F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-反應(yīng)過程中的分子形貌變化
張明波 宮利東
(1遼寧中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)藥學(xué)院,遼寧大連116600;2遼寧師范大學(xué)化學(xué)化工學(xué)院,遼寧大連116029)
F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-反應(yīng)過程中的分子形貌變化
張明波1,2宮利東2,*
(1遼寧中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)藥學(xué)院,遼寧大連116600;2遼寧師范大學(xué)化學(xué)化工學(xué)院,遼寧大連116029)
雙分子親核(SN2)反應(yīng)是重要的基本有機反應(yīng)之一,其中電子從親核基團向離去基團的轉(zhuǎn)移發(fā)揮著關(guān)鍵作用.利用從頭計算方法CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ和我們發(fā)展的分子形貌理論,對反應(yīng)F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-進行了研究,給出了反應(yīng)過程中分子形狀和電子轉(zhuǎn)移的動態(tài)變化圖像.結(jié)果表明,沿內(nèi)稟反應(yīng)坐標,從反應(yīng)開始到生成反應(yīng)前復(fù)合物,親核試劑F-的分子內(nèi)稟特征輪廓在緩慢收縮,而其上的電子密度在緩慢增大.此后,F的輪廓迅速膨脹,電子密度急劇下降,尤其是從過渡態(tài)到產(chǎn)物復(fù)合物的過程中.而在反應(yīng)過程中,離去基團Cl的輪廓一直在收縮,其上的電子密度一直在增大.對反應(yīng)過程中電子所受到作用勢的研究表明,隨著反應(yīng)的進行,電子在F與C間受到的作用勢逐漸降低,而在C與Cl間受到的作用勢逐漸升高,清楚地展現(xiàn)反應(yīng)過程中F與C間化學(xué)鍵生成和C與Cl間化學(xué)鍵斷裂的動態(tài)過程.
從頭計算;分子形貌理論;SN2反應(yīng);電子轉(zhuǎn)移;反應(yīng)機理
1 Introduction
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution(SN2)reactions are one of the fundamental organic reactions,which have been paid great attention from both theoretical and experimental points of view.1-10In particular,halogen exchange reactions of CH3X+Y-→CH3Y+X-(X and Y are halogen atoms),as the simplest prototypes for SN2 reactions,have been extensively studied.11-15Some features of this kind of reactions have been well established.Both theoretical and experimental studies indicate that the preferred gas-phase reaction pathway of such reaction involves a backside attack of the halide ion,Y-,at the carbon atom followed by the familiar“Walden inversion”of the CH3group.16The resulting potential energy profile can be characterized by two local-minima,formed by the association of halide ion with the dipolar halomethane due to the strong attraction between them and separated by a central barrier.1
Lots of computational studies have been performed on the SN2 reactions,which have provided quantitative information about the reaction energy potential profiles.14,17-21Various methods including HF,MP2,QCISD,CCSD(T),and G2(+)have been used to study the title reaction,presenting a central barrier ranging from 0 to 26 kJ·mol-1.17-21The barrier obtained with MP2(full)/6-31++G**is 25.56 kJ·mol-1.19Studies performed by Gonzales et al.20indicate that B3LYP method gave a transition structure too low in energy compared to CCSD(T)method. By using CCSD(T)method with a basis set of aug-cc-pVQZ, Botschwina et al.21present a definitive theoretical study,recommending that the central barrier should be(13.8±1.3)kJ·mol-1.
Chemists are interested in not only obtaining accurate results for energetics of chemical reactions,but also exploring other important factors during the reaction process,such as the spatial and electron density changing features.For SN2 reactions,some progresses have already been made toward this end.22-25For instance,by subdividing the charge density and energy into contributions from spatially defined fragments of the total system,Bader et al.22presented a detailed study of the redistribution of the charge density and energy changes for the two gas SN2 reactions.Knoerr and Eberhart23employed several density-based parameters to predict the reactivity of a series of SN2 reactions,and showed that the obtained results correlated well with those from energy-based parameters.Using an ab initio modern valence bond calculation,Blavins and Copper24investigated the influence of the strength of nucleophile and the size of R group on the electronic rearrangements in a series of SN2 identity reactions(X-+RX,X=F,Cl).Geerlings and coworkers25interpreted the variations of the exothermicity and the central barrier of the SN2 reactions(CH3X+Y-→CH3Y+X-) with halogenatoms X and Y,in terms of the hard and soft acids and bases principle(HSAB).In addition,they found that the increase in the electronegativity of Y will decrease the central barrier,but increase the exothermicity of the reactions.
