A ten-fold coordinated high-pressure structure in hafnium dihydrogen with increasing superconducting transition temperature induced by enhancive pressure
Yan-Qi Wang(王妍琪), Chuan-Zhao Zhang(張傳釗), Jin-Quan Zhang(張金權(quán)), Song Li(李松),Meng Ju(巨濛), Wei-Guo Sun(孫偉國(guó)), Xi-Long Dou(豆喜龍), and Yuan-Yuan Jin(金園園),?
1Department of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
2School of Physical Science and Technology,Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China
3College of Physics and Electronic Information,Luoyang Normal University,Luoyang 471022,China
4Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,China
Keywords: transition metal dihydrogen,first principles,phase transition,superconducting transition temperature
1.Introduction
High pressure is an excellent external condition.Under high pressure, the volume of the material is compressed and the spacing between atoms or molecules in the material is gradually reduced, resulting in the overlap of electronic orbitals of adjacent atoms, resulting in the phase transition in the structure of the material.These new structures present distinctive physical and chemical properties.Kotmoolet al.[1]predicted the phase transition of the boride RuB4under high pressure with the transition sequence ofP63/mmc →C2/c →Immmand the corresponding transition pressures of 198 GPa and 388 GPa,respectively.Moreover,they also confirmed that the hardness value of theImmmphase (19.7 GPa) is much higher than that of theC2/cstructure (7.6 GPa).[1]In the oxide, Dekuraet al.[2]demonstrated that TiO2has a phase transition of cotunnite-type to Fe2P-type(P-62m)structure at 161 GPa through the x-ray diffraction measurement.There is a reduction of band gap from 3.0 eV to 1.9 eV across the phase change, which improves the photocatalytic activity of TiO2.[2]Xinet al.also verified the phase transition process ofPm-3→Cm →P1→I41mdunder high pressure in the nitride ZnN6and theI41mdphase has an excellent energy densities of 4.70 kJ/g.[3]In the meantime,there are also numerous interesting phase transitions in other compounds under high pressure.To better understand them,our attention has focused on other compounds.
Metal hydrides exhibit peculiar electron–phonon coupling under high pressure, making them potential superconducting materials.The researches of metal hydride superconducting materials under high pressure can be mainly divided into two aspects.One to is to uncover new compounds with excellent superconductivity under high pressure.Recent theoretical and experimental studies suggest that LaH10,which has a face-centered cubicFm-3mstructure,exhibits superconducting at temperatures as high as 250 K.[4–7]The critical temperatures of YLuH12can reach 283 K at 120 GPa.[8]Besides, a large number of researches exhibited that CaH6,[9]YH10,[10]and HfH10,[11]have the estimatedTcof 220 K–235 K,303 K,and 213 K–234 K under high pressures, respectively.The other is to generate new structures through the pressureinduced phase transition for the hydrides,which can be stable at ambient pressure.It is evident that the superconductivity of these high-pressure new structures surpasses that observed under ambient pressure condition.For example, YH3crystal forms a semiconductor hcp-structured at ambient pressure,but the predictedTcfor the high-pressure structure fcc-YH3can achieve 40 K at 17.7 GPa.[12]Both aspects on the superconductivity of the metal hydrides aim to reveal the maximalTcof each metal hydrides,which is urgently for investigating theTcvariation process under increasing pressure.Some structures,such asP63/mmc-CrH3(76 GPa–200 GPa),[13]P6/mmm-VH5(125 GPa–250 GPa),[14]I4/mmm-FeH5(150 GPa–300 GPa),[15]I4/mmm-ScH4(120 GPa–250 GPa),[16]andFm-3m-ThH10(100 GPa–300 GPa),[17]exhibit a decreasing trend inTcwith pressure increasing.Some are the opposite (e.g.,R-3m-VH (150 GPa–250 GPa),[14]Immm-ScH8(300 GPa–400 GPa),[18]andIm-3m-MgH6(300 GPa–400 GPa)[19]).In addition, the pressure dependence ofTcof other metals is weak (e.g.,P6mm-WH5(230 GPa–300 GPa),[20]Fm-3m-YH10(250 GPa–350 GPa)[21]).The trend ofTcvariation upon further compression provides guidance for achieving maximalTcfor each metal hydride,thereby motivating us to explore theTcvariation trend with the increasing pressure for the novel structures of the metal hydrides under high pressure.
Hafnium is a typical early transition metal element.Previous theoretical and experimental investigations have shown that HfH2is the only known hafnium hydride found to be stable under ambient conditions.[22–24]Through the research of the phase transition and superconducting properties of HfH2crystal at 0 GPa–300 GPa, Liuet al.[25]indicated that the phase transition of HfH2isI4/mmm →Cmma →P21/mat 180 GPa and 250 GPa,respectively.TheTcvalues ofI4/mmmat 1 atm (1 atm=1.01325×105Pa),Cmmaat 180 GPa, andP21/mat 260 GPa are 47 mK–193 mK, 5.99 K–8.16 K, and 10.62 K–12.8 K,respectively.[25]Later on,Dudaet al.calculatedTcvalues that are similar to each other.[26]However, it remains unclear whether new structures of HfH2emerge under higher pressure(>300 GPa)and what is the trend for the superconducting transition temperature of these new structures with pressure increasing.These two questions have promoted further investigation into HfH2material at higher pressures.
In this work, we extend the research pressure range of HfH2material to 0 GPa–500 GPa and find that HfH2has a phase transition sequence ofI4/mmm →Cmma →P-3m1 at 220.21 GPa and 359.18 GPa, respectively.Among them, the freshP-3m1 structure is firstly discovered in transition metal dihydrides.The structural characteristics, dynamic stability,mechanical properties,hardness,electronic structure,bonding properties,and superconductivity of three stable structures of HfH2are systematically investigated.It is found that the coordination number of HfH2evolution process is 8→9→10 with pressure increasing.The calculatedTcofP-3m1 at 500 GPa is 19.737 K.It is worthy noting that the values ofTcexhibit an upward trend with pressure further increasing.
2.Methods
In order to extensively explore the highpressure phases of HfH2, we employed the CALYPSO code,[27,28]an unbiased structure prediction method based on the particle swarm optimization algorithm.Structure searches are conducted by using unit cells containing up to six formula units(f.u.) in the pressure range of 0 GPa–500 GPa.The superior efficiency of this method has been proved in various systems.[29–35]The followup structural optimizations and electronic structure calculations under different pressures were performed within density functional theory in the Viennaab initiosimulation package (VASP).[36]We utilized the Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof(PBE) exchange–correlation function in generalized gradient approximation (GGA)[37,38]by using plane wave basis set and projection augmented wave (PAW)[39]method.Moreover,functional was used with valence electrons of 5p66s25d2and 1s1and cutoff radii of 2.5 a.u.and 0.8 a.u.to deal with Hf and H atoms,respectively.The cutoff energy of 800 eV for the plane-wave basis expansion of the electronic wave functions and a densek-point sampling with the grid spacing less than 2π×0.03 ?A-1in the Brillouin zone were selected to ensure that all the enthalpy calculations are well converged to better than 1 meV/atom.The electron localization functions(ELF)[40,41]were also computed by using VASP with ELF diagrams plotted in Visualization for Electronic and STructural Analysis (VESTA).[42]For Bader charge transfer analysis, the Bader’s quantum theory of atoms in molecules analysis method[43]was utilized.The phonon dispersion were computed by using the PHONOPY code with the supercell and finite displacement method.[44,45]The electron–phonon coupling(EPC)were computed within the linear response theory through the QUANTUM ESPRESSO package[46]with a kinetic energy cutoff of 80 Ry (1 Ry=13.6056923 eV).In the first Brillouin zone, theq-point mesh of the electron–phonon interaction matrix elements adopted 4×4×4 for each considered structure.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Crystal structure and structural phase transition
Firstly,based on the CALYPSO method for crystal structure prediction with 1–6 formula units (f.u.) per simulation cell,seven low-energy candidate HfH2structures(Cmma,P4/nmm,I4/mmm,P-3m1,R-3m,Fm-3m, andP21/m) are predicted over a wide pressure range of 0 GPa–500 GPa.The crystal structures and structural parameters of the above seven low-energy structures under ambient pressure are summarized in Fig.S1 and Table S1 of supplementary information.A series of the earlier known HfH2structures (e.g.,Fm-3m,Cmma,P4/nmm, andI4/mmm)[47–51]is successfully replicated within a specific pressure range, which demonstrates the effectiveness of the CALYPSO method adopted in structure search of HfH2.To further clarify the high-pressure structural phase transition of HfH2, we plot the enthalpy–pressure curve (relative to the reference phaseI4/mmm) in Fig.1(a).As shown in Fig.1(a),the tetragonalI4/mmmphase is the most stable structure under ambient pressure, which is also the common ground-state configuration of the group IVB of dihydrides (HfH2, ZrH2, and TiH2)[25,47,52–54]and contrary to other transitionmetal dihydrides (VH2, NbH2, CrH2,CoH2)[14,49–51,55,56]whose ground-state configuration adopts the cubicFm-3mstructure.With the increase of pressure,theI4/mmmphase is no longer stable until the first phase transition occurs at 220.21 GPa.The orthorhombicCmmaphase becomes an energetically advantageous structure over the pressure range of 220.21 GPa–359.18 GPa, identical to the highpressure phase raised by Liuet al.[25]Above a higher pressure of 359.18 GPa,an extraordinary trigonalP-3m1 phase is the most energetically favorable and maintained at least up to 500 GPa.Hence,we can conclude that the phase transition sequence of HfH2under high pressure isI4/mmm →Cmma →P-3m1 with the respective transition pressures of 220.21 GPa and 359.18 GPa.This structural transformation can be further verified by the volume–pressure curve of HfH2under the pressure range of 0 GPa–500 GPa, as displayed in Fig.1(b).Herein, obvious volume collapses of 0.5% and 0.9% are uncovered at the transformation pressures of 220.21 GPa and 359.18 GPa, respectively.Subsequently, we focus our attention mainly on the novelP-3m1 crystal to show its particularly structural characteristics, electronic structure, and superconductivity while also discussing the similar properties for the previously proposedI4/mmmandCmmastructures.
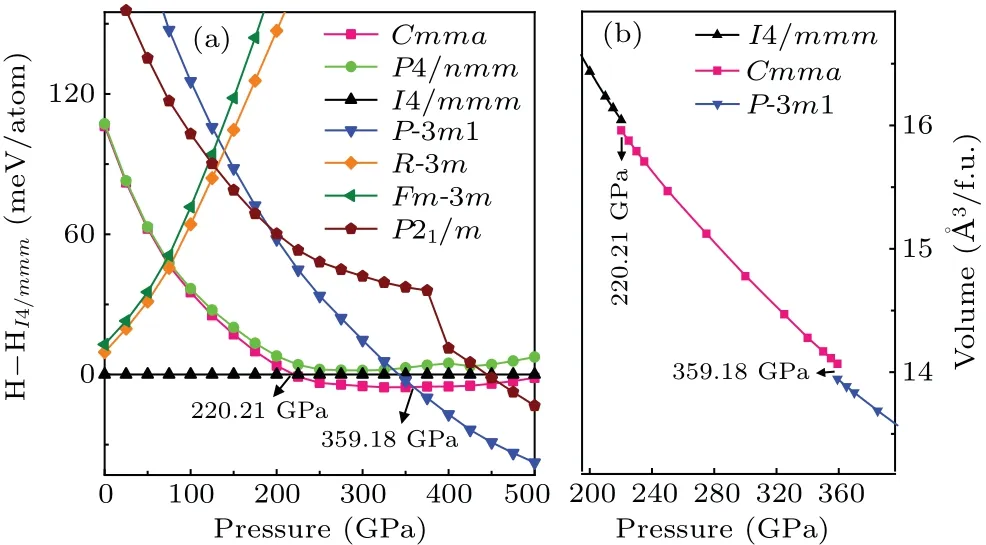
Fig.1.(a) Enthalpy–pressure curves of HfH2 with respect to the I4/mmm phase and(b)volume–pressure relations for HfH2.
