Effect of low high-density lipoprotein levels on mortality of septic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shao-hua Liu, Huo-yan Liang, Hong-yi Li, Xian-fei Ding, Tong-wen Sun, Jing Wang
1 General ICU, the First Aff iliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Key Laboratory of Critical Care Medicine,Zhengzhou 450052, China
2 Department of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine, the First Aff iliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China
KEY WORDS: High-density lipoprotein; Sepsis; Mortality; Meta-analysis
INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by the dysregulation of a host’s response to infections,[1]which is further complicated by an altered metabolic state. The mortality rate of sepsis remains high,[2,3]but t he potential mechanism is unclear. It has been widely accepted that the inflammatory mediators which alter the body’s metabolic state play an important role in the pathogenesis of sepsis.[4]There are also no specific or effective treatments available for sepsis, therefore, it will be of great interest to f ind a new approach to prevent and treat sepsis.
N otably, the effects of high-density lipoproteins(HDL) on sepsis have become a hot topic. The 2016 European Guidelines for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention shows a lower risk of cardiovascular events when HDL levels are above 40 mg/dL in men or above 45 mg/dL in women.[5]Nevertheless, when HDL levels of septic patients decrease to 33.6 mg/dL or even 20 mg/dL, there were signif icant correlations with a higher risk[6]or mortality[7]of sepsis. It is reported that HDL can clear lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and other pathogenic lipids through the liver, wherein receptors such as the HDL receptor, scavenger receptor and class B type I are bonded to the pathogenic lipids during the sepsis process.[8-10]Some studies[11,12]reported HDL has the highest aff inity to both toxin lipoteichoic acid and LPS,which is benef icial for decreasing the ability to actively regulate the innate immune response. H DL is able to maintain t he endothelial function and repair,[13]which are important for mediating the inflammatory response in the process of sepsis. In addition, HDL also prevents peroxide damage and stimulates the endothelial cells secreting endothelial nitric oxide synthetase.[12,14]
G iven the evidence of its role in the pathogenesis of sepsis, HDL may be a potential predictor of the risk of sepsis or the prognosis in septic patients. I n recent years,an increasing number of studies[6,15-20]have reported that lower HDL levels are related to an increased risk of sepsis and the mortality in septic patients. However, the results among the published studies remain controversial,and consolidating the available information to assess the association between HDL levels and sepsis is imperative.
METHODS
The methods of this meta-analysis is in compliance with the Preferred Repo rting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (P RISMA) criteria.[21]We searched the MEDLINE (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed), EMBASE (www.embase.com) and Cochrane CENTRAL (www.cochranelibrary.com) databases for articles published in English from the inception of the databases to September 30, 2019. The proceed of search was presented in Figure 1. We used the combination of“cholesterol”, “l(fā)ipoprotein”, “l(fā)ow-density lipoprotein”,“high-density lipoprotein”, “severe sepsis”, “septic shock”, and “critically ill patients” as the keywords.We also manually-searched the 參考文獻(xiàn) of the included articles. The literature s earches were performed independently by HL and HL. When disagreement occurred between different evaluators, the f inal decision was made by the third researcher. In addition, the EndNote X7 software was used for literature screening process.
Inclusion criteria
Studies were considered suitable for inclusion in this meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (1)patients with sepsis, severe sepsis or septic shock were enrolled; (2) when the studies observed the risk of sepsis,not all of the enrolled patients were septic patients; (3)the levels of HDL were divided into lower or higher level groups according to the median concentration or the levels were set by the designers in the initial studies;(4) the mortality or risk of sepsis was measured; (5) all the patients were adults; and (6) language was English.Studies were excluded if they lacked outcome data,were animal researches, provided only an association of lipoprotein levels and patients with other illnesses but not sepsis, or reported outcomes that were between non-HDL lipoprotein levels and sepsis. If the full text was not available or the article was a review, it would be excluded.
Data extracted
All the suitable data were independently extracted based on the aforementioned inclusion and exclusion criteria. The objective outcomes were the risk odds ratios (ORs) or mortality of sepsis among septic patients.The data of each study were listed as: the last name of the first author, publication year, country, study design,population, mean age, mean levels of HDL, study period and reported outcomes.
Bias of risk assessment
In this meta-ana lysis, the risk of bias in each study was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS).[22]The highest score that would be awarded from the NOS assessment was nine: in cohort selection, the comparability of the cohort design and analysis and the adequacy of the outcome measures were awarded a maximum of four points,two points and three points, respectively; higher than or equal to seven points was considered as high quality.[22]
Primary outcome
In this article, we extracted the outcomes including risk[6,23]and mortality[7,20,24-26]of sepsis as primary outcomes.
