NO-cGMP-K channel-dependent anti-nociceptive activities of methanol stem bark extract of Piptadeniastrum africanum (Mimosaceae) on rats
Mbiantcha Marius, Almas Jabeen, Ateufack Gilbert, Shabana U. Simjee, Bomba Tatsinkou Francis Desire, Nida Dastagir
1Laboratory of Animal Physiology and Phytopharmacology, Faculty of Science, University of Dschang, P.O. Box 67, Dschang, Cameroon
2Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research, International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi,Karachi 75270, Pakistan
3H.E.J. Research Institute of Chemistry, International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, Karachi 75270, Pakistan
1. Introduction
With a prevalence of over 72.4%[1], and as major symptom of the majority of diseases (trauma, inflammation, arthritis cancer), pain affects the entire world population. Nevertheless, understanding its signaling pathways, its transmission and maintenance, is important in improving its management[2]. Pain is a multifactorial disease which can affect different types of organs. Thus, without adequate treatment, acute pain can lead to chronic pain. It includes neuropathic and inflammatory pain which is the most frequent. These pains are still regarded as a problem in medical practice and remain without satisfactory treatment[3,4]. Chronic pain occurs as a consequence of alterations in the nerves (peripheral) and the central nervous system resulting in hyperalgesia and/or allodynia[5-7].
The induction of chronic inflammatory pain with chemical such as carrageenan in rat causes initially the release of inflammatory mediators such as bradykinin followed by a synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins and sympathetic amines[8]. These mediators will induce the development of inflammatory nociception by decreasing pain threshold at the level of primary afferent neurons[9].Moreover, during this process, there is an increase of intracellular guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) production by nitric oxide(NO) through the activation of guanylate cyclase. However, it is well documented that, anti-nociceptive effect is observed withL-arginine in the model of hyperalgesia caused by carrageenan in the rat,and this effect is inhibited in presence of NO and guanylyl cyclase(methylene blue) inhibitors[10,11]. Equally in the same process, there is an opening of ATP-sensitive K+channels (KATP) mediated via the stimulation of protein kinase G by cGMP[12]. Chronic consumption of chemotherapeutic agents such as vincristine in patient suffering cancer are known to induce the development of peripheral neuropathy in at least 30% to 40% of cases[13-16].
Pharmacological management of neuropathic pain includes anticonvulsants (gabapentin and carbamazepine), analgesics (tramadol and fentanyl patches) and tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline).Despite their limited effectiveness and side effects related to their use,these molecules remains the therapeutic option for neuropathic pain treatment[17,18]. Thus, nowadays, it is important to found out new therapeutic agents for management of neuropathic with higher efficacy and less sides effects[19].
Piptadeniastrum africanum(P. africanum), also calledPiptadenia africanaHook. f., is a big tree belonging to the family Mimosaceae family. This plant is mostly founded in Senegal, Soudan, Ouganda,Congo, Northen Angola and Eastern Cameroon. Its stem bark is traditionally used in Cameroon for the treatment of ailments such as wounds, edema, constipation, aneamia, gastric ulcer, rheumatism,fever, pneumonia, meningitis, rheumatism and pain[20-22]. Studies on this plant revealed their antibacterial, antiulcerogenic activities[23-25]as well as antiproliferative, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties[26,27]. Also, our previous work on the same plant revealed it anti-arthritis effect[28]. The phytochemical analysis ofP. africanumroots showed the presence of compounds such as saponins, alkaloids,triterpenoids, steroids and flavonoids[29].
Based on the previous work, this work aims to determine the potential role of nitric oxide-cyclic-guanosine monophosphate-K+channels(NO-cGMP-K+) and or endogenous opioids pathway in the analgesic process of methanol extract of stem bark ofP. africanumusing inflammatory pain model induced by carrageenan injection into rat paw. Also, it aims to evaluate the anti-hyperalgesic effect of extract in neuropathic pain model induced by vincristine.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental animals
Wistar rats (138) weighing in average 175 g (3 months age, both sexes) were used. Inflammatory pains assay was conducted with males while females were used in neuropathic pain induced model. They were bred and provided by the H.E.J. Research Institute of Chemistry,International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, Pakistan, animal house. Prior to experiments, animals were acclimatized for 7 d under specific condition [12 h light/dark cycle,50%-80% humidity and (22±1) ℃temperature] and freely received standard rodents diet with filter water[28].
Animals management and treatment protocol (No. 1209004) followed the Institutional Animal Care, Use and Standards Committee of International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi, Pakistan[28]. All experiments (n=6) were conducted at particular time of 08.30 and 12.30 h, to minimize environments variation effects.
2.2. Collection and preparation of plant material
Fresh stem bark fromP. africanum(Hook. f.) were collected in Bokito district, Central Region of Cameroon and authentication was made at the National Herbarium (Yaounde, Cameroon) in reference to the stored voucher specimens N°12115/SRF. After being reduced into small pieces, plant material was shade dried and grounded into fine powder, which served for extraction. Thus, 200 g of plant powder were macerated for 3 d in 1.5 L of methanol (W:V) and after filtration with whatman filter paper, the obtained filtrate was concentrated in a rotary evaporator (65 ℃), giving 18.81 g of methanolic extract, equivalent to 28.08% yield[28].
2.3. Treatment regimen
P. africanumstem bark (PAME) (250 and 500 mg/kg), diclofenac(50 mg/kg) and vehicle [5% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) + PBS] were administered orally one hour before carrageenan induction.
2.4. Carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia
2.4.1. Mechanical hyperalgesia
The effect of PAME (250 and 500 mg/kg), diclofenac (50 mg/kg) and vehicle (5% DMSO + PBS) on mechanical hyperalgesia was measured with the analgesimeter (UGO Basile, Italy) paw pressure[30,31]. The hind paw of the rat, placed in a pressure applicator, was stimulated by increasing pressure (cut-off of 250 g) until vocalisation or withdrawal.The nociceptive threshold value was considered as the force (g)obtained.
2.4.2. Thermal hyperalgesia
The effect of PAME (250 and 500 mg/kg), diclofenac (50 mg/kg)and vehicle (5% DMSO + PBS) on thermal hyperalgesia was evaluated with the UGO Basile plantar test apparatus (Italy)[32]. Individually, the rat was introduced into a glass acrylic box (18 cm ×8 cm×8 cm). After habituation (10 min), a radiant heat stimulus (50 W) was projected on the paw through an opening (oval-shaped, 5 mm×10 mm). In order to avoid tissue damage in animals, a maximum stimulation time of 20 s was used in case of non-reaction of the animal.
For each rat, mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia were performed before the oral administration of different treatments and carrageenan(0.1 mL, 2% dissolved in 0.9% NaCl) was injected 1 h after. Other measures of the thickness of the hind paw followed the injection of carrageenan, precisely 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h after.
