Truth telling for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Henan, China
Lian-Qun Zhang, Pei-Nan Chen, Hai-Ling Wang, Li Sun, Xue-Ke Zhao, Xin Song, Min-Jie Wu, Tang-Juan Zhang, Ling-Fen Ji, Wei-Li Han, Zong-Min Fan, Yuan Yuan, Hai-Jun Yang, Jian-Po Wang, Fu-You Zhou, Yi-Jun Qi, Li-Dong WangAnyang Tumor Hospital, Anyang 000, China;Henan Key Laboratory for Esophageal Cancer Research of The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 00, China;The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 00, China;The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 0008, China;Key Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Immunology, College of Medicine, Henan University, Kaifeng 700, China
Truth telling for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Henan, China
Lian-Qun Zhang1,2, Pei-Nan Chen2,3, Hai-Ling Wang2,4, Li Sun2, Xue-Ke Zhao2, Xin Song2, Min-Jie Wu2, Tang-Juan Zhang2, Ling-Fen Ji2, Wei-Li Han2, Zong-Min Fan2, Yuan Yuan1, Hai-Jun Yang1, Jian-Po Wang1, Fu-You Zhou1, Yi-Jun Qi5, Li-Dong Wang21Anyang Tumor Hospital, Anyang 455000, China;2Henan Key Laboratory for Esophageal Cancer Research of The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, China;3The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450014, China;4The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450008, China;5Key Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Immunology, College of Medicine, Henan University, Kaifeng 475004, China
Objective: This study aims to investigate the truth-telling status and the relevant factors of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients in Henan, China.
Truth telling; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; diagnosis
Introduction
Efficient communication between clinicians and patients can release mental stress and improve life quality during medical management of cancer patients. Disclosure of true diagnosis to patients is an essential precondition1,2. Truth telling to cancer patients varies in nations with different cultures and traditions3. In Western countries, approximately 80%–90% clinicians fully reveal true diagnoses to cancer patients4,5. By contrast, truth telling is infrequent in Asian countries6,7.
Situations of truth telling also vary for malignant cancersarising from different body parts. For cancers that are exposed or easily touchable, such as breast cancer and craniofacial cancer, diagnosis is inclined to be disclosed7,8. For example, as much as 63.2% craniofacial cancer patients are informed about their diagnosis7. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common cancers worldwide and the fourth most frequent cause of cancerrelated deaths in China9,10. Mortality rate of ESCC varies greatly among different regions and mortality in Henan Province is among the highest in China10,11. To date, few investigations have reported the status of truth telling of ESCC patients in Henan. Henan is a region with the highest incidence and mortality for ESCC. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the following: (1) the current situation of truth telling for ESCC patients, (2) the style of truth telling for ESCC patients, and (3) the factors influencing the different attitudes of truth telling for ESCC patients.
Materials and methods
Study subjects
From April to June 2015, a cross-sectional study using questionnaires was given to family members of 301 inpatients with newly confirmed diagnosis of ESCC recruited from three affiliated hospitals of Zhengzhou University including the First, the Second, and Tumor Hospital and the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology (Anyang Tumor Hospital). All family members of patients aged above 18 years showed normal communicative competence. The family members of ESCC patients were personally interviewed at the time of discharge by trained investigators involved in this study. Patient’s children were preferentially considered into the investigation if a spouse was not available. Siblings were seldom chosen. No negative emotions were triggered among all participants. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Anyang Tumor Hospital.
Criteria of family history of cancer (FHC), education level, vocation, tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage, and hospital administrative level
People who completed nine years’ compulsory education are likely to recognize the Chinese character “Cancer” because its handwriting is not readily recognizable by under-educated people. Thus, nine years’ compulsory education was set as our stratification criterion for education level. Manual workers include factory workers, farmers, and unemployed people. Mental workers include teachers, doctors, and civil servants. The criterion of a positive FHC is defined as more than two first-degree family members of malignant cancer victims within three generations. In addition, the patient was directly successive to his/her cancer-bearing relatives. Based on TNM stage of tumors amended by the American Cancer Society in 2002, stages of ESCC are defined as 0, I, IIa, IIb, III, IVa, and IVb. The hospitals located in provincial capitals are directly managed by the provincial Department of Health and the municipal hospital by local municipal health authority in China.