Statistical analysis
The outcomes of this study were mortality and risk odds ratio between lower and higher HDL levels in septic adult patients. The pooled effect of each outcome was conducted. In order to assess the heterogeneity among the included studies, we used a random effects model to calculate OR and 95% CI from each included study. The I2and P values were used to evaluate the heterogeneity of each included studies, in which the variability was caused by heterogeneity rather than sampling error.[27,28]When I2equaled 51%–74% or greater than 74%, the heterogeneity was considered as moderate or high,respectively. Because the number of each outcome was relatively small, the publish bias was not performed in this meta-analysis. The statistical analyses in this study was performed by using STATA 14.0.provided by the included study. The baseline information about the analyzed studies is presented in Table 1.
RESULTS
Study selection
Totally 1,524 art icles were identified from these databases, and 250 articles were removed due to duplication. Forty-one studies remained after preliminary screening by title and abstract, and f inally seven articles comprising 791 patients met inclusion criteria and were enrolled in this study. The selection process of this study is presented in Figure 1.
Study characteristics
Seven eligible articles reported the association of septic patients and HDL levels. Two articles[6,23]indicated the relation of lower HDL levels and the risk of sepsis,five studies[7,20,24-26]presented the outcomes that were associated with HDL levels in septic patients. Then, we extracted the ORs and 95% CIs for dichotomous data.Any missing data were calculated based on the raw data
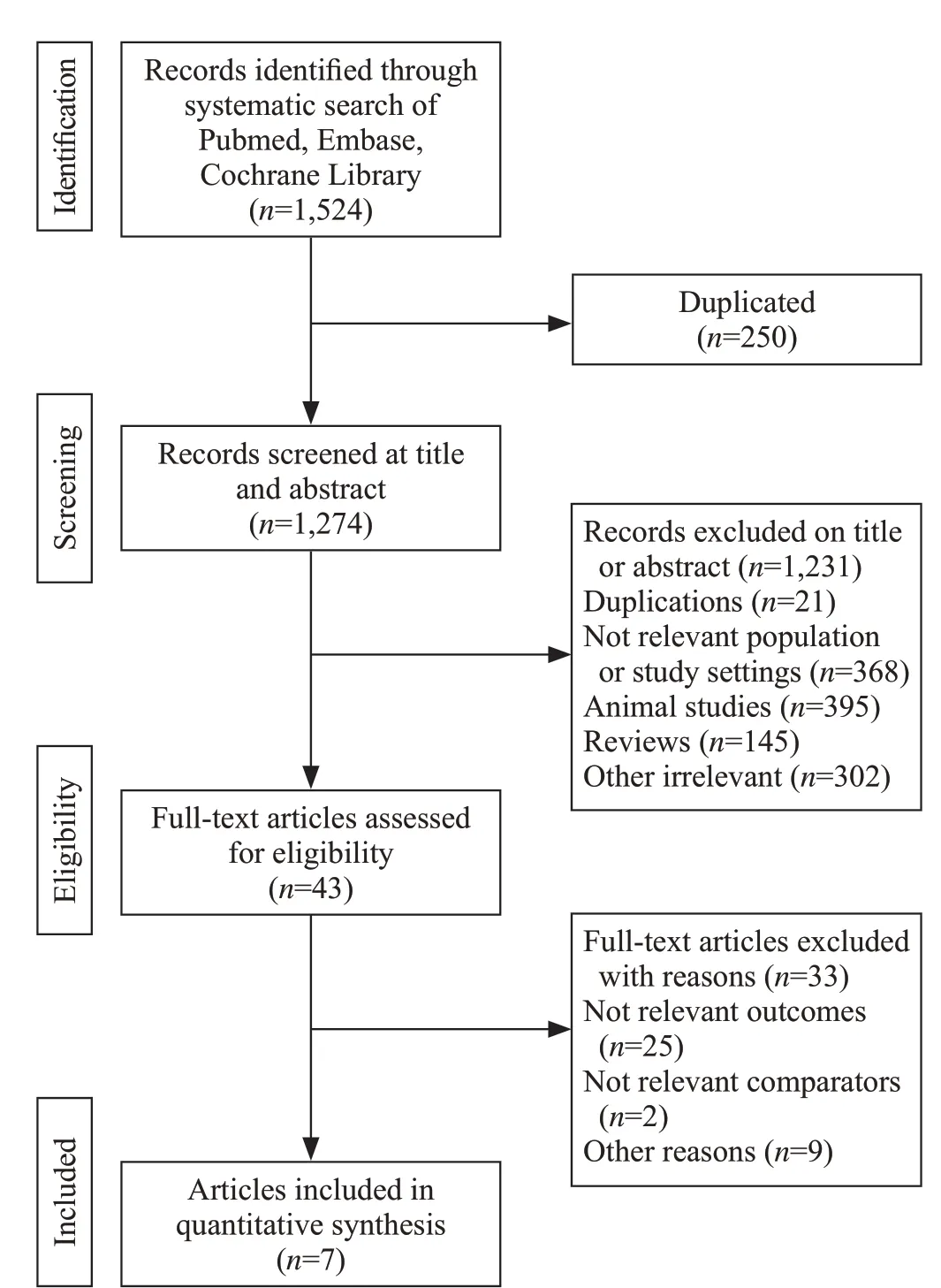
Figure 1. Flow-process diagram of the study selection.
