A Comparative Study of Development and Reform of Urban-Rural Integration in Chengdu and Chongqing Based on System Theory
Gao Jie
Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences
Abstract: Chengdu and Chongqing, as two core cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, have always been in the front rank of development and reform of urban-rural integration in China. But due to different basic conditions, ideas and priorities are different in the two cities. This paper establishes an analysis framework based on system theory, conducts a systematic comparison on the development and reform of urban-rural integration in the two cities to achieve a comprehensive comparison study and finds out that: (a) Owing to different basic conditions, Chengdu and Chongqing have adopted different reform ideas and measures. Chengdu places more emphasis on systematic advancement, while Chongqing attaches more importance to key breakthroughs. (b) Chengdu’s high level shows that in the practice of urban-rural integration, independent policies and measures in local areas have limited effects. System efficiency can surpass the sum of local areas’ efficiencies only if a systematic method is adopted to comprehensively promote policies and measures for institutional innovations in various fields.
Keywords: system theory, the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, development and reform of urban-rural integration, comparison
In January 2020, Xi Jinping, general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee, presided over the sixth meeting of the Central Committee for Financial and Economic Affairs, where he stressed that the construction of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle should be advanced to create a major growth pole for high-quality development in China’s western region. In October 2021, a master plan for the construction of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic Circle was officially promulgated, marking the beginning of a new plan for the construction of the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle towards accelerated high-quality development. As two core cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle, Chengdu and Chongqing were approved to become the pilot areas for urban-rural comprehensive reform in 2007 and became the national pilot areas for urbanrural integration development in 2019. Chengdu and Chongqing have always been at the forefront of the development and reform of urban-rural integration in China, and both have carried out a series of reforms and explorations on the institutional mechanisms that restrict the development of urban-rural integration. However, reform ideas and priorities of the two cities are different due to different basic conditions. Under the guidance of system theory, this paper systematically compares the development and reform of urban-rural integration in Chengdu and Chongqing, outlines the key points of cooperation and mutual learning based on similarities and differences, and provides a reference for deepening cooperation between Chengdu and Chongqing in the development and reform of urbanrural integration to promote joint development of the Chengdu-Chongqing region and form important growth poles of high-quality development in western China.
Establishment of a Theoretical Analysis Framework
Review of Relevant Literature
The development of the Chengdu-Chongqing region is one of the key areas of research in the field of regional economics in China. Lin Ling, Cheng Biding, Dai Bin, and other experts’ research on ideas and reform paths of Chengdu-Chongqing regional development provides important theoretical support for relevant planning and policymaking in the Chengdu-Chongqing region (Lin, Liao, & Liu, 2005; Lin, 2007; Lin, 2012; Cheng, 2008; Dai, 2011). From April 2016 when the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration Development Plan was promulgated, to January 2020 when the Strategic Plan of Further Building the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle was stipulated, research on the development of the Chengdu-Chongqing region has also been deepening. It is widely recognized in academia that there are significant regional differences between Chengdu and Chongqing, providing the conditions for deepening cooperation and promoting integrated development. Geng et al. (2018), based on the theories of regional economic growth and of supply and demand, comparatively analyzed the development characteristics of Chengdu and Chongqing using data on economic growth from 1986 to 2016, and discussed the regional development paths and strategies of Chengdu and Chongqing as two separate cities. Li (2019), drawing on data regarding economic development indicators of the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration from 2008 to 2018, measured and presented the spatial and temporal differences in the economic development of the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration by means of multi-dimensional mathematical statistics and spatial statistics, and discussed relevant causes and mechanisms. Jin (2020) measured the industrial and functional divisions of labor between the central cities and their peripheral cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle from 2003 to 2017, and discovered that the industrial and functional divisions of labor between Chengdu and Chongqing as central cities and their peripheral cities showed different trends of evolution: The industrial and functional divisions of labor between Chengdu and its peripheral cities gradually increased while the industrial and functional divisions of labor between Chongqing and its peripheral cities declined slightly. Shi et al. (2021) proposed that the spatial structure can be optimized by seeking “the driving force from the dual-city, breakthroughs at both flanks, and expansion around the axis area and support to the pole,” thus creating a development landscape featuring complementary strengths and shared prosperity across the entire region. Overall, comparisons between Chengdu and Chongqing as two central cities in the Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle are a focus of academic attention, but relevant research is mostly concerned with the regional industrial divisions of labor and spatial structures of urban agglomeration without systematically comparing the two cities’ institutional reforms and policy innovations.
Basic Viewpoint of System Theory
For more than half a century, “system” has attracted the attentions of many scholars at home and abroad as a research object. In the 1920s, Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, an Austrian-American biologist, founded the general system theory, and the publication of About General System Theory in 1945 marked the formation of the system theory. According to the general system theory, a system is composed of interrelated components. These components can be concrete substances or abstract organizations, which interact with each other in a system to form the characteristics of the system. The operation of the system composed of these components has certain goals, and any changes in the components or their structures in the system may affect and change the characteristics of the system (Bertalanffy, 1987). The system has the basic characteristics of integrity, openness, dynamic correlation, hierarchy, and order. The system method is a methodology formed under the guidance of general system theory, and its main point is to reveal the system characteristics and movement laws within the system and the relationships between the system and its elements, among elements, and between the system and external environment, to find the best solutions to.