Data collection
All processes were conducted under the informed consent of family members. First, general information including gender, age, address, therapeutic methods, and TNM stage was collected by consulting the medical records. Then, questionnaires were given to family members of ESCC patients to investigate the current situation and style of truth telling for ESCC patients, FHC, education level, vocation, and the attitude of family members to truth telling. The questionnaire took approximately 20 min. This study was in accordance with the ethical standards and the Helsinki Declaration.
Statistical analysis
Two-sided Chi-square test was employed to determine the significant differences in the univariate analyses. The dependent variable was truth telling for ESCC patients. The independent variables included gender, age, FHC, education level, vocation, income, hospital grade, TNM stage, and the attitude of family members to truth telling. In addition, unconditional logistic regression was employed in multifactor analysis to assess which of the independent variables best predicted preference toward the disclosure of ESCC patients among the factors significantly associated in the univariate analyses. SPSS 19.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was utilized for our data analyses. Odds ratios (ORs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using the maximum likelihood method. A P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Characteristics of patients
In family members of 330 in-patients with newly diagnosed ESCC patients (within the previous two months), 301 (91.2%) completed questionnaires, whereas 29 (8.8%) refused to complete. Their reasons for refusal had not been inquired with regard to ethics. The distribution of demographic and clinical features is shown in Table 1. A total of 65.4% patients were males with a mean age of 63.3 years (standard deviation 8.3). TNM stage of 33 patients without surgery was unavailable.
Current situation and style of truth telling for ESCC patients
In 301 ESCC patients, 175 patients (58.1%) were not informed of their own diagnosis. Among the 126 patients who knew of their cancer diagnoses, only 5 (4.0%, 5/126) were informed of their diagnoses by doctors, 39.7% (50/126) by relatives, and 56.3% (71/126) patients knew the truth on their own either through gaining access to medical test reports, medical records, or bedside card.