2.5. PGE2-induced mechanical hyperalgesia
One hour after oral treatment of animal with 5% DMSO, PAME(500 mg/kg) or diclofenac (50 mg/kg), each animal received 0.1 nmol of PGE2by paw under the subplantar aponevreous. The frequency reaction to paw pressure stimulus was measured before PGE2injected and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h after PGE2was injected[33]. In another register,to verify the therapeutic effect, the medications were administered 1 h(orally) after PGE2and mechanical hyperalgesia was estimated in the same way[34].
2.6. Involvement of NO/cGMP/K+ pathway or participation of endogenous opioids
The contribution of NO/cGMP/K+pathway and/or endogenous opioids in the modulation of PAME anti-nociceptive activity were determine by the method described previously by Dinget al[35] and Mbiantchaet al[33] with small modifications. For each experiment,each animal was subject to a single use 60 min before carrageenan injection, PAME (500 mg/kg,p.o.) or the vehicle (10 mg/kg,p.o.)used for dissolving PAME were given orally. Several antagonists and agonists substances were used to verify the participation or not of NO/cGMP/K+pathway and/or endogenous opioids in the modulation of PAME anti-nociceptive activity. Opioid antagonist and agonist (20 mg/kg of naloxone and 5 mg/kg of morphine, bothi.p.), nitric oxide synthase inhibitor and substrate for nitric oxide synthase (90 mg/kg ofL-NAME and 200 mg/kgL-arginine, bothi.p.), soluble guanylyl cyclase inhibitor (1 mg/kg of methylene blue,i.p.) or KATP-channel blocker and opener (5 mg/kg of glibenclamide and 2 mg/kg of diazoxide, bothi.p.)pretreated groups of animals were added and the antagonists were given before (15 min) PAME. Sixty minutes after PAME administration,carrageenan test was carried out as described earlier. The dose selections for carrageenan (2%), the drugs (agonist and/or antagonist) were based on our preliminary investigation and from works references[33].
2.7. Induction of neuropathic pain with vincristine and treatment
Vincristine-induced neuropathy in rats was performed as described[36].Briefly, an intraperitoneal injection of 100 μg/kg of vincristine sulphate was administered to the rats during two series of five successive working days (days 1-5 and days 8-12) with 2 d off. Baseline measurements of the reaction latency of maximum force applied until paw withdrawals or vocalisations indicative of pain were taken 30 min after the injection of the vincristine using the Randall-Selitto test. The rats were divided into 3 groups of 6 rats each and were treated with PAME (500 mg/kg,p.o.),morphine (5 mg/kg,p.o.) or 5% DMSO (vehicle). Treatments were given from the first day before the injection of vincristine and continued daily until day 15.
2.8. Behavioral assessment of neuropathic pain
Three sets of pain assessment tests: mechanical hyperalgesia induced with an analgesiometer (UGO Basile, Italy), thermal hyperalgesia induced with the hot plate [(51±0.5) ℃] (Ugo Basile, Monvalle VA,Italy) and cold allodynia using cold water at 4 ℃ were used to evaluate the analgesic effects of PAME in the vincristine-induced neuropathic pain on days 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 and 15.
Mechanical hyperalgesia induced by analgesiometer was performed as described earlier in the case of inflammatory pain.
Thermal hyperalgesia was performed in the rats after the vincristineinduced neuropathy using the hotplate as previously described[37].Briefly, the animals were gently dropped onto the hot plate that was preheated to (51±0.5) ℃ and cut-off latency of 20 s was observed.
Cold hyperalgesia was evaluated by immersing the rat’s tail into water at 4 ℃ as previously described[38]. The inactivity for a rat to withdrawal its tail was determinate with a digital timer with a cut-off of 20 s and the duration of immersion was noted[33].
2.9. Biochemical and hematological estimations
Anesthetic ether was administered to rats on day 16, the thoracic cavity was opened and through cardiac puncture, blood was collected into a tube filled with anticoagulant (EDTA) and used in determining Hematological parameters by usual Laboratory standard method[33];while another free EDTA tube containing blood was centrifuged(4 900 rpm/5 min) to obtain serum, used for measurement of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and creatinine levels[39].
2.10. Chemicals and drugs
L-arginine,L-NAME, methylene blue, glibenclamide, carrageenan,PGE2, diclofenac, morphine, diazoxide, naloxone chloridrate and DMSO were acquired from Sigma (Sigma Chemical Co., USA).5% DMSO (DMSO + PBS) has been used to dissolve methylene blue, diclofenac, morphine and glibenclamide whereas carrageenan,L-NAME, diazoxide, naloxone chlorydrate andL-arginine were diluted in saline solution. PGE2(stock solution) was prepared in absolute ethanol (0.5 mg of PGE2for 1 mL ethanol) and diluted in sterile saline(less than 0.1% ethanol in the injected solution).
2.11. Statistical analysis
The data of this study (expressed as Mean±standard error,n=6)were statistically analyzed by Graph pad prism Version-5.0.1 software for Windows. These data were analyzed by either one way ANOVA plus Tukeypost hoctest or two way ANOVA plus Bonferonni aspost hoctest. The data was considered statistically significant whenP-value<0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of PAME on carrageenan-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia
Carrageenan into the rat’s paw induced significant (P<0.001)mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. Four hours after carrageenan injection, the reaction latency period was reduced to 63.56% and 64.94%, respectively for mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. Both diclofenac (50 mg/kg,p.o.) and PAME (500 mg/kg,p.o.), significantly improved the latency period with a respective reduction of 36.87%and 23.25% to the mechanical hyperalgesia and 42.77% and 33.03%to the thermal hyperalgesia (Figures 1 and 2).
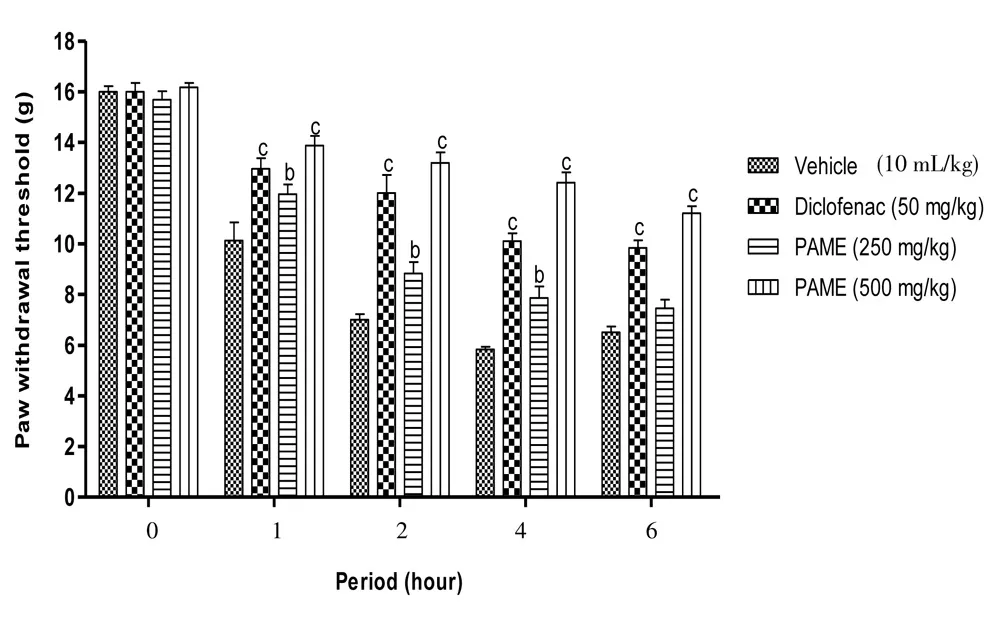
Figure 1. Effect of oral administration of PAME on mechanical hyperalgesia in carrageenan inflamed rat paw.Treatments were given 1 h before intraplantar injection of carrageenan (100 μL). n=6 rats per group. bP<0.01, cP<0.001 compared to vehicle.