Theoretical Analysis Framework of This Study
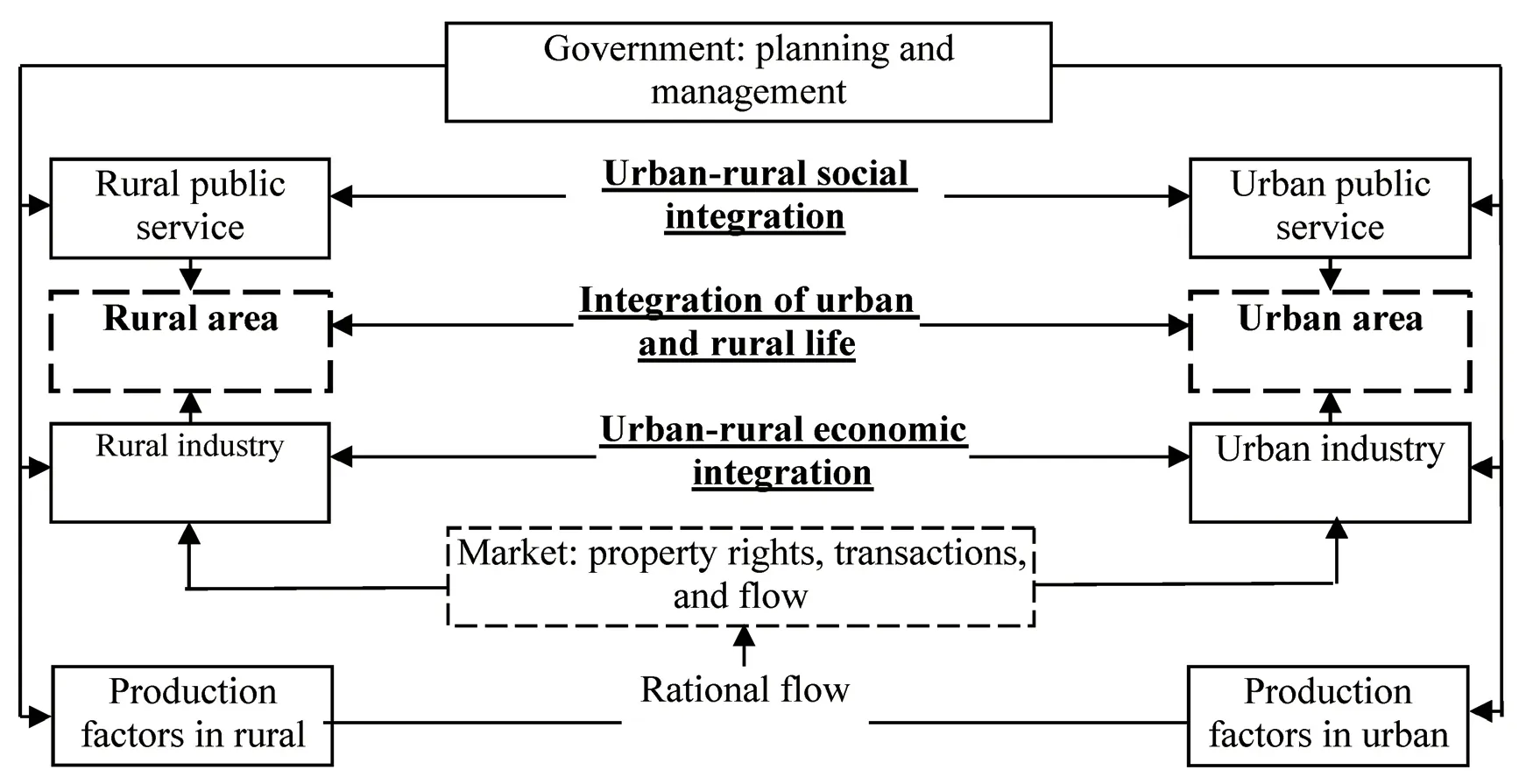
Figure 1 Analysis framework of development and reform of urban-rural integration based on system theory Note: The underlined items are system targets and the solid boxes refer to subsystems.
From the perspective of system science, the integration of urban and rural areas is essentially a process in which social and economic aspects are interrelated, restricted, and interacted. Therefore, this study needs the guidance of system theory, especially the open complex system theory and its methodology. We regard the development and reform of urban-rural integration as a giant and complex system. According to the basic viewpoint of the system theory, we mainly analyzed its system objectives, subsystem composition, and system structure (i.e., the relationships between system and subsystems and between each subsystem). Through the research on the related theories of the development and reform of urban-rural integration, we put forward the following theoretical framework.
From the perspective of the system goal, the development and reform of urban-rural integration is the overall goal that the system needs to achieve. Under the overall goal, the system is supported by three sub-goals, including urban-rural economic integration, urban-rural social integration, and integration of urban and rural life. From the perspective of subsystem composition, it consists of four subsystems, including the planning management subsystem, the production factor subsystem, the urban-rural industry subsystem, and the public service subsystem. From the perspective of internal relationships, firstly, the planning management subsystem acts on the urban-rural industry subsystem, the production factor subsystem, and the public service subsystem through government means, and determines industrial layouts, industrial structures, production factor allocation efficiency, and public service provision levels. Second, the production factor subsystem acts on the urban-rural industry subsystem through market means, and the market allocation level of production factors determines the internal power of industrial development, thus affecting the industrial development levels. Finally, the urban-rural industry subsystem and public service subsystem directly act on urban and rural areas, which determine the realization of urban-rural integration development goals. The urban-rural industry subsystem determines the urban-rural economic integration levels and provides a material basis for urban-rural integration development. Balanced public service is the most direct means to promote urban-rural coordinated development and provides a guarantee for the development of other subsystems.