Univariate analysis for factors affecting truth telling
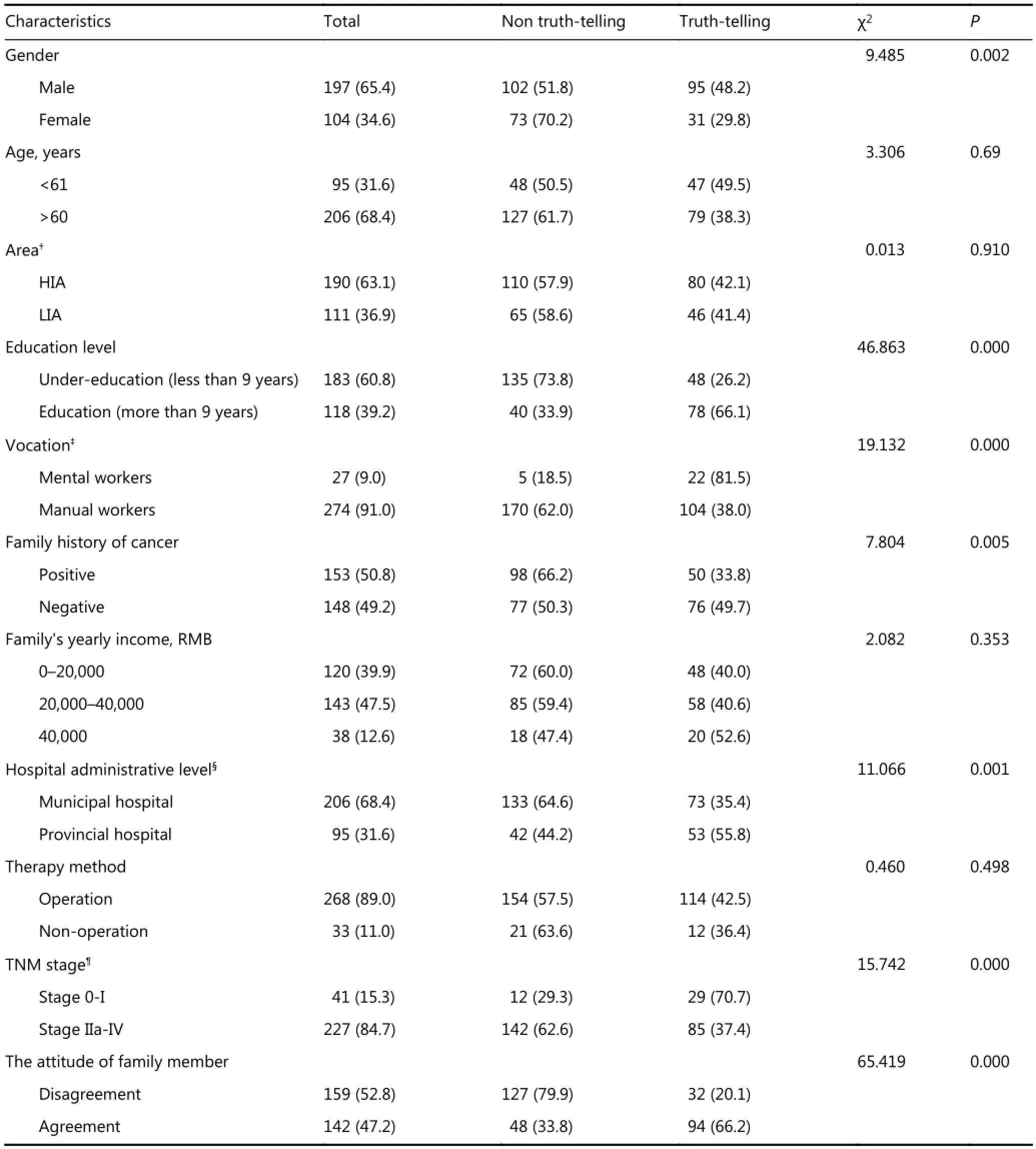
Table 1 Univariate analyses for factors affecting truth-telling (n=301)
Univariate analyses were performed to determine the factors affecting truth telling in Henan. Moreover, its results indicated that gender, FCH, education level, vocation, hospital administrative level, TNM stage, and the attitude of family members toward truth telling were statistically significant factors affecting truth-telling rate (P<0.05). However, age, region, income, and therapeutic methods showed no statistical significance (Table 1).
The attitude of agreement and disagreement for disclosure of true diagnosis was similar. The frequency of truth telling for ESCC patients (66.2%) was strikingly higher in consented family compared with its counterpart (20.1%, P<0.000, Table 1). Male ESCC patients accounted for approximately two-thirds of total patients (197/104). The frequency of truth telling for ESCC patients was remarkably higher for males than that of females (48.2% vs. 29.8%, P<0.000, Table 1). Most ESCC patients had under-education level (183/301). The percentage of truth telling was notably lower in undereducated patients than others with more than nine years of education (26.2% vs. 66.1%, P<0.05, Table 1). The overwhelming majority of the ESCC patients were manual workers (274/301). The frequency of truth telling for ESCC patients was noticeably lower in manual workers compared with that of mental workers (81.5% vs. 38.0%, P<0.000, Table 1). Approximately half of ESCC patients exhibited FHC (153/301). The percentage of truth telling for patients with a positive FCH was significantly higher than that of patients with a negative FCH (49.7% vs. 33.8%, P=0.005, Table 1). ESCC patients with TNM stages IIa-IV accounted for 84.7% of total patients (227/268). The percentage of truth telling for patients with TNM stages IIa-IV was significantly lower than that of patients with TNM stages 0-I (37.4% vs. 70.7%, P=0.000, Table 1). Most ESCC patients recruited in the present study were hospitalized in a municipal hospital (206/301). The percentage of truth telling for patients hospitalized in municipal hospitals was significantly lower than those in provincial hospitals (35.4% vs. 55.8%, P=0.001, Table 1).