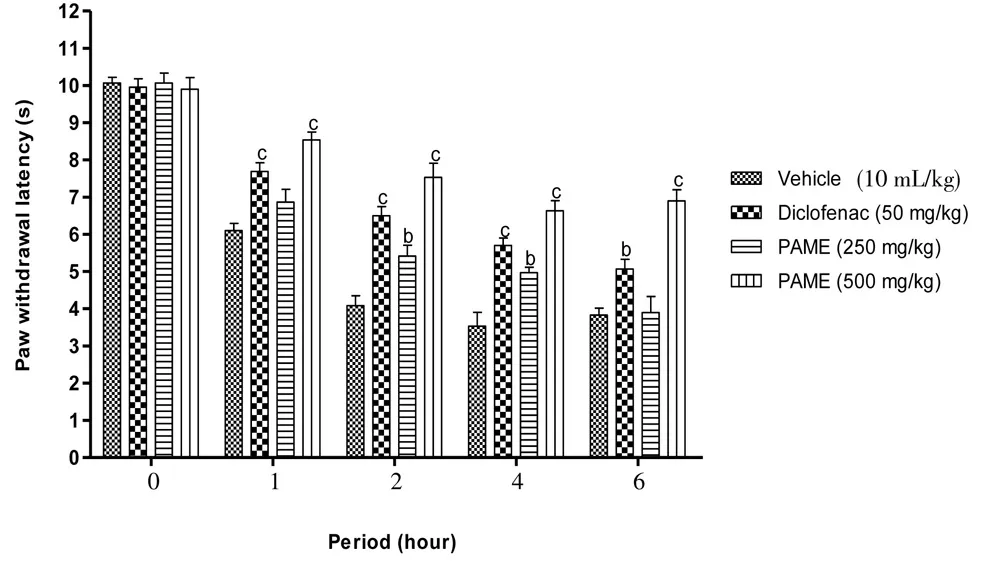
Figure 2. Effect of oral administration of PAME on mechanical hyperalgesia in carrageenan inflamed rat paw.Treatments were given 1 h before intraplantar injection of carrageenan (100 μL). n=6 rats per group. bP<0.01, cP<0.001 compared to vehicle.
3.2. Effects of PAME on PGE2-induced mechanical hyperalgesia
After administration of PGE2into the paw, it developed a painful hypersensitivity in animals. PGE2-induced hyperalgesia was significantly (P<0.001) reduced by diclofenac and PAME after administration for preventive measures (Figure 3A). In addition,as revealed in Figure 3B, PAME as well as diclofenac significantly(P<0.001) inhibited PGE2? induced hyperalgesia when given as a therapeutic scheme of treatment. In both cases (Figure 3A and 3B) at the second hour, effect of PAME was more pronounced than that of diclofenac with inhibition percentage of 80.0% for extract, 38.0% for diclofena in Figure 3A, 88.5% for extract and 61.0% for diclofenac in Figure 3B.
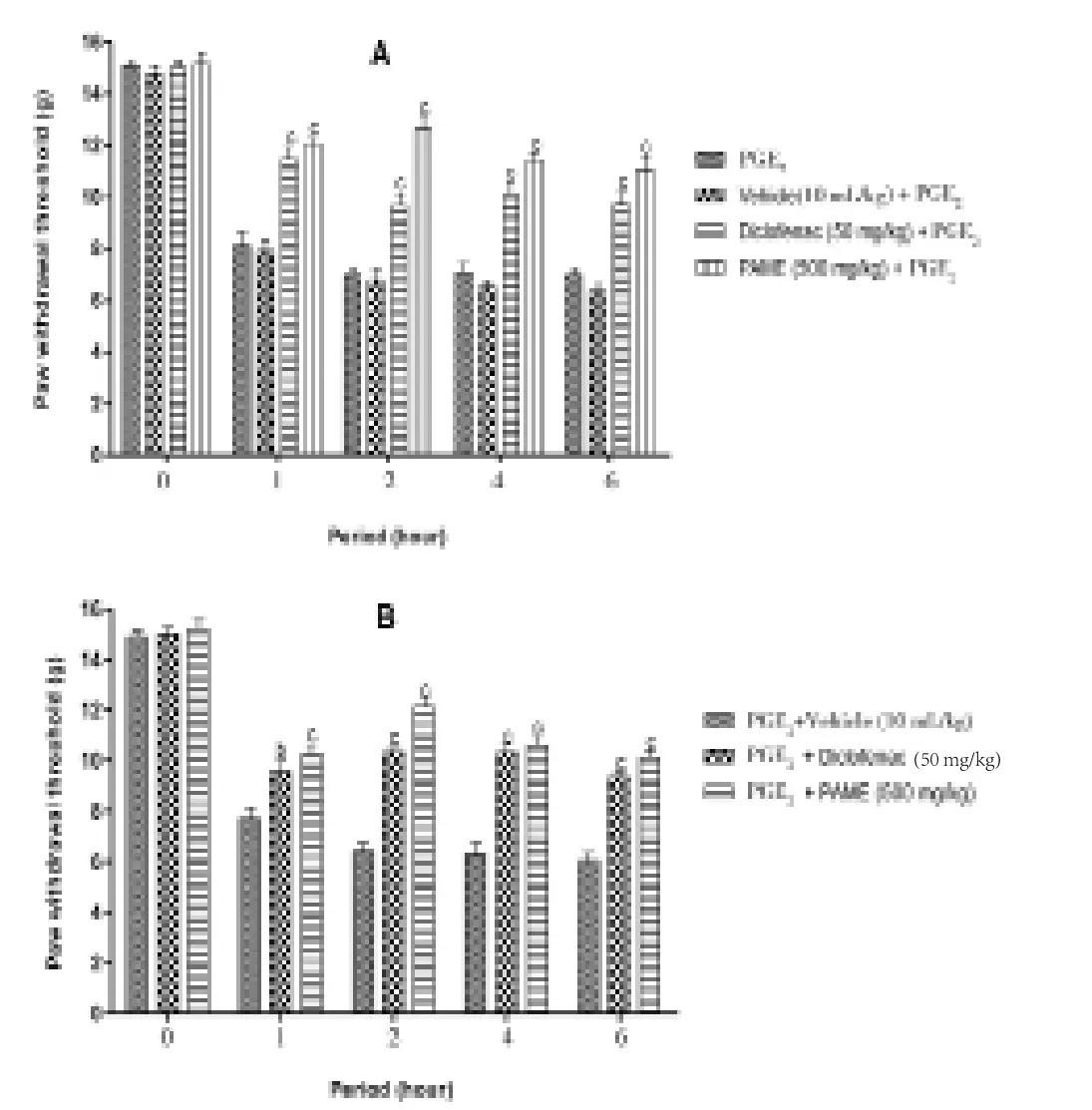
Figure 3. Effect of oral administration of PAME on mechanical hyperalgesia in PGE2 (100 μL) inflamed rat paw.In panel (A), animals were treated 1 h before PGE2 injection and pain response was evaluated before treatment and after PGE2 injection. In panel (B),treatments were given orally 1 h after PGE2 and response to pain was evaluated before PGE2 injection and after treatment. n=6; bP<0.01; cP<0.001 significantly different compared to vehicle.