Comparison of the Development and Reform Systems of Urban-Rural Integration in Chengdu and Chongqing
Starting from the national pilot areas for balancing urban and rural comprehensive coordinated reforms, both cities have carried out a large number of reforms and explorations. Chengdu has actively explored the aspects of determining, registering, and certifying rural property rights ownership and orderly transfers, urban and rural unified household registration system reforms, village-level public service and social management reforms, and grassroots governance mechanism innovations, and has achieved fruitful reform results. Several of its reform measures provided a basis for the revision of national laws and the introduction of relevant policies. Chongqing’s land ticket trading system reforms, migrant workers’ household registration system reforms, and rural three-rights mortgage financing system reforms have also achieved great influence. In 2019, the western part of Chengdu and that of Chongqing simultaneously became the pilot areas for urban-rural comprehensive reform, further clarifying the experimental focuses of reform, including promoting the free flow of urban and rural elements, and building a platform for the coordinated development of urban and rural industries.
Planning Management Subsystems: Comparison of Spatial Development Strategies
With the advancement of urbanization, both cities have implemented spatial optimization strategies that are beneficial to the development and reform of urban-rural integration (see Table 1). In the report of the 13th CPC Municipal Congress in 2017, Chengdu clearly stated that the scope of the central city would be expanded to 11 administrative districts plus high-tech zones and the Tianfu New District. It would implement the cross strategy of “advancing eastward, expanding southward, controlling westward, reforming northward, and excellently developing the center,” and promoting the transformation from “two mountains with one city” to “one mountain with two wings.” In the 2020 municipal government report, Chongqing clearly put forward that the main metropolitan area would be composed of 21 districts to form a spatial pattern of “one district, two clusters.” Both cities strive to create conditions for deepening the integration of urban and rural development by widening the urban development framework and promoting the expansion of urban core areas.
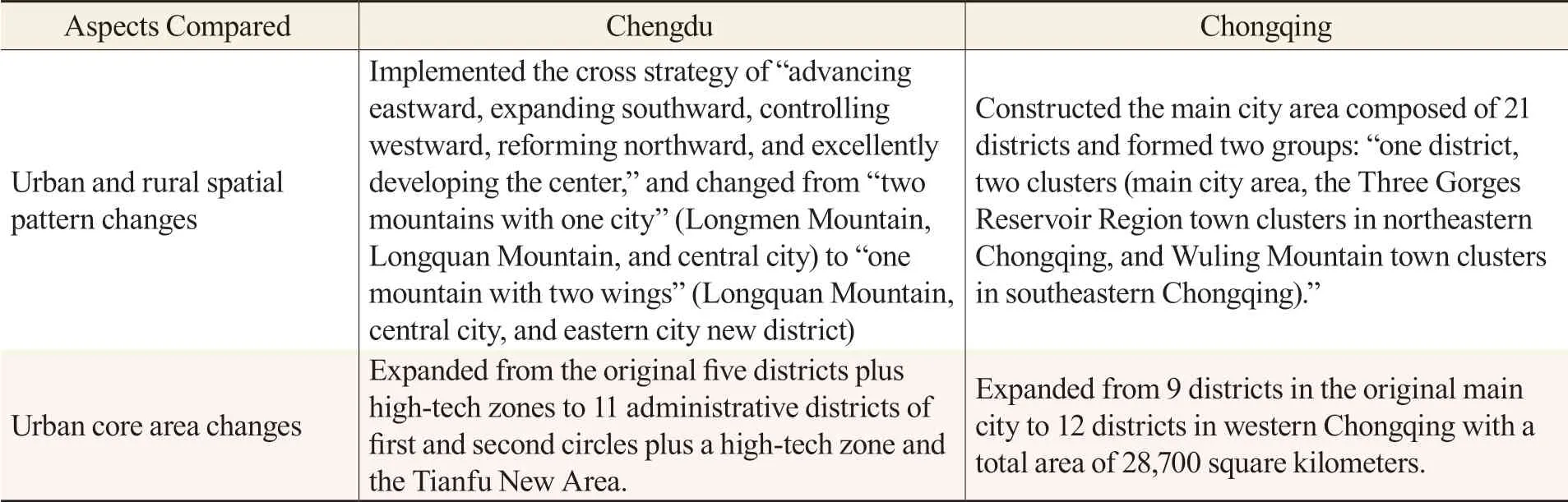
Table 1 Comparison of Urban and Rural Spatial Development Strategies Between Chengdu and Chongqing
Production Factor Subsystem
Labor force elements: comparison of household registration system reforms.
The household registration system is an important institutional factor that determines the mobility and allocation efficiency of labor factors. Chengdu and Chongqing both took the household registration reform as a key point of reform and innovation. Both cities carried out the household registration system reform earlier in China and issued household registration reform policies with pioneering significance in China in 2010 (see Table 2). On August 1, 2010, Chongqing issued theImplementation Measures for Rural Residents’ Household Registration System Reform in Chongqing(Trial), which further reduced the restrictions on the conditions of “transferring rural households into cities,” and set the household registration conditions at three levels which moderately relaxed the registrations in the main urban areas, further opened the registration in the districts and counties, and fully opened the registration in towns. Farmers settling in the municipality will enjoy urban employment, social security, housing, education, medical care, and other public services, but they need to give up rural contracted lands, homesteads, forests, etc. In 2010, Chengdu issued theOpinions on Realizing Free Migration of Residents by Unified Household Registration in Chengdu’s Urban and Rural Areas, which clearly means that the difference between urban and rural resident identities was eliminated. Residents could move freely, and the registered place of household registration is to be consistent with the actual residence. Farmers could settle in cities with their rural property rights instead of using them in exchange for employment social security.
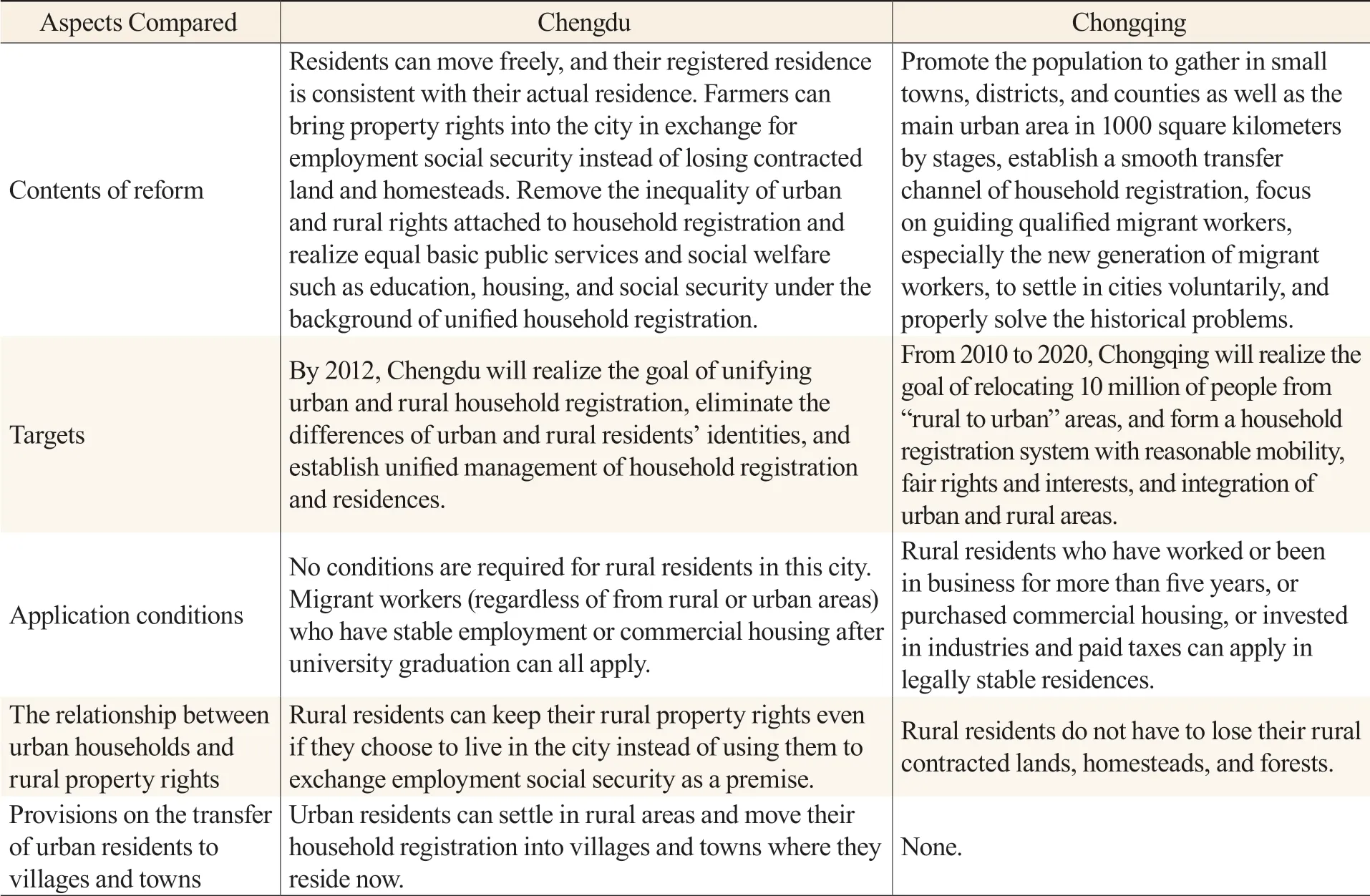
Table 2 Comparison of Household Registration System Reforms Between Chengdu and Chongqing
After entering the stage of urban-rural integration development, both cities have issued opinions on deepening the reform of the household registration system according to theOpinions of the State Council on Further Promoting Reform of the Household Registration System(see Table 3). Specifically, Chengdu issued theOpinions of the Chengdu Municipal Government on the Implementation of Promoting Reform of the Household Registration Systemand supportive management measures in 2017. The city started a new household registration policy featuring a dualtrack scheme encompassing conditional and cumulative score household registration, established a comprehensive residence permit system, and implemented a uniform household registration policy for both urban and rural populations within or outside the city, thereby achieving “zero threshold” for the rural population seeking house renting and household registration. In 2015, Chongqing issued theOpinions of Chongqing Municipality on the Implementation of Promoting Reform of the Household Registration System. According to the Opinions, the previous condition that rural people needed to give up their rural properties in order to be eligible to urban household registration was abandoned. Instead, the municipality started to implement a uniform household registration system for both urban and rural populations and gradually loosened the household registration conditions for relocated populations within the municipality. For non-local people wishing to obtain household registration, a steady and orderly approach has been adopted, and the Opinions proposed the tentative establishment of a household registration system by a cumulative score for non-local people within the central urban function area and the urban function expansion area, as well as the implementation of the residence permit system. However, the approaches and methods of applying for household registration based on residence permits have not been clarified. Comparatively, Chengdu adopted a uniform household registration policy for urban and rural populations within or outside the city and clarified the detailed rules for household registration based on residence permit scores, introducing a larger extent of reform.