Recently,Yang et al.26-37have developed a novel model for describing a molecule,the molecular face theory(MFT),based on the potential acting on an electron in a molecule(PAEM). The molecular face is an intrinsic characteristic of molecule, which can present the molecular shape and electron density distribution at the same time.In addition,the molecular recognition and regioselectivity involved in Markovnikov reactions of alkenes have been successfully explained in terms of MFT.36More recently,the molecular face surface area(MFSA)and molecular face volume(MFV)were defined and calculated by a program of our own.It is found that the MFSA and MFV had significant linear correlations with those of the commonly used hard-sphere model and the electron density isosurface.37
Previous studies have shown that the essence of a SN2 reaction is the transfer of an electron from the nucleophile to the leaving group,and thus the tendency of electron transfer is closely related to the reactivity of a SN2 reaction.38The goal of this work is not to obtain quantitative information about the potential energy surface,which has been well done by others,but to describe the spatial changing and electron transfer features during the reaction course of F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-in a more vivid way by applying the MFT.
2 Theoretical and computational details
2.1 Molecular face theory
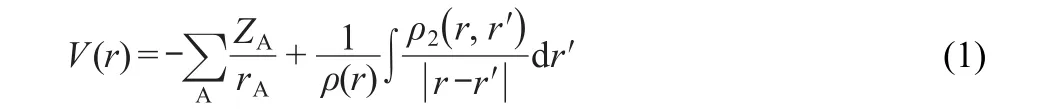
We first introduce the potential acting on an electron in a molecule,on which the definition of the molecular face(MF) is based.For a molecule in electronic ground state,the PAEM can be expressed as32where the first term on the right of Eq.(1)is the attractive potential from all nuclei,the second term is the repulsive potential created by other electrons in the system;ZAis the nuclear charge of atom A,rAis the distance between the electron considered and the nucleus A,summation involving index A is over all atomic nuclei;ρ(r)represents the one-electron density of an electron appearing at position r,and ρ(r,r?)is the two-electron density function,i.e.the probability of finding one electron at r and at the same time finding another electron at r?.

Considering an electron move within a molecule,its kinetic energy varies with its position relative to other particles in the molecule.If at a special position r,its energy is the same as the potential acting on it,which means that its average kinetic energy is equal to zero,and then r is called a classical turning point of the electron movement.Assuming that the potential,i.e. PAEM,is equal to the minus value of the first vertical ionization potential of this molecule,then we have the classical turning point equation of this electron movement,V(r)=-I,where I is the first vertical ionization potential of the molecule.The molecular intrinsic characteristic contour(MICC)can be defined as the assembly of the classical turning points as the following expression.26-31,34-37in which G denotes the MICC.The MICC has a clear physical meaning as it is an iso-PAEM contour where the PAEM(or one-electron energy)equals the minus ionization potential(-I) of the molecule.Thus,the MICC is a characteristic boundary of the electron movement;outside it is classical-forbidden while inside it is classical-permitted for an electron movement. The electron density distribution on the MICC called frontier electron density or molecular face electron density(MFED),35-37is also a remarkable feature of a molecule.The MFED is a direct indicator of electrophilic and nucleophilic stereo-reactivity and molecular interactions,including hydrogen bonding.35,36When MFED is mapped on the MICC,the MF is defined.35-37The MF,figuratively speaking,can be viewed as an intuitive“face”or an intrinsic characteristic“fingerprint”of a molecule,and it provides not only the spatial but also electron density distribution information of a molecule.
2.2 Computational details
In the present work,all geometrical structures considered were optimized at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ level,39-41which has been shown to be necessary to obtain reliable results for the reaction.42With the same model,vertical ionization potentials of these structures were calculated,which is a prerequisite for obtaining the MICC.The calculations mentioned above were carried out with Gaussian 03 program.43
The PAEM and physical quantities in Eq.(1)were calculated by the configuration interaction method with all single and double substitutions in conjunction with 6-31+G(2d,p)basis set using the ab initio MELD program44and the in-house program developed by us.By a large number of calculations,the PAEM was obtained at each point of a grid covering the molecule, with certain spacing between the grid points.According to Eq. (2),the MICC was obtained by interpolation.Visualization plots of MF were implemented by the MATLAB 7.045and a program of our own.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 MFs of CH3F and CH3Cl
At first,we calculated the molecular faces of CH3F and CH3Cl,presented in Fig.1,where the MFED is denoted by the color index on the right of the picture.So the magnitude of MFED is represented by its darkness,that is,the darkest place has the maximum MFED,and the brightest place has the minimum MFED.It can be seen that the MFs of CH3F and CH3Cl are similar to each other in both shape and electron density distribution.For both of halomethanes,the electron density on the halogen atom region is larger than that on the methyl group region.This is consistent with the fact that in a halomethane the halogen atom can draw bonding electrons towards itself,due to its higher electronegativity relative to methyl group.It has been well established both theoretically and experimentally that the backside attack of the halide ion on the halomethane is more favorable for a SN2 reaction than that from the frontside.42The observed stereoselectivity may partly be explained by difference in the electron density on the MF.Since the nucleophile is negatively charged,larger electron density is unfavorable for the access of the nucleophile due to electrostatic repulsion.So the attack of nucleophile on electron-deficient backside of the halomethanes is preferable to the attack on the electron-rich frontside.