Risk of bias assessment
According to the score of risk of bias in the NOS assessment, the quality of included studies was considered as a high quality and therefore showed a low risk of bias in this meta-analysis. The details of the risk of bias of included studies are reported in Table 2.
Effects of low HDL levels on sepsis
The primary outcome in the 7 observational studies[6,7,20,23-26]showed that lower HDL had no signif icant relationship with the risk of sepsis (OR for each 1 mg/dL increase, 0.94; 95% CIs 0.86–1.02; Figure 2), whereas lower HDL levels were related to an increased mortality rate in septic patients (for below about median HDL levels 2.00; 95% CIs 1.23–3.24; Figure 3). Unfortunately,due to the reason that the HDL levels in both survivors and non-survivors were performed as median and interquartile, we could not pool the outcomes among included studies.
Publication bias assessment
We used the funnel plots (Figure 4) and Egger’s regression (Figure 5) asymmetry tests to assess the potential publication bias in included studies, which evaluated the mortality between lower and higher HDL levels in septic patients. The result showed that there was a signif icant publication bias (P=0.01).
Trim and f ll analysis
The trim a nd f ill analysis (Figur e 6) were performed to evaluate the robust model of the included articles that evaluated the mortality in lower and higher HDL levels among septic patients. The result showed that there was a need to add a new study that may be a source of the potential publication bias, and the model was not robust.
DISCUSSION
This meta-analysis demonstrated that lower HDL levels are related to an increased mortality in septic patients. This is the first systematic review study and meta-analysis to elucidate the association between lipoprotein levels and the risk of sepsis as well as the mortality of septic patients. The results of this metaanalysis indicate that HDL levels can be considered as an interesting factor for prevention and treatment of sepsis.
Studies[29-31]on animal models of sepsis have reported that HDL can ameliorate the adverse consequences of sepsis, for example, leading to decreased cytokine levels and organ dysfunction, increasing LPS clearance, and improving survival. One of the mechanisms by which the HDL improved the outcomes of sepsis in animal models is a higher affinity of the HDL receptors to LPS and other pathogenic lipids compared to the inflammatory factors, resulting in an increased clearance o f those pathogenic compounds via the liver. Subsequently,the anti-endotoxin and anti-inflammation properties of HDL were confirmed in human studies.[32,33]Moreover,Murch et al[8]showed HDL can activate the sphingosines binding to sphingosine s receptors, and then exert the effect of bacterial killing or reduce the bacterial growth,thereby improving the inflammatory response in sepsis.In addition, HDL was found to protect LDL against oxidation,[34]help to maintain normal microvascular structure and endothelial integrity during the period of infection[35]and promote the removal of LPS from activated monocytes.[36]Additionally, some studies have shown that patients with lower LDL levels had an increased risk of sepsis and worse outcomes.[5,26]These potential protective effects of HDL may significantly decrease the risk of sepsis and improve the prognosis of septic patients, but this correlation requires further clinical studies. Despite extensive research, lipid prof iles are rarely measured or interpreted in the clinical management of sepsis[37]and are not even mentioned in the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines.[38]Moreover,HDL like presepsin, is not only a diagnostic predictor of early phase of sepsis but also a prognostic predictor of sepsis.[39]However, whether HDL levels lead to an increased risk of sepsis and mortality in septic patients remains controversial. Therefore, our finding provides evidence that low HDL levels have no signif icant effect on the risk of sepsis, but increase the mortality rate in septic adult patients.