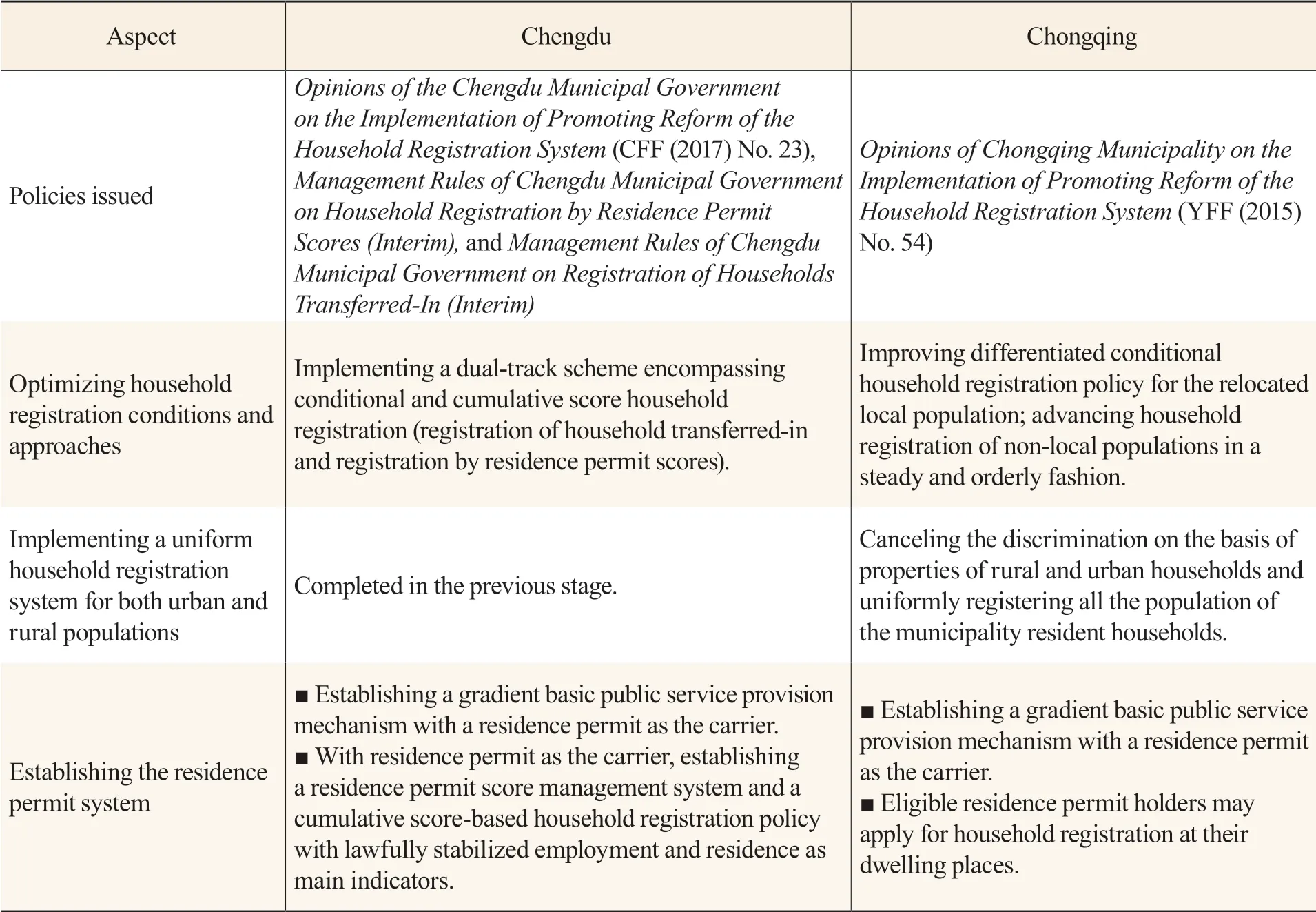
Table 3 Comparison of the New Round of Household Registration Reform in Chengdu and Chongqing
Additionally, both cities are paying attention to guiding urban talents to go to the countryside. Chengdu is the first city that has formulated the rural planner policy and has introduced and trained more than 13,000 professionals and technical who are talents urgently needed, such as rural planners and technology leaders. Chongqing has also implemented the policy for encouraging “artists and three types of professionals” (engineers, planners, architects, and artists) to go to the countryside. The reform directions of the two cities are basically similar, and the specific contents can be further communicated and learned from each other.
Land elements: comparison of rural land system reforms.
Chengdu has made many explorations in promoting the integration of urban and rural land systems. It started the reform of the rural land property rights system in 2008 and formed a systematic reform mechanism, including confirming the right to issue certificates, building a trading platform, and transforming the circulation policy. Although Chongqing also made some attempts, it failed to fully integrate all the aspects. Firstly, Chengdu has fully completed the actual measurement and confirmation of land and housing property rights throughout the city. Chongqing also started the reform of its rural land property rights system following Chengdu, but it did not carry out the confirmation and certification of rural land throughout the city and only implemented the confirmation and certification of forest rights in line with the national forest rights reform. Secondly, in terms of building a trading platform, Chengdu has taken the lead in establishing a relatively complete circulation platform system and is at the forefront of the country in system architecture, functional responsibility positioning, guarantee system establishment, and policy support. Chongqing has established a rural land exchange, which focuses on the transactions of “l(fā)and ticket,” which is an indicator linked to urban and rural construction land. At the same time, Chongqing provides services for the transfer of rural land’s contractual management rights.
With respect to the innovations of collective construction land transfers, both cities focused on pilot projects for market access of collective construction land. In 2015, the Pidu District of Chengdu and the Dazu District of Chongqing were included in the list of pilot projects of the Ministry of Land and Resources for carrying out reforms on the “Three Types of Land.” The two local governments are formulating relevant policies for market access of collective construction land. The difference between the two cities is that Chengdu places more emphasis on realizing the same rights and prices for collective construction land and urban land. It clearly stated that “the right to use collective construction land can be transferred by mortgage” and “the right to use collective construction land can be transferred by agreement, bidding, auction or listing.” On the other hand, Chongqing emphasized: “To support the rights of rural collective construction land and paid and reasonable circulation and transfer of quotas across regions by using the quotas replacement and turnover policy of construction land.”