3.2 Variables for depicting the variations of MF
To get a full view of the variations of the MFs during the SN2 reaction considered,six snapshots on the C3vpotential energy surface(PES)were considered.Besides the prereaction complex c,the transition structure d,and the product complex e,another two structures,a and b on the reactant side of the PES and one structure f on the product side were also considered.The geometries of c,d and e were obtained by geometrical optimization at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ level with a geometrical constraint of C3vsymmetry.Under the same constraint,the structures of a,b and f were optimized by fixing the bond length of r(C―F)at 0.348,0.320,and 0.143 nm,respectively.The geometries obtained are listed in Table 1,together with the ionization potentials and the Mulliken charges calculated with the same method.The reaction barrier we obtained without zero-point energy correction is 8.36 kJ·mol-1,consistent with result ofAngel and Ervin,42calculated at the same level,but lower than the value((13.8±1.3)kJ·mol-1)of the benchmark calculation at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVQZ level.21The difference is due to relatively small basis set adopted by us,according to the work of Gonzales et al.,20who have performed a systematic study on the effect of basis set on the reaction barrier of the same reaction.
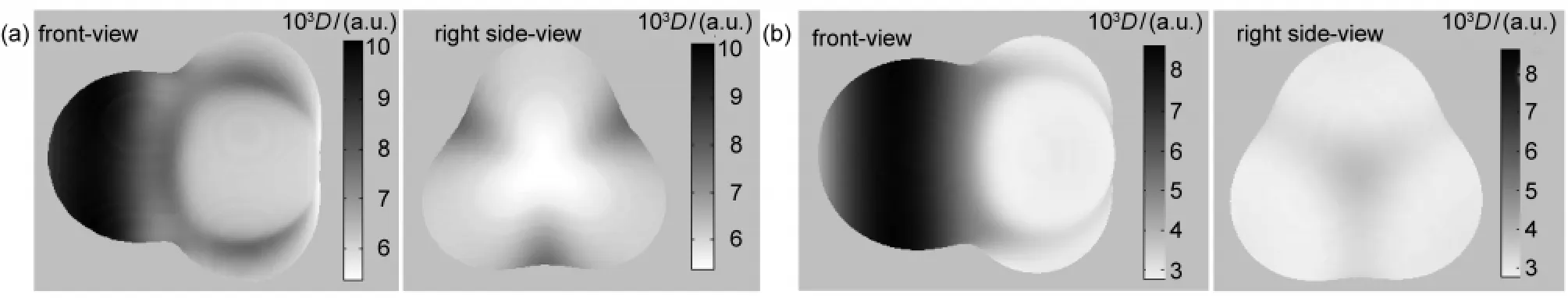
Fig.1 Molecular faces of(a)CH3F and(b)CH3ClD:electron density
To display the MFs,the following visual angle is chosen:the atoms F,C,and Cl are positioned along the C3vaxis from left to right in turn;keep one of F―C―H plane perpendicular to the paper plane with the hydrogen atom pointing outward.To quan-titatively demonstrate the changing features of molecular face, we defined several parameters.Fig.2 is one of the C3vcut-plane of the MFs of structure a.The C3vaxis has four crossing points with the MF of structure a,starting from left side of atom F,denoted by Fout,Fin,CF,and Cloutin turn.In the case of structure f (see Fig.3(f)),the corresponding four points are denoted by Fout,CCl,Clin,and Clout.In the following,the distances from these points to the corresponding nuclei and electron densities on these points are employed to delineate the spatial and electron density variations of MF during the reaction course.For example,the distance from the point of Foutto the fluorine nucleus is denoted by r(Fout),and the electron density on Foutis denoted by D(Fout).