Multivariate analysis of independent factors affecting truth telling
Furthermore, multivariate analysis showed that vocation (OR=3.74, 95% CI 1.19–11.76, P=0.024), TNM stage (OR= 2.62, 95% CI 1.11–6.20, P=0.028), education level (OR=2.46, 95% CI 1.25–4.86, P=0.009), hospital administrative level (OR=2.19, 95% CI 1.14–4.19, P=0.018), FHC (OR=1.93, 95% CI 1.04–3.57, P=0.037), and the attitude of family members (OR=5.97, 95% CI 3.24–11.02, P=0.000) remained an independent factor influencing diagnosis disclosure. The attitude of family members was the most important factor for truth telling (Figure 1).
Discussion
This study revealed that 41.9% ESCC patients were informed about their true diagnosis in Henan. Nevertheless, the main approaches of informing cancer patients with ESCC of their true diagnosis were not from clinical practitioners but from their family members or learnt on their own. Only 4% of ESCC patients were told by doctors. This result may be due to the following reasons. First, Chinese doctors do not incline to tell the true diagnosis to cancer patients for fear of negative consequences after truth telling12. China has a typical Eastern culture, and Chinese medical ethics is mainly influenced by the Confucian culture with an intention of protecting patients from harm by concealing sorrowful information13. Sixty-five percent of Chinese oncologists believe that they should not disclose confirmed diagnosis to advanced cancer patients12. Second, predicting the response of patients in clinical practice after hearing bad diagnosis is difficult. The doctors-in-charge choose to inform their family members instead of directly telling cancer patients to avoid the responsibility of the negative outcome probably related to true diagnosis telling. In general, this phenomenon is also legal7. The majority of patient family members ask the responsible doctors to conceal the true diagnosis because they suppose that a feeling of despair and hopelessness would ensue after hearing sorrowful information14,15. In Asia, a
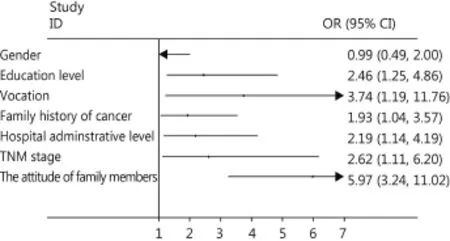
Figure 1 Multiple logistic regression for factors affecting truth telling. Multiple logistic regression revealed that the most important factors for truth telling are vocation, TNM stage, education level, hospital administrative level, FHC, and the attitude of family members.
family generally has an overriding role over an individual in terms of medical management16,17. A “family-consent for disclosure” approach is commonly adopted18. In China, family members of cancer patients play a decisive role in communication between doctors and patients, which has an important influence on truth telling to cancer patients14. Our results showed that 39.7% patients were informed by their family members. The attitude of family members was the most important factor affecting disclosure of true diagnosis to patients. The OR of truth telling for ESCC patients with family agreement increased by a factor of 5.94 compared with those with disagreement. Most family members, however, do not agree with informed diagnosis to cancer patients. They think that informed patients may develop depression. This condition is not conducive to treatment. By contrast, others consider that informed patients are likely to comply with treatment and have good treatment responses (Table 2). Obviously, the attitudes of family members were determined by the subsequent consequences after truth telling.
Eighty five percent Chinese cancer patients want to know their diagnoses15. In this era of readily available information, patients can obtain access to their diagnostic information through various ways. Therefore, tumor patients have an important influence on truth telling for themselves. In line with several previous investigations7,19,20, our results indicated that educated patients defined as completion of nine-year compulsory education tend to have high rate of knowing true diagnosis. Obtaining access to information on the diseases by multiple approaches including television, Internet, and medical organizations with advances of current technology is easy for educated patients. Thus, patients with high education level generally have more knowledge about malignant tumors and are willing to know their true diagnosis and to comply with medical treatment compared with under-educated patients21.