3.2.Structural characteristics and coordination number
To elucidate the structural features and the coordination environments for theI4/mmmphase at 1 atm, theCmmaphase at 300 GPa,and theP-3m1 phase at 400 GPa,we depict their structure diagrams in Fig.2 and summarize the structural parameters in Table S2.Based on Table S2, the lattice constants ofI4/mmmstructure under ambient pressure area=b= 3.52890 ?A andc= 4.35240 ?A, which are highly consistent with the previous results (a=b= 3.48130 ?A,c=4.29830 ?A) derived by Liuet al.[25]TheI4/mmmstructure at atmospheric pressure is composed of an HfH8cuboid.In this HfH8cuboid,each Hf atom is located at the body center with eight equal Hf–H separation of 1.71 ?A, two types H–Hf–H angles of 48°and 80°, and the shortest H–H contact is 2.17 ?A.In theCmmaphase under 300 GPa, one Hf atom is surrounded by three types of H atoms with the distances of 1.75 ?A, 1.83 ?A, and 1.87 ?A, respectively, and the H–Hf–H angles vary between 60°and 90°.Besides, the shortest H–H contact is 1.81 ?A.These results show that the coordination number of Hf increases from 8 to 9 with the formation of H-sharing HfH9hendecahedrons.Compressed under 400 GPa, theP-3m1 structure has the lattice constants:a=b=2.62060 ?A,c=4.77939 ?A,where Hf atoms at the 2d Wyckoff sites are coordinated by three inequivalent H atoms at 2d site,1b site,and 1a site,respectively.The Hf–H separation varies from 1.68 ?A to 1.95 ?A and the shortest H–H separation is 1.57 ?A.In addition,the H–Hf–H angle varies between 51°and 125°.TheP-3m1 structure consists of strongly distorted 10-fold HfH10dodecahedron,which is rarely observed in other transition metal hydrides.It is noteworthy that H2or H3units are absent in three stable crystals as the shortest H–H bond is much longer than that of free H2molecule(0.75 ?A)or H3unit(<1.00 ?A).[57–60]Moreover,the H coordination number of Hf atom becomes larger with the increase of pressure,and its growth mode is to insert an H atom at the bottom of the polyhedron in turn, which is similar to the growth mode of TiO2and VO2.[61–63]Interestingly, it is evident that the sharing mechanism of polyhedral small units in HfH2varies with the coordination number.With the occurrence ofI4/mmm →Cmma →P-3m1 phase transition, it can be clearly noticed that theI4/mmmstructure with 8 coordination number is mainly edge sharing, and theCmmastructure with 9 coordination number is edge and surface sharing until theP-3m1 structure with 10 coordination numbers is essentially transformed into surface sharing.

Fig.2.Crystal structures of three stable HfH2 phases ((a) I4/mmm phase at 1 atm, (b)Cmma phase at 300 GPa, and (c) P-3m1 phase at 400 GPa),together with metal coordination polyhedra,with blue and red spheres representing Hf and H atoms,respectively.
3.3.Electronic properties and bonding features
The electronic band structures and density of states(DOS)are calculated to investigate the electronic properties ofI4/mmmat 1 atm,Cmmaat 300 GPa andP-3m1 at 400 GPa of HfH2(see Fig.3).In the meantime, considering that the spin–orbit coupling (SOC) effect of the heavy Hf atoms can induce band splitting on the metallic band structure in the conventional superconductor, we compare the electron band structures with and without the SOC effect in Fig.S2.It is found that the SOC effect has little influence on electronic band dispersion near the Fermi level.Thus, the subsequent calculations are conducted without considering SOC.As displayed in Figs.3(a), 3(c), and 3(e), these three structures exhibit metallic characteristics because of the overlap between the conduction band and the valence band.This conclusion can also be confirmed by Figs.3(b), 3(d), and 3(f), for there is large total density of states at the Fermi level (EF).The region between two the peaks on both sides of the Fermi level is known as pseudogap and the narrow pseudogap system is corresponding to ionic bonding characteristic.It can be clearly found from Figs.3(b),3(d),and 3(f)that the pseudoenergy gaps of these three structures are very narrow,which reveals that HfH2is a typical ionic bonding material.In these three stable phases of HfH2crystal, the density of states at the Fermi level is mainly contributed by the Hf d state,which is similar to some early transition metal dihydrides(CrH2,[13]ZrH2,[47]VH2,[51]and TiH2[53]).Furthermore, theP-3m1 phase at 400 GPa possesses a largest Hf-d electronic density of states(0.963(state/eV)/f.u.) at Fermi level,which is much higher than that ofI4/mmm(0.323 (state/eV)/f.u.) at 1 atm andCmma(0.880(state/eV)/f.u.) at 300 GPa,which indicates that the phase transition significantly improves the Hf-d electronic density of states at Fermi level.Meanwhile, as exhibited in Fig.S3,the calculated Hf-d electronic DOSs ofP-3m1 structure at Fermi level under 360 GPa, 400 GPa, 450 GPa,and 500 GPa all present an increasing trend.

