Function of macrophage-derived exosomes in chronic liver disease:From pathogenesis to treatment
Shi-Yi Xiang,Kai-Li Deng,Dong-Xue Yang,Ping Yang,Yu-Ping Zhou
Abstract Chronic liver disease (CLD) imposes a heavy burden on millions of people worldwide.Despite substantial research on the pathogenesis of CLD disorders,no optimal treatment is currently available for some diseases,such as liver cancer.Exosomes,which are extracellular vesicles,are composed of various cellular components.Exosomes have unique functions in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating cell communication,which are associated with the occurrence of disease.Furthermore,they have application potential in diagnosis and treatment by carrying diverse curative payloads.Hepatic macrophages,which are key innate immune cells,show extraordinary heterogeneity and polarization.Hence,macrophage-derived exosomes may play a pivotal role in the initiation and progression of various liver diseases.This review focuses on the effects of macrophage-derived exosomes on liver disease etiology and their therapeutic potential,which will provide new insights into alleviating the global pressure of CLD.
Key Words: Chronic liver disease;Macrophage;Exosomes;Function;Etiology;Treatment
INTRODUCTION
Chronic liver disease (CLD) imposes a heavy burden on millions of people worldwide.A total of 1.5 billion people worldwide had suffered from CLD by 2017[1].Approximately 2 million individuals worldwide die each year from liver disease[2].Chronic hepatitis,cirrhosis and liver cancer are the three main CLDs.Among the ranked global causes of death,cirrhosis is 11th,while hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is 16th[3].We reviewed numerous studies and found that the pathogenesis of CLD is multifactorial.Most liver diseases are associated with steatosis,oxidative stress,alcoholism,inflammation[4],the environment,the microbiome,metabolism,and genetic factors[5].However,in addition to liver transplantation,current therapy consists only of eliminating the etiology and treating the complications of cirrhosis[6].Therefore,the exploration of the pathogenic mechanism and identification of optimal treatment strategies are urgently needed.
Exosomes can be released into biological fluids by all cells under physiological or pathological conditions.Exosomes are produced by budding and have apparent molecular heterogeneity because of various membrane-related protein complexes.Exosomes contain components including RNAs,DNAs,lipids,proteins,amino acids,and metabolites[7].These soluble and extracellular components can enter cells through endocytosis and plasma membrane invagination,which involve the surface proteins on exosomes[8].Substances within exosomes stimulate recipient cells,thereby altering signal transduction pathways[9].Therefore,by carrying these payloads,exosomes can mediate intercellular communication[10].When exosomes are taken up by other cells,the components alter the phenotype of recipient cells and disrupt the dynamic equilibrium of cellular transformation,demonstrating their unique functions in maintaining cellular homeostasis[11,12].Furthermore,exosomes may serve as biomarkers or therapeutic targets in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases[9,11,13].At present,exosomes have been widely studied in liver diseases.In alcoholic liver disease (ALD)[14],alcohol increases the generation of exosomes,which is due to autophagic damage and the destruction of autophagosomes or lysosomes.During the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[15],hepatocytederived exosomal microRNA (miR)-192-5p can activate proinflammatory macrophages.In liver fibrosis[16],activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) release fibrogenic vesicles.Furthermore,engineered exosomes can be used for drug delivery.For instance,Tanget al[17] showed that exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) modified to carry small interfering RNA or an antisense oligonucleotide targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)could directly inhibit STAT3 to treat fibrosis.Louet al[18] also modified exosomes from MSCs to carry miR-199a-3p,which improved the chemotherapy sensitivity of liver cancer,proving that exosomes can be used as novel therapeutic agents by acting as nanocarriers to deliver drugs or molecules.In conclusion,exosomes can drive or inhibit disease progression and have potential utility in liver disease therapy.
Macrophages are the core cellular component of the liver and are crucial in maintaining organ homeostasis and coping with liver injury[19].As key immune cells,they contribute to the development of hepatic disease by polarizing into diverse phenotypes in response to microenvironmental stimulation[20] or expressing their heterogeneity through the production of cytokines,cell surface markers,and transcriptomes[21].Due to the specific physiological roles of macrophages,the involvement of macrophage-derived exosomes in the development and progression of liver disease has been extensively studied.For instance,relaxin is an antifibrotic peptide hormone that affects vasodilation,thereby alleviating fibrosis and protecting organs through its cognate G protein-coupled receptor relaxin family peptide receptor 1.A study showed that after binding to receptors expressed by hepatic macrophages,relaxin can change the phenotype of macrophages,and macrophages can release exosomes to promote relaxin-mediated HSC dormancy and alleviate hepatic fibrosis (HF)[22].In vitro,interleukin-6 (IL-6) treatment upregulated exosome generation-related genes,stimulating the release of miR-223-rich exosomes from macrophages,which can transfer and reduce the expression of fibrogenic TAZ in liver cells to alleviate liver fibrosis[23].However,macrophage-derived exosomes can also accelerate disease progression;for example,exosomes derived from macrophages treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) promote liver fibrosis[24],and exosomes derived from M2 macrophages can mediate HCC metastasis[25].At present,determining how to use macrophage-derived exosomes to treat disease has become a research hotspot.Studies have shown that macrophagederived exosomes can be used as natural nanocarriers to deliver proteins[26] or drugs[27],induce immune activation and participate in immunotherapy[28].Overall,investigating the various physiological functions of macrophage-derived exosomes can lead to a better understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment of CLD.
This review discusses the biology and physiological functions of exosomes,focusing on exosomes derived from macrophages in the etiology of liver disease,as well as the possible use of exosomes in diagnosis,prognosis,and treatment,which will help in the search for the best therapeutic strategies for liver disease and contribute to reducing the global burden of liver disease (Figure 1).