Patients with a positive FHC are more likely to know their true diagnoses than those without FHC. A positive FHC is widely recognized as a risk factor for cancer. Their family background can make them acute to their heritable risk from the symptoms. Therefore, patients with a positive FHC are willing to take physical and genetic examinations for tumors22-25. Similarly, women with a positive FHC of breast cancer have sense of breast self-examination23,24and people with an FHC of skin cancer pay attention to sun protection25. In summary, a positive FHC enables people to know well about prevention and therapy of malignancy.
Patients engaging in mental work are more likely to be informed about their true diagnoses than those engaging in manual occupation. In China, mental workers are usually well educated. Moreover, workmates in the same field may share common information. This finding may possibly explain why mental workers have high disclosure rate. Chinese oncology clinicians tend to inform patients of true diagnosis on the condition that patients have an early-stage cancer. This finding was also the same case for family members evidenced by high percentage of early-stage cancer patients to be informed with their diagnosis.
In addition, this study showed that the high administrative level of hospital generally representing high professional skills (the population viewpoint) in China is likely to disclose true diagnosis. The hospitals located in provincial capitals are directly managed by the provincial Department of Health and the municipal hospital by local municipal health authority in China. Therefore, patients with serious diseases or are rich are frequently referred to the provincial hospital. Our research indicates that physicians in a provincial hospital have a good understanding of truth telling and tend to reveal the truth to the patients. Although few patients were told by doctors, the attitude of doctors for truth telling may hint the next of kins to have the patients informed.
Multivariate analysis showed that gender did not contribute to truth telling although more male patients (48.2%, 95/197) were informed on true diagnosis than female patients (29.8%, 31/104). This difference may correlate witheducation level because the frequency of nine-year education completion for male patients (52.8%, 104/197) was remarkably higher than that of female patients (13.5%, 14/104).
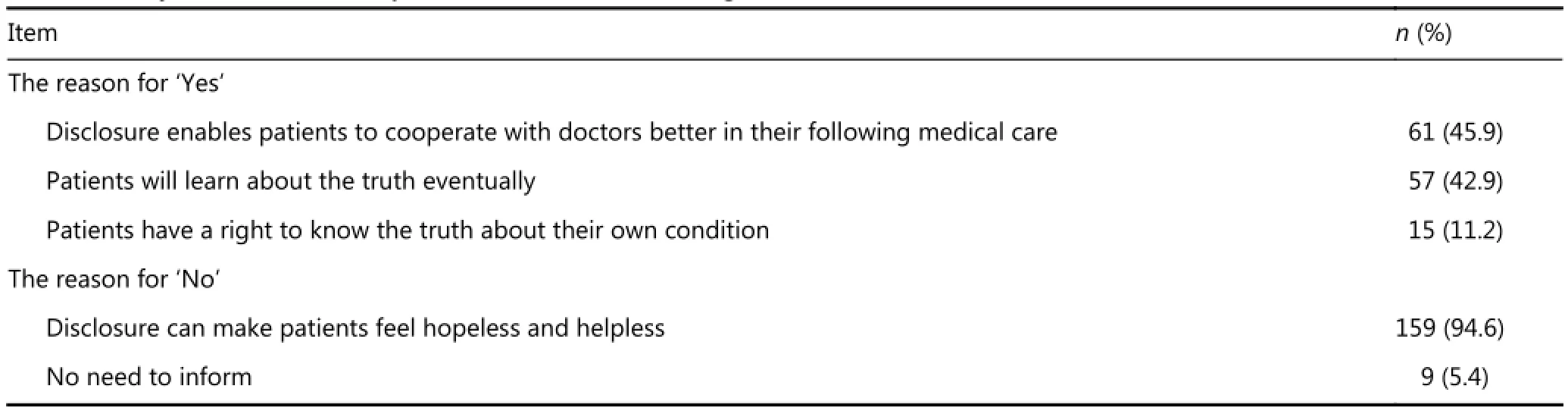
Table 2 The justifications of family members toward truth telling
Several limitations in the present study exist. First, we did not consider the attitude of ESCC patients at the meantime, which needs further investigation7. Second, we randomly asked one of the first-degree relatives of in-patients without involving all family members. Third, 77.8% patients were farmers from rural areas and may not represent ESCC patients in the city. Lastly, the sample size in this study was relatively small. Large-scale surveys should also be conducted in the future.