3.3. Involvement of NO/cGMP/K+ pathway or participation of endogenous opioids
Figure 4 revealed the probable mechanisms implicated in antinociception effect of PAME. The effect of PAME or morphine or diazoxide was significantly canceled in animals having previously receivedL-NAME (inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase) (Figure 4A), methylene blue (inhibitor of guanylate Cyclase) (Figure 4B),glibenclamide (KATP?channel blocker) (Figure 4C) or naloxone(opioid antagonist) (Figure 4D).L-arginine alone significantly(P<0.05) enhanced the anti-nociceptive effect of PAME (Figure 4A).
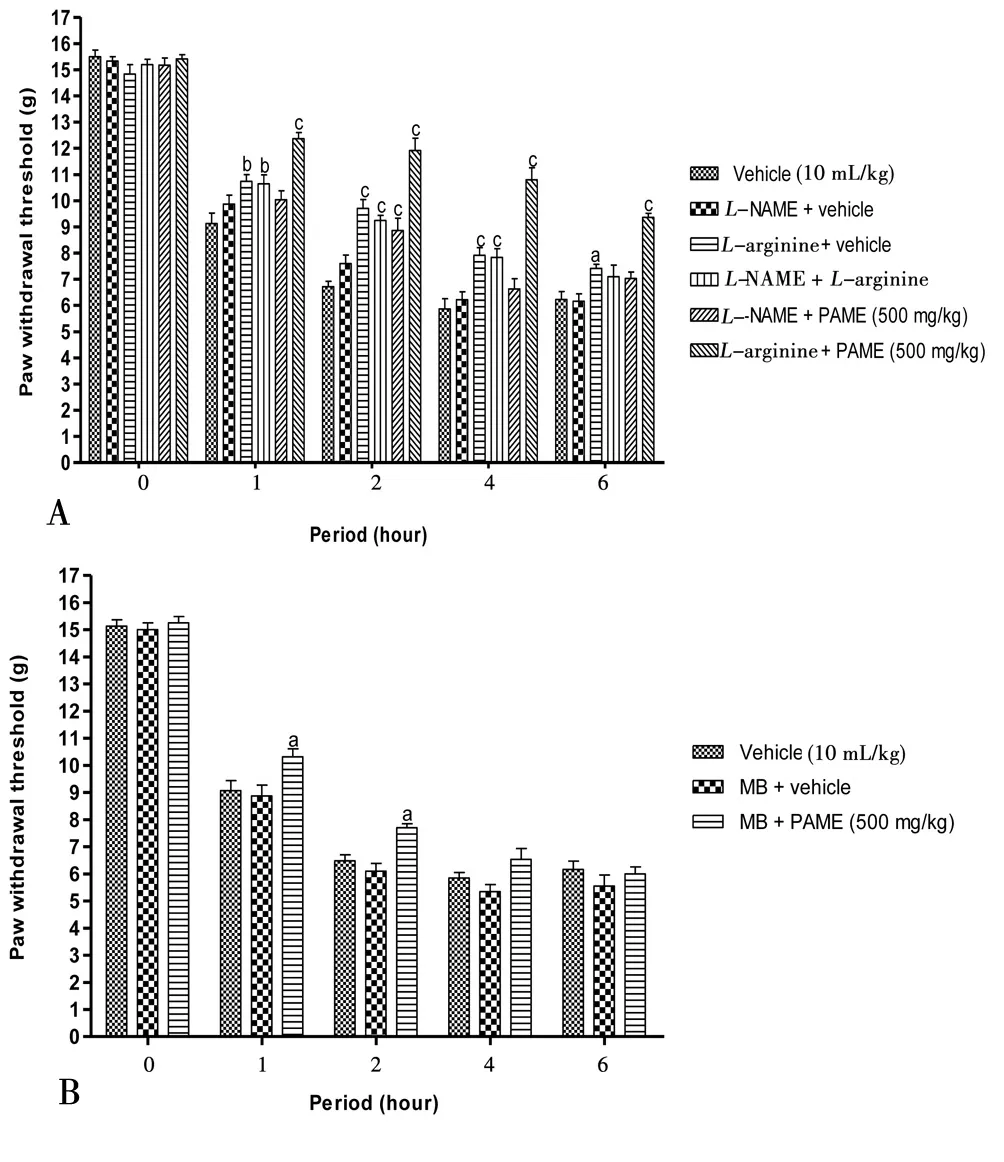
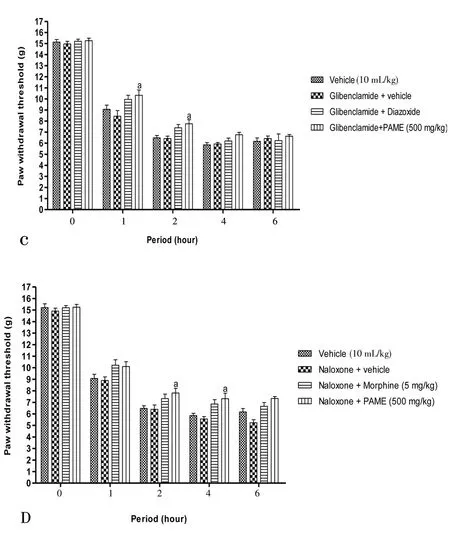
Figure 4. Effect of L-NAME (90 mg/kg, i.p.) and L-arginine (200 mg/kg,i.p.) (A), methylene blue (1 mg/kg, i.p.) (B), glibenclamide (5 mg/kg, i.p.)(C), naloxone (20 mg/kg, i.p.) (D) with oral administration of PAME on mechanical hyperalgesia in carrageenan inflamed rat paw.n=6. aP<0.05, bP<0.01, cP<0.001 significantly different compared to vehicle.
3.4. Effect of PAME in neuropathic pain induced by vincristine
In all animals having received no treatment (vincristine + vehicle),a progressive increase of sensibility, installation of peripheral neuropathy characterize by an increase of mechanical, heat and tail cold hyperalgesia were observed (Figures 5). PAME or morphine,administered before injection of vincristine, significantly protected animals by preventing installation of hyperalgesia. This protection was significant against installation of mechanical and tail cold hyperalgesia from 6th day, then against heat hyperalgesia from 7th day. The protective effect of PAME against mechanical, heat and tail cold hyperalgesia was significantly higher than that of morphine.