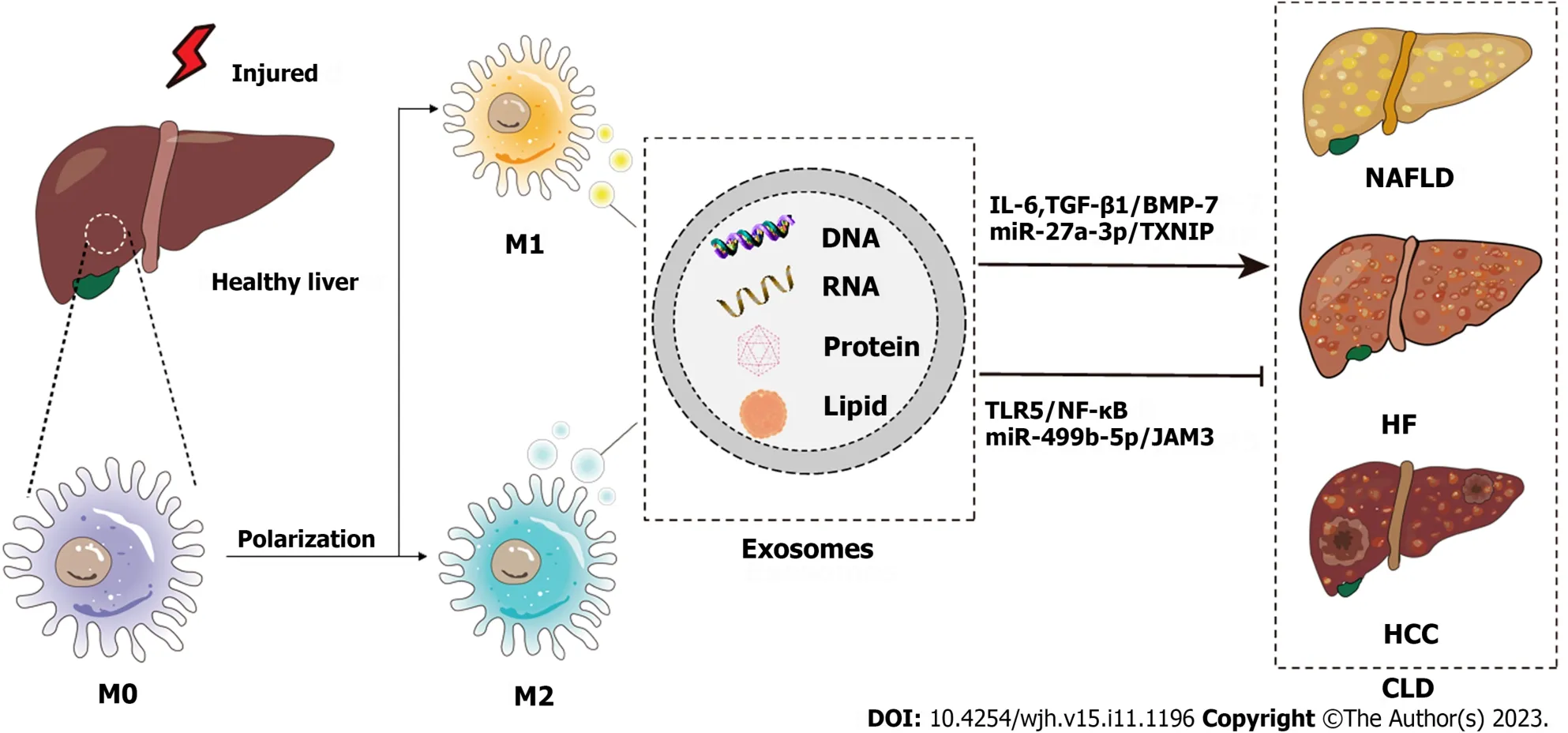
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease from the perspective of macrophage-derived exosomes. Injured livers activate macrophages to secrete exosomes that encapsulate RNAs,DNAs,lipids,proteins,etc.,which influence the development of chronic liver disease through various signaling pathways.CLD: Chronic liver disease;NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease;HF: Hepatic fibrosis;HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma;IL-6:Interleukin-6;TGF: Transforming growth factor;BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein;TXNIP: Thioredoxin-interacting protein;TLR: Toll-like receptor.
OVERVIEW OF MACROPHAGE-DERIVED EXOSOMES
Exosomes are a subtype of extracellular vesicles secreted by all cells and are widely distributed in various body fluids.These factors mediate cell-to-cell communication and play specific roles in normal physiological functions and the occurrence of diseases.Macrophages are important immune cells in the human body,and their unique heterogeneity and phenotype result in different physiological effects.In addition,macrophage-derived exosomes participate in the occurrence of diseases in various systems.
Biology of exosomes
Exosomes are small nanoscale vesicles with diameters of 30-150 nm[29].They originate in endosomes and form mature exosomes during interactions with other vesicles or organelles[8].First,the cell invaginates the cell membrane through budding to generate clathrin bodies,which enter the cytoplasm and form early endosomes[30,31].Late endosomes mature from early endosomes by interacting with the Golgi complex,which can form intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) by invagination of the restrictive membrane[10].ILVs are then further endocytosed to generate multivesicular bodies(MVBs),which are known as multivesicular endosomes[8].Ultimately,MVBs have two outcomes: Some MVBs enter the lysosomal pathway and are degraded by the lysosome,while others fuse with the cell membrane and release multiple vesicular structures into the extracellular matrix as exosomes[31].Therefore,the biogenesis of exosomes can be divided into the following processes: Budding,envelope invagination,MVB production,and MVB release.All cells,whether normal or abnormal,can release exosomes,and cancer cells release more exosomes than other cells[9].Exosomes can exhibit unique characteristics based on their cell origin and material composition.As a double lipid-encapsulated vesicle,exosomes contain a variety of substances,such as DNAs,RNAs,lipids,and proteins,and the composition or contents of these vesicles vary depending on the cell source[32].Moreover,exosomes can be isolated from various types of body fluids,such as plasma[33],serum[34],and urine[35].In summary,exosomes are tiny vesicles secreted by various cells,and their secretion mechanism is related to membrane fusion.In addition,secreted exosomes can be widely distributed throughout the body,enabling them to play a role in a variety of systems.
Function of exosomes
Because structure determines function,the function of exosomes is dependent on their complex and specific characteristics,which are determined by the cell type from which they are derived.Exosomes can be involved in the immune response,antigen presentation,cell migration,cell differentiation,tumor invasion,and other processes.The most important function of exosomes is to mediate intercellular communication[9].Exosomes transfer cargo to recipient cells by binding to cell surface receptors,undergoing plasma membrane fusion,or through the endocytic system[36],which can activate signaling pathways,alter gene expression,or regulate the overall function of the recipient cell.For example,the decrease in hsa_circ_0074854 carried by exosomes secreted by HCC cells can inhibit M2 macrophage polarization,thus delaying the migration and invasion of HCC cells[37].Cancer-associated fibroblasts can transfer exosomal miRNAs directly to tumor cells and enhance their cell-related functions,such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance[38].Therefore,exosomes can mediate material exchange between cells,are involved in cellular communication,and reflect the different physiological functions of cells;thus,they are often used as biomarkers of diseases or targeted delivery vectors of substances.The expression levels of some miRNAs in serum exosomes are significantly upregulated in patients with pancreatic cancer;thus,some miRNAs are considered useful markers for the early diagnosis and progression of pancreatic cancer[39].The delivery of engineered exosomes loaded with an iron shedding inducer [erastin(ER)] and photosensitizer (rose bengal) into tumor tissue can specifically induce ferroptosis in HCC cells,which can be used as a new treatment strategy for malignant tumors[40].In conclusion,exosomes have wide-ranging functions.Whether as carriers of substances or as signaling factors,exosomes have powerful cellular communication functions,which is an area for future basic research to determine clinical applications.