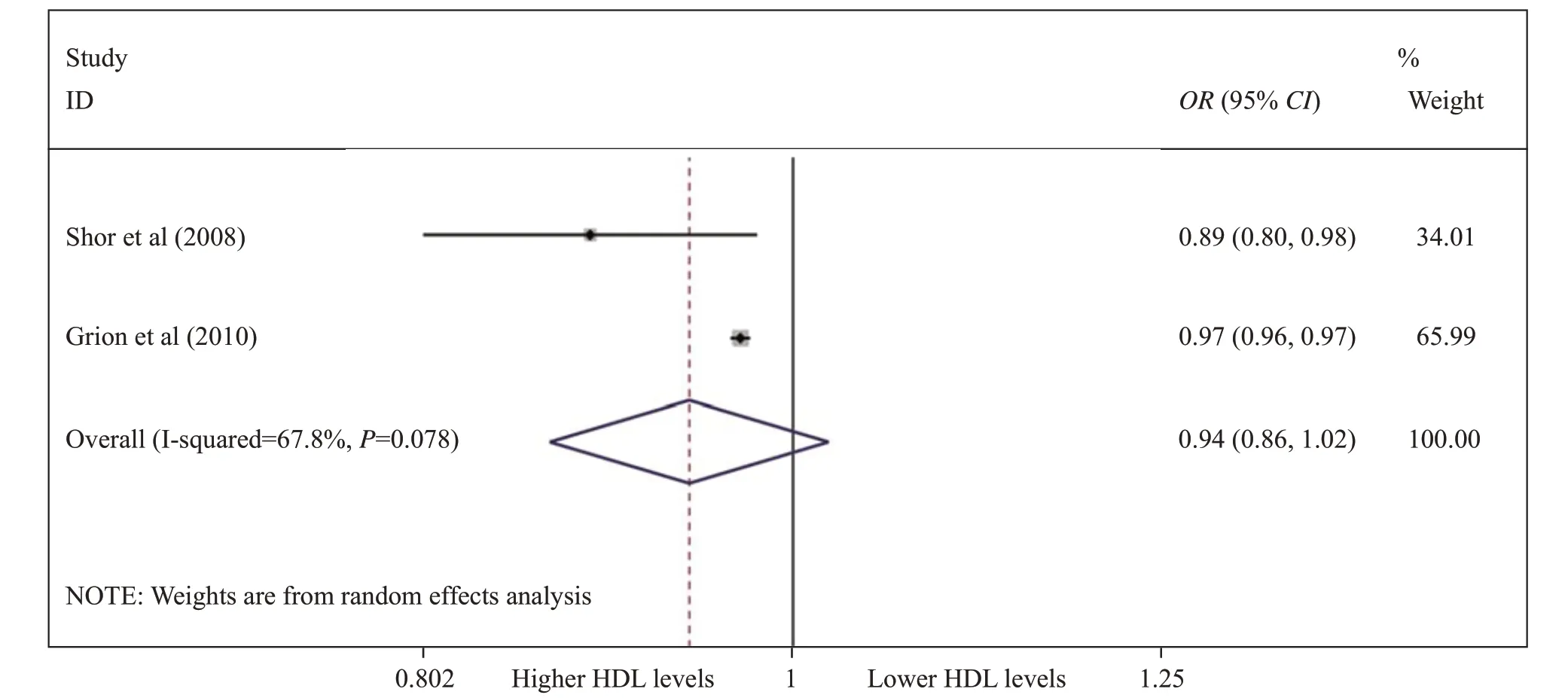
Figure 2. Forest plot showing the signif icance of the association between lower HDL levels (for each 1 mg/dL HDL) and risk of sepsis in the two groups according to the random effects model.
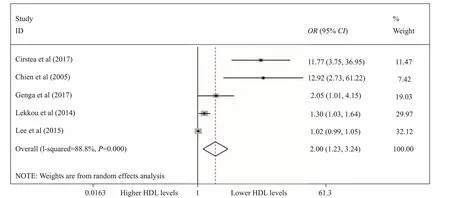
Figure 3. The association between lower HDL levels (for below median HDL levels) and mortality in the two groups according to the random effects model performed by forest plot.