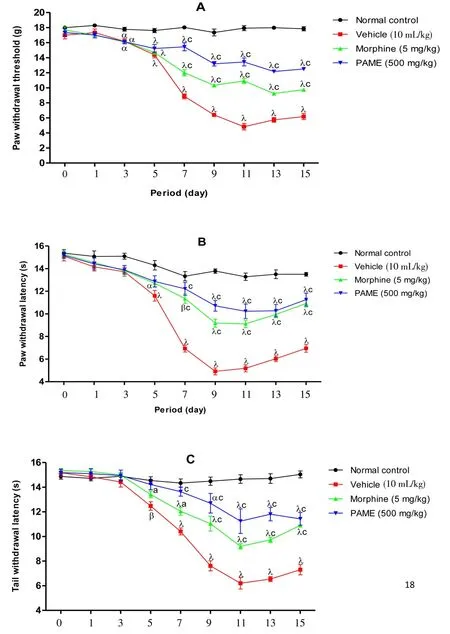
Figure 5. Effect of methanol extract of PAME on mechanical hyperalgesia(A), heat hyperalgesia (B) and tail cold hyperalgesia (C) in vincristine-induced neuropathic pain.Data were expressed as mean±SEM, n=6 rats per group. αP<0.05; β P<0.01; λP<0.001 significantly different compared to normal control;cP<0.001 significantly different compared to vincristine and vehicle group.
3.5. Effect of PAME on hematological and serum parameters
The significant increase (P<0.001) in levels of platelets, white blood cell (WBC) and the significant decrease in levels of red blood cell(RBC) (P<0.01), haemoglobin (Hb) (P<0.001) and hematocrit(P<0.05) were observed in untreated group. However, the treatment with PAME (500 mg/kg) and morphine (5 mg/kg) revealed an significant increase in Hb (P<0.05), RBC (P<0.05) and hematocrit(P<0.05). In a similar way, the PAME (500 mg/kg) significantly reduced the increase of platelets (P<0.001) and WBC (P<0.01) and finally, their results were very close to those of animals of the normal control group (Table 1).
3.6. Effect of PAME on biochemical parameters
As a result of vincristine-induced neuropathic pain, the serum levels of AST, ALT, ALP and creatinine were increased significantly(P<0.001) in control group. These enzyme levels were altered by treatment with PAME and morphine. The level of AST, ALT, ALP and creatinine were significantly (P<0.001) decreased by treatment with PAME (500 mg/kg) and morphine (5 mg/kg) (Table 2).
4. Discussion
Our previous work onP. africanumextracts showed its analgesic properties on acute pain model (acetic acid, formalin and analgesimeter test)[27] and anti-arthritis effect induced by CFA administration in rats joint paw[28]. There is little evidence in the literature ofP. africanumconcerning analgesic properties. A study by Diffoum[27] reported that aqueous and methanol extracts ofP.africanum(250 and 500 mg/kg) reduced the latent period of hind paw leakage after formalin injection and the number of abdominal contractions after acetic acid injection; it is also reported that these extracts delay the time of withdrawal of the paw in normal animals on model of pain induced by pressure using ananalgesymeter. In the present study, the effects of PAME on thermal or mechanical hyperalgesia induced by carrageenan and PGE2, the importance of NO/cGMP/K+pathway or endogenous opioids receptors in this antinociceptive activity and the protective effect of the extract against the neuropathic pain induced by vincristine was shown.
The intra-plantar (i.pl) injection of carrageenan into the right paw of rats provoked a significant hypersensivity when compared with saline group. Administration of PAME (250 and 500 mg/kg) as well as diclofenac (50 mg/kg) significantly reduced hypersensitivity in treated animals. The model of inflammatory hyperalgesia caused by subcutaneous injection of carrageenan into the paw of animals(preferably rodents) is widely used[40,41]. In this model, physiological and biochemical changes occurred over a short time course and limited to the affected limb[32]. After induction of inflammatory hyper-nociception, the receptors of primary nociceptor neurons are sensitized by the many mediators produced[42]. After injection of carrageenan, the production of TNF-α increases followed by that of IL-1 β and IL-6, then the level of PGE2increases by stimulation of COX followed by an increase in the production of IL-8 which stimulates the release of sympathetic amines[43,44]. These inflammatory mediators produced after administration of carrageenan cause inflammatory pain and hyperalgesia by direct action on the target (receptors) present on peripheral terminations of neurons[45,46].Local changes, the development of secondary hyperalgesia followed by central changes are mainly caused by sensitization of the peripheral nociceptors of primary affections after carrageenan injection[47,48]. In addition the central sensitization that occurs causes the development and maintenance of the chronic phase of hyperalgesia[49,50]. Herein,our results revealed that, PAME significantly reduced the mechanical hyperalgesia caused by carrageenan (intra-plantar injection). In Addition, the anti-nociceptive activity of PAME was preserved until the 6th hour. These results indicate that PAME interferes with pain sensitivity (acute) as well as the expression of many mediators including prostaglandins. PAME were tested on the hyperalgesia model induced by PGE2. After injection of PGE2, prostanoid peripheral nerve receptors are sensitized resulting in activation of protein kinase A followed by hyperalgesia development[51,52]. In addition the presence of PGE2leads to an increase in the production of NO which leads to an increase in capillary permeability and vasodilatation with consequent development of the sensitivity ofpainful fibers and edema[53]. The results obtained in this part show that, the anti-nociceptive activity of PAME is higher when the PGE2is administered after treatment.

Table 1Influence of PAME on hematological parameters after vincristine induced neuropathic pain in rats.
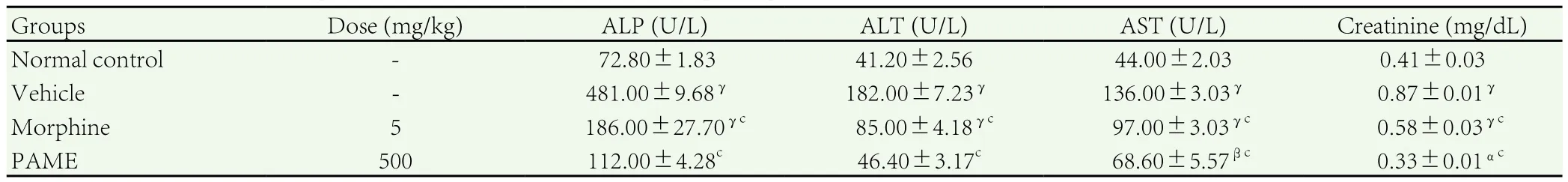
Table 2Effect of PAME on biochemical parameters in vincristine induced neuropathic pain in rats.
