Antibody-based neuronal and axonal delivery vectors for targeted ligand delivery
PERSPECTIVE
Antibody-based neuronal and axonal delivery vectors for targeted ligand delivery
Targeted ligand delivery (TLD) or selective delivery of cargo to peripheral axonal and neuronal compartments is a useful strategy for several unmet clinical and preclinical needs relevant to the health and diseases of peripheral nervous system (PNS). Potentially, PNS organization and architecture can be exploited to achieve TLD. As a tissue peripheral nerves are widely distributed and interact directly with almost all other tissues of the mammalian body. Peripheral neurons are highly polarized cells with long axonal processes and structural specializations along their length and termini. The neuronal projections are organized into discrete bundles of peripheral nerves that hugely vary in their size and fiber type constitution (sensory, motor, and autonomic) and wire the entire body along different planes and depths along their paths. The polarized nature of peripheral neuronal and axonal compartments provide an opportunity to access these compartments at the axonal termini of peripheral neurons, which are typically not segregated by blood-tissue (neural) barriers and relatively accessible to circulating materials. Materials entering axonal termini can be distributed throughout the respective axonal and neuronal compartment by retrograde transport systems that are integral to neurons.
Peripheral nerves are prone to injury and disease because of their unique structure, widespread distribution, varied size, high surface to volume ratios and metabolic demands, and interactions with internal and external environments. The peripheral neuropathies, disorders of peripheral nerves, are common, associated with enormous morbidity and costs, and have an estimated prevalence of 8% in persons 55 years and older and 2.4% in general population. The economic burden of peripheral neuropathy is increasing as the US and developed world's population ages, making the prevention and treatment of peripheral neuropathies an important public health issue. Peripheral neuropathies are heterogeneous in etiology, varied in severity, and have diverse yet limited repertoire of pathologic alterations. Notably, the location and extent of axonal and/ or neuronal injury is the single most important determinant of severity and recovery in all peripheral nerve disorders including diseases that primarily afflict Schwann cells and/or myelin. An important issue in this context is that with current clinical and laboratory measures it is very difficult to assess the location and extent of axonal injury or repair in nerve trunks once the targets are completely denervated, as these measures are entirely dependent on target innervation. Moreover, a vast majority of neuropathic disorders do not have specific treatments, thus, prevention or protection from injurious factors is preferable, whenever feasible. Ligand based direct and/or indirect visualization of nerve bundles can address some of these issues related to assessment of injured nerves and prevention of injuries commonly associated with all types of surgical procedures. Further, despite our extensive understanding of neurobiology of neurotrophic factors, the translation of this knowledge in preventing neuronal degeneration and enhancing neural repair has been particularly slow. A major reason for this is lack of reliable methodologies allowing TLD (selective delivery) of these molecules to specific neuronal and axonal compartments in PNS.
Broadly, selective neuronal and axonal delivery vectors (NADVs) could be used for specific TLD to visualize peripheral axonal and neuronal compartments as a preventive and/or diagnostic strategy and modulate their function as a therapeutic approach to address some of the unmet needs discussed in the preceding section. In our initial proof of concept study (Massaad et al., 2015) we have used an anti-ganglioside monoclonal antibody (mAb) as NADV for cargo delivery to peripheral neuronal and axonal compartments. We hypothesized that anti-ganglioside antibodies can bind cell surface gangliosides and be internalized by axonal membranes analogous to several bacterial toxins (cholera, tetanus, and botulinum). Gangliosides, sialic acid-containing glycans, are the predominant sialoglyco conjugates in the mammalian PNS. GM1, GD1a, GD1b, and GT1b are the most abundant gangliosides in the neuronal and axonal compartments of mammalian nerves (Yu and Saito, 1989). These moieties localize in the outer leaflet of plasma membranes. The head-groups of gangliosides on cell surface are accessible to lectins in vicinity including bacterial toxins and antibodies. Gangliosides are known to constantly cycle to and from the plasma membrane by endosomal sorting, and specific bacterial toxins are known to use specific gangliosides and their recycling apparatus to internalize and in some cases be retrogradely transported in neurons. However, evidence suggests that endocytic cargoes used by different toxins may be different. With respect to tetanus (TT) and botulinum (BoT) neurotoxins, they both bind and are internalized at the neuromuscular junctions (NMJ). Whereas most serotypes of BoT are locally retained at NMJ where they act by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, TT is sorted via the retrograde transport to the neuronal cell body in the spinal cord where it then traffics trans-synaptically to exert its toxic action on inhibitory spinal interneurons. The axonal retrograde transport mechanisms are similar for all exogenous materials destined to reach spinal neurons, differences reside in the type of retrograde motor used. TT heavy chain has highest affinity for complex ganglioside GT1b for binding and internalization. Although tetanus toxin labeling of the nervous system from the blood stream has been demonstrated (Fishman and Carrigan, 1988), its further development as an in vivo label for live nerve imaging or delivery vector has not been pursued because of preexisting and widespread induced immunity against this toxin fragment (Ramakrishnan et al., 2015). Moreover, TT carriers are not acidified during retrograde transport, indicating that the toxin escapes lysosomal targeting and thus add to the protein load of host cells and TT can spread beyond spinal motor neurons by transsynaptic spread that potentially limits targeting of peripheral motor or spinal neurons. We postulated that antibodies may not have some of these limitations and they maybe appropriate tools because of extensive clinical experience in their use as therapeutic and diagnostic tools.