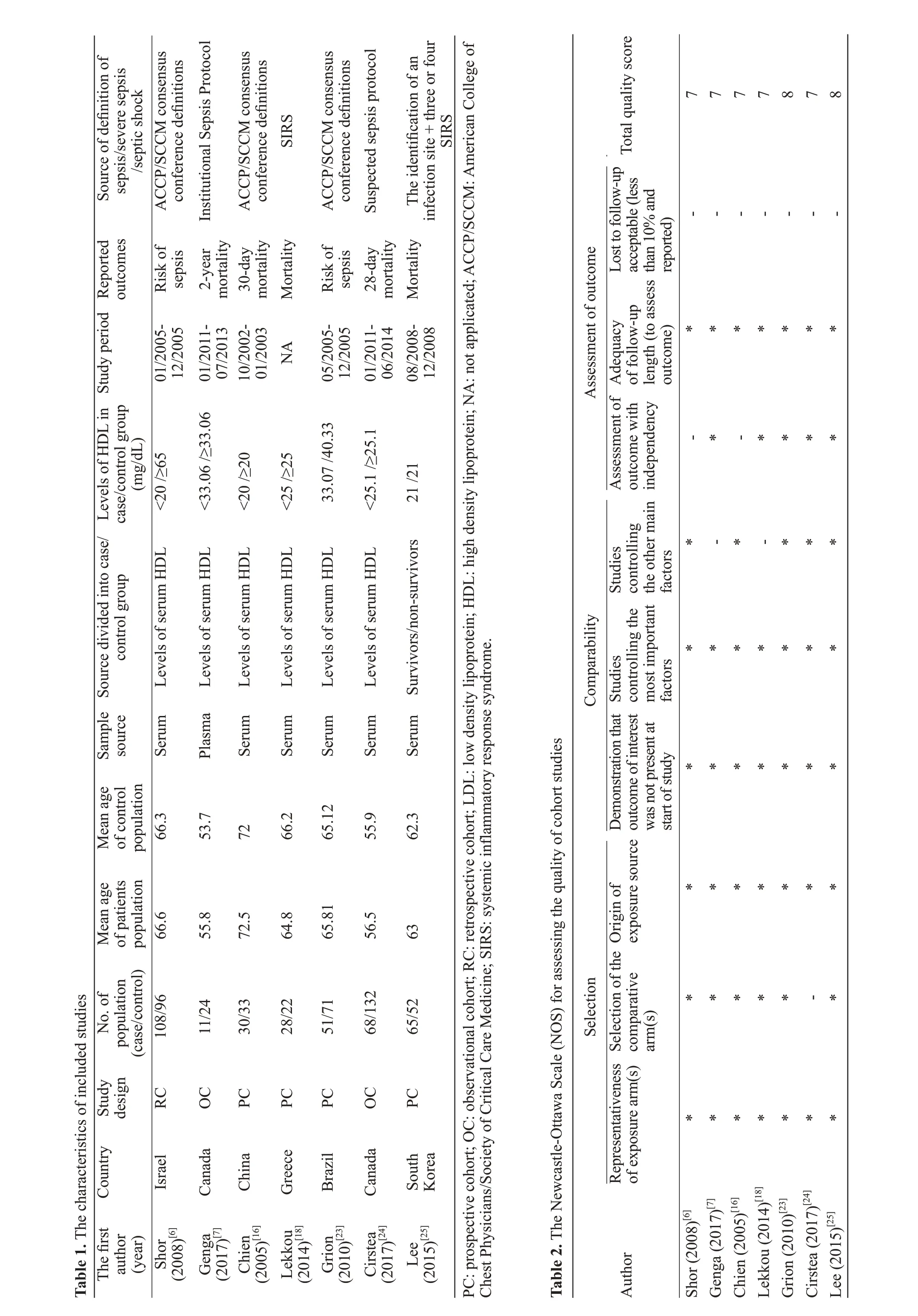
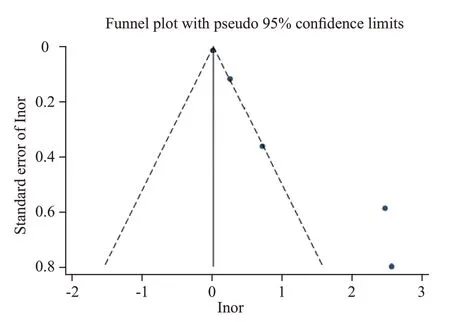
Figure 4. Funnel plot showed that it was asymmetry, suggesting potential publication bias may exist in mortality rates of lower and higher HDL levels among septic patients.