Exosomes derived from macrophages
Macrophages are immune cells that can be found in most tissues and serve numerous roles[41].For instance,macrophages are derived from monocytes and have phagocytic functions;these cells can engulf and kill intracellular parasites,bacteria,and tumor cells,as well as aging and abnormal cells,which is critical for immune defense,immune stability,and immune surveillance.In addition,macrophages are uniquely heterogeneous.In a dynamically changing microenvironment,macrophages can exhibit two phenotypes that perform different functions: Classically activated macrophages (M1) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2)[42].M1 macrophages can be activated by LPS alone or in combination with T-helper 1 (Th1) cytokines [such as interferon (IFN)-γ and granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor] and can produce proinflammatory cytokines,such as IL-1β,IL-6,IL-12,IL-23,tumor necrosis factor(TNF)-α,chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand (CXCL) 1-3,CXCL8-10,chemokine (C-C motif) ligand (CCL)2-5,and CCL11.Therefore,M1 macrophages are able to mediate functions such as antigen presentation,Th1 immune reactions,proinflammatory effects,pathogen elimination,and antitumor activity[43-46].However,M2 macrophages can be further divided into M2a,M2b,M2c,and M2d subtypes and can release complex cytokines.Specifically,when injury causes an acute inflammatory response or organ fibrosis,inflammatory factors such as IL-4 and IL-13 activate M2 macrophages to transform into M2a macrophages to inhibit inflammation,mediate damage repair and promote fibrosis.In response to LPS and immune complexes,M2 macrophages can be transformed into M2b macrophages,which can regulate immunity and induce the occurrence of infection and cancer.Glucocorticoids,IL-10,and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)can induce the polarization of M2 macrophages to M2c macrophages,which perform functions such as phagocytosis,immunosuppression,and tissue remodeling.Moreover,M2d macrophages are induced by toll-like receptor (TLR)agonists and adenosine A2A receptor ligands to cause angiogenesis and promote cancer.M2 macrophages can produce various cytokines,including Arg1,CCL17,CCL22,IL-10,IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α,IL-12,IL-10,TGF-β,CXCL13,and IL-10,which can mediate numerous functions,including inhibiting inflammation,wound healing,the Th2 immune response,anaphylaxis,fibrosis,immune regulation,supporting tumors,promoting infection,and angiogenesis[47-51].Therefore,when homeostasis is disrupted,the polarization of different macrophage phenotypes occurs,which means that macrophages are remarkably plastic cells (Figure 2).
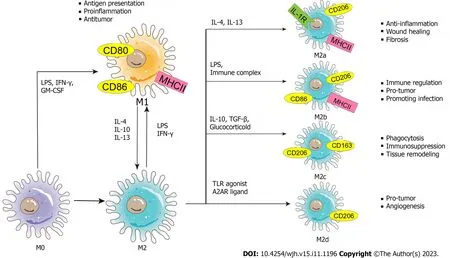
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the phenotypes and functions of macrophage polarization. The nature macrophage can be activated by a variety of influencing factors (such as lipopolysaccharide,interferon-γ,granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor,etc.) and polarized into two phenotypes -classically activated macrophages and alternatively activated macrophages.Exosomes carry stimulatory factors to activate macrophages.Macrophages themselves secrete exosomes to form a signal transmission network between macrophages and other cells.(M0: M0 macrophage;M1: M1 macrophage;M2: M2 macrophage;M2a: M2a macrophage;M2b: M2b macrophage;M2c: M2c macrophage;M2d: M2d macrophage;LPS: Lipopolysaccharide;IFN-γ: Interferon-γ;GM-CSF: Granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor;IL: Interleukin;TLR: Toll-like receptor;A2AR: A2A receptor;MHC: Major histocompatibility complex;TGF: Transforming growth factor.
Macrophages are capable of secreting exosomes,and macrophage-derived exosomes are present in multiple systems.In addition,macrophage-derived exosomes are involved in various diseases and act as therapeutic targets and drug carriers.In recent years,research has mainly focused on the involvement of macrophage-derived exosomes in systemic diseases.For instance,in multimicrobial sepsis,lactate promotes macrophages to release exosomes containing lactated/acetylated high mobility box-1 (HMGB1),which increases endothelial cell permeability and accelerates sepsis.Therefore,reducing circulating levels of exosomal HMGB1 be a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of sepsis[52].In head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC),the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) HOTTIP in exosomes secreted by M1 macrophages upregulates the TLR5/NF-κB signaling pathwayviathe competing sponges miR-19a-3p and miR-19b-3p to inhibit the progression of HNSCC[53].In the respiratory system,Weiet al[54] found that the exosomes derived from M2 macrophages in patients with lung adenocarcinoma could encapsulate miR-942,and these exosomes enhanced the invasion and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells and promoted angiogenesis by regulating FOXO1 protein to alleviate β-catenin inhibition.In addition,macrophage-derived exosomes are also valuable in the treatment of chronic pulmonary fibrosis[55] and asthma[56].In the circulatory system,macrophage-derived exosomes accelerate atherosclerosis in patients with diabetes[57],but they can also be used for myocardial tissue repair in acute myocardial infarction[58].Moreover,macrophage-derived exosomes can serve as carriers for drug delivery.In a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (AD),macrophage-derived exosomes could carry silybin,allowing it to cross the blood-brain barrier and reduce astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation and improve cognitive deficits in AD mice[59].In conclusion,macrophage-derived exosomes are widely distributed in the body and are associated with a variety of systemic diseases,and exosomes can play an important role in the treatment of diseases by acting as therapeutic targets or drug carriers.Given the importance of macrophages in the physiology of the liver,much research has been devoted to the link between macrophage-derived exosomes and the onset of CLD.Therefore,this review focuses on the impact of macrophagederived exosomes on the etiology and treatment of CLD.
MACROPHAGE-DERIVED EXOSOMES IN CLD
CLD has impacted tens of thousands of patients worldwide,its pathogenesis has been explored,and its therapeutic regimen has been optimized.In recent years,there has been intensive study of the function of macrophage-derived exosomes in some diseases.In this review,the use of macrophage-derived exosomes to treat NAFLD,HF,HCC,and other liver diseases is discussed in the context of pathogenesis and therapeutic potential.