These results lead us to think that PAME would act on prostaglandin receptors, and the cascade of biochemical reactions involved after activation of the receptors of PGE2. In the order to verify the participation of the opioids and the NO/cGMP/K+pathways in the analgesic activity of PAME, several antagonists and agonists substances were used as previously described. The results reveal that,the antinociceptive activity of PAME is associated to an important implication of the endogenous opioid pathway. This is justified by the fact that, the presence of naloxone significantly reduces the antinociceptive effect of PAME. It is known that, opioid agonists such as morphine cause the opening of sensitive potassium channels after their binding to opioid receptors[54]. In addition, activation of NO/cGMP pathway with opening of ATP? sensitive K+channel play an important role in the mechanism of anti-nociception of morphine[55,56]. To verify this option, we studied the effect of various antagonists on PAME antinociception, namelyL-NAME,MB, glibenclamide, respectively known as inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, guanylyl cyclase inhibitor and blocker of K+ATP-channels.Interestingly, the result revealed that, pre-treatment of rats withL-NAME, MB or glibenclamide, significantly reversed the antinociceptive effects of PAME. These data confirm the hypothesis that, PAME could induced it anti-nociceptive activity by fixing on opioid receptors and activating the NO/cGMP signaling pathway,causing an opening of K+channels. This observation corroborate the results obtained by Negreteet al[57], in which they demonstrated that, in inflammatory state, local analgesic effects observed by opioid administration is mainly mediated through the stimulation of the peripheral nitric oxide-cGMP-protein kinase G (PKG)-ATP-sensitive K+(KATP) channels signaling pathway. Moreover, the analgesic activities induced by compounds such as diclofenac and dipyrone are also known to interfering with NO/cGMP/K+pathways[58-60]. It can then be suggested that, PAME inhibits acute inflammatory pain by interfering with PGE2, opioid and NO/cGMP/K+pathways. So,another probability is that, PAME might prevent chronic pain. This suggestion was assessed by testing PAME on vincristine-induced neuropathic pain.
Vincristine is an antineoplastic agent commonly used for the treatment of a number of cancer, including Hodgkin’s disease and small cell lung cancer[61]. Its major limiting side effect is peripheral neuropathy[62,63]. Pretreatment with PAME significantly reduced mechanical hyperalgesia and cold allodynia induced by vincristine administration. This important activity was observed and conserved during the 14 days of treatment. These results corroborate those obtained in acute inflammatory pain. Moreover, phytochemical study of methanolic extract of PAME revealed the presence of compounds such as oleanic acid which is a pentacyclic triterpene known for its analgesic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity[64,65]. So, the analgesic effect of PAME may be partially due to the presence of that compound.
Cancer causes the death of one fifth of the population and it is difficult today to prevent or heal it. So, the treatment available nowadays presents many side effects in particular hematological effects[66]. Secondary hematological effects has reached the anticancer chemotherapy in humans are the same order as that found in rats[67]. Lahouelet al[68] and Raguenez-Viotteet al[69]have demonstrated that, after administration of anticancer drugs(doxorubicine, belustine) in rats, single dose are capable to induce hematological disorder. This hematological toxicity was observed with all anticancer drugs[70], even those for natural origin such as vincristine[66]. In addition, Upmanyuet al[71] showed that, the administration of vincristine in rats causes an important increase in serum enzyme levels such as ALT, AST and ALP. It is clear from our investigation that, the levels of platelets, WBC, AST, ALT, ALP and creatinine were increased significantly and the levels of RBC,hematocrit and Hb were significantly decreased in non-treated group.PAME or morphine treated group significantly improved the level of all hematological (platelets, WBC, RBC, Hb and hematocrit) and biochemical (AST, ALT, ALP and creatinine) parameters compared to non-treated group. These results suggest that, oral administration of PAME not only protect against the neuropathic pain development but also prevent the development of side effects (hematologic and hepatic) induced by vincristine administration.
The evidences presented here suggest that, PAME when given orally possesses anti-nociceptive properties against inflammatory and neuropathic pain. The data obtained also confirm the involvement of opioid and NO/cGMP/K+pathways in its analgesic effect and can justify its used in Cameroonian folks medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the study participants; the staff of diagnostic laboratory of Dr. Panjwani Center for Molecular Medicine and Drug Research, University of Karachi, Pakistan, for the collection of blood samples and biochemical analysis. The authors wish to express their gratitude to TWAS (Academy of Science of Developing Countries) and International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences staff member.
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. LEKEUFACK Martin who was involved in the drafting and critical revision of this manuscript.
[1] Thomas E, Peat G, Harris L, Wilkie R, Croft PR. The prevalence of pain and pain interference in a general population of older adults: crossselectional findings from the North Staffordshire Osteoathritis Project(NorStop).Pain2004;110(1-2): 361-368.
[2] Emerich BL, Ferreira RCM, Cordeiro MN, Borges MH, Pimenta AMC,Figueiredo SG, et al. δ-Ctenitoxin-Pn1a, a peptide fromPhoneutriani griventerspider venom, shows antinociceptive effect involving opioid and cannabinoid systems, in rats.Toxins2016;8: 106. doi:10.3390/toxins 8040106.
[3] Mendell JR, Sahenk Z. Painful sensory neuropathy.N Engl J Med2003;348: 1243-1255.
[4] Hansson PT, Dickenson AH. Pharmacological treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain conditions based on shared commonalities despite multiple etiologies.Pain2005;113(3): 251-254.
[5] Besson JM. The neurobiology of pain.Lancet1999;353: 1610-1615.
[6] Millan MJ. The induction of pain: An integrative review.Prog Neurobiol1999;57: 1-164.
[7] Zimmermann M. Pathobiology of neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol2001;429: 23-37.
[8] Kulkarni SK, Mehta AK, Kunchandy J. Anti-inflammatory actions of clonidine, guanfacine and B-HT 920 against various inflammagen-induced acute paw oedema in rats.Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther1986;279: 324-334.
[9] Cunha TM, Verri Jr WA, Valerio DA, Guerrero AT, Nogueira LG, Vieira SM, et al. Role of cytokines in mediating mechanical hypernociception in a model of delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice.Eur J Pain2008;12: 1059-1068.
[10] Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide: physiology,pathophysiology, and pharmacology.Pharmacol Rev1991;43: 109-142.
[11] Duarte IDG, Lorenzetti BB, Ferreira SH. Peripheral analgesia and activation of thenitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway.Eur J Pharmacol1990;186: 289-293.
[12] Soares AC, Leite R, Tatsuo MA, Duarte ID. Activation of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels: mechanism of peripheral antinociceptive action of the nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside.Eur J Pharmacol2000;400(1):67-71.
[13] Gomber S, Dewan P, Chhonker D. Vincristine induced neurotoxicity in cancer patients.Ind J Pediatr2010;77: 97-100.
[14] Scripture CD, Figg WD, Sparreboom A. Peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel: recent insights and future perspectives.Curr Neuropharmacol2006;4: 165-172.
[15] Joseph EK, Levine JD. Comparison of oxaliplatin- and cisplatin-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat.J Pain2009;10: 534-541.