In our feasibility study (Massaad et al., 2015), we used an anti-GT1b mAb, for axonal and neuronal labeling in live mice because of its ganglioside specificity of GT1b, which is similar to that of heavy chain of TT. We have previously reported that this anti-GT1b mAb has widespread PNS axonal and neuronal binding by immunocytochemistry (Gong et al., 2002). We examined this mAb as NADV for delivery of fluorescent cargo to visualize nerves in animal studies, with implications for surgical imaging and monitoring nerve integrity and repair. This is relevant as iatrogenic transection or injury of nerves during surgical procedures can produce substantial and sometimes irreversible chronic patient morbidity that include sensory (numbness, chronic pain), motor (muscle weakness, cramping), and/or autonomic dysfunction (sphincteric and sexual dysfunction, ileus). Nerves of small caliber and terminal nerve branches without distinct epineurium and perineurium that terminate in viscera and organs are particularly difficult to visualize and more vulnerable during surgery. Large nerve trunks are usually identified by their anatomical relationships and nerve stimulation is used occasionally to monitor motor nerves especially when surgical procedures risk large nerve trunks. These measures do not prevent injury to small caliber nerves or to small terminal nerves innervating viscera and organs such as in the abdomen and pelvis including prostate. Developing technologies like optical coherence tomography or laser confocal microscopy have specific applications mostly restricted to superficial nerves. Tracing dyes or reagents used for retrograde and anterograde labeling in animals have several limitations and are not useful for diffuse labeling of nerves with systemic administration. Recently, feasibility of using fluorescently labeled peptides has been shown to live label the small peripheral nerve bundles invested by epineurium and perineurium after systemic administration (Whitney et al., 2011). These peptides do not bind neuronal or neuroglial (Schwann cells) elements and, therefore, unlikely to label terminal nerve twigs innervating targets such as viscera that lack distinct epineurium, perineurium and endoneurium. Since these peptides do not bind neuronal and axonal elements of peripheral nerves, thus, they are not suitable to monitor axonal integrity, degeneration, and regeneration, features that are of critical importance to assess health and disease of the nerves. These issues are also relevant to the surgical management of peripheral nerve injuries in continuity (reviewed in (Sheikh, 2010)).
Our study used an antibody as NADV for TLD of fluorescent cargo (mAb-dylight 550 conjugate) for tracing and surgical imaging. Dose-determining studies showed that a single nanomolar (~3—5 nmol) systemic injection of the mAb was sufficient for tracing and live imaging. Overall, there was widespread labelling of somatic sensory and motor nerve fibers and neurons. Both small and large sensory axons and neurons were labelled. In fact, live monitoring of corneal innervation was used prior to more invasive surgical imaging. Visualization of all major peripheral nerves, their small branches, and motor innervation of thin strap muscles such as intercostals was feasible. Neuronal soma and nerve termini had more pronounced labeling than large peripheral trunks. For example, surgical imaging visualized the entire extent of sciatic nerve and its terminal branches even at 24 hours after mAb administration. We postulate this finding reflects simultaneous exposure, uptake, and retrograde transport of antibody by short and long terminal branches. Tracing and histological studies showed labeling of the entire extent of sciatic nerve, its terminal branches, and parent neurons in the spinal cord and DRGs. Tracing and live macroscopic imaging were concordant (Figure 1). Pharmacokinetic studies showed that for surgical imaging useful contrast developed 24 hours after injection, peaked on days 3—6 post-injection, started to decline on post-injection day 10 and later time points. Tracing and live imaging showed widespread labeling of autonomic nerve fibers in the abdominal and pelvic viscera. There was very strong labeling of the hollow viscera like the stomach and small and large intestines, and the urinary bladder. Labeling of the small visceral bundles was more intense than larger somatic nerve trunks. The urinary bladder had the most intense signal amongst abdominal and pelvic viscera and neural network on prostate surface could also be visualized. Sciatic nerve crush studies were used to determine whether this mAb can detect axon degeneration and regeneration in nerve stumps distal to injury and found that live imaging can detect axon degeneration and regeneration in large nerve trunks. The subcellular distribution of these antibodies was determined and it appears that the majority of the intraneuronal and intraaxonal mAbco-localized with early and late endosomes.