Fig.3.Electronic band structures for(a)I4/mmm phase at 1 atm,(c)Cmma phase at 300 GPa and(e)P-3m1 phase at 400 GPa,and total and partial density of states for(b)I4/mmm phase at 1 atm,(d)Cmma phase at 300 GPa,and(f)P-3m1 phase at 400 GPa,of three stable HfH2 phases.

Fig.4.The electron localization functions(ELF)of three stable HfH2 phases: (a)(001)plane for the I4/mmm phase at 1 atm,(b)(100)plane for the Cmma phase at 300 GPa,and(c)(010)plane for the P-3m1 phase at 400 GPa.

Table 1.Calculated Bader charges of Hf and H atoms in three stable HfH2 phases,with δ representing the quantity of electric charge transferred from Hf atom to H atom.
To further uncover the bonding nature in three HfH2configurations, the electron localization functions (ELFs) which can accurately describe the bond type are computed, and the results are depicted in Fig.4.Low ELF value (less than 0.5) corresponds to ionic bond or metal bond while higher ELF value(larger than 0.5)corresponds to covalent bond.As shown in Fig.4, the ELF values around the H atom in three HfH2phases are close to 1,while those of the Hf sites are quite low.Moreover,the ELF values between Hf and the nearest H atom are smaller than 0.5,demonstrating that no electrons are localized toward the neighboring Hf–H connection.Both aspects above illustrate that the Hf–H bonds in three HfH2crystals should be ionic.In addition, the ELF value toward the neighboring H–H connection displays no electron localization,thus stating that no covalent interaction exists for neighboring H–H.This conclusion is in excellent accordance with the H–H bond length analysis.To further disclose the bonding characteristics between Hf and H atoms for three HfH2phases, the Bader maded charge analysis,[43]and the results are shown in Table 1.For three stable HfH2phases,there are large amounts of charge transferring from Hf to H atoms,which further verifies the ionic characteristic of the Hf–H bond.This prediction of the charge transferring from Hf to H atoms can be demonstrated by the element electronegativity.Based on the periodic law,[64]the electronegativity value of the Hf element (1.3) is much smaller than that of the H element(2.2),demonstrating that the charge should transfer from Hf to H atoms.This ionic bonding characteristic can also be seen in VH2,[51]TaH4,[65]FeH6[66]YH6,[67]and CaH6.[9]However,the ionic characteristic for the H atom is contrary to that of many hydrogenrich compounds, such as InH3,[57]GeH4,[58]OsH6,[60]and RuH6,[68]where the H atoms are either bonded to the nearest H atoms to form an H2or H3unit,and/or covalently bonded toM(M=In,Ge,Os,and Ru)atoms to formM–H bonds.Overall,the analysis results of DOS,ELF,and Bader all reveal the ionic characteristic between Hf and H atoms.
3.4.Mechanical properties and hardness
The elastic constants of theI4/mmm,Cmma,andP-3m1 structures for HfH2under corresponding pressure are calculated with the identical strain–stress means.[69]The computed consequences above are listed in Table S3.At the same time,the values of shear modulusG, bulk elastic modulusB,B/G,Young’s modulusE,and Poisson’s ratioνof three stable HfH2structures can be derived from the calculated elastic constants on the basis of the Voigt–Reuss–Hill (VRH) method.[70]According to the mechanical stability criteria,[70]all three crystals satisfy mechanical stability under the corresponding pressure.Poisson’s ratio is a key physical quantity to describe the internal bonding property of the material.For the metallic material,the valueνis usually 0.33.[71]From Table S3,the values of Poisson’s ratioνfor the three structures are slightly larger than 0.33,which indicates that three stable HfH2phases should be metallic.In addition, to assess the values of Vickers hardness for three stable HfH2configurations, we compute their hardness values by using the empirical formula for material hardness prediction proposed by Tianet al.:[72]Hν=0.92K1.137G0.708,whereK=G/B.The calculation results are also summarized in Table S3.The hardness values ofI4/mmm,Cmma, andP-3m1 structures under corresponding pressures are 1.90 GPa,1.01 GPa,and 2.07 GPa,respectively.It should be noteworthy that the low hardness for HfH2may be related to the ionic properties between transition-metal and hydrogen atoms.[73]
3.5.Dynamical properties and electron–phonon coupling
To explore the dynamical stability ofI4/mmm,Cmma,andP-3m1,we have calculated their phonon dispersion curves and the projected phonon density of states (see Fig.5).As plotted in Fig.5 (left and middle), the phonon dispersion curves confirm the dynamical stabilities of these three structures,as evidenced by the absence of any imaginary frequency in the whole Brillouin zone.From Fig.5 (left and middle),the low-frequency bands come from the vibration of the Hf atoms while the high-frequency bands are mainly correlated with the vibration of the H atoms.This phenomenon should be ascribed to the much heavier atom mass of hafnium atom than hydrogen atom.