With respect to compensated renouncement of contracted management right of rural land, the Liangping District of Chongqing Municipality, as the national pilot zone for rural reform, experimented with compensated renouncement of the right of the contracted management of rural land in 2016, creating a renouncement mechanism featuring multi-player synergy and encompassing “the contract issuing party has the renouncement channel, the withdrawal party has the renouncement intention, the undertaking party has the demand for land, and the government has the policy for support,” and a diversified land exit model characterized by an “integration of land exit and use.” Although Chengdu did not become the national pilot zone for the reform, it still managed to issue theGuiding Opinions of The Chengdu Municipal Government on Normalizing the Exit from Contracted Management Right of Rural Land(Interim), aiming to normalize the exit procedures for contracted management right of rural land and substantially protect rural residents’ interests in land.

Table 4 Comparison of Pilot Reforms of Rural Land in Chengdu and Chongqing
Capital elements: comparison of rural financial innovation.
Both cities have tried to play a guiding role for financial funds, developing new financial institutions in rural areas, and innovating in financial products concerning rural property rights. They have a strong commonality in specific measures, among which the reform of the rural “three rights” mortgage financing system in Chongqing and the agricultural loan system (Nong Dai Tong) in Chengdu are the most prominent reform highlights. Through improving the relevant policy system, standardizing the operational process, and establishing risk compensation and guarantee mechanisms, Chongqing’s rural “three rights” mortgage financing system reform has reduced the institutional obstacles for mortgage financing of rural land’s contractual management rights, rural residential houses and forest rights. Chengdu’s agricultural loan system (Nong Dai Tong) is a rural financial service platform established in July 2017 based on the reforms related to mortgage financing of rural property rights. It integrates the information of financing supply and demand through the platform of “Internet Plus Finance,” which not only realizes accurate information exchange between agricultural business entities and financial institutions, but also addresses the issue that financial institutions are unwilling to provide agricultural loans in consideration of risk sharing. Comparatively, the two reforms are highly complementary. Chongqing provides a more systematic and innovative policy while Chengdu accelerates the alignment of market supply and demand through “Internet Plus” technology, which can be the starting point for the next cooperation.
Urban-Rural Industry Subsystems: Comparison of Industrial Development Orientations
Based on respective advantages, such as transportation area and historical evolution of industrial formation, Chengdu and Chongqing have their own emphasis on industrial development orientations. Chengdu is a consumption center while Chongqing is an important manufacturing base. According to the industrial orientations specified in the 13th Five-Year Plan concerning the two cities (see Table 5), Chengdu emphasizes the balanced development of manufacturing and service industries while Chongqing clearly regards manufacturing as the main driving force of its economy. From this point of view, Chongqing is closer to the industrial policy orientation of giving priority to the development of heavy industry in the early stage of forming urban-rural economic dualism in China, and its employment absorption capacity for industries may become a major obstacle in the process of urbanization while Chengdu is not only more developed in the service industry, but also more inclined to labor-intensive industries in industrial structure, and its employment absorption pressure in the process of urbanization is relatively less.
Public Service Subsystem: Comparison of Urban and Rural Public Service Reforms
Both cities have focused on the implementation of relevant reforms to promote the equalization of urban and rural public services. In terms of public services, Chengdu has mainly taken the following measures. Through the establishment of a transportation network system integrating urban and rural areas, Chengdu has comprehensively carried out standardized construction and upgrading of public facilities for such fields as rural education, culture, and health, comprehensively improved the level of rural infrastructure, and taken the lead in establishing a basic insurance system for the elderly and a basic medical insurance covering both integrating urban and rural areas. Through comprehensively supporting reforms in public finance, village-level public services, and social management, the social security gap between urban and rural residents has been greatly narrowed, and the basic balance of urban and rural public services in health care, social security, culture, and environmental protection has been achieved at the institutional level. Chongqing got started with improving the allocation mechanism for achieving balance in public resources, promoted the reform of the division of financial affairs and expenditure responsibilities of basic public services, determined the scope of common financial affairs in basic public services, and increased investments in basic public services in urban and rural areas. It formulated the Implementation Plan for Standardized Construction of Basic Public Services in Chongqing, and comprehensively promoted the equalization of basic public services in urban and rural areas in terms of education, health, elderly care, and culture.

Table 5 Comparison of Industrial Development Orientations Between Chengdu and Chongqing During the 13th Five-Year Plan Period
Conclusion
In 2007, the two cities were approved as the national pilot areas for urban-rural comprehensive reform. At that time, Chengdu covered an area of 12,400 square kilometers and governed 19 districts (county-level cities) and counties, with a resident population of 12.58 million and an urbanization rate of 62.6 percent. Chongqing then had an area of 82,400 square kilometers and 40 districts (counties). At the end of 2007, Chongqing’s resident population was 28.16 million, and its urbanization rate was 48.3 percent. Due to different basic conditions, Chengdu and Chongqing have adopted different reform ideas and measures. Chengdu places more emphasis on systematic advancement while Chongqing attaches more importance to key breakthroughs. The reform of Chengdu’s planning management, production factors, industry, and public services is relatively balanced and coordinated, and its reform of urban and rural planning integration is implemented first, laying a foundation for the integration of production factors, industrial development, and public services. Its reform measures to promote the free flow of production factors, such as land, labor, and capital between urban and rural areas are also coordinated with industrial development measures, such as balanced development of the manufacturing service industry and the integration of agricultural, commercial, cultural, and tourism development. The integration of urban and rural transportation and the equalization of public services, such as medical care and education not only promote the integration of urban and rural society, but also provide strong support for the free flow of urban and rural production factors and coordinated development of industries. This systematic way is conducive to achieving focused fruitful local results. However, Chongqing has made breakthroughs in key areas, such as “l(fā)and ticket” transactions and the reform for the household registration system of migrant workers. The reform of these key aspects has helped Chongqing achieve remarkable results in improving economic efficiency, but it is insufficient in improving the balance of urban and rural development. From the perspective of three sub-goals of urban-rural economic integration, social integration, and life integration, the development results of urban-rural integration between Chengdu and Chongqing do differ in some aspects (Table 6).