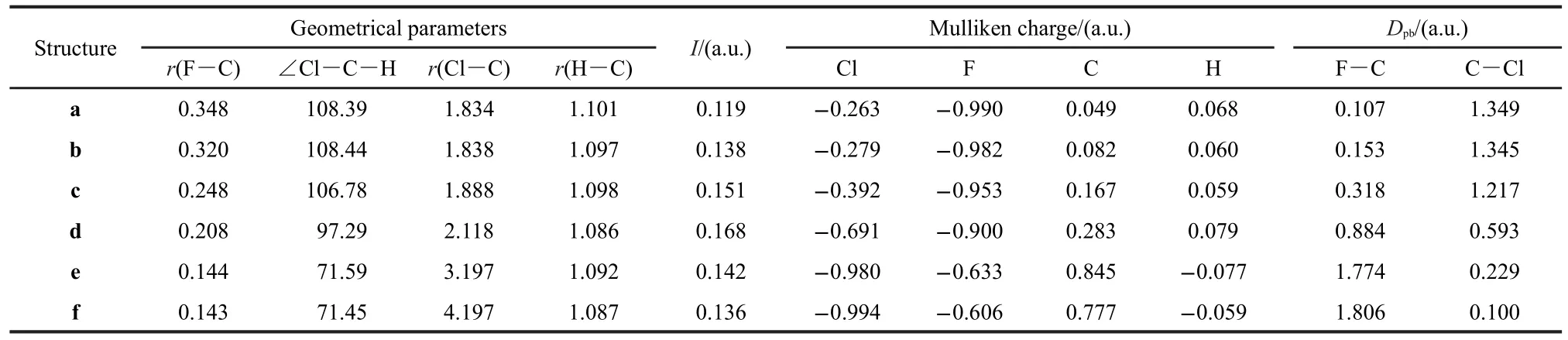
Table 1 Geometrical parameters(length in nm and angle in degree),vertical ionization potentials,Mulliken charges and Dpbcomputed with CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ level
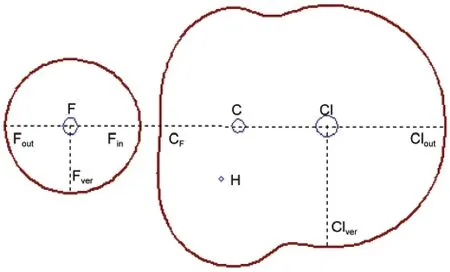
Fig.2 Representative characteristic points employed to delineate the shape and electron density evolutions of the reaction system
3.3 Variations of MFs during the reaction course
The MFs of each structure(a-f)involved in the reaction pathway are depicted in Fig.3(a-f),respectively.Representative charateristic distances and electron densities on the MFs for structures(a-f)are listed in Table 2.Note that in the following discussion,we use F and Cl to represent fluorine and chlorine element regardless of their true charged state for the sake of simplicity.
For structure a,where r(C―F)=0.348 nm,the contour of F keeps separated from that of CH3Cl,as shown in Fig.3(a).This means that there exists a classical forbidden region for electron movement between F and CH3Cl and electrons transfer from F to CH3Cl is prohibited.An impressing feature of Fig.3(a)is that the electron density on the F is evidently larger than that on CH3Cl.D(Fout)is tens of times larger than D(Clout)as listed in Table 1.This indicates that at this moment the extra electron of system mainly locates on the F,which is supported by the calculated Mulliken charge of F(-0.990 a.u.).Our calculations show that r(Fin)is 0.016 nm longer than r(Fout),which means that the contour of F expands towards CH3Cl and the interpolarization between F and CH3Cl has taken place.
As F approaches further to CH3Cl,forming the structure b, where r(C―F)=0.320 nm,the MF of F begins to contact with that of CH3Cl,as shown in Fig.3(b).It is evident that the contour of Fis strongly polarized and swells towards CH3Cl.In the structure b,the classical forbidden region between F and CH3Cl disappears,so the electrons begin to flow between them.This can be viewed as a starting point for the bond forming between F and CH3Cl.However,the electron density on F region remains larger than CH3Cl,as reflected by the color of MF.The Mulliken charge of F(-0.982 a.u.)still keeps close to-1,which indicates that no evident electron transfer occurs as yet.
Structure c is a prereaction complex formed between F andCH3Cl.As shown in Fig.3(c),the contour of F has fused with that of CH3Cl into a whole in structure c.The electron density on the F region is still larger than that on the Cl region,as indicated by the color of MF of Fig.3(c).According to our calculations,D(Fout)is 7.473×10-3a.u.,much larger than D(Clout),being 0.594×10-3a.u..The Mulliken charges of Cl and F are-0.392 and-0.953 a.u.,respectively,which indicates that the extra electron still locates on F atom by now.
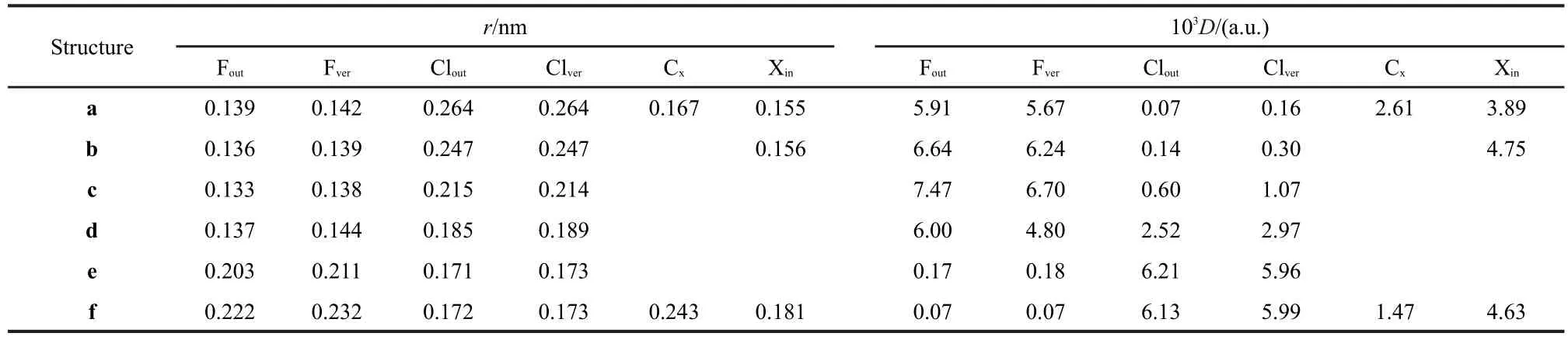
Table 2 Representative characteristic distances and electron densities on the MFs
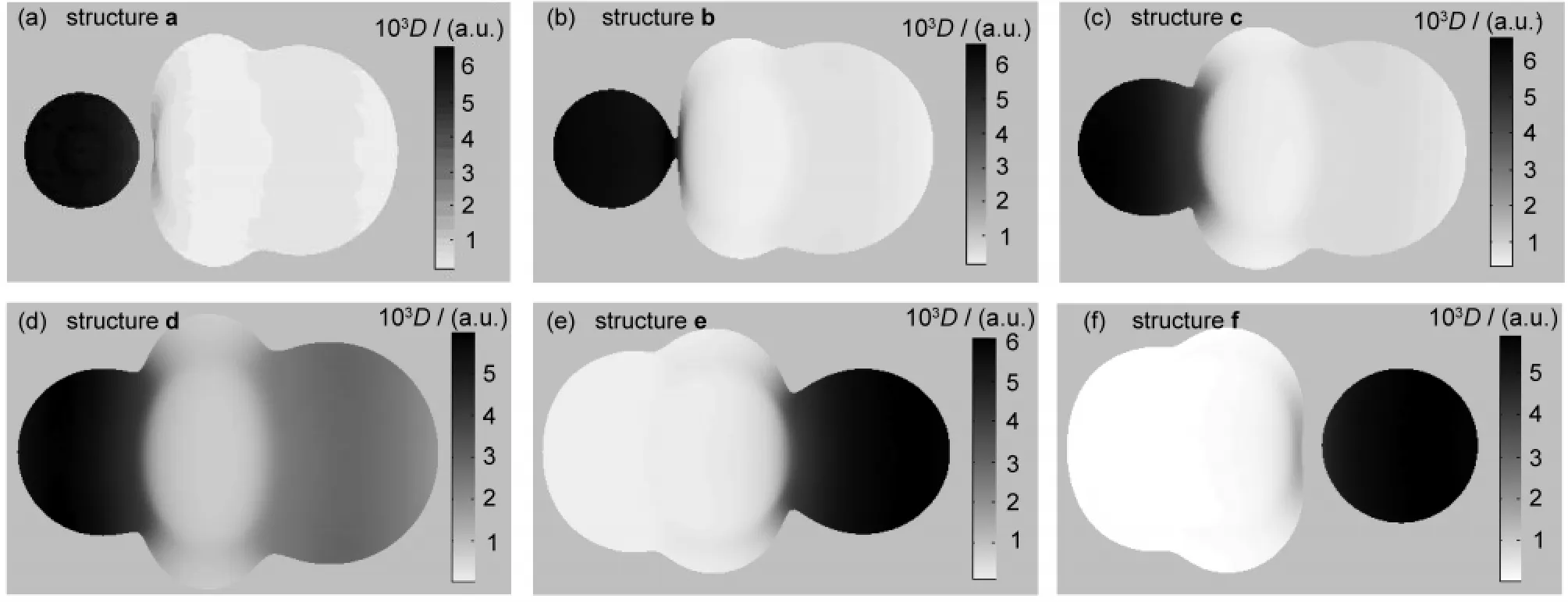
Fig.3 Variations of the MF through the reaction of F-+CH3Cl→Cl-+CH3F
Structure d is the transition state for the title reaction.As shown in Fig.3(d),the electron density on the MF of F becomes evidently smaller than the previous structures,while that of Cl becomes larger.This indicates that the extra electron has transferred from F to Cl to a certain degree.But the color of MF for F is still darker than that of Cl.In accord with this, the Mulliken charge of F(-0.900 a.u.)is more negative than that of Cl(-0.691 a.u.).Therefore,the electron transfer has only partly fulfilled at the transition state.
The most obvious changes of the MFs take places from structure d to e,and the latter is the product complex of the reaction.The MF of e is shown in Fig.3(e).The conjoint part between F and C swells evidently with a 0.67 a.u.increasement of r(Fver),while the region that between Cl and C shrinks inward with a 0.16 a.u.decreasement of r(Clver).At the same time,the electron densities on the MF of F greatly decrease dozens of times,and D(Fout)and D(Fver)decrease from 6.00× 10-3and 4.80×10-3a.u.to 0.17×10-3and 0.18×10-3a.u.,respectively;while the electron densities on the MF of Cl greatly get larger,as a result,D(Clout)and D(Clver)consumedly exceed the corresponding D(Fout)and D(Fver).The Mulliken charge of Cl (-0.980 a.u.)also becomes more negative than that of F (-0.633 a.u.),which indicates that the extra electron of the system has almost totally transferred to Cl.This indicates that there is strong bonding effect between F and C,and the bonding interaction of Cl and C gets weaker.
In structure f,the contour of Cl has separated with that of CH3F completely as shown in Fig.3(f).Similar to the structure a,a classical forbidden region for electron movement appears between CH3F and Cl.There exists evident difference in the electron densities on the MFs of CH3F and Cl.The electron density of Cl region is much larger than that of the CH3F. D(Fout)is 0.07×10-3a.u.,while D(Clout)is 6.13×10-3a.u..This implies that the extra electron is totally localized in the region of Cl,which is corroborated by the calculated Mulliken charge of Cl(-0.994 a.u.).
It is also interesting to note that the volumes of F and Cl change through the reaction process.In general,the volume of F increases while that of Cl decreases.For instance,from structure a to f,r(Fver)increase from 0.142 to 0.232 nm;on the contrary,r(Clver)decreases from 0.264 to 0.173 nm.Essentially,the molecular face is an iso-PAEM contour,and the variations in atomic size reflect the changes of their electron density.
3.4 Variation of PEAM through the reaction
Essentially,chemical reaction is a process,in which electron redistribution occurs among the reagents.So it is natural to describe a chemical reaction with the property of electrons in molecules.Bader contributed distinctive work in this field with atoms in molecule(AIM)theory,which has been widely used to study bond forming/breaking with a certain extent of success.46
Bond-forming between two reagents means that they can share their electrons with each other.That is to say,electrons are permitted to shuttle between two atoms in case of bonding. The PAEM is the potential felt by an electron in a molecule and thus reflects the easiness for an electron moving from one position to another.So the PAEM can be used as an indicator for the bond strength between two atoms.Here,we calculated the PAEM along the F―C―Cl axis for the six structures shown in Fig.3,and the variations of the PAEM were depicted in Fig.4.It can be seen that the PAEM at atomic nuclei is negatively infinite and rises sharply as the distance of electron to the nucleus increases.This means that there exists a potential well around each nucleus,which traps electrons around the vi-cinity of nuclei as much as possible.Our previous studies32showed that the PAEM surface has a saddle point along a chemical bond,and the energy gap from it to the energy level of zero is defined as Dpb.Dpbhas good linear correlations with the force constant and bond length,and hence characterizes the strength of chemical bond.The calculated Dpbfor the structures considered were listed in Table 1.
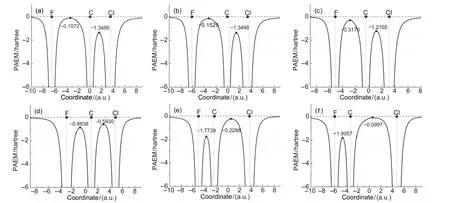
Fig.4 Variations of the PAEM along the F―C―Cl axis through the reaction course
In structure a,F and CH3Cl are far from each other,the highest point of the PAEM between F and C atom is-0.1072 a.u., which is higher than the minus of the ionization potential (-I=-0.119 a.u.).This implies that,at this moment,electrons of each reagent are localized to itself and no exchange between them is permitted.For structure b,the highest point of PAEM between atoms F and C is-0.153 a.u.,which is lower than the corresponding-I(-0.138 a.u.).So from this point,electrons are allowed to flow between two reagents and a chemical bond begins to form between F and C.As two reagents get closer gradually,viz.from structure c to f,the PAEM between F and C lowers gradually,indicating that more electrons can shuttle between two atoms and C―F bond is strengthened gradually. In contrast,the PAEM between the leaving group Cl and C increases from-1.345 to-0.010 a.u.gradually as the reaction proceeds,indicating that as the Cl―C bond gets weaker and weaker,the movement of electrons between them gets more and more difficult and their previously shared electrons are getting localized to the region of each own.In terms of above descriptions,we can see that the PAEM can loyally reflect the processes of bonding-forming and bond-breaking during the title reaction.
4 Conclusions
Using the newly developed molecular face theory,in combination with a high level ab initio CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ method,the shape changing and electron transfer during the reaction course of F-+CH3Cl→Cl-+CH3F are vividly presented.It is found that the electron density mapped on the MFs of CH3F and CH3Cl can soundly explain stereoselectivity for the attack of a nucleophile.As F approaches CH3Cl,evident interpolarization effect is presented by the MFs.In addition,the variations in electron density on the contours can well reflect the electron transfer features,and the sizes of the nucleophile and leaving groups are closely related to the reaction process.Investigations on the potential acting on an electron in a molecule (PAEM)show that,as the reaction progresses,the PAEM gradually decreases between fluorine and carbon,while it gradually increases between carbon and chlorine.This shed light on the dynamic processes of bond-forming between F and C atoms and bond-breaking between C and Cl atoms.The molecular face model can loyally reflect the essential features of shape evolution and electron transfer involved in a reaction.Both the MF and PAEM can be utilized as a useful tool to describe the dynamic progress of the title reaction.
(1) Brauman,J.I.;Olmstead,W.N.;Lieder,C.J.Am.Chem.Soc. 1974,96,4030.
(2) Glukhovtsev,M.N.;Bach,R.D.;Pross,A.;Radom,L.Chem. Phys.Lett.1996,260,558.
(3) Flanagin,L.W.;Balbuena,P.B.;Johnston,K.P.;Rossky,P.T. J.Phys.Chem.1995,99,5196.
(4) Wladkowski,B.D.;Brauman,J.I.J.Phys.Chem.1993,97, 13158.
(5) Duke,A.J.;Bader,R.F.W.Chem.Phys.Lett.1971,10,631.
(6) Tachikawa,H.;Igarashi,M.Chem.Phys.Lett.1999,303,81.
(7) Li,C.;Ross,P.;Szulejko,J.E.;McMahon,T.B.J.Am.Chem. Soc.1996,118,9360.
(8) Hase,W.L.;Sun,L.;Song,K.Science 2002,296,875.
(9) Hase,W.L.Science 1994,266,998.
(10) Katherine,V.;Benjamin,I.J.Phys.Chem.C 2011,115,2290.
(11) Glukhovtsev,M.N.;Pross,A.;Radom,L.J.Am.Chem.Soc. 1995,117,2024.
(12) Chandrasekhar,J.;Smith,S.F.;Jorgensen,W.L.J.Am.Chem. Soc.1985,107,154
(13) Zhang,J.;William,L.H.J.Phys.Chem.A 2010,114,9635.
(14) Parthiban,S.;Oliveira,G.;Martin,J.M.L.J.Phys.Chem.A 2001,105,895.
(15) DeTuri,V.F.;Hintz,P.A.;Ervin,K.M.J.Phys.Chem.A 1997, 101,5969.
(16) Chabinyc,M.L.;Craig,S.L.;Regan,C.K.;Brauman,J.I. Science 1998,279,1882.
(17) Wolfe,S.Can.J.Chem.1984,62,1465.
(18) Shi,Z.;Boyd,R.J.J.Am.Chem.Soc.1990,112,6789.
(19) Glukhovtsev,M.N.;Pross,A.;Radom,L.J.Am.Chem.Soc. 1996,118,6273.
(20) Gonzales,J.M.;Cox,R.S.,III;Brown,S.T.;Allen,W.D.; Schaefer,H.F.,III.J.Phys.Chem.A 2001,105,11327.
(21) Botschwina,P.;Horn,M.;Seeger,S.;Oswald,R.Ber. Bunsen-Ges.Phys.Chem.1997,101,387.
(22) Bader,R.F.W.;Duke,A.J.;Messer,R.R.J.Am.Chem.Soc. 1973,95,7715.
(23) Knoerr,E.K.;Eberhart,M.E.J.Phys.Chem.A 2001,105,880.
(24) Balvins,J.J.;Copper,D.L.J.Phys.Chem.A 2004,108,914.
(25) Safi,B.;Choko,K.;Geerlings,P.J.Phys.Chem.A 2001,105, 591.
(26) Yang,Z.Z.;Davidson,E.R.Int.J.Quantum Chem.1996,62, 47.
(27) Yang,Z.Z.;Zhao,D.X.Chem.Phys.Lett.1998,292,387.
(28) Gong,L.D.;Zhao,D.X.;Yang,Z.Z.J.Mol.Struc.-Theochem 2003,636,57.
(29)Yang,Z.Z.;Zhao,D.X.;Wu,Y.J.Chem.Phys.2004,121, 3452.
(30) Zhang,M.B.;Yang,Z.Z.J.Phys.Chem.A 2005,109,4816.
(31)Yang,Z.Z.;Gong,L.D.;Zhao,D.X.;Zhang,M.B.J.Comput. Chem.2005,26,35.
(32) Zhao,D.X.;Gong,L.D.;Yang,Z.Z.J.Phys.Chem.A 2005, 109,10121.
(33) Gong,L.D.;Zhao,D.X.;Yang,Z.Z.Sci.China Ser.B-Chem. 2005,48,89.
(34) Shi,H.;Zhao,D.X.;Yang,Z.Z.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2007, 23,1145.[石 華,趙東霞,楊忠志.物理化學(xué)學(xué)報,2007,23, 1145.]
(35) Zhao,D.X.;Yang,Z.Z.J.Theor.Comput.Chem.2008,7,303.
(36)Yang,Z.Z.;Ding,Y.L.;Zhao,D.X.ChemPhysChem 2008,9, 2379.
(37) Gong,L.D.;Yang,Z.Z.J.Comput.Chem.2010,31,2098.
(38) Polo,V.;Gonzalez,N.P.;Silvi,B.;Andres,J.Theor.Chem.Acc. 2008,120,341.
(39) Purvis,G.D.,III;Bartlett,R.J.J.Chem.Phys.1982,76,1910.
(40) Scuseria,G.E.;Janssen,C.L.;Schaeffer,H.F.,III.J.Chem. Phys.1988,89,7382.
(41) Woon,D.E.;Dunning,T.H.,Jr.J.Chem.Phys.1993,98,1358.
(42)Angel,L.A.;Ervin,K.M.J.Phys.Chem.A 2001,105,4042.
(43) Frisch,M.J.;Trucks,G.W.;Schlegel,H.B.;et al.Gaussian 03, RevisionA.01.Gaussian Inc.:Pittsburgh,PA,2003.
(44)Davidson,E.R.MELD Program Description;ESCOM:New York,1990.
(45) Matlab 7.0,Release 14;The Mathworks Inc.:Natick,MA,2005.
(46) Bader,R.F.W.Accounts Chem.Rev.1985,18,9.
December 27,2011;Revised:March 7,2012;Published on Web:March 8,2012.
Evolution of the Molecular Face during the Reaction Process of F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-
ZHANG Ming-Bo1,2GONG Li-Dong2,*
(1College of Pharmacy,Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Dalian 116600,Liaoning Province,P.R.China;2School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Liaoning Normal University,Dalian 116029,Liaoning Province,P.R.China)
Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution(SN2)reactions are among the fundamental organic reactions,in which electron transfer from the nucleophilic group to the leaving group plays an essential role.We use a high-level ab initio CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVDZ method in conjunction with our previouslydeveloped molecular face(MF)theory,to investigate the SN2 reaction F-+CH3Cl→CH3F+Cl-.Dynamic representations of molecular shape evolution and electron transfer features throughout the reaction are vividly presented.It is found that along the intrinsic reaction coordinate(IRC),from the beginning of the reaction to the prereaction complex,the molecular intrinsic characteristic contour(MICC)of the nucleophile (F-)contracts slowly,while the electron density on the MICC increases slowly.The MICC of F then expands quickly,and the electron density decreases sharply,especially from the transition state to the product complex.However,for the leaving group(Cl),the MICC contracts,and the electron density increases all along the reaction.Investigations of the potential acting on an electron in a molecule(PAEM)show that,as the reaction progresses,the PAEM gradually decreases between fluorine and carbon,while it gradually increases between carbon and chlorine.This study enhances our understanding of the dynamic processes of bond-forming between F and C atoms and bond-breaking between C and Cl atoms.
Ab initio calculation;Molecular face theory;SN2 reaction;Electron transfer;Reaction mechanism
10.3866/PKU.WHXB201203082
?Corresponding author.Email:gongjw@lnnu.edu.cn;Tel:+86-411-82158977.
The project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(21133005,21073080,21011120087,20703022).
國家自然科學(xué)基金(21133005,21073080,21011120087,20703022)資助項目
O641