[16] Deng L, Guindon J, Vemuri VK, Thakur GA, White FA, Makriyannis A,et al. The maintenance of cisplatin- and paclitaxel-induced mechanical and coldallodynia is suppressed by cannabinoid CB(2) receptor activation and independent of CXCR4 signaling in models of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy.Mol Pain2012;8: 71.
[17] Van den Bent MJ. Prevention of chemotherapy-induced neuropathy:leukemia inhibitory factor.Clin Cancer Res2005;11: 1691-1693.
[18] Dworkin RH, O’Connor AB, Audette J, Baron R, Gourlay GK,Haanpaa ML, et al. Recommendations for the pharmacological management ofneuropathic pain: an overview and literature update.Mayo Clin Proc2010;85(3 Suppl): S3-S14. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2009.0649.
[19] Amoateng P, Adjei S, Osei-Safo D, Ameyaw EO, Ahedor B, N’guessan BB, et al. A hydro-ethanolic extract ofSynedrella nodiflora(L.) Gaertn ameliorates hyperalgesia and allodynia in vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in rats.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol2015;26(4): 383-394.
[20] Jiofack RB.Piptadeniastrum africanum(Hook). Brenan. In: Louppe D,Oteng-Amoako AA, Brink M. (eds).Prota 7(1): Timbers/Bois d’oeuvre 1. PROTA. Netherlands: Wageningen; 2008.
[22] Noumi E, Yomi A. Medicinal plants used for intestinal diseases in Mbalmayo Region, Central Province, Cameroon.Fitoterapia2001;72:246-250.
[22] Betti JL. Medicinal plants sold in Yaounde markets, Cameroon.Afr Study Monogr2002;23: 47-64.
[23] Pathak N, Gohil P, Patel NB, Kasture S, Jivani N, Bhalodia Y. Curative effect ofAlbizia lebbeckmethanolic extract against adjuvant arthritis-with special reference to bone erosion.Int J Pharm Sci & Drug Res2009;1(3):183-187.
[24] Mengome LE, Feuya TGR, Eba F, Nsi-Emvo E. Antiproliferative effect of alcoholic extracts of some gabonese medicinal plants on human colonic cancer cells.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med2009;6(2): 112-117.
[25] Assob JCN, Kamga HLF, Nsagha DS, Njunda AL, Nde PF, Asongalem EA, et al. Antimicrobial and toxicological activities of five medicinal plant species from Cameroon Traditional Medicine.BMC Complement Altern Med2011;11: 70.
[26] Ateufack G, Domgnim MCE, Mbiantcha M, Dongmo FBR, Nana D,Kamanyi A. Gastroprotective and ulcer healing effects ofPiptadeniastrum africanumon experimentally induced gastric ulcers in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med2015;15: 214.
[27] Diffoum JB.Propriétés analgésiques et anti-inflammatoires de l’extrait aqueux desécorces de Piptadeniastrum africanum (Mimosaceae)chez le rat. LAPHYPHA, UDs: Thèse de MASTER 2012; 94.
[28] Mbiantcha M, Almas J, Shabana SU, Nida D, Aisha F. Anti-arthritic property of crude extracts ofPiptadeniastrum africanum(Mimosaceae) in complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med2017;17: 111.
[29] Note OP, Tapondjou AL, Mitaine-offer AC, Miyamoto T, Pegnyemb DE, Lacaille-Dubois MA. Triterpenoid saponins fromPiptadeniastrum africanum(Hook. f.) Brenan.Phytochem Lett2013;6(4): 505-510.
[30] Kishore L, Singh R. Effects of different homeopathic potencies ofCephalendra indicain treatment of neuropathic pain in streptozotocin induced diabetes.Bull Fac Pharm (Cairo Univ)2017;55: 273-280.
[31] Hajimashhadi Z, Aboutaleb N, Nasirinezhad F. Chronic administration of [Pyr1] apelin-13 attenuates neuropathic pain after compression spinal cord injury in rats.Neuropeptides2017;61: 15-22.
[32] Deuis JR, Vetter I. The thermal probe test: A novel behavioral assay to quantify thermal paw withdrawal thresholds in mice.Temperature2016;3(2): 199-207.
[33] Mbiantcha M, Ngouonpe WA, Dawe A, Yousseu NW, Ateufack G.Antinociceptive activities of the methanolic extract of the stem bark ofBoswellia dalzieliiHutch. (Burseraceae) in rats are NO/cGMP/ATPSensitive-K+channel activation dependent.J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med2017; 12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6374907
[34] Nguelefack TB, Dutra RC, Paszcuk AF, Lemosde AE, Calixto JB. TRPV1 channel inhibition contributes to the antinociceptive effects ofCroton macrostachyusextract in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med2015;15: 293.
[35] Ding Y, Yao P, Hong T, Han Z, Zhao B, Chen W. The NO-cGMP-PKG signal transduction pathway is involved in the analgesic effect of early hyperbaric oxygen treatment of neuropathic pain.J Headache Pain2017;18: 51.
[36] Chiba T, Oka Y, Sashida H, Kanbe T, Abe K, Utsunomiya I, et al.Vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathic pain and expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in rat.J Pharmacol Sci2017;133:254-260.
[37] Bhardwaj HC, Muthuraman A, Hari KSL, Navis S. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potentials of ambroxol in ameliorating vincristine induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats.J Neuroinfect Dis2016;7:202. doi:10.4172/2314-7326.1000202.
[38] Khangura RK, Bali A, Kaur G, Singh N, Jaggi SA. Neuropathic pain attenuating effects of perampanel in an experimental model of chronic constriction injury in rats.Biomed Pharmacother2017;94: 557-563.
[39] Mehta A, Sethiya N, Mehta C, Shah G. Anti-arthritis activity of roots ofHemidesmus indicusR. Br. (Anantmul) in rats.Asian Pac J Trop Med2012;5(2): 130-135.
[40] Dai SP, Huang YH, Chang CJ, Huang YF, Hsieh WS, Tabata Y, et al.TDAG8 involved in initiating inflammatory hyperalgesia and establishing hyperalgesic priming in mice.Sci Rep2017;7: 41415. doi: 10.1038/srep41415.
[41] Milovanovi? M, Vu?kovi? S, Prostran M, Trailovi? S, Jovanovi? M.L-arginine-no system participates in the analgesic effect of flunixin meglumine in the rat.Acta Vet Beograd2016;66(1): 103-114.
[42] Barbosa ALR, Pinheiro CA, Oliveira GJ, Torres JNL, Moraes MO,Ribeiro RA, et al. Participation of the NO/cGMP/K+ATP pathway in the antinociception induced by Walker tumor bearing in rats.Braz J Med Biol2012;45: 531-536.
[43] Chan BK, Haron H. Insights into putative health implications of gelam(Melaleuca cajuputi) honey: Evidence fromin-vivoandin-vitrostudies.Med Sci2016;4(3): doi:10.3390/medsci4010003.
[44] Vilar MSA, Souza GL, Vilar DA, Leite JA, Raffin FN, Barbosa-Filho JM,et al. Assessment of phenolic compounds and anti-inflammatory activity of ethyl acetate phase ofAnacardium occidentaleL. Bark.Molecules2016;21: 1087. doi:10.3390/ molecules21081087
[45] Binshtok AM, Wang H, Zimmermann K, Amaya F, Vardeh D, Brenner GJ, et al. Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors.J Neurosci2008;28:14062-14073.