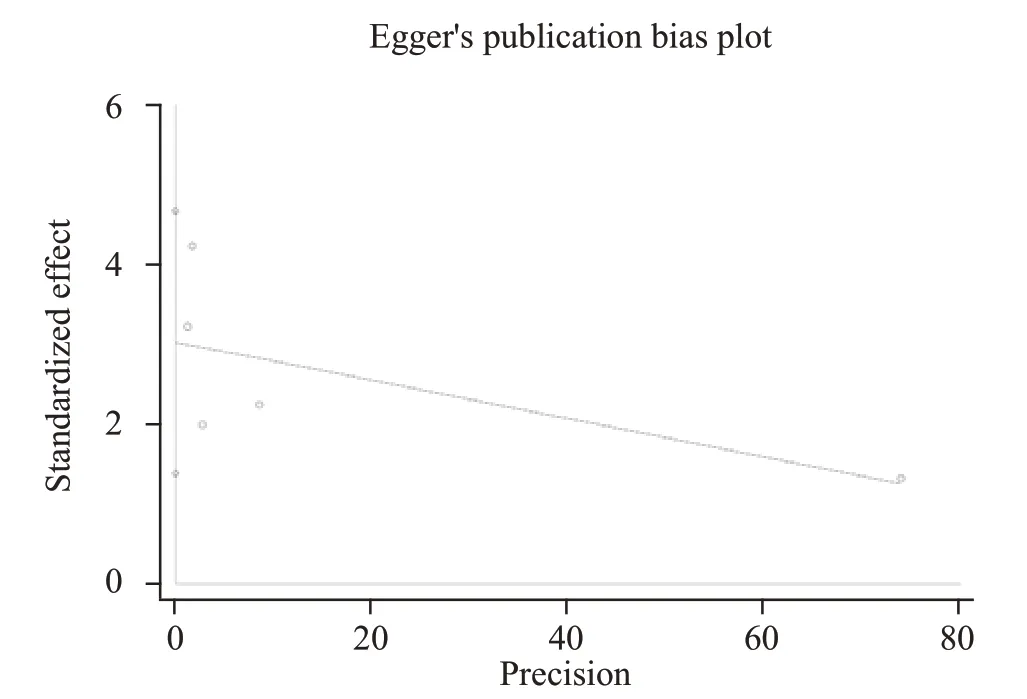
Figure 5. Egger's linear regression showed there was a significant publication bias existing in mortality of lower and higher HDL levels among septic patients.
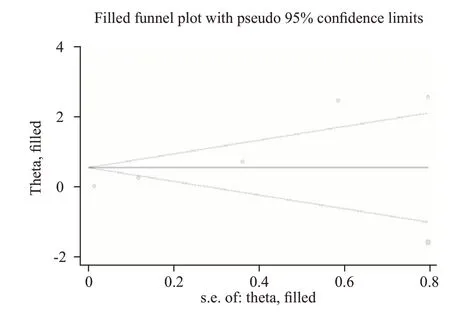
Figure 6. Trim and f ill analysis to conf irm whether the robust model for mortality in septic patients with lower and higher HDL levels.
Dellinger et al[40]showed that phospholipid emulsion did not reduce 28-day all-cause mortality of severe sepsis patients. Comparatively, Pajkrt et al[33]suggested that reconstituted HDL infusion in human can inhibit LPS effects in humans. Additionally, Musher et al[41]reported that the association between acute infection (including sepsis) and myocardial infarction (showing acute inflammation), in which acute infection could increase the risk of cardiovascular events, especially myocardial infarction. Interestingly, the author proposed a notable clinical problem of whether statins provided a benef it to all patients with acute infection. Statins are the f irst-line lipid-lowering medications that mainly decrease LDL levels and increase HDL levels. Willeit et al[42]suggested that when baseline lipoprotein levels were 30 mg/dL,the hazard ratios (HRs) for cardiovascular events were 1.11 (95% CI 1.00–1.22); interestingly, the HRs for on-statin lipoprotein were 1.43 (1.15–1.76) for 50 mg/dL or higher. The results of the study indicated that an increased baseline and on-statin lipoprotein showed an independent, approximately linear relation with the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, low HDL levels were associated with a higher mortality among septic patients as shown in this meta-analysis.
This meta-analysis has several strengths. First, the included articles were from cohort studies, of which 4 were prospective cohort studies. Second, the risk of bias assessment showed a low risk of bias. Third, we used generic inverse variance to calculate the pooled effect of ORs and their 95% CIs evaluated the association of lower HDL levels and risk or mortality levels. Finally,the result of the sensitivity analysis showed that this pooled effect model was robust and reliable.
In addition, this study has some weaknesses.Although we aimed to perform a comprehensive search of the relevant articles, some studies may not have been published due to negative outcomes. Second, statins can decrease the levels of LDL and increase the levels of HDL, and many included studies did not report whether statins were used or not; thus, the conclusion needs to be drawn from original studies to control this main confounding factor. Third, there were various def initions of lower HDL levels, which may be confounding factors for the pooled results. Finally, this is a limitation that no randomized controlled trials included in this metaanalysis.