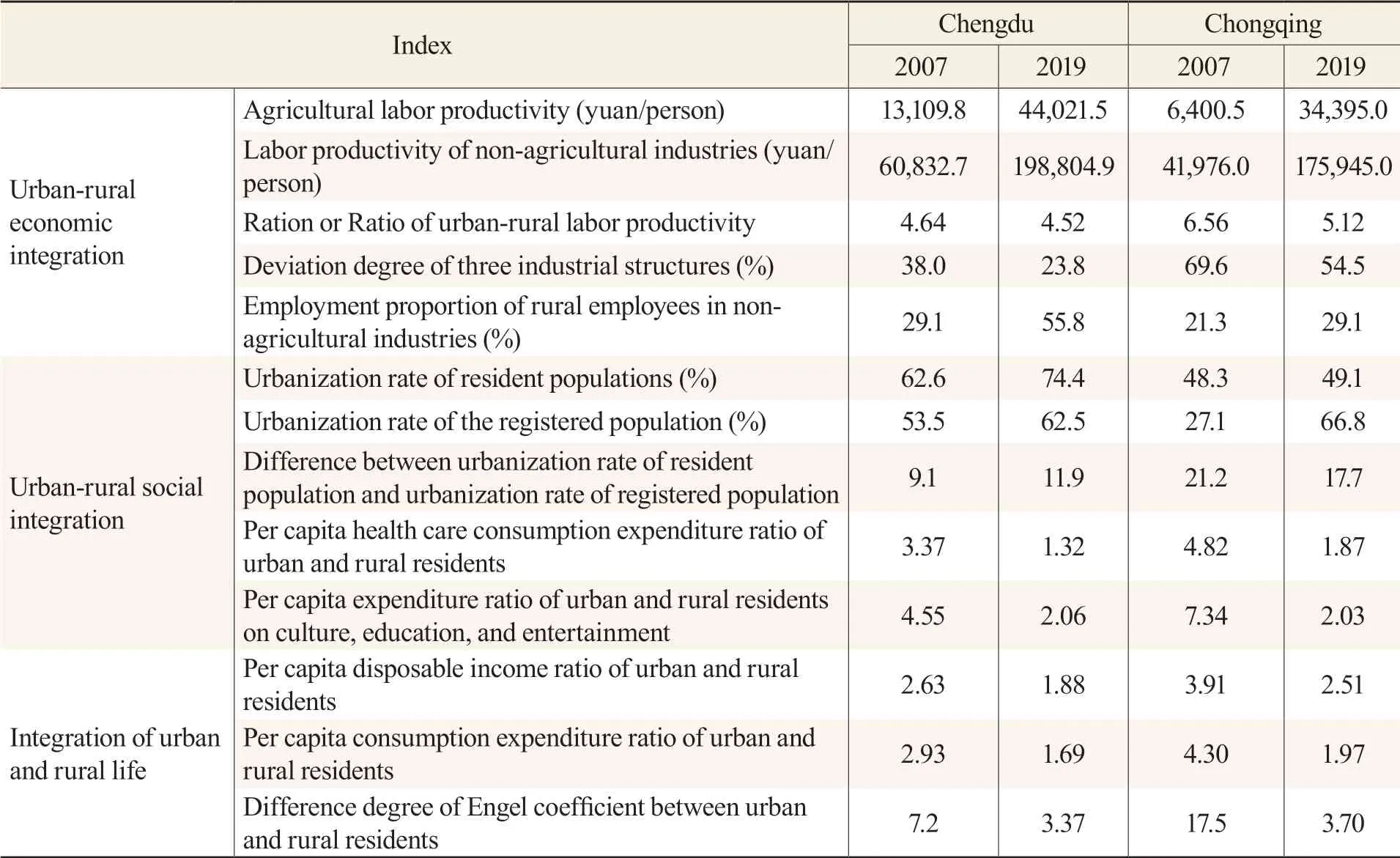
Table 6 Comparison of Development Levels of Urban-rural Integration Between Chengdu and Chongqing in 2007 and 2019
In the aspect of urban-rural economic integration, five indicators were selected for analysis: agricultural labor productivity, non-agricultural labor productivity, urban-rural labor productivity ratio, deviation degree of three industrial structures, and employment proportion of rural employees in nonagricultural industries. Agricultural labor productivity, non-agricultural labor productivity, and urbanrural labor productivity ratios reflect the operational efficiency and differences between urban and rural economic systems. The deviation degree of three industrial structures is an important method used by academia to measure whether industrial structures and employment structures are balanced. The closer the absolute value of industrial structure deviation degree is to 0, the higher the matching degree between industrial structures and employment structures is (Liu, 2019). The employment proportion of rural employees in non-agricultural industries reflects the development degree of rural non-agricultural industries, and this index can reflect the integration degree of urban and rural industries. Compared with the data in 2007 and 2019, all indicators of Chengdu and Chongqing have been significantly optimized. The ratio of labor productivity between urban and rural areas in Chongqing has been reduced from 6.56 to 5.12, and the gap between urban and rural economic development efficiency has been significantly reduced, which is closely related to the reform of its key areas. The deviation degree of Chengdu’s three industrial structures has been reduced from 38.0 to 23.8, the symmetry between employment structures and output value structures has been further improved, and the proportion of non-agricultural employment of rural employees has increased from 29.1 percent to 55.8 percent. According to the comparison of data 2019, the labor productivity of Chengdu’s agricultural and non-agricultural industries is higher than that of Chongqing, and the ratio of urban-rural labor productivity is lower than that of Chongqing so the difference between urban and rural labor productivities is smaller than that of Chongqing. The deviation degree of three industrial structures is lower than that of Chongqing so the employment structures and output value structures are relatively symmetrical, and the industrial structure benefit is higher. The employment proportion of rural employees in non-agricultural industries is 26.7 percent higher than that in Chongqing, and the level of urban-rural economic integration is relatively high.