Conclusions
Disclosure of true diagnosis to ESCC patients is not prevalent in Henan China with only 41.9% patients informed. The attitude of family members was the most important factor affecting truth telling. The present study suggests that disclosure of ESCC diagnosis may be improved through consultation with family members of ESCC patients, particularly among patients with a negative FHC, poor education, manual occupation, and advanced stages.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81472323), Top Talent Support Project of Zhengzhou University (Grant No. ZDGD13001), and Innovation Scientists and Technicians Troop Construction Projects of Henan Province, China (Grant No. 3047).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
1.Lee MK, Baek SK, Kim SY, Heo DS, Yun YH, Park SR, et al. Awareness of incurable cancer status and health-related quality of life among advanced cancer patients: A prospective cohort study. Palliat Med 2013; 27: 144–54.
2.Justo Roll I, Simms V, Harding R. Multidimensional problems among advanced cancer patients in Cuba: Awareness of diagnosis is associated with better patient status. J Pain Symptom Manage 2009; 37: 325–30.
3.Baile WF, Lenzi R, Parker PA, Buckman R, Cohen L. Oncologists' attitudes toward and practices in giving bad news: An exploratory study. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 2189–96.
4.Novack DH, Plumer R, Smith RL, Ochitill H, Morrow GR, Bennett JM. Changes in physicians' attitudes toward telling the cancer patient. JAMA 1979; 241: 897–900.
5.Thomsen O, Wulff HR, Martin A, Singer PA. What do gastroenterologists in Europe tell cancer patients? Lancet 1993; 341: 473–6.
6.Qasem AA, Ashour TH, Al-Abdulrazzaq HK, Ismail ZA. Disclosure of cancer diagnosis and prognosis by physicians in Kuwait. Int J Clin Pract 2002; 56: 215–8.
7.Wang DC, Guo CB, Peng X, Su YJ, Chen F. Is therapeutic nondisclosure still possible? A study on the awareness of cancer diagnosis in china. Support Care Cancer 2011; 19: 1191–5.
8.Costantini M, Morasso G, Montella M, Borgia P, Cecioni R, Beccaro M, et al. Diagnosis and prognosis disclosure among cancer patients. Results from an Italian mortality follow-back survey. Ann Oncol 2006; 17: 853–9.
9.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65: 87–108.
10.Chen WQ, He YT, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Zou XN, et al. Esophageal cancer incidence and mortality in china, 2009. J Thorac Dis 2013; 5: 19–26.
11.Tran GD, Sun XD, Abnet CC, Fan JH, Dawsey SM, Dong ZW, et al. Prospective study of risk factors for esophageal and gastric cancers in the linxian general population trial cohort in china. Int J Cancer 2005; 113: 456–63.
12.Jiang Y, Li JY, Liu C, Huang MJ, Zhou L, Li M, et al. Different attitudes of oncology clinicians toward truth telling of different stages of cancer. Support Care Cancer 2006; 14: 1119–25.
13.Fan RP, Li BF. Truth telling in medicine: The Confucian view. J Med Philos 2004; 29: 179–93.
14.Wang DC, Peng X, Guo CB, Su YJ. When clinicians telling the truth is de facto discouraged, what is the family's attitude towards disclosing to a relative their cancer diagnosis? Support Care Cancer 2013; 21: 1089–95.
15.Sun W, Wang Z, Fang S, Li M. Factors influencing the attitudes of Chinese cancer patients and their families toward the disclosure of a cancer diagnosis. J Cancer Educ 2015; 30: 20–5.
16.Elwyn TS, Fetters MD, Gorenflo W, Tsuda T. Cancer disclosure in japan: Historical comparisons, current practices. Soc Sci Med 1998; 46: 1151–63.
17.Li EC, Wang Z, Zhang WY, Zhao LY. Three basic modes for patients' clinical decision-making in China. Chin J Integr Med 2014; 20: 876–80.