CONCLUSION
This is the f irst systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate an association between lower HDL levels and the risk of sepsis and mortality in septic patients. These results suggest that lower HDL levels are associated with an increased mortality rate of septic patients, but not with the risk of sepsis. Further original studies are needed to support these findings. Furthermore, the information on this article indicated that the HDL may be considered as a predictor for prognosis in septic patients. More importantly, the question from this study should be considered whether the cutoff value of HDL levels for preventing the sepsis are the same as that for cardiovascular disease, which may be confirmed in the further clinical researches.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:Not needed.
Conflicts of interest:The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Contributors:SL proposed and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the f inal version.
REFFERENCE
1 Shankar-Hari M, Phillips G, Levy M, Seymour C, Liu V,Deutschman C, et al. Developing a New Definition and Assessing New Clinical Criteria for Septic Shock: For the Third International Consensus Def initions for Sepsis and Septic Shock(Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016;315(8):775-87.
2 Czupryna P, Garkowski A, Moniuszko A, Pancewicz S,Ciemerych A, Zajkowska J. Patients with sepsis in infectious diseases department in years 1997-2010 - epidemiology and clinical features. Przegl Epidemiol. 2013; 67(3):429-34,535-8.
3 Vincent JL, Pereira AJ, Gleeson J, Backer D. Early management of sepsis. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2014;1(1):3-7.
4 Dendoncker K, Libert C. Glucocorticoid resistance as a major drive in sepsis pathology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;35:85-96.
5 Piepoli MF, Hoes AW, Agewall S, Albus C, Brotons C, Catapano AL, et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice(constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation(EACPR). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(29):2315-81.
6 Shor R, Wainstein J, Oz D, Boaz M, Matas Z, Fux A, et al. Low HDL levels and the risk of death, sepsis and malignancy. Clinical Research in Cardiology. 2008;97(4):227-33.
7 Roveran Genga K, Lo C, Cirstea M, Zhou G, Walley KR,Russell JA, et al. Two-year follow-up of patients with septic shock presenting with low HDL: the effect upon acute kidney injury, death and estimated glomerular f iltration rate. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2017;281(5):518-29.
8 Murch O, Collin M, Hinds CJ, Thiemermann C. Lipoproteins in inflammation and sepsis. I. Basic science. Intensive Care Med.2007;33(1):13-24.
9 Walley KR, Thain KR, Russell JA, Reilly MP, Meyer NJ,Ferguson JF, et al. PCSK9 is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and septic shock outcome. Sci Transl Med.2014; 6(258):258ra143.
10 Guo L, Zheng Z, Ai J, Huang B, Li XA. Hepatic scavenger receptor BI protects against polymicrobial-induced sepsis through promoting LPS clearance in mice. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(21):14666-73.
11 Levels JH, Abraham PR, van den Ende A, van Deventer SJ.Distribution and kinetics of lipoprotein-bound endotoxin. Infect Immun. 2001;69(5):2821-8.
12 Levels JH, Abraham PR, van Barreveld EP, Meijers JC, van Deventer SJ. Distribution and kinetics of lipoprotein-bound lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 2003;71(6):3280-4.
13 Kon V, Yang H, Fazio S. Residual Cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease: role of high-density lipoprotein. Arch Med Res.2015;46(5):379-91.
14 Jones T, Wong H, Meyer N. HDL cholesterol: A “pathogen lipid sink” for sepsis? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;199(7):812-4.
15 Barlage S, Gnewuch C, Liebisch G, Wolf Z, Audebert FX, Gluck T, et al. Changes in HDL-associated apolipoproteins relate to mortality in human sepsis and correlate to monocyte and platelet activation. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35(11):1877-85.
16 Chien YF, Chen CY, Hsu CL, Chen KY, Yu CJ. Decreased serum level of lipoprotein cholesterol is a poor prognostic factor for patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia that required intensive care unit admission. J Crit Care. 2015;30(3):506-10.
17 Lagrost L, Girard C, Grosjean S, Masson D, Deckert V, Gautier T, et al. Low preoperative cholesterol level is a risk factor of sepsis and poor clinical outcome in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Crit Care Med.2014;42(5):1065-73.
18 Lekkou A, Mouzaki A, Siagris D, Ravani I, Gogos CA. Serum lipid profile, cytokine production, and clinical outcome in patients with severe sepsis. J Crit Care. 2014;29(5):723-7.
19 Shor R, Wainstein J, Oz D, Boaz M, Matas Z, Fux A, et al. Low serum LDL cholesterol levels and the risk of fever, sepsis, and malignancy. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2007;37(4):343-8.
20 Chien JY, Jerng JS, Yu CJ, Yang PC. Low serum level of highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol is a poor prognostic factor for severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2005;33(8):1688-93.
21 Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62(10):1006-12.
22 Wells GSB, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M,Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Available at:http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm.Accessed 2019.