In the aspect of urban-rural social integration, five indicators were selected for analysis: urbanization rate of the resident population, urbanization rate of the registered population, difference between urbanization rates of the resident population and the registered population, per capita expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents on health care, and per capita expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents on culture, education, and entertainment. Based the special national conditions of China’s household registration system, it is necessary to consider the urbanization rates of the resident population and the registered population to comprehensively evaluate the urbanization development level. The difference between the urbanization rates of the resident population and the registered population can reflect the restrictions of the household registration system on the mobility of urban and rural populations to a certain extent. The per capita expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents on health care, cultural education, and entertainment can reflect the balanced degree of urban and rural residents in public services, such as medical care, education, and culture from different aspects. The urbanization rates of Chengdu’s resident population and registered population are much higher than those of Chongqing, and the difference between them is much lower than that of Chongqing so the flow of the population between urban and rural areas is relatively high, and the urbanization process of the population is leading. From 2007 to 2019, the difference between the urbanization rate of Chongqing’s resident population and that of its registered population decreased from 21.2 percent to 17.7 percent, but the difference between the two is still at a high level and 5.8 percentage points higher than that of Chengdu. This reflects that on the one hand, Chongqing’s household registration reform has achieved certain results, but at the same time, it is still restricted by the reform progress of other subsystems, such as industry. In terms of the consumption expenditure ratio of urban and rural public services, the balance level of urban and rural public services in both places has been significantly improved. The per capita expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents on health care of Chengdu is lower than that of Chongqing while the per capita expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents on culture, education, and entertainment of Chengdu is slightly higher than that of Chongqing.
In the aspect of integration of urban and rural life, three indicators were selected for analysis: the per capita disposable income ratio of urban and rural residents, the per capita consumption expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents, and the difference degree of Engel’s coefficient between urban and rural residents. The per capita disposable income ratio of urban and rural residents is the most commonly used indicator in academia to comprehensively reflect the degree of urban-rural dual structures while the per capita consumption expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents and the difference degree of Engel’s coefficient between urban and rural residents can comprehensively reflect the difference degree of living standards between urban and rural residents. Whether it is 2007 as the starting point of reform or 2019 to reflect the effectiveness of reform, the per capita disposable income ratio of urban and rural residents and the per capita consumption expenditure ratio of urban and rural residents in Chengdu are lower than those in Chongqing, and the per capita disposable income ratio of urban and rural residents is only 1.88. According to international experience,①It is generally believed that when the urban-rural income ratio is ≥2, the city is in the state of urban-rural dual structure. When the ratio is equal to or more than 1.25 but less than 2, it is in the transition period from dual structure to urban-rural integration. When the ratio is less than 1.25, its process of urban-rural integration is basically completed.Chengdu has entered the transition period from urban-rural dual structures to urban-rural integration while Chongqing is still in the state of urban-rural dual structures. The difference of Engel’s coefficient between urban and rural residents in the two cities is close to and less than five percent.①The difference between urban and rural Engel coefficients can be defined as the difference between the Engel coefficient of non-rural residents and the Engel coefficient of urban residents. It is generally considered that when the difference of Engel coefficients is less than 5 percent, the quality of life of urban and rural residents tends to be the same. When the difference is 5-10 percent, the quality of life is quite different, and the city concerned is in the transitional period from dual structure to urban-rural integration. When the difference is more than 10 percent, there is still a great gap in the quality of life between urban and rural areas, and the dual structure between urban and rural areas is obvious.
The development of urban-rural integration involves all aspects of economy and society and touches on deep institutional obstacles. The goal is not to remove the limitations and obstacles in a certain local area, but to promote profound changes comprehensively and systematically in various systems and fields, and finally form an institutional mechanism for urban and rural integration, thus laying an institutional foundation for realizing scientific and harmonious development. Therefore, it is urgent to study the goal, structure, and function of the development of urban-rural integration from a systematic point of view. Chengdu represents a city which has entered the middle-to-last stage of urbanization, and the gap between its urban and rural areas is relatively moderate while Chongqing represents a city which urbanization rate is still around 50 Chengdu has the conditions to adopt systematic advancement while Chongqing can adopt key-point-based reform Chengdu’s high level shows that in the practice of urban-rural integration, independent policies and measures in local areas have limited effects. System efficiency can surpass the sum of local areas’ efficiencies only if a systematic method is adopted to comprehensively promote policies and measures for institutional innovations in various fields.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2022年1期
Contemporary Social Sciences2022年1期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- A Study of the Rain Classroom-Based Teaching Mode of College English for Art or Physical Education Majors
- Research on the Collaborative Innovation Model in Regional Social Governance
- Analysis of the Concept and Connotation of the New Economy and Reconstruction of Its Development Path: A Study Based on Chengdu’s Practices
- An Empirical Study on the Relationship Between the Scale of International Students from ASEAN and China’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment
- A Brief Introduction to Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences
- Requirements for Submissions