[46] Jin X, Gereau RW. Acute p38-mediated modulation of tetrodotoxinresistant sodium channels in mouse sensory neurons by tumor necrosis factor-alpha.J Neurosci2006;26: 246-255.
[47] Barr GA, Wang S, Weisshaar CL, Winkelstein BA. Developmental changes in pain and spinal immune gene expression after radicular trauma in the rat.Front Neurol2016;7: 223. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00223.
[48] Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Segelcke D, Schug SA. Postoperative pain-from mechanisms to treatment.Pain Reports2017;2: e588.
[49] Nakabayashi K, Sakamoto J, Kataoka H, Kondo Y, Hamaue Y, Honda Y, et al. Effect of continuous passive motion initiated after the onset of arthritis on inflammation and secondary hyperalgesia in rats.Physiol Res2016;65: 683-691.
[50] Peirs C, Williams SPG, Zhao X, Walsh CE, Gedeon JY, Cagle NE, et al.Dorsal horn circuits for persistent mechanical pain.Neuron2015;87(4):797-812. doi:10.1016/ j.neuron.2015.07.029.
[51] St-Jacques B, Ma W. Prostaglandin E2/EP4 signalling facilitates EP4 receptor externalization in primary sensory neuronsin vitroandin vivo.Pain2013;154: 313-323.
[52] Lin CR, Amaya F, Barrett L, Wang H, Takada J, Samad TA, et al.Prostaglandin E2receptor EP4 contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.J Pharmacol Exp Ther2006;319: 1096-1103.
[53] Melgaard L, Hersini KJ, Gazerani P, Petersen LJ. Retrodialysis: a review of experimental and clinical applications of reverse microdialysis in the skin.Skin Pharmacol Physiol2013;26: 160-174.
[54] Kaserer T, Lantero A, Schmidhammer H, Spetea M, Schuster D. μ Opioid receptor: novel antagonists and structural modeling.Sci Rep2016;6:21548; doi: 10.1038/srep21548.
[55] Zakariaa ZA, Sani MHM, Kadir AA, Kekc TL, Salleh MZ. Antinociceptive effect of semi-purified petroleum ether partition ofMuntingia calaburaleaves.Rev Bras Farmacogn2016;26: 408-419.
[56] Liu F, Ni W, Zhang J, Wang G, Li F, Ren W. Administration of curcumin protects kidney tubules against renal ischemiareperfusion injury (RIRI)by modulating nitric oxide (NO) signaling pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem2017;44: 401-411.
[57] Negrete R, Hervera A, Leanez S, Martin-Campos JM., Pol O. The antinociceptive effects of JWH-015 in chronic inflammatory pain are produced by nitric oxide cGMPPKG- KATP pathway activation mediated by opioids.PLoS ONE2011;6(10): e26688. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026688.
[58] Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpelon AC, Fattori V, Manchope MF, Mizokami SS, Casagrande R, et al. Naringenin reduces inflammatory pain in mice.Neuropharmacology2016;105: 508-519.
[59] Mohamad AS, Akhtar MN, Zakaria ZA, Perimal EK, Khalid S, Mohd PA,et al. Antinociceptive activity of a syntheticchalcone, Flavokawin B on chemical and thermal models of nociception in mice.Eur J Pharmacol2010;647: 103-109.
[60] Amarante LH, Alves DP, Duarte ID. Study of the involvement of K+channels in the peripheral antinociception of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist bremazocine.Eur J Pharmacol2004;494: 155-160.
[61] Mora E, Smith EML, Donohoe C, Hertz DL. Vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy in pediatric cancer patients.Am J Cancer Res2016;6(11): 2416-2430.
[62] Kumar V, Mishra A, Nagarajan K, Singh BK, Bajaj U. Ameliorative effect of green lipped mussel extract on vincristine-induced painful neuropathy in rats.J Pharmacol Drug Metab2014;1: 1-7.
[63] Siau C, Bennett GJ. Dysregulation of neuronal calcium homeostasis in chemotherapy evoked painful peripheral neuropathy.Anesth Analg2006;102: 1485-1490.
[64] Dinkova-Kostova AT, Liby KT, Stephenson KK, Holtzclaw WD, Gao X, Suh N, et al. Extremely potent triterpenoid inducers of the phase 2 response: Correlations of protection against oxidant and inflammatory stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA2005;102(12): 4584-4589.
[65] Su D, Gao Y, Dai W, Hu Y, Wu Y, Mei Q. Helicteric acid, oleanic acid,and betulinic acid, three triterpenes fromHelictere sangustifoliaL., inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in HT-29 colorectal cancer cells via suppressing NF-κB andSTAT3 signaling. Evid BasedComplement Alternat Med2017. doi.org/10.1155/2017 /5180707.
[66] Khalid MH, Akhtar MN, Mohamad AS, Perimal EK, Akira A, Israf DA, et al. Antinociceptive effect of the essential oil ofZingiber zerumbetin mice:Possible mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol2011;137: 345-351.
[67] Lahouel M, Boulkour S, Segueni N, Fillastre JP. The flavonoids effect against vinblastine, cyclophosphamide and paracetamol toxicity by inhibition of lipid peroxydation and increasing liver glutathione concentration.Pathol Biol2004;52: 314-322.
[68] Lahouel M, Viotte G, Sumereau, Morin JP, Fillastre JP. Haematotoxicity ofdoxorubicin and CCNU and of their association in rats.Drugs Exptl Clin Res1987;13(10): 593-599.
[69] Raguenez-Viotte G, Lahouel M, Ducastelle TH, Morin JP, Fillastre JP.CNU adriamycin association induces earlier and more server nephropathy in rats.Arch Toxicol1988;61(4): 282-291.
[70] Kawabata TT, Chapman MY, Kim DH, Stevens WD, Holsapple MP.Mechanisms ofin vitroimmunosuppression by hepatocyte-generated cyclophosphamide metabolites and 4-hydroxyl cyclophosphamide.Biochem Pharmacol1990;40(5): 927-9350.
[71] Upmanyu R, Dvivedi J, Saxena Y. Hepatotoxic effects of vincristine: an experimental study on albino rats.Indian J Physiol Pharmacol2009;53(3): 265-270.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2018年3期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2018年3期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- A comprehensive review on clinical outcome of probiotic and synbiotic therapy for inflammatory bowel diseases
- Synsepalum dulcificum extracts exhibit cytotoxic activity on human colorectal cancer cells and upregulate c-fos and c-jun early apoptotic gene expression
- Diet containing seeds of Buchholzia coriacea accelerates healing of acetic acid induced colitis in rats
- Antidiabetic potential of methanol extracts from leaves of Piper umbellatum L. and Persea americana Mill.
- Synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles from leaf of Litchi chinensis and its biological activities
- Antioxidant and antiglycation properties of two mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars from Senegal