23 Grion CMC, Cardoso LTQ, Perazolo TF, Garcia AS, Barbosa DS, Morimoto HK, et al. Lipoproteins and CETP levels as risk factors for severe sepsis in hospitalized patients. European Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2010;40(4):330-8.
24 Cirstea M, Walley KR, Russell JA, Brunham LR, Genga KR,Boyd JH. Decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is an early prognostic marker for organ dysfunction and death in patients with suspected sepsis. J Crit Care. 2017;38:289-94.
25 Lee SH, Park MS, Park BH, Jung WJ, Lee IS, Kim SY, et al.Prognostic implications of serum lipid metabolism over time during sepsis. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:789298.
26 Lekkou A, Mouzaki A, Siagris D, Ravani I, Gogos CA. Serum lipid profile, cytokine production, and clinical outcome in patients with severe sepsis. J Crit Care. 2014;29(5):723-7.
27 Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a metaanalysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539-58.
28 Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557-60.
29 Guo L, Ai J, Zheng Z, Howatt DA, Daugherty A, Huang B, et al.High density lipoprotein protects against polymicrobe-induced sepsis in mice. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(25):17947-53.
30 McDonald M, Dhadly P, Cockerill G, Cuzzocrea S, Mota-Filipe H, Hinds C, et al. Reconstituted high-density lipoprotein attenuates organ injury and adhesion molecule expression in a rodent model of endotoxic shock. Shock. 2003;20(6):551-7.
31 Netea MG, Demacker PN, Kullberg BJ, Boerman OC,Verschueren I, Stalenhoef AF, et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-def icient mice are protected against lethal endotoxemia and severe gram-negative infections. J Clin Invest.1996;97(6):1366-72.
32 Birjmohun RS, van Leuven SI, Levels JH, van’t Veer C,Kuivenhoven JA, Meijers JC, et al. High-density lipoprotein attenuates inf lammation and coagulation response on endotoxin challenge in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2007;27(5):1153-8.
33 Pajkrt D, Doran JE, Koster F, Lerch PG, Arnet B, van der Poll T, et al. Antiinflammatory effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein during human endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1996;184(5):1601-8.
34 Mackness MI, Durrington PN, Mackness B. How high-density lipoprotein protects against the effects of lipid peroxidation. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2000;11(4):383-8.
35 Chung DW, Chen J, Ling M, Fu X, Blevins T, Parsons S, et al.High-density lipoprotein modulates thrombosis by preventing von Willebrand factor self-association and subsequent platelet adhesion. Blood. 2016;127(5):637-45.
36 Kitchens RL, Wolfbauer G, Albers JJ, Munford RS.Plasma lipoproteins promote the release of bacterial lipopolysaccharide from the monocyte cell surface. J Biol Chem.1999;274(48):34116-22.
37 Green P, Theilla M, Singer P. Lipid metabolism in critical illness.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2016;19(2):111-5.
38 Osborn TM, Phillips G, Lemeshow S, Townsend S, Schorr CA,Levy MM, et al. Sepsis severity score: an internationally derived scoring system from the surviving sepsis campaign database.Crit Care Med. 2014;42(9):1969-76.
39 Zou Q, Wen W, Zhang XC. Presepsin as a novel sepsis biomarker. World J Emerg Med. 2014;5(1): 16-9.
40 Dellinger RP, Tomayko JF, Angus DC, Opal S, Cupo MA,McDermott S, et al. Efficacy and safety of a phospholipid emulsion (GR270773) in Gram-negative severe sepsis: results of a phase II multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, dosef inding clinical trial. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(11):2929-38.
41 Musher DM, Longo DL, Abers MS, Corrales-Medina VF.Acute infection and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med.2019;380(2):171-6.
42 Willeit P, Ridker PM, Nestel PJ, Simes J, Tonkin AM, Pedersen TR, et al. Baseline and on-statin treatment lipoprotein(a)levels for prediction of cardiovascular events: individual patient-data meta-analysis of statin outcome trials. Lancet.2018;392(10155):1311-20.
 World journal of emergency medicine2020年2期
World journal of emergency medicine2020年2期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- Information for Readers
- Food poisoning associated methemoglobinemia: Time to wake up
- Acute obstructive f brinous laryngotracheobronchitis induced by severe glyphosate surfactant intoxication:A case report
- A young lady presenting to the emergency department with blue lips: A case study with review of literature
- Outcome predictors for severely brain-injured patients directly admitted or transferred from emergency departments to a trauma center
- An unexpected electrocardiogram sign of subacute left ventricular free wall rupture: Its early awareness may be lifesaving