NAFLD
NAFLD is the most common CLD and is recognized as a global public health problem.The pathogenesis of NAFLD is complex[5,60].During the pathogenesis of NAFLD,hepatic damage caused by inflammation,oxidative stress,and lipotoxicity eventually cause collagen deposition and fiber regeneration,which lead to liver fibrosis[61].During this process,obesity,type 2 diabetes,resistance to insulin,HSC activation,the environment,genetics,and other factors accelerate the progression of liver injury.However,due to the complexity of the pathophysiology and the heterogeneity of disease phenotypes,there is currently no specific drug to treat NAFLD.Healthy lifestyle interventions and weight loss are mostly used to prevent this disease in high-risk groups,and individualized combination therapy is often used to treat patients[62].Only a better understanding of the pathogenesis and progression of this disease can provide a more accurate treatment plan.Therefore,we focused on the role of exosomes in NAFLD and their potential use in treatments.
The study of macrophage-derived exosomes in the pathogenesis and treatment of NAFLD has made considerable and remarkable progress and has potential applications in NAFLD therapy.For example,in sepsis associated with NAFLD,exosomes released by Trem2-deficient macrophages carry a large amount of miR-106b-5p and cause abnormal mitochondrial structure and energy metabolism in hepatocytes by blocking mitofusin 2 (Mfn2),which accelerates the progression of NAFLD and increases the susceptibility of NAFLD patients to sepsis[63].In addition,miR-155-rich exosomes secreted by adipose tissue macrophages improved insulin sensitivity and maintained glucose homeostasis in obese mice[64].Similarly,miR-69 released from M2 macrophages had the same effect[65].In obese individuals,macrophage-derived exosomes are increased and delivered to hepatocytes,thereby regulating obesity-related insulin resistance[66] (Figure 3).In conclusion,exosomes derived from macrophages typically carry different cargos and transfer them between liver cells,and these exosomes can not only initiate but also delay the progression of NAFLD.
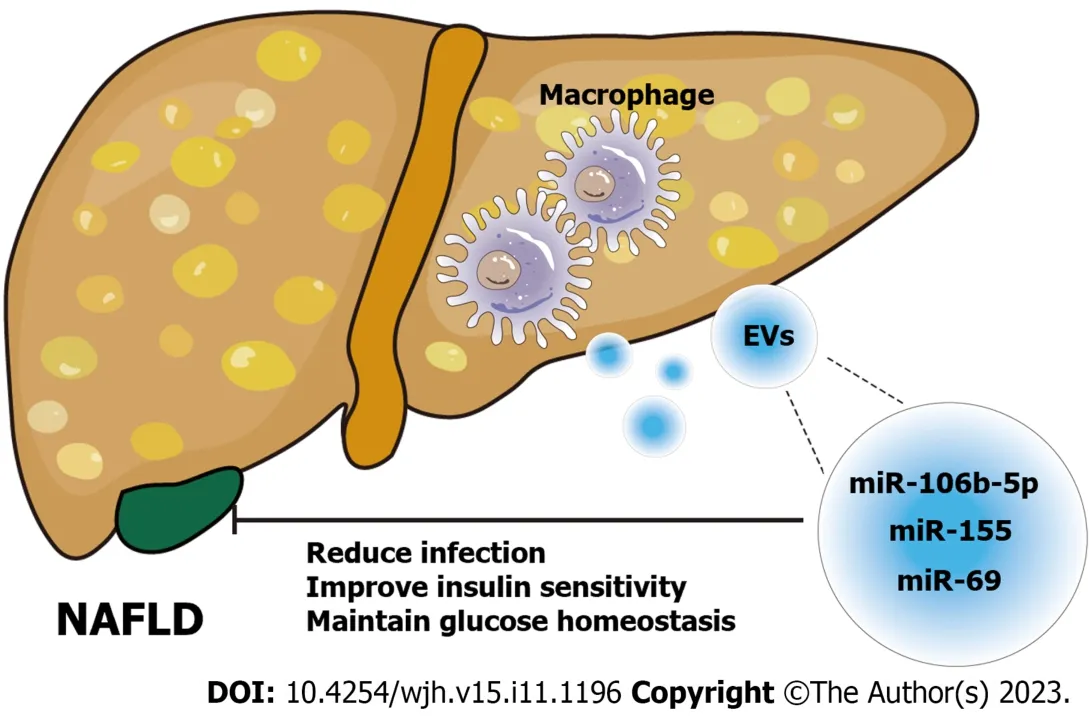
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of the role of macrophage-derived exosomes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Exosomes derived from macrophages carry different microRNAs (miR-106b-5p[63],miR-155[64],miR-69[65]) to act on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease cells and alleviate the disease progression by regulating liver homeostasis.NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease;EVs: Extracellular vesicles;miRNA: MicroRNA.
HF
HF is a dynamic and highly integrated molecular,cellular,and tissue process involving most types of CLD that undergo repeated substantial liver damage and continuous activation of inflammatory responses[67].During these processes,the activation of hepatic myofibroblasts results in the secretion of extracellular matrix proteins,including collagen,which can lead to fibrous scars and,eventually,the development of HF[68].If not treated in time,HF will progress to cirrhosis,HCC,and eventually liver failure,but unfortunately,the only treatment that can achieve a complete cure is liver transplantation[69].Previously,hepatic macrophages,which are specific immune cells,were shown to be important in the progression of HF.Macrophages mediate various functions in fibrotic liver homeostasis,disease progression,and injury recovery and are considered potential targets to protect against fibrosis[21].Notably,intercellular crosstalk between hepatic macrophages and HSCs is vital for stimulating HSC activation[24].Therefore,exosomes derived from macrophages are important for intercellular crosstalk during the pathogenesis of HF.
Recent studies have shown that exosomes derived from different sources are involved in the pathogenesis,diagnosis,and potential treatment of HF.This review will focus on research on macrophage-derived exosomes in HF.On the one hand,exosomes derived from macrophages accelerate HF.For instance,when THP-1 macrophages were treated with LPS,the exosomes secreted by these cells were changed,and the alteration in miRNA correlated with HF progression,increasing fibrotic gene expression and promoting HSC replication and activation[24].Similarly,another study showed that exosomes secreted by LPS-treated macrophages could overexpress miR-500,which promoted the proliferation and activation of HSCs to accelerate the progression of fibrosis by inhibiting MFN2[70].Denget al[71] found that exosomes derived from LPS-treated macrophages could increase the expression levels of collagen-1 and alpha-smooth muscle actin in JS1 cells.According to recent research,LPS stimulation enhances the expression of miR-155-5p in macrophage-derived exosomes,which facilitates the activation of HSCs,resulting in oxidative stress and collagen production[72].Autophagy contributes to the progression of liver damage in the early stages of liver fibrosis,and CCL4 can exacerbate autophagy,which causes M1 macrophages to polarize and secrete exosomes rich in miR-423a-5p to encourage HSC activation and control HF[73].The miRNAs carried by macrophage-derived exosomes in these examples could accelerate HF,but they were also shown to be expressed at high levels in serum,which suggested that these miRNAs can be used as biomarkers for the diagnosis of fibrosis.On the other hand,exosomes derived from macrophages can be used to delay HF.Hepatic macrophages are important mediators of relaxin-mediated amelioration of HF.When the relaxin receptor on macrophages binds to relaxin,their phenotype can be changed from the profibrogenic phenotype to the pro-resolution phenotype,and the pro-resolution phenotype can secrete exosomal miR-30a-5p to inhibit the growth of HSCs.Therefore,nanoparticle-mediated delivery of miR-30a-5p can alleviate liver fibrosis[22].In another recent study,phillygenin,an active ingredient in the Chinese medicine Forsythiae Fructus,was shown to inhibit StarD13-targeted M1 macrophage exosomal miR-125b-5p to reduce HSC activation,thereby alleviating the progression of liver fibrosis[74].Macrophagederived exosomes can also delay or treat the occurrence of NAFLD-HF.For instance,miR-411-5p is present in exosomes secreted by M2 macrophages and can suppress HSC activation in NAFLD[75].In contrast,miR-223-enriched exosomes suppressed the expression of profibrotic TAZ to inhibit the development of NAFLD[23].Kupffer cells (KCs) are a special type of macrophage in the liver that can also produce exosomes.In nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH),KCs deliver endogenous miR-690 to HSCsviaexosomes,which can help treat HF in NASH by suppressing the expression of profibrotic genes[65].These results demonstrate that macrophage-derived exosomes can alleviate the progression of HF and interact with HSCs (Figure 4).Therefore,research on macrophage-derived exosomes in HF mainly focuses on the crosstalk between macrophages and HSCs,and the mechanisms are diverse and should be analyzed from multiple perspectives.Since the search for a better treatment strategy for HF is ongoing,future studies should focus on how to use macrophage-derived exosomes to diagnose or treat HF.
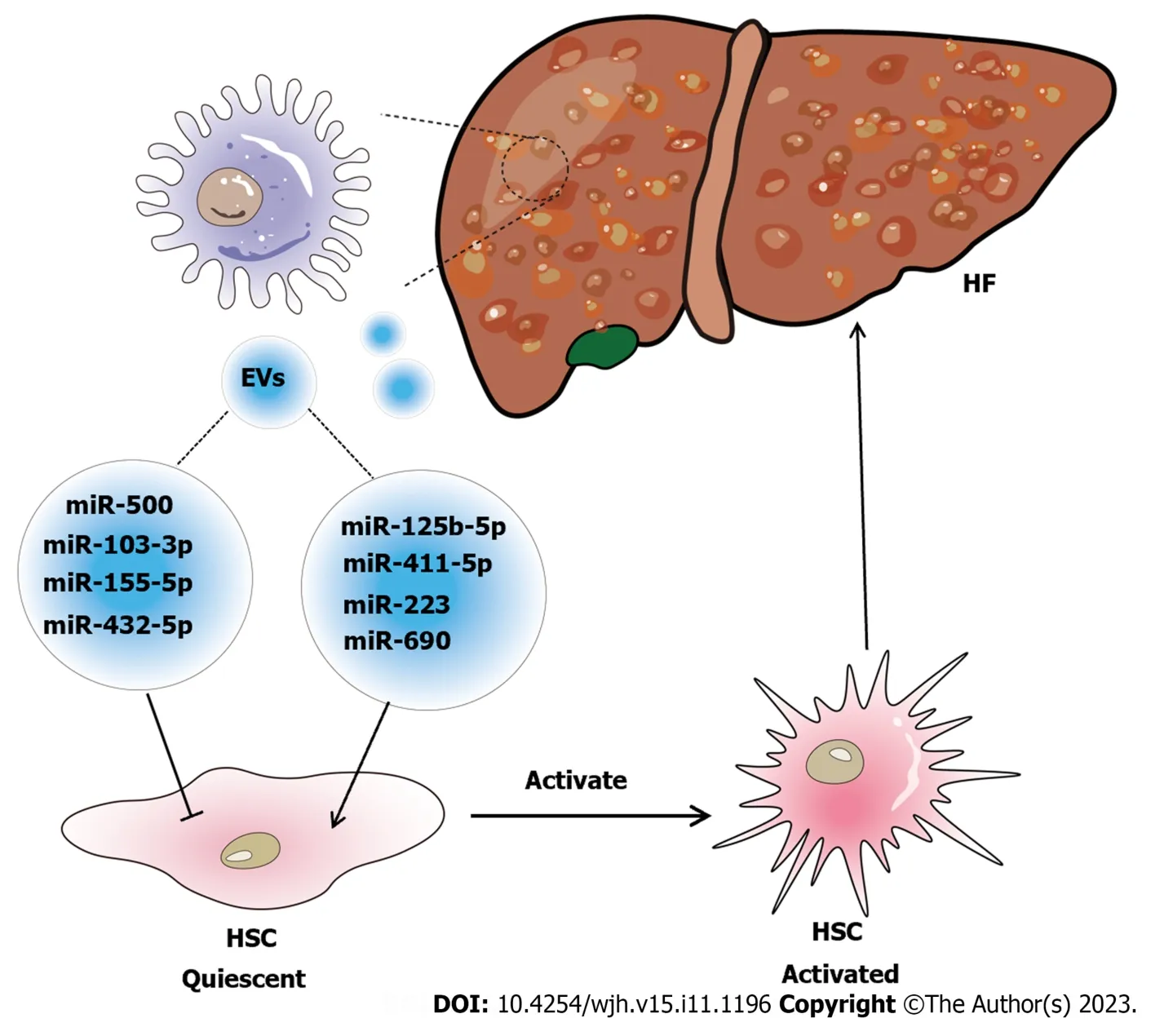
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the relationship between macrophage-derived exosomes and hepatic fibrosis. Exosome-mediated communication between macrophages and hepatic stellate cell (HSC) influences the disease progression of hepatic fibrosis (HF).Special substances carried in exosomes,such as microRNAs (miR-103-3p[24];miR-500[70];miR-155-5p[72];miR-432-5p[73];miR-125b-5p[74];miR-411-5p[75];miR-690[65];miR-223[23],are signaling factors that induce the activation of HSC to form cirrhosis or inhibit the activation of HSC to alleviate HF.EVs: Extracellular vesicles;HSC: Hepatic stellate cell;HF: Hepatic fibrosis.
HCC
Worldwide,HCC is one of the most common causes of cancer death,and HCC is a major type of liver cancer,accounting for more than 90% of cases[76].HCC is caused by many pathogenic factors,and its prognosis is poor.Most patients are diagnosed with advanced HC,for which chemotherapy and immunotherapy are by far the best treatment options[77].Therefore,the burden of HCC in the world is still severe,and it is important to continue to find new methods for early diagnosis and treatment to improve HCC prognosis.Because exosomes mediate cell communication and carry substances that can be exchanged between cells,macrophages can take up exosomes released by tumor cells in the tumor microenvironment,which affects tumor growth or metastasis by altering macrophage phenotypes.For example,Liet al[78] found that exosomes produced by HCC contain abundant levels of lncRNA TUC339,which alters macrophage phenotype,ultimately accelerating the rapid growth of tumors by promoting tumor immune evasion.In addition,another study showed that ER-stressed HCC cells released exosomal miR-23a-3p,which upregulated programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in macrophages and inhibited T-cell functions,thereby ameliorating tumor progression[79].Similarly,ERstressed HepG2 cell-derived exosomes promoted the expression of cytokines through the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway,and these exosomes ultimately led to the immunosuppression of macrophages and promoted tumor growth[80].These results indicate the close connection between exosomes secreted by hepatic carcinoma cells and macrophages,and the impact on macrophages has a robust effect on the growth of HCC.Therefore,we discuss the role of macrophagederived exosomes in HCC,including the mechanism and application value in diagnosing or treating HCC (Figure 5 and Table 1).
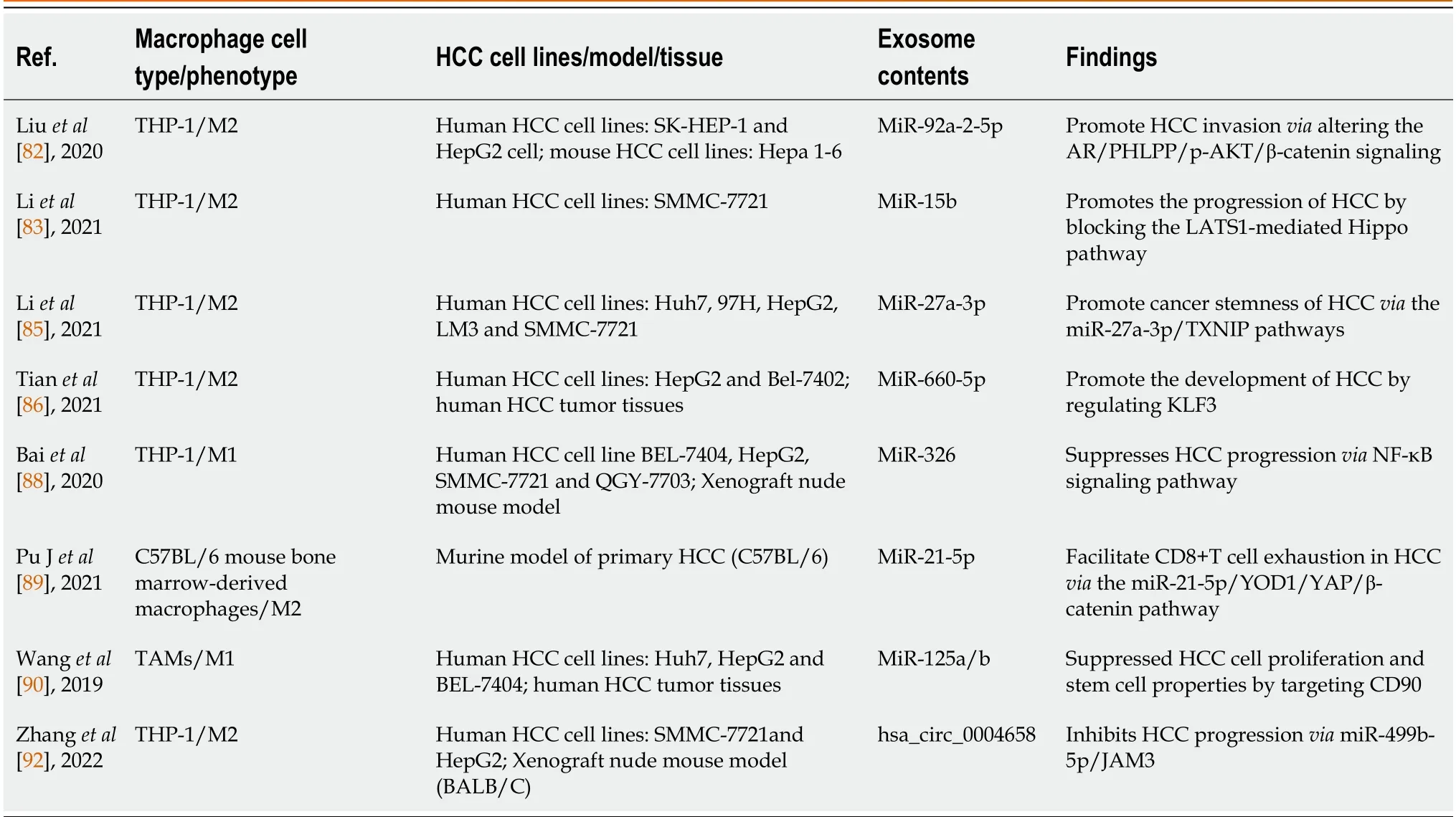
Table 1 Association of the macrophage-derived exosomes with hepatocellular carcinoma
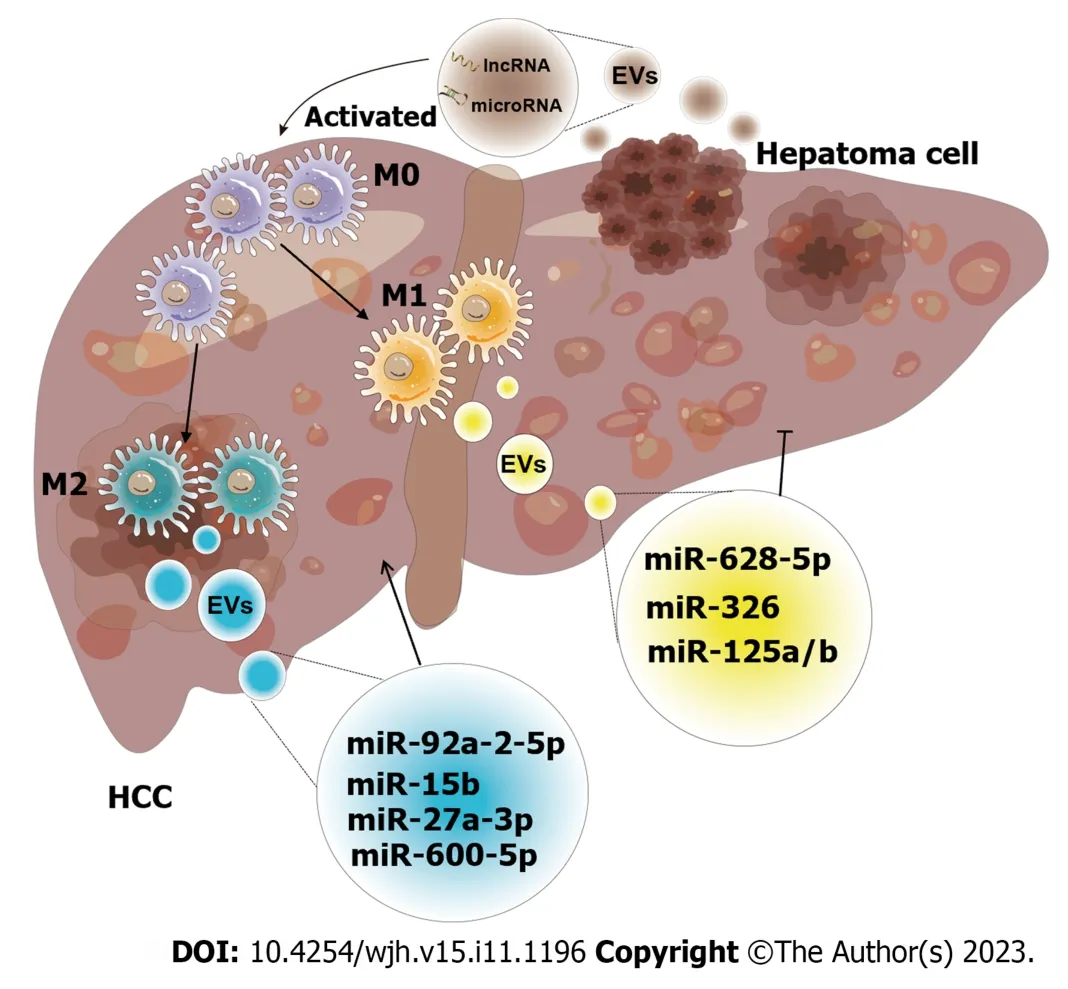
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the effect of exosomes derived from macrophages on hepatocellular carcinoma. The crosstalk of exosomes between macrophages and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) affects tumor progression.Both exosomes released by macrophages and HCC have unique intracellular components,including a variety of mRNAs,microRNAs,long non-coding RNAs,lipids,etc.These intracellular components are utilized as communicators to induce pathways that result in increased or inhibited cell proliferation,invasion,and other hallmarks of malignancy (M0: M0 macrophage;M1: M1 macrophage;M2: M2 macrophage;miR-92a-2-5p[82];miR-15b[83];miR-27a-3p[85];miR-660-5p[86];miR-628-5p[87];miR-326[88];miR-125a/b[90]).EVs: Extracellular vesicles;HCC:Hepatocellular carcinoma;miRNA: MicroRNA;lncRNA: Long non-coding RNA.
Studies have shown that exosomes derived from macrophages mainly promote the growth and invasiveness of HCC.According to recent research,tumor-associated macrophage (TAM)-derived exosomal lncRNAs increase aerobic glycolysis and cell growth in HCC by controlling the miR-548s/ALDH1A3 pathway,thereby contributing to disease malignancy[81].Liuet al[82] discovered that the miRNAs in exosomes secreted by macrophages were altered,and these miRNAs could reduce androgen receptor (AR) expression and translation to enhance the invasion of HCC.In addition,miR-15b was increased in the exosomes of arsenite-treated macrophages,and this factor could be delivered to HCC cells to promote HCC[83].Exosomes produced by M2-polarized macrophages could induce TGF-β1/bone morphogenetic protein 7 pathway imbalances and promote the invasiveness of liver cancer[84].Similarly,Liet al[85] reported that M2 macrophage-derived exosomes were rich in miR-27a-3p,and these exosomes could promote cancer cell stemnessviathe miR-27a-3p/thioredoxin-interacting protein pathway.Moreover,miR-660-5p-rich M2 macrophage-derived exosomes could promote liver cancer development by downregulating KLF3[86].These results indicate that some substances loaded in exosomes can promote tumor growth,invasion,and metastasis,which can provide new insights into the pathogenesis of HCC.
In addition,these results increase enthusiasm for using exosomes in cancer treatment.For example,exosomal miR-628-5p generated by M1 macrophages prevented the m6A alteration of circFUT8,which prevented the proliferation of HCC[87].Additionally,M1 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-326 inhibited HCC cells from proliferating,forming colonies,migrating,invading,and promoting apoptosis by decreasing the expression of NF-κB[88].Exosomes released by M2 macrophages could also prevent HCC.M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-92a-2-5p enhanced liver cancer invasion,and preclinical research showed that inhibiting miR-92a-2-5p in macrophages could reverse the effect of coculture on AR and weaken the invasion of HCC[82].MiR-21-5p in exosomes derived from M2 macrophages could enter HCC tissue and deplete CD8+T cells,providing new insights into tumor immunotherapy[89].Another team showed that the levels of miR-125a and miR-125b in exosomes secreted by TAMs could inhibit HCC stem cells[90].Chenet al[91] recently showed that IL-2 was an important factor that further regulated TAM-derived exosomal miRNAs to enhance the inhibition of cancer progression.Likewise,RBPJ+/+macrophage-derived exosomes could also suppress neoplasms[92].Further study of the effects of these exosomes in the treatment of liver cancer would provide important value in the search for early diagnostic screening markers for patients,which will help in the development of novel schemes for clinical treatment and is critical for reducing the burden of HCC patients worldwide.
Other CLD
The range of CLDs is varied;in addition to NAFLD,HF,and HCC,CLDs also include alcoholic fatty liver disease,viral liver disease,and immune liver disease.Current research into the role of macrophage-derived exosomes in other liver diseases also deserves attention.
Viral hepatitis is a liver disease caused by infection by various hepatitis viruses.The prognosis is generally good,but due to inappropriate lifestyles and untimely treatment,some cases progress to more serious liver diseases,such as liver failure.Therefore,some studies have explored the relationship between exosomes and viral hepatitis.A study showed that macrophage-derived exosomes could spread to hepatocytes and promote IFN-α-induced hepatitis B virus (HBV)resistance,and these factors relied on the main pathways of viral invasion[93].Antiviral molecules can also enter hepatocytes through internalized INF-α-treated macrophage-derived exosomes,thereby reducing the replication of HBV[94].Similarly,exosomes released from Tlr3-activated macrophages are enriched in many hepatitis C virus (HCV)-resistant miRNAs,and when these exosomes are taken up by HCV hepatocytes,they can mediate anti-HCV activity by inhibiting HCV replication in cells,which suggests a potential treatment for HCV[95].These studies show that in viral liver diseases,exosomes carrying antiviral substances are transmitted from macrophages and absorbed by diseased liver cells;thus,these exosomes are therapeutic carriers,indicating a potential novel treatment method for viral hepatitis.In ALD,the main causative factor is alcohol intake.Alcohol stimulation increases the expression of miR-155 and increases the release of macrophage-derived exosomes by reducing lysosome-associated proteins in the liver,leading to the dysregulation of lysosomal autophagy[14].Alcohol exposure can increase the number of miR-27a-rich exosomes produced by monocytes,which can polarize primitive monocytes into M2 macrophages[96].In another study,macrophage-derived exosomes were shown to participate in immune regulation in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis[97].A recent study showed that Concanavalin A could promote the release of exosomes from type I macrophages and that these exosomes contained the lncRNA H19,which induced apoptosis in autoimmune liver disease cells,suggesting a new avenue for developing treatments for autoimmune liver diseases[98].In summary,research on exosomes in liver diseases has increased,which is conducive to exploring new treatments for CLD in the future.
CONCLUSION
The role and potential therapeutic value of exosomes in CLD have been the focus of research in recent years.Understanding the mechanism by which macrophage-derived exosomes affect liver diseases is critical for identifying their roles in liver disease pathogenesis and improving their therapeutic effects.In liver disease,macrophages can be activated and polarized.These activated macrophages secrete exosomes that carry various miRNAs and proteins,and these substances are encapsulated in exosomes and transferred from cell to cell.Macrophage-derived exosomes disrupt normal signaling between parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells in the liver,ultimately leading to liver damage and can act on specific targets to activate or inhibit signaling pathways and mediate related pathological processes.Thus,macrophage-derived exosomes are involved in the diagnosis of liver disease as biomarkers,and the signaling targets of these exosomes can also be used as potential therapeutic targets,providing more novel strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of liver disease.This article reviewed the mechanism and functions of macrophage-derived exosomes in liver diseases.
Currently,the link between macrophage-derived exosomes and liver diseases has mostly focused on a subset of liver diseases,such as NAFLD,HF,and HCC.However,the occurrence and development of CLDs are complicated processes involving multiple causes,stages,and links.In response to viral infection,alcohol intake,a high-fat diet,and drugs,liver inflammation and cellular degeneration first occur,which are accompanied by a series of adaptive events in the liver,including autophagy,aging,and the innate immune response,but these events can further aggravate liver damage,such as the activation of HSCs,leading to the accumulation of extracellular matrix and HF.Without early treatment,HF can further develop into cirrhosis,HCC,and even liver failure.Thus,some of the pathological stages of CLD overlap and further evolve.However,most current studies have only been conductedin vivoandin vitro,which limits the research object to a single liver disease while ignoring the role of macrophage-derived exosomes in the complex pathogenesis of CLD.Therefore,it is important to provide new ideas for subsequent studies so that researchers can focus on the role of macrophage-derived exosomes in different stages of CLD,which will be valuable to understanding the pathogenesis and treatment of many complex liver diseases.
Additionally,it has been found that different stimuli can cause macrophages to polarize into M1 and M2 cells and that M2 cells can then further differentiate into many subtypes.However,at present,there is still a lack of research on the mechanism by which these different isoforms release exosomes and the released exosome contents,which can be the focus of future research.In terms of clinical applications,techniques for extracting and purifying exosomes are improving,but determining how to amplify and change these extracted exosomes into a form that can be used in clinical settings requires cooperation and communication between different fields to develop a better treatment plan to reduce the global burden of CLD.
In the future,the development of exosomes is expected to shift from basic research to clinical applications.In recent years,exosomes have been recognized as potential biological treatments and drug delivery vehicles for the treatment of a variety of diseases.Compared with commonly used nanoparticles,macrophage-derived exosomes have the advantages of low immunogenicity and escape from macrophage phagocytosis.However,there are still gaps in clinical trials of macrophage-derived exosomes for the treatment of CLD.Before clinical translation,we urgently need to confirm which exosome components have profound diagnostic and therapeutic value,especially as accurate biomarkers that reflect disease status,target membrane segments,and critical cargo involved in the disease process.In addition,these systemically delivered exosomes tend to become trapped in nonspecific organs,particularly the liver,lungs,and spleen,resulting in inadequate target doses.Surface modifications for targeted delivery may provide an opportunity to enhance or expand the innate therapeutic value of exosomes.To improve the stability and delivery efficiency of natural exosomes,emerging biological nanotechnology provides a new option for precise material delivery.By designing exosome-like nanovesicles and membrane-camouflaging nanoparticles,the loading and delivery efficiency of effective substances of natural exosomes can be improved.In future clinical treatment of CLD,exosomes from macrophages can carry key effective substances and act as drug carriers after targeted modification or nanotechnology engineering and finally realize individualized targeted therapy,making great contributions to relieving the pressure of global liver diseases.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Xiang SY performed the writing,prepared the figures and tables;Xiang SY and Deng KL designed the outline and coordinated the writing of the paper;Yang DX,Yang P,and Zhou YP provided review of the draft versions of the paper prior to submission of the final version;and all authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Supported byNingbo Natural Science Foundation,No.2022J229;and the Project of Ningbo Leading Medical &Health Discipline,No.2022-S04.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORCID number:Yu-Ping Zhou 0000-0003-0693-4747.
S-Editor:Wang JJ
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Cai YX
 World Journal of Hepatology2023年11期
World Journal of Hepatology2023年11期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Metabolomics in chronic hepatitis C: Decoding fibrosis grading and underlying pathways
- Evaluation of a protocol for rifaximin discontinuation in critically ill patients with liver disease receiving broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
- Global burden of cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases due to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,1990-2019
- Risk of hepatitis B reactivation in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms treated with ruxolitinib
- Budd-Chiari syndrome in children: Challenges and outcome
- Letter to editor ‘Non-invasive model for predicting high-risk esophageal varices based on liver and spleen stiffness’