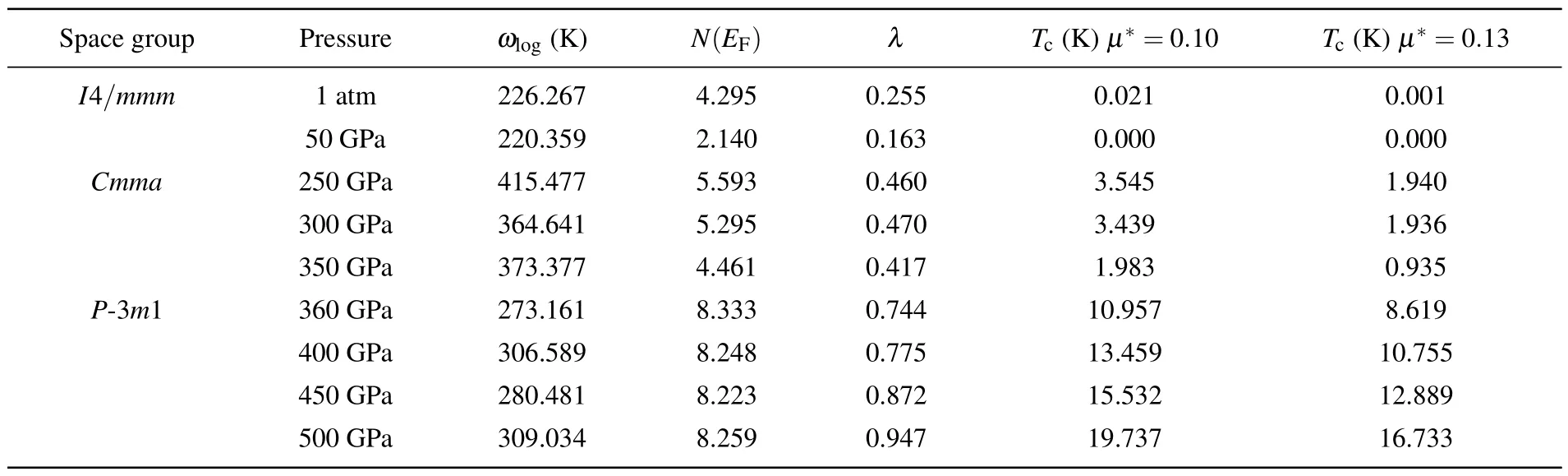
Table 2.Calculated values of electron–phonon coupling parameters λ,electronic density of states at the Fermi level N(EF)(states/spin/Ry/unit cell), logarithmic average phonon frequency ωlog, and superconducting critical temperatures Tc of I4/mmm,Cmma, and P-3m1 at different pressures.

Fig.5.Phonon dispersion curves (left), projected phonon density of states(middle), and Eliashberg spectral function α2F(ω)together with electron–phonon integral λ(ω)(right)of three stable HfH2 phases,for(a)I4/mmm at 1 atm,(b)Cmma at 300 GPa,and(c)P-3m1 at 500 GPa.