18.Akabayashi A, Fetters MD, Elwyn TS. Family consent, communication, and advance directives for cancer disclosure: A Japanese case and discussion. J Med Ethics 1999; 25: 296–301.
19.Olajide TO, Ugburo AO, Habeebu MO, Lawal AO, Afolayan MO, Mofikoya MO. Awareness and practice of breast screening and its impact on early detection and presentation among breast cancer patients attending a clinic in Lagos, Nigeria. Niger J Clin Pract 2014; 17: 802–7.
20.Brokalaki EI, Sotiropoulos GC, Tsaras K, Brokalaki H. Awareness of diagnosis, and information-seeking behavior of hospitalized cancer patients in Greece. Support Care Cancer 2005; 13: 938–42.
21.Kabore FA, Kambou T, Zango B, Ouédraogo A. Knowledge and awareness of prostate cancer among the general public in Burkina Faso. J Cancer Educ 2014; 29: 69–73.
22.Mai PL, Vadaparampil ST, Breen N, McNeel TS, Wideroff L, Graubard BI. Awareness of cancer susceptibility genetic testing: The 2000, 2005, and 2010 national health interview surveys. Am J Prev Med 2014; 46: 440–8.
23.Kulakci H, Ayyildiz TK, Yildirim N, Ozturk O, Topan AK, Tasdemir N. Effects of breast cancer fatalism on breast cancer awareness among nursing students in Turkey. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015; 16: 3565–72.
24.Celik S, Tasdemir N, Sancak H, Demirel M, Akman O, Kara M. Breast cancer awareness among turkish nursing students. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014; 15: 8941–6.
25.Butler DP, Lloyd-Lavery A, Archer CMG, Turner R. Awareness of and attitudes towards skin-cancer prevention: A survey of patients in the UK presenting to their general practice. Clin Exp Dermatol 2013; 38: 338–43.
Cite this article as: Zhang L,Chen P, Wang H, Sun L, Zhao X, Song X, et al. Truth telling for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Henan, China. Cancer Biol Med. 2017; 14: 83-9. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0090
Li-Dong Wang
E-mail: ldwang2007@126.com
Received November 5, 2016; accepted December 19, 2016. Available at www.cancerbiomed.org
Copyright ? 2017 by Cancer Biology & Medicine
Methods:A cross-sectional study from April to June 2015 using questionnaires was given to 301 family members of hospitalized ESCC patients based in three affiliated hospitals of Zhengzhou University (i.e., The First Hospital, The Second Hospital, and Tumor Hospital) and Anyang Tumor Hospital.
Results: Among the 41.9% (126/301) hospitalized ESCC patients who knew of their true diagnoses, only 4.0% patients were informed by their corresponding responsible doctors, 39.7% by their family members, and 56.3% by themselves. Univariate analyses showed that disclosure of confirmed ESCC diagnosis to patients was correlated with gender, family history of cancer (FHC), education level, vocation, hospital administrative level, and attitudes of family members (P < 0.05). Furthermore, multivariate analysis indicated that attitude of family members was the most important and an independent factor for diagnosis disclosure. Those patients with a negative FHC, under-education, manual occupation, advanced stages, and hospitalized in municipal hospitals exhibited a low rate of truth telling.
Conclusions:Truth telling for ESCC patients in Henan is not prevalent and may be improved through consultation with family members, particularly for patients with a negative FHC, poor education, manual occupation, and advanced stages.
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2017年1期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2017年1期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- Erratum to Bcl-2 expression is a poor predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis of andropause-age patients
- Metformin prevents hormonal and metabolic disturbances and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon carcinogenesis in non-diabetic rats
- Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion
- Estimation of lung cancer burden in Australia, the Philippines, and Singapore: an evaluation of disability adjusted life years
- A pilot study of radiologic measures of abdominal adiposity: weighty contributors to early pancreatic carcinogenesis worth evaluating?
- Association of genotypes of rs671 within ALDH2 with risk for gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in the Chinese Han population in high- and low-incidence areas