Negative controls consisted of non-specific IgG administration to wild-type mice and anti-ganglioside mAb injections to transgenic mice lacking complex gangliosides, both of which showed no antibody uptake and fluorescent signal. Validation studies demonstrated that in vivo biodistribution of GT1b mAb radiolabeled with89Zr was concordant with tracing and live imaging studies. Confirmation of neuronal andaxonal labeling by GT1b mAb was validated in the transgenic Thy1-YFP mice, in which yellow fluorescence protein is exclusively expressed in somatic neurons and axons.
Can these antibodies be used for delivery of other cargos and applications? Delivery of MRI contrast agents to neurons and axons in organs and in intact and injured nerves can be noninvasively imaged with MRI and may address several clinical needs (Sheikh, 2010). In this context, we have chemically conjugated GT1b mAb to gadolinium DTPA. Gadolinium and its conjugates shorten T1-relaxation time and give hyperintense signal enhancement on T1-weighted scans. Phantom scans were performed on GT1b-Gadolinium conjugates to confirm shortening of T1-relaxation time (Zhang and Sheikh, unpublished observations) and we plan to use this reagent in future MRI studies to image animal nerves. Besides imaging, selective delivery of bioactive molecules (cargo) to neuronal andaxonal compartments can be used for modulation of their functions. In this context, these antibodies could be used for delivery of specific bioactive molecules including enzymes, proteins, peptides, and small molecules that can enhance neuronal regeneration in cell culture studies but have failed to show comparable benefit in animal studies likely due to inefficient delivery totarget neuronal/axonal compartments. Antibody-based NADVs could allow more efficient TLD of such molecules thereby improving target cell (neuronal) bioavailability and limiting off-target deleterious effects (nonneuronal tissues and cells). Since our studies show that anti-ganglioside mAb localizes to lysosomal compartment, enzyme replacement therapy is another potential application of this approach in neuronal lysosomal storage disorders like Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff, which can have anterior horn cell phenotype.
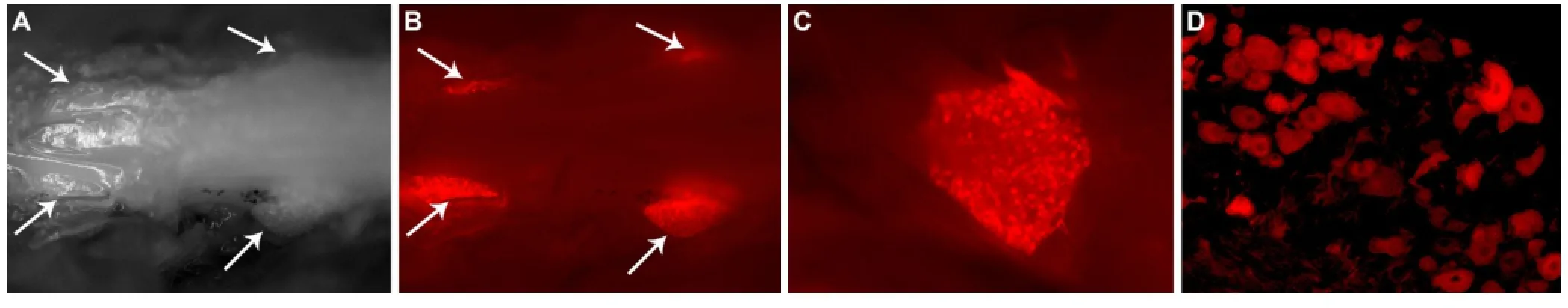
Figure 1 Live imaging and tracing of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) with GT1b mAb.