Considering the metal behavior of three stable HfH2phases under high pressure, we calculate the values of their electron–phonon coupling(EPC)parameterλ,the logarithmic average phonon frequencyωlog,and electron density of states at Fermi levelN(EF) to predict their potential superconductivity.The superconducting temperature is estimated by using the Allen–Dynes modified McMillan equation to be
Among them, the values of empirical constantμ*describing the Coulomb shielding effect are 0.10 and 0.13, respectively,as shown in Table 2.It can be found that theTcvalue always decreases as the value ofμ*increases.Although the predictedTcofI4/mmmis only 21 mK under ambient pressure,the estimatedTcvalue of theCmmaphase at 300 GPa is 3.931 K and the estimatedTcof theP-3m1 structure can reach 19.737 K under 500 GPa.Subsequently,we probe into the relationships between the pressure and the superconducting critical temperatureTcfor three stable HfH2phases, in order to reveal the internal reasons for the change of the superconducting critical temperatureTcof HfH2.Based on Table 2, it can be clearly seen that theTcvalues ofI4/mmmandCmmaare negatively correlated with the pressure.On the contrary,theTcofP-3m1 presents a positive correlation with the pressure,which is relatively rare in transition metal hydrides.The trends of electron–phonon coupling parameterλwith the pressure intuitively lead to the trends ofTcfor the three stable phases under pressure.ForP-3m1 phase with increasedTc,the calculated value of EPC parameterλis 0.744 at 360 GPa, 0.775 at 400 GPa,0.872 at 450 GPa, and 0.947 at 500 GPa, respectively, which emphasizes that the electron–phonon coupling strength ofP-3m1 is improved with the pressure increasing.To understand this coupling mechanism, the Eliashberg EPC spectral functionα2F(ω)and its integralλofI4/mmmat 1 atm,Cmmaat 300 GPa,andP-3m1 at 500 GPa are analyzed in Fig.5(right).The calculation shows that the low-frequency vibrations below 5 THz from the heavy Hf atoms contribute 86% of the totalλ,while the high-frequency vibrations(30 THz–40 THz)related to H atoms merely account for 14% of the totalλinI4/mmmphase.For theCmmaphase, low-frequency vibrations(below 10 THz)contribute 80%,and high-frequency vibrations(40 THz–80 THz)only contribute 20%of the totalλ.TheP-3m1 phase exhibits a similar trend,where the projected phonon density of states at frequency less than 12 THz is contributed by Hf atom vibrations, which makes contribution to the most (85%) of the electron–phonon coupling coefficientλ, as shown in Fig.5(right).These results highlight that the electron–phonon coupling in three stable HfH2structures are dominated by the low-frequency Hf atom vibrations, which can also be demonstrated by the obvious Hf-d electronic density of states at Fermi level.Therefore, the significantly improvedTcvalue of the high-pressure novelP-3m1 structure is probably due to the enhanced d-state of Hf atoms at Fermi level.Meanwhile, the increase of Hf-d electronic DOS with pressure growing can improve the electron–phonon coupling,which further leads theTcvalue ofP-3m1 phase to increase.
4.Conclusions
In summary,the stable phases of HfH2crystal within the pressure range of 0 GPa–500 GPa are determined by combining CALYPSO crystal structure prediction with first-principles calculations.The HfH2crystal transforms a structural phase transition sequence ofI4/mmm →Cmma →P-3m1 under 220.21 GPa and 359.18 GPa,respectively.Besides two known phases, namely,I4/mmmandCmma, an unexpected trigonalP-3m1 structure with 10-fold coordinated under high pressure is uncovered for the first time.Phonon dispersion curves and elastic constant calculations suggest that these three configurations are dynamically and mechanically stable.The consequences of electronic band structure and density of states show that three HfH2polymorphs have metallic properties.Further analysis on the electron localization function and Bader charge demonstrates that the HfH bond in three HfH2crystals should be ionic.In addition, the calculated superconducting critical temperatureTcofI4/mmmat 1 atm,Cmmaat 300 GPa, andP-3m1 at 500 GPa are 21 mK,3.931 K,and 19.737 K, respectively.Meanwhile, the pressure dependence of the superconducting critical temperature forP-3m1 phase exhibits a positive correlation trend,whileI4/mmmandCmmastructures show negative correlation trends.This exceptional phenomenon ofP-3m1 structure is mainly responsible for the stronger electron–phonon coupling which is dominated by Hfd orbits.
Acknowledgements
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.11804031 and 11904297), the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Hubei Province, China (Grant No.Q20191301), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Grant No.SWUKT22049), and the Chongqing Talent Plan for Young Top Notch Talents,China(Grant No.202005007).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Robustness of community networks against cascading failures with heterogeneous redistribution strategies
- Identifying multiple influential spreaders in complex networks based on spectral graph theory
- Self-similarity of complex networks under centrality-based node removal strategy
- Percolation transitions in edge-coupled interdependent networks with directed dependency links
- Important edge identification in complex networks based on local and global features
- Free running period affected by network structures of suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons exposed to constant light