Sarcopenia in hepatocellular carcinoma:Current knowledge and future directions
Abhilash Perisetti,Hemant Goyal,Rachana Yendala,Saurabh Chandan,Benjamin Tharian,Ragesh Babu Thandassery
Abstract Liver cancer is the second most occurring cancer worldwide and is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths.Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common (80%-90%) type among malignant liver cancers.Sarcopenia occurs very early in HCC and can predict and provide an opportunity to improve muscle health before engaging in the treatment options such as loco-regional,systemic,and transplant management.Multiple prognostic stating systems have been developed in HCC,such as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer,Child-Pugh score and Albumin-Bilirubin grade.However,the evaluation of patients’ performance status is a major limitation of these scoring systems.In this review,we aim to summarize the current knowledge and recent advances about the role of sarcopenia in cirrhosis in general,while focusing specifically on HCC.Additionally,the role of sarcopenia in predicting clinical outcomes and prognostication in HCC patients undergoing loco-regional therapies,liver resection,liver transplantation and systematic therapy has been discussed.A literature review was performed using databases PubMed/MEDLINE,EMBASE,Cochrane,Web of Science,and CINAHL on April 1,2021,to identify published reports on sarcopenia in HCC.Sarcopenia can independently predict HCC-related mortality especially in patients undergoing treatments such as loco-regional,surgical liver transplantation and systemic therapies.Basic research is focused on evaluating a balance of anabolic and catabolic pathways responsible for muscle health.Early clinical studies have shown promising results in methods to improve sarcopenia in HCC which can potentially increase prognosis in these patients.As sarcopenia occurs very early in HCC,it can predict and provide an opportunity to improve muscle health before engaging in the treatment options such as loco-regional,systemic,and transplant management.Further,sarcopenia measurement can obviate the confounding caused by the abdominal ascites in these patients.The use of sarcopenia can add to the existing scoring systems to better prognosticate the HCC.
Key Words:Sarcopenia;Skeletal muscle;Hepatocellular carcinoma;Cirrhosis;Outcomes;Liver cancer
lNTRODUCTlON
Primary liver cancers include hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and other non-HCC tumors.Primary liver cancers are the second most lethal cancer worldwide,fourth leading cause of cancer mortality and sixth frequently diagnosed cancer per year[1].HCC is the most common cancers among the primary liver cancers,which constitutes 90% of cases.HCC usually develops within a liver cirrhosis (cirrhotic-HCC,80% of cases),and rarely with no appreciable cirrhosis or advance fibrosis (non-cirrhotic-HCC,20% of cases)[2].Due to aggressive nature of HCC,prognosis is poor.This is compounded by delay in the treatment,limiting life expectancy and management options.Early identification of high-risk features for appropriate stratification,and prognostication in HCC is paramount to alter the disease course and improve survival.Several prognostic staging systems and biomarkers have been developed to identify the patients at risk of poor prognosis[3].Some of these include Cancer of the Liver Italian Program,Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC),Child-Pugh score,Chinese University Prognostic Index score,the Hong-Kong Liver Cancer stating system and Japan Integrated Staging.Further,biomarkers such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP),des-γcarboxyprothrombin AFP-L3,vascular endothelial growth factor,and angiopoietin 2 were used as independent prognostic factors in advanced tumors[4].However,current available staging and prognosticative systems lack parameters that consider nutritional,functional and performance status[5].Although long-term prognosis is dependent on the liver reserve and staging of the cancer,poor performance can significantly affect clinical outcomes in HCC patients.The use of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group classification with BCLC could provide an assessment of patients functional status.
Rosenberg[6] introduced the term“Sarcopenia,”which was coined from the Greek word“sarx,”or“flesh,”and“penia,”or“l(fā)oss.”It can be defined as loss of skeletal muscle mass,quality,strength with a reduction in the motor unit number,atrophy of type muscle fibers[7],and can contribute to frailty,functional impairment,and disability[8-11].Three most commonly used diagnostic criteria used for sarcopenia include“muscle mass”(height-adjusted),“muscle strength,”and/or“physical performance”[12].A focus on muscle function has shown to be a powerful predictor of clinically relevant outcomes rather than muscle mass alone[13].Recently,body mass index (BMI)-adjusted mass is found to be a better predictor of adverse outcomes than height-adjusted muscle mass[14,15].Further,multiple muscles or groups of muscles could be utilized to assess sarcopenia.Some of the most commonly used muscles include the paraspinal muscle area (psoas muscle,quadratus lumborum,transverse spinal muscle,erector spinae muscles) and triceps muscles (mid-arm circumference).Loss of skeletal muscle mass can affect static,dynamic and isokinetic strength[16].It can also be associated with a decline in the maximum oxygen consumption (at a rate of 3%-8% per decade of life starting from 30 years) which ultimately leads to a decrease in overall functioning[17].Dynamic changes in skeletal muscle mass and function can occur with changes in hormones (daily insulin,glucagon),anabolic steroids,corticosteroids,thyroid (month-to-month),and immune mediators [interleukin (IL)-1,tumor necrosis factor,and IL-2].Primary sarcopenia is noted to be due to physiological states such as aging and secondary causes (acute or chronic illness)[18].Individuals with cancer may deplete up to 80% of their muscle mass.Further,sarcopenia can be noted in as high as 80% and 60% of patients with upper gastrointestinal and lung cancers,respectively[19].Pre-therapeutic sarcopenia is noted with highest prevalence in esophageal and small-cell lung cancers and could have severe consequences in terms of post-operative complications,chemotherapy-related toxicity,and poor overall survival (OS)[20].
Cross-sectional imaging is commonly performed in HCC patients for diagnosis,surveillance,and treatment response[19].It is logical to use this cross-sectional imaging to evaluate skeletal muscle mass simultaneously for valuable information to assess the prognosis and treatment outcomes.Additionally,patients with cirrhosis and HCC commonly develop ascites spuriously increasing the abdominal girth and weight.Despite this increase,significant proportion of these patients have decreased muscle mass leading to“sarcopenic obesity[21].”Use of an objective tool (which is measurable and reproducible) to assess the survival of HCC patients with ascites remains a challenge.Furthermore,methods to assess the prognosis of HCC patients during/after loco-regional (radiofrequency ablation,radioembolization,chemoembolization),liver transplantation,and systemic therapy (chemotherapy,immunotherapy) could have a long-lasting impact on these individuals.One such objective method is to use sarcopenia to assess the patient response and overall could assist in OS in HCC patients[14,22-34].Therefore,this manuscript aims to describe the role of sarcopenia in the management and prognosis in HCC.Furthermore,we aim to describe and summarize the methods to improve sarcopenia to enhance the survival of patients undergoing treatment for HCC.
LlTERATURE SEARCH
An electronic search was performed using databases PubMed/MEDLINE,EMBASE,Cochrane,Web of Science,and CINAHL on April 1,2021,to identify published reports on sarcopenia in HCC.We used the following search terms-“carcinoma,hepatocellular”or“cancer,hepatocellular”and ”sarcopenia”or“sarcopenias”.A total of 4762 articles were published on sarcopenia and 167571 on hepatocellular cancers.Both basic science and clinical studies were included.A combined search revealed 2289 articles over the last 12 mo.The authors AP and HG reviewed the articles independently.Clinical reviews,case reports,and case series were excluded.A manual search was performed by evaluating the references from included studies and related articles in multiple databases.If any discrepancies,these articles were re-reviewed by the author RT.After removing non-relevant/duplicates/non-English language articles,including a manual search,80 full length published articles were finally reviewed.
HCC AND SARCOPENlA
Secondary sarcopenia is a common finding in patients with cirrhosis.Reduction in protein synthesis can lead to a decrease in lean body mass seen in cirrhotics[26].Protein catabolism seen in disease processes such as neoplasms can lead to significant loss of muscle mass and it can be seen up to 40% of patients with liver cirrhosis[35].Sarcopenia can be associated with an increased risk of encephalopathy,post-transplant mortality,infections,treatment effectiveness,and quality of life[36-38].Patients with cirrhosis who were diagnosis with HCC showed accelerated sarcopenia up to 30-40% at the time of diagnosis[39,40].Sarcopenia in these patients can independently predict HCC-related mortality along with decompensated cirrhosis,performance status,TNM staging,and BCLC class[41,42].However,each of these have limitations with biggest being lack of prognostication,inability to provide comprehensive tool to assess complex interactions between cirrhosis,HCC and functional capacity[43].Further,factors responsible for survival differ significantly among patients with compensated and decompensated cirrhosis[44].
As HCC occurs over time in patients with underlying chronic liver disease,assessment of skeletal muscle mass and change overtime can provide important details about deterioration of the disease.A number of tumor-related factors (cytokines and myokines) can change the skeletal muscle mass which can assist to further refine these scoring systems.Furthermore,cirrhotic have ascites,disproportionate loss of muscle compared to fat (altering BMI) leading to difficulty in interpreting bioimpedance,anthropometric measurements.Hence use of tools to integrate degree of sarcopeniarelated measurements by CT-based techniques can offer ways to predict change in these patients[45,46].
BlOLOGlCAL BASlS OF SARCOPENlA lN HCC
Sarcopenia is the condition characterized by loss of muscle strength,mass,and functional ability.The pathophysiology of this muscle loss can be multifactorial (hormonal,inflammatory,age-related,chronic liver and non-liver states,drug induced).Loss of muscle anabolic activity with nutritional deficiency can further worsen sