The influence of collision energy on magnetically tuned 6Li–6Li Feshbach resonance
Rong Zhang(張蓉) Yong-Chang Han(韓永昌) Shu-Lin Cong(叢書林) and Maksim B Shundalau
1Department of Physics,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
2DUT-BSU Joint Institute,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
3Physics Department,Belarusian State University,Minsk,Belarus
Keywords: Feshbach resonance,collision energy, 6Li–6Li system
1. Introduction
Cold and ultracold atomic quantum gases play important roles and have broad application prospects in modern physics. Researches related to cold atomic systems include Bose–Einstein condensate,[1–4]superfluid,[5–7]atomic clocks,[8–10]topology,[11]etc.Compared to cold and ultracold atoms, molecules have some unique and superior properties. For the additional internal degrees of freedom of molecules, the interactions of molecules with external fields are more complicated. For instance, the interaction between molecules and extern electric fields can be induced by electric dipole moment.[12]Due to these properties,cold and ultracold molecules have many profound applications in different aspects,[13]including molecular dynamics control,[14,15]high resolution spectroscopy and quantum control,[16,17]tests of fundamental physical laws,[18]quantum simulations and quantum simulators,[19]chemical reactions.[20,21]Cold and ultracold molecules also play important roles in a great variety of fundamental researches, such as chemistry physics, precision measurements,few-body and many-body physics.[22–25]Thus,the investigations of the cold and ultracold molecules attract many researchers’attention.
In order to produce cold and ultracold molecules, researchers have developed different kinds of experimental approaches which can be generally divided into two categories.One is the direct cooling method, including external field decelerations by electric, magnetic and optical fields,[26,27]buffer-gas cooling,[28]and collisional cooling,[29]etc.It is hard to produce ultracold molecules through the direct cooling method.[30]The other is the indirect cooling method. This method assembles two constituent ultracold atoms to form an ultracold molecule.[31]It can only be used in the situation that constituent atoms can be trapped and cooled to ultralow collision energies by using laser cooling.
Feshbach resonance (FR), as an important phenomenon in the scattering processes of ultracold atoms and molecules,is widely applied to the molecular indirect cooling.[32]A Feshbach resonance occurs when the closed channel and the open channel degenerate energetically.[33]This results in a resonance enhancement in the cross section. Through ramping magnetic fields across Feshbach resonances, colliding atoms can be coupled to form molecules in specific weakly bound states.[34]The molecules formed in this way is Feshbach molecules. Deeply bound molecules can be obtained by state transfer techniques, such as microwave radiation and magnetic field ramping.[35]It is worth noticing that the present FR is a special case of rovibrational resonance in magnetic field. There are FRs in photo interaction,[36–38]electron scattering,[39]heavy particle scattering,[40]nuclear physics,[38]photonics,[41]nanoscale structures,[42]etc.
One way to achieve Feshbach resonance is to adjust the energy difference between the open and the closed channels by tuning the magnetically field.[33]This corresponds to the magnetically tuned Feshbach resonance.The experimental approaches to detect magnetic Feshbach resonance including detection using inelastic collisional trap loss, elastic collisions and optical radiation.[43–45]The other way to achieve resonant coupling is optical Feshbach resonance.[46]Magneticlly tuned Feshbach resonance usually takes place in collisions of alkalimetal atomic systems, while the optical Feshbach resonance occurs in alkali-earth-metal atomic systems.[47,48]In magnetically tuned Feshbach resonance, interaction between atoms which is described by the scattering length,can be controlled by magnetic field. In optical Feshbach resonance, the resonance width can also be controlled. Based on Feshbach resonance,one can control the interaction strength between atoms and study the scattering characteristics.
6Li is the lightest isotope among all alkali metals.Numerous works have been carried out on the Feshbach resonance related to6Li. Yeet al.attained a degenerate Fermi gas of6Li in contact with a Bose–Einstein condensate of84Sr.[49]Bartensteinet al.observed three wide s-wave Feshbach resonances at 834.1, 690.4, and 811.2 Gs in6Li–6Li system by utilizing radio-frequency spectroscopy.[50]The resonance widths of the three resonance positions are-300,-122.3,and-222.3 Gs,respectively. Streckeret al.verified a narrow resonance at 543.8 Gs in6Li–6Li collision complex and utilized it to convert the ultracold6Li atoms gas into ultracold molecules.[51]They chose this narrow resonance position for two reasons.First, it is convenient to sweep over a narrow magnetic field in experiment. Second, compared with broad resonances,the production of hot atomic pairs can be decreased in narrow resonances.[52,53]Schuncket al.reported three p-wave resonances of 159.14, 185.09, and 214.94 Gs of6Li–6Li complex via a joint experimental and theoretical study.[54]The scattering channels of these three resonances areaa,ab, andbb,respectively.[33]Another two s-wave resonances were also determined. One is 543.28 Gs, the other is within 822 Gs–834 Gs.
Due to the properties of6Li Feshbach resonances,6Li has been applied in many researches. Weakly bound6Li2molecules were produced through three-body recombination near the 550 Gs Feshbach resonance with the number of the sample up to 3×105.[55]6Li atoms were evaporatively cooled below 600 nK near a Feshbach resonance and a BEC of up to 9×105molecules was observed.[56]Lompeet al.investigated the inelastic decay of the6Li atom–dimer collisions and observed that the resonant enhancement is correlated with the crossing between Efimov trimer states and the atom-dimer continuum.[57]Feshbach resonance was also used to make the mixture of the clouds of6Li and7Li atoms to reach the superfluid regime.[58]
Among the above mentioned Feshbach resonance positions of6Li–6Li, we are interested in the s-wave resonance near 543 Gs and the p-wave resonance near 185 Gs. Recently,Liet al.investigated the three-atom recombination process around the narrow s-wave magnetic Feshbach resonance at 543.3 Gs,and it was found that the three-atom recombination follows a universal behavior determined by the long-range van der Waals potential and can be described by a set of rate equations in which three-body recombination proceeds via successive pairwise interactions.[59]For the p-wave resonance near 185 Gs, there exists a doublet structure of 4 mGs, which is ascribed to the dipole–dipole interaction.[60]As reported in other cold atom systems,e.g.,85Rb–87Rb,the scattering characters are strongly dependent on the collision energy.[61]Thus,we are motivated to take these two specific resonances near 185 Gs (p wave) and 543 Gs (s wave) as examples, to study the influence of the collision energy on the6Li–6Li system.
In order to study two-body scattering interaction, we need to solve a set of radial coupled-channel equations.There are several ways to solve such equations, including the multichannel quantum-defect theory(MQDT),the asymptotic bound state model (ABM), and the coupled-channel method (CC).[32,62]Among these theoretical treatments, the CC method has taken into account all the relevant channels and the interactions among them in the entire internuclear separation range. Thus, in this work, we use CC method to calculate the cross sections of the resonance positions at different collision energies from 1 μK·kBto 100 μK·kB. The influence of collision energy on the resonance positions,resonance widths, the amplitudes of the total cross sections, as well as the splitting width of the p-wave resonance are investigated.
The paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we briefly introduce the theory.In Section 3,we discuss the effect of collision energy on the s- and p-wave Feshbach resonances for the6Li–6Li collision. In Section 4, the conclusions are summarized.
2. Theoretical method
The Hamiltonian of two colliding6Li atoms in the presence of external magnetic fieldBis given by

whereBis the magnetic field which is alongzaxis of the space-fixed coordinate frame.γeandγLiare the electronic and nuclear gyromagnetic ratios of the6Li atom respectively. ?sand ?iare the electronic and nuclear spin angular momenta,respectively,and the subscripts 1 and 2 denote the indexes of the two atoms.

whereVS(R)is the adiabatic interaction potential of the collision complex in the total spin state.S=s1+s2(I=i1+i2)is the total electronic(nuclear)spin of the6Li2molecule andMS(MI) is its projection onzaxis (the direction of the magnetic field). In the6Li2system,s1=s2=1/2 andS=0, 1,corresponding to the singlet and triplet electronic states, respectively.
The matrix elements of operator ?V(R)expressed in fully uncoupled basis is shown as

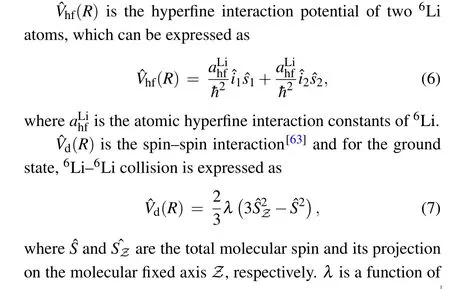
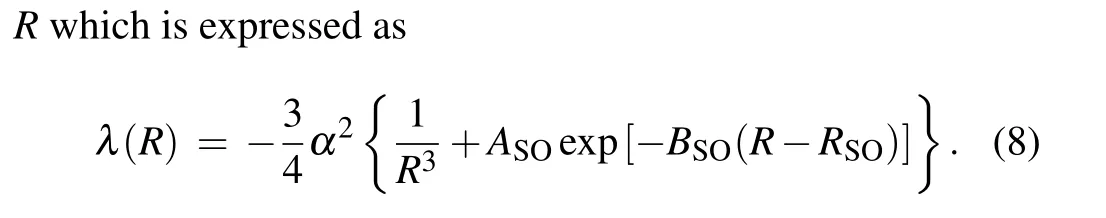
The first term ofλ(R) results in the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction and the second term is the second order spin–orbit contribution, which is much smaller than the first term and well ignored in the present study. For a given partial wavel,the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction can split the resonance position according to different|ml|.
The matrix element of spin–spin interaction can be expanded in the fully uncoupled basis
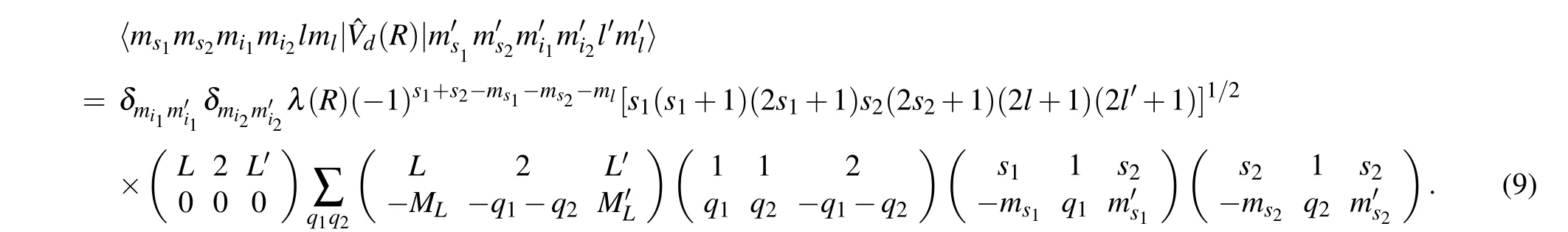
The coupled-channel equations can be obtained by substituting Eq.(1)into the time-independent Schr¨odinger equation.The coupled-channel equations can be solved through using the log-derivative method.[32]The scattering channel (α,l),withαdenoting the atomic basis|f1mf1,f2mf2〉, is related to the channel basis which can be obtained by diagonalizing the hyperfine and Zeeman Hamiltonian. The open channel threshold energy is set to be 0. Thus the total energy of the collision complex equals to collision energy ˉh2k2/2μ. The log-derivative matrixY(R) is propagated from the minimum(Rmin)to the maximum(Rmax)ofR. TheKmatrix is obtained fromY(Rmax)
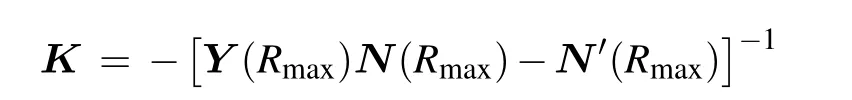
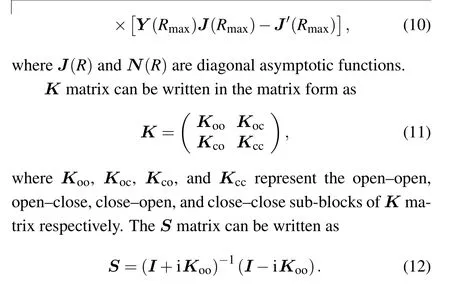
The scattering cross section calculated in this paper is elastic scattering cross section. The elastic scattering cross section of a specific scattering channel energyEαis expressed as
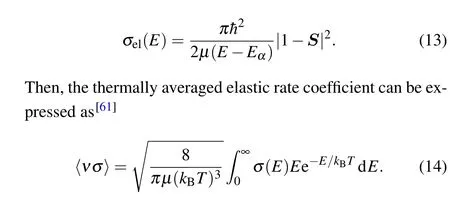
3. Results and discussion
6Li–6Li is a homonuclear Fermion system,so we need to consider the exchange antisymmetry. The electronic and nuclear spins of6Li are 1/2 and 1, respectively. High partial waves are neglected because of their extremely tiny contributions compared to s and p waves. And there is no coupling between s- and p-wave resonances because the external field used is only magnetic field. We consider the dipole–dipole interaction because it has an effect on p-wave resonance splitting. The Zeeman state energies of the6Li–6Li complex for the s and p waves are presented in Figs.1(a)and 1(b),respectively.
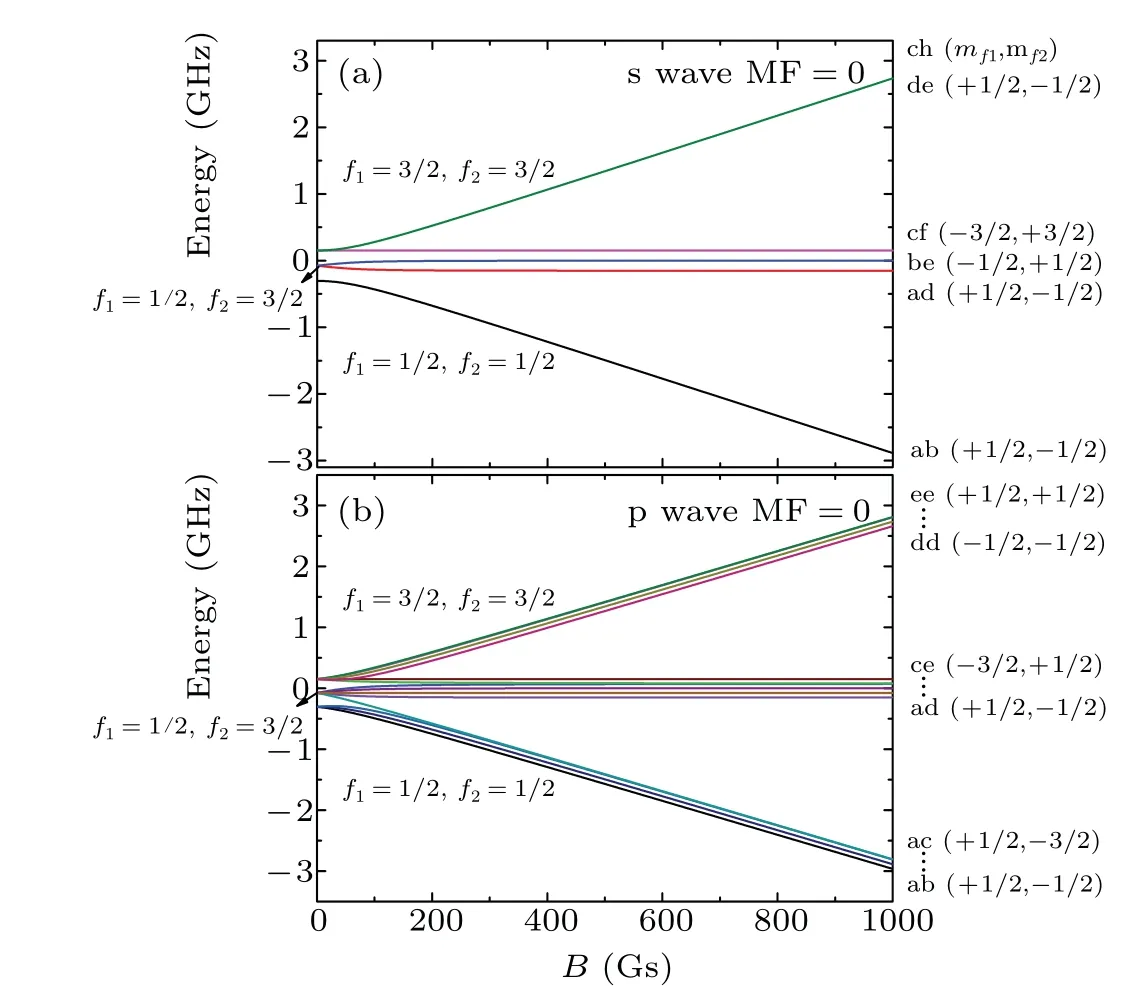
Fig. 1. Zeeman state energies of (a) s wave and (b) p wave for the 6Li–6Li complex.
The adiabatic singlet and triplet interaction potentials are obtained from Ref.[64]and are shown in Fig.2. We first calculated the scattering length and resonance positions of6Li2at the collision energy of 1 μK·kB. For s wave, the FR position we calculated is 543.152 Gs and the resonance width is 0.085 Gs. For p wave,the resonance positions are 185.109 Gs(|ml|=0)and 185.113 Gs(|ml|=1),respectively. These theoretical calculations are in good agreement with the previous experimental observations,as shown in Table 1.
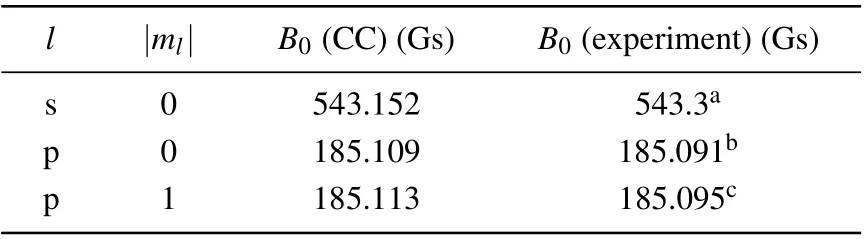
Table 1. The FR positions B0 of CC calculations and experiments.

Fig.2. The singlet and triplet adiabatic interaction potentials for the 6Li–6Li collision complex. The units,Rvdw and Evdw,correspond to 4.7840896 Bohr and 1594.194158 cm-1,respectively.
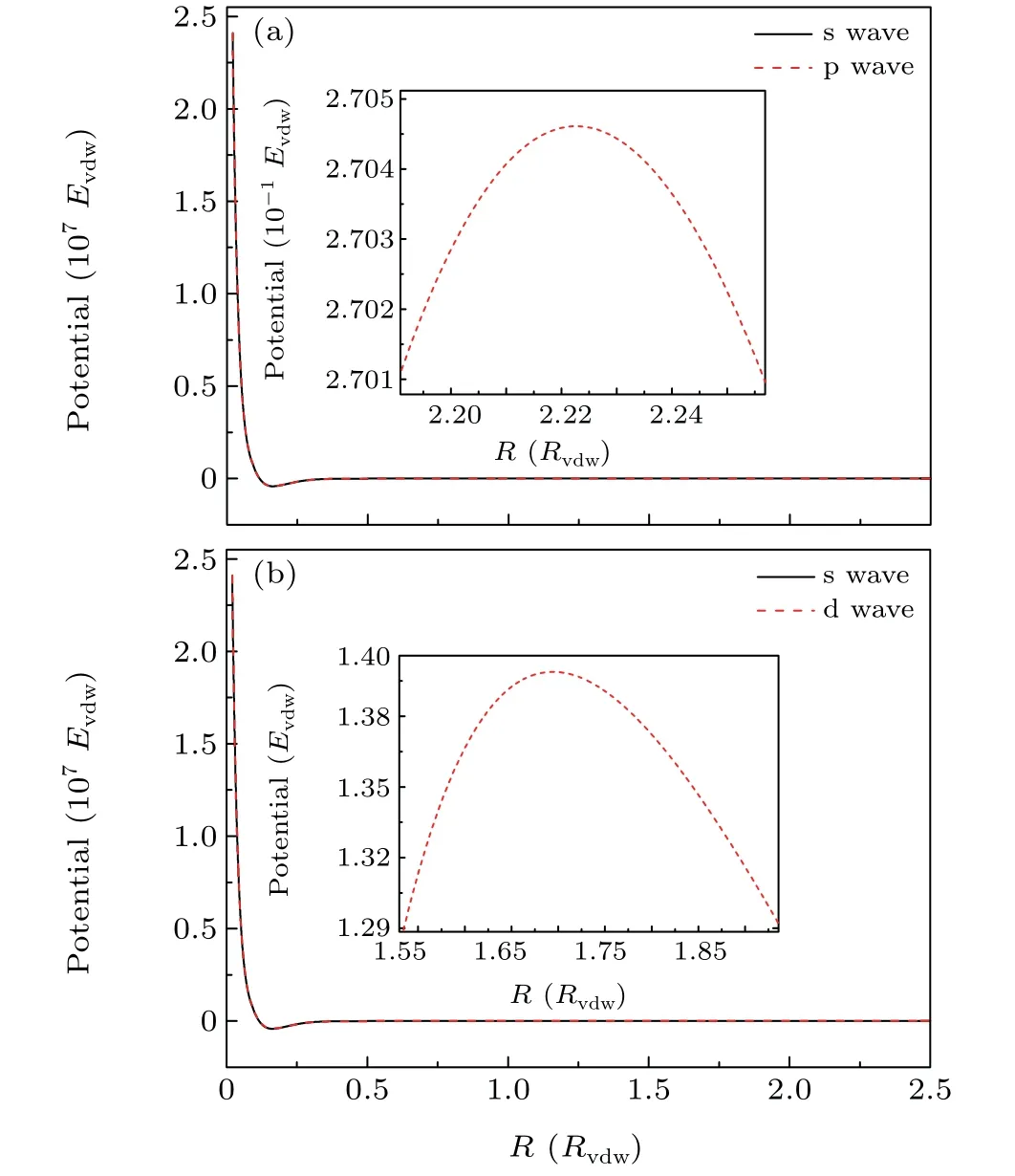
Fig.3. The singlet potential including the centrifugal potentials of(a)s and p waves, (b) s and d waves. Inset: Partial enlarged details of the potential barrier.
The effective singlet potential including the centrifugal potentials ?l2/2μR2of the s and p waves are shown in Fig.3(a).The inset shows the potential barrier of p wave. For comparison, the effective singlet potentials for s and d waves are shown in Fig.3(b)with the inset plot shows the potential barrier of d wave. The potential barriers of p and d waves are 7970.799 μK·kBand 41226.177 μK·kB,respectively. On one hand, the potential barrier of the d wave is much higher than that of the p wave. Thus,the influence of d wave on the FR is less significant than that of p wave. On the other hand,the potential barrier height of d wave is much larger than the upper limit of the collision energy we concerned,i.e., 100 μK·kB.Thus,d wave has almost no contribution to the total scattering section.Figure 4 is the sum of the scattering sections of different partial waves at 100 μK·kB. The solid black curve is the sum of the scattering sections of s and p waves. The dashed red curve is the sum of the scattering sections of s, p, and d waves. We observe that these two curves are almost on top of each other. This further indicates that the effect of d wave on the total scattering section can be ignored. Consequently, we focus on the scattering characters of s and p waves.

Fig. 4. The sum of cross sections of different partial waves at 100 μK·kB.The solid black curve is the sum of the cross sections of s and p waves. The dashed red curve is the sum of the cross sections of s,p,and d waves.
The cross sections near 543 Gs of s wave and 185 Gs of p wave (ml=0, +1,-1) at three different collision energiesE=1,50,and 100 μK·kBare plotted in Fig.5. Firstly,with the increase of the collision energy, the peak locations of the above four FRs shift towards the higher magnetic field. It is because at the higher collision energy,higher magnetic field is required to increase the energy difference between the scattering and closed channels. Additionally,the shifting amplitudes for the FRs of s wave and p wave are different. For the collision energy increasing fromE=1 μK·kBto 100 μK·kB,the former varies from 543.152 Gs to 543.895 Gs with an increase of~0.75 Gs;while the latter,taking the FR of p wave(ml=0)for example, shifts from 185.109 Gs to 185.953 Gs, which is a relatively larger shift of~0.85 Gs. This indicates that with the variation of collision energy, the change of energy difference between the scattering and closed channels related to the s-wave FR of 543 Gs is more sensitive to the variation of the magnetic field than that of p-wave FR of 185 Gs.
Secondly, with the increase of the collision energy, the peak magnitude varies.For FR of s wave near 543 Gs,the peak magnitude decreases dramatically. As seen in Fig. 5(a), the maximum cross section atE=100 μK·kBis smaller than that atE=1 μK·kBby over 2 orders.On the contrary,for FRs of p wave(ml=0,+1,-1),the peak magnitude atT=100 μK·kBis much higher than that atT=1 μK·kB. Moreover,the variation tend of the peak magnitude with the three collision energies is different among the three FRs of p wave(ml=0, +1,-1).On one hand,the maximal cross section for FR of p wave(ml=0) first decreases and then increases whenEincreases from 1 μK·kBto 100 μK·kB, as shown in Fig. 5(b). On the other hand,the peak magnitude for FRs of p wave(ml=+1,-1),first increases and then decreases,as shown in Figs.5(c)and 5(d). This indicates that the variation of collision energy may also affect the coupling strength between the open and closed channels.
We further investigated the variation of the scattering cross sections for the four FRs by varying the collision energy fromE=1 μK·kBto 100 μK·kBwith the interval of 1 μK·kB, and for each given collision energy, the magnetic fieldBis scanned with the interval of 0.001 Gs. As shown in Fig. 6(a), the resonance width of s-wave FR near 543 Gs,which we follow the same definition as Ref.[33],is 0.085 Gs.It does not change with the collision energy. Consistent with the above findings in Fig.5,with the increase of the collision energy,the cross section of the s-wave FR gradually vanishes at relatively higher magnetic field,indicating that the coupling strength between the open channel and the closed channel of this s-wave resonance declines. For the FRs of p wave, although there is no proper definition of the resonance width of p wave,it can be seen from the cross sections in Figs.6(b)–6(d),that the peak magnitude and width for each resonance both increase with the collision energy. Thus, we can conclude that the increasing collision energy enhances the coupling between the open and closed channels for the FRs of the p wave. Such different behaviors between the s-and p-wave FRs are because that there is a centrifugal potential barrier for the p-wave collision, while there is no barrier for the s-wave collision. The p-wave FR is more sensitive to the increase of the collision energy than the s-wave FR,since to achieve the p-wave FR,the open-channel wavefunction requires more collision energy to overcome(or tunneling through)the barrier before it resonates with the close channels.
Although the location, the magnitude and the width of the peak of the cross section varies with the collision energy,the doublet structure for the p-wave FR remains the same. In Fig.7,we present the cross sections of p-wave FR at 1 μK·kBand 100 μK·kB,respectively. There is always a 4-mGs splitting between the|ml| = 0 and 1 resonance positions. The splitting is caused by the dipole–dipole interaction, which is denoted in Eq. (7). When magnetic field increases, the shift amplitude of the resonance peak of|ml|=0 equals to that of|ml|=1. And this causes the constant splitting width of pwave resonance.
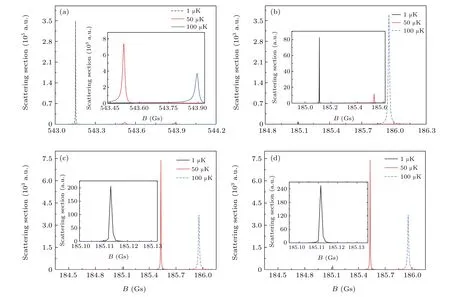
Fig. 5. The cross sections near 543 Gs of s wave and 185 Gs of p wave (ml =0, +1, -1) at three different collision energies E =1, 50 and 100 μK·kB.Panels (a)–(d) present the modulation of collision energy on s- and p-waves (ml =0, +1, -1) Feshbach resonances, respectively. Inset: Partial enlarged details of the cross sections.

Fig.6. The cross sections near 543 G(s wave)and 185 Gs(p wave,ml =0,+1,-1)with the variations of magnetic field and collision energy.

Fig. 7. The cross sections of p-wave FR near 185 Gs (|ml|=0, 1) at (a)1 μK·kB and(b)100 μK·kB.
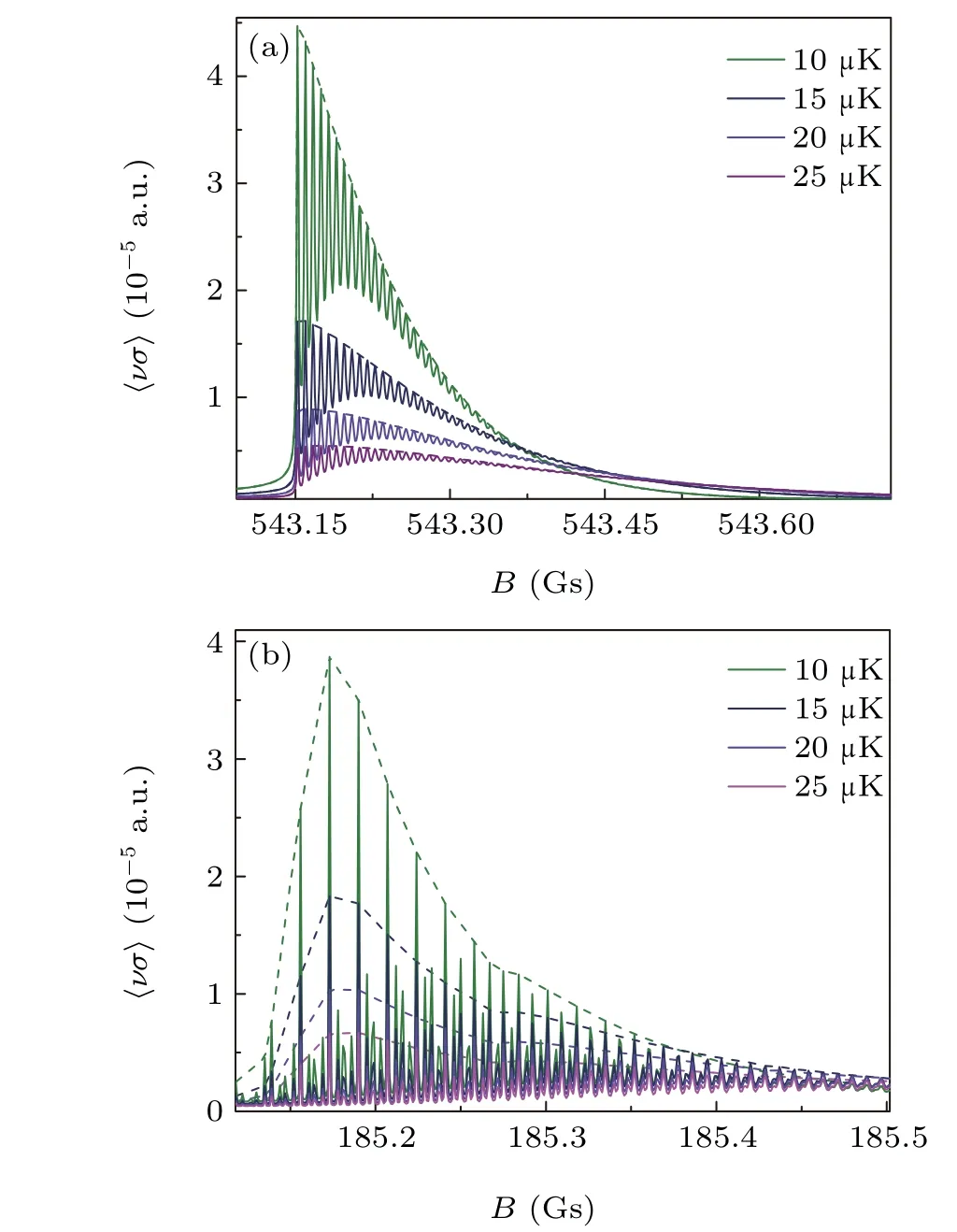
Fig. 8. The thermally averaged elastic rate coefficient 〈νσ〉 varies with the magnetic field B in the vicinity of 543 Gs(a)and 185 Gs(b),respectively,for T =10,15,20,25 μK. The dash curve is the envelope of the corresponding〈νσ〉curve.
In experiment, the empirical resonance positions are not measured at a fixed collision energy but rather at a certain temperature, and hence the measured resonance positions represent some sort of average over the different resonant positions at different collision energies. Based on the above cross section in the collision energy range[1,100]μK·kB,we can obtain the integral of Eq.(14),i.e.,the thermally averaged elastic rate coefficient〈νσ〉, for a relatively smaller temperature range from 10 μK to 25 μK. The variation behavior of〈νσ〉withBin the vicinities of 543 Gs and 185 Gs are shown in Figs.8(a)and 8(b),respectively,for four specific temperatures of 10,15,20,and 25 μK.There are complicated substructures for each curve in Fig. 8, and we also note that although the tiny 4 mGs doublet structure is distinguishable in the cross section, it does not present in the thermally averaged elastic rate coefficient〈νσ〉. This is because the interval for the sampled collision energy(δE=1 μK·kB)is relatively large compared to either the narrower width of the cross section or the tiny doublet structure. Thus, to obtain an accurate integral of Eq.(14),i.e.,to keep the high resolution or finesse for such a small doublet structure in the thermally averaged elastic rate coefficient, one has to use even denser grids not only for the magnetic field but also for the collision energy,which is quite computationally consuming. Since the doublet structure has already been represented and discussed in the cross section,we now qualitatively discuss the variation of the rate coefficient with temperature. It can be expected that with increase of the grid densities of the magnetic field and the collision energy, those substructures and peaks in the〈νσ〉curve may merge and show a primary distribution.[61]Thus, to focus on the whole variation trend of the rate coefficient,we plot an additional envelope for each〈νσ〉curve by artificially connecting the major peaks with the dashed curve. Generally, with increase of the temperature, the amplitude of the envelope of〈νσ〉gradually decreases,however its peak position does not vary obviously. This is because that with the increase of the temperature, the contribution from the high collision energy component increases.
4. Conclusion
We have investigated theoretically the effect of collision energy on magnetically tuned Feshbach resonance (FR) for the ultracold6Li–6Li system. Based on the coupled-channel(CC) method, we obtain the s- and p-wave cross sections for the collision energy ranging from 1 μK·kBto 100 μK·kB.The FR positions at 1 μK·kBare 543.152 Gs for s wave and 185.109 Gs,185.113 Gs for p wave(|ml|=0,1),respectively.The resonance width of s wave is 0.085 Gs and it does not change with collision energy. There exists a 4 mGs dipolar splitting between the|ml|=0 and 1 resonances of p wave.
With the increase of collision energy, the resonance positions near 543 Gs(s wave)and 185 Gs(p wave)are shifted to higher magnetic fields. The feature of s-wave FR gradually vanishes, while the feature of p-wave FR become obvious as the collision energy increases. The dipolar splitting of p wave does not change with the variation of collision energy,indicating that the shift amplitude of the|ml|=0 resonance equals to that of|ml|=1.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFA0306503), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21873016 and 12174044),the International Cooperation Fund Project of DBJI (Grant No. ICR2105), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Grant No.DUT21LK08).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Switchable terahertz polarization converter based on VO2 metamaterial
- Data-driven parity-time-symmetric vector rogue wave solutions of multi-component nonlinear Schr¨odinger equation
- Neutron activation cross section data library
- Multi-phase field simulation of competitive grain growth for directional solidification
- A novel similarity measure for mining missing links in long-path networks
- Effects of electrical stress on the characteristics and defect behaviors in GaN-based near-ultraviolet light emitting diodes