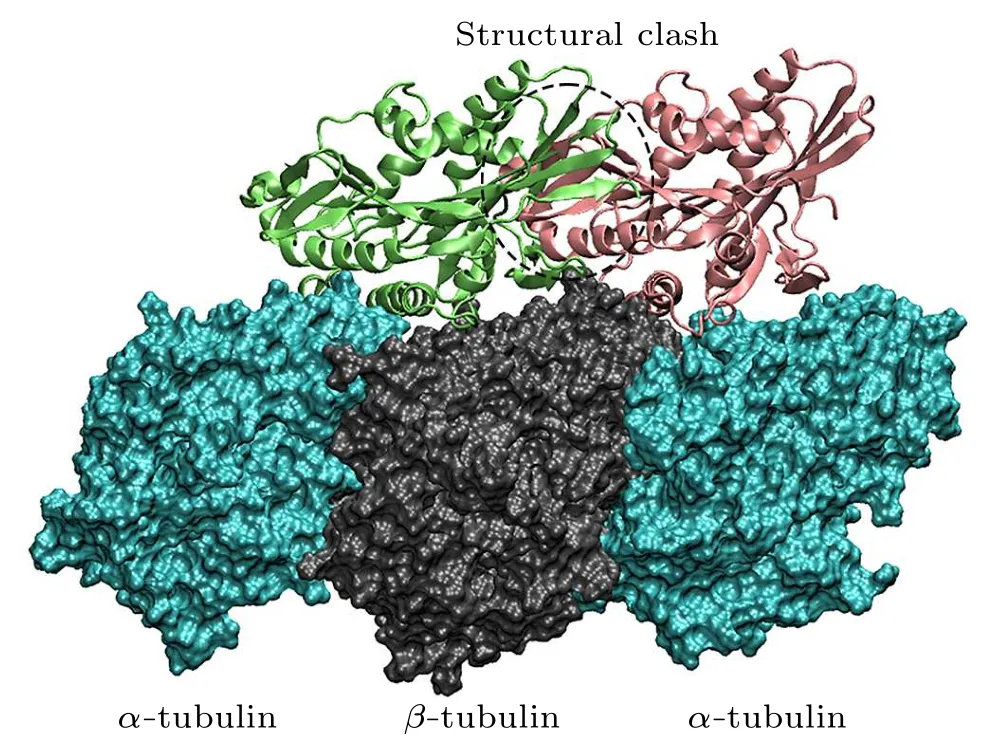
Fig.6.The exclusive binding of kinesin-1 to the microtubule.When the motor domain of kinesin-1 binds to the α-β groove, the other motor domain cannot bind to the adjacent β-α groove due to the structural clash.
The CTT is considered to be intrinsically disordered.[65,73]Its conformation is affected not only by the tubulin it belongs to, but also by the adjacent tubulin.However,there is only oneα-tubulin and oneβ-tubulin in the models of this work.Without the surrounding tubulin structures,the models cannot correctly describe the dynamical behavior of the CTT.Thus, in the modeling, both theα-CTT and theβ-CTT are excluded.Therefore,the process of the biased attraction of motor domain byβ-CTT to theα-βgroove cannot be directly observed through the simulation trajectories.The models are designed to simulate the second step of the binding of motor domain to microtubule.In this step,the attraction of CTT to the motor domain is completed and the motor domain begins to interact with theα-andβ-tubulins.
4.Conclusion
Microtubule provides the walking track for kinesin-1 and participates in the controlling of the mechanochemical cycle of kinesin-1.The proper binding of kinesin-1 to the microtubule is important for the functions of microtubule.In the walking process of kinesin-1, the motor domain docks to the groove betweenα-andβ-tubulins(theα-βgroove),which is the binding site of kinesin-1 on the microtubule.By using the molecular dynamics method,we find that the motor domain of kinesin-1 can bind stably to theα-βgroove.However, due to the variations of amino-acid sequences of theα- andβtubulins, the motor domain binds loosely to theβ-αgroove.The C-terminal tail of theβ-tubulin, which locates in theαβgroove, is longer than that of theα-tubulin and has more negatively charged residues.The biased binding of motor domain to theβ-tubulin also facilitates the binding of kinesin-1 to theα-βgroove.We propose a two-step mechanism for the discrimination of motor domain to theα-βgroove andβαgroove.Firstly, the long and strongly negatively charged C-terminal tail ofβ-tubulin attracts the kinesin-1 close to theα-βgroove and,secondly,the perfect match in both geometry and interaction ensures stable binding of kinesin-1 to theα-βgroove.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China(Grant No.A2020202007)and the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.11605038).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Corrigendum to“Reactive oxygen species in plasma against E.coli cells survival rate”
- Dynamic decision and its complex dynamics analysis of low-carbon supply chain considering risk-aversion under carbon tax policy
- Fully relativistic many-body perturbation energies,transition properties,and lifetimes of lithium-like iron Fe XXIV
- Measurement of the relative neutron sensitivity curve of a LaBr3(Ce)scintillator based on the CSNS Back-n white neutron source
- Multilevel optoelectronic hybrid memory based on N-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 film with low resistance drift and ultrafast speed
- Investigation of Ga2O3/diamond heterostructure solar-blind avalanche photodiode via TCAD simulation