What has to happen for this preclinical study to be translated? Anti-ganglioside antibodies can induce immune nerve injury and previous experimental work, including our own, indicates that this antibody-mediated nerve injury exclusively depends on interactions of Fc portion of IgGs with innate immune effectors, i.e., complement and Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) (Halstead et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2014). It is important to emphasize that endoneurial inflammatory milieu is necessary for anti-ganglioside antibody-induced neuropathy in experimental models and these antibodies have no neuropathic effects on intact nerves (Zhang et al., 2014). Silencing the Fc portion with antibody-engineering can provide antibodies that do not interact with complement and FcγRs, thus precluding this potential risk. The pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of anti-GT1b mAb requires a latent interval of few days for maximal in vivo labeling of the nerves. To address this issue, antibody fragments can be engineered that retain their ganglioside specificity but have improved pharmacodynamics (antigen affinity and internalization) and pharmacokinetics allowing short interval between antibody administration and nerve labeling and visualization. Such engineered reagents with enhanced pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics can then be humanized. Further, we have some anti-ganglioside mAbs in our repository that have selective binding to small and large sensory and motor neuronal and axonal compartments (Gong et al., 2002) and additional reagents can be developed for autonomic neurons and axons for selective targeting of different neuronal populations.
Dr. Sheikh is supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NIH/NINDS; grants R01 NS42888, R01 NS54962, R21NS087467).
Kazim A. Sheikh*, Gang Zhang
Department of Neurology, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, Houston, TX, USA
*Correspondence to: Kazim A. Sheikh, M.D., kazim.sheikh@uth.tmc.edu.
Accepted: 2016-03-22
orcid: 0000-0003-2263-1500 (Kazim A. Sheikh)
Fishman PS, Carrigan DR (1988) Motoneuron uptake from the circulation of the binding fragment of tetanus toxin. Arch Neurol 45:558-561.
Gong Y, Tagawa Y, Lunn MP, Laroy W, Heffer-Lauc M, Li CY, Griffin JW, Schnaar RL, Sheikh KA (2002) Localization of major gangliosides in the PNS: implications for immune neuropathies. Brain 125:2491-2506.
Halstead SK, Zitman FM, Humphreys PD, Greenshields K, Verschuuren JJ, Jacobs BC, Rother RP, Plomp JJ, Willison HJ (2008) Eculizumab prevents anti-ganglioside antibody-mediated neuropathy in a murine model. Brain 131:1197-1208.
Massaad CA, Zhang G, Pillai L, Azhdarinia A, Liu W, Sheikh KA (2015) Fluorescently-tagged anti-ganglioside antibody selectively identifies peripheral nerve in living animals. Sci Rep 5:15766.
Ramakrishnan G, Pedersen K, Guenette D, Sink J, Haque R, Petri WA, Jr., Herbein J, Gilchrist CA (2015) Utility of recombinant fragment C for assessment of anti-tetanus antibodies in plasma. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 82:11-13.
Sheikh KA (2010) Non-invasive imaging of nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol 223:72-76.
Whitney MA, Crisp JL, Nguyen LT, Friedman B, Gross LA, Steinbach P, Tsien RY, Nguyen QT (2011) Fluorescent peptides highlight peripheral nerves during surgery in mice. Nat Biotechnol 29:352-356.
Yu RK, Saito M (1989) Structure and localization of gangliosides. In: Neurobiology of Glycoconjugates (Margolis RU, Margolis RK, eds), pp 1-42. Plenum Publishing Corporation.
Zhang G, Bogdanova N, Gao T, Song JJ, Cragg MS, Glennie MJ, Sheikh KA (2014) Fcgamma receptor-mediated inflammation inhibits axon regeneration. PLoS One 9:e88703.
10.4103/1673-5374.182685 http∶//www.nrronline.org/
How to cite this article: Sheikh KA, Zhang G (2016) Antibody-based neuronal and axonal delivery vectors for targeted ligand delivery. Neural Regen Res 11(5):712-714.
 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2016年5期
中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)2016年5期
- 中國(guó)神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Recovery of injured fornical crura following neurosurgical operation of a brain tumor: a case report
- Gender difference in the neuroprotective effect of rat bone marrow mesenchymal cells against hypoxiainduced apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells
- Vitamin B complex and vitamin B12levels after peripheral nerve injury
- Methylprednisolone microsphere sustained-release membrane inhibits scar formation at the site of peripheral nerve lesion
- A self-made, low-cost infrared system for evaluating the sciatic functional index in mice
- Methylprednisolone exerts neuroprotective effects by regulating autophagy and apoptosis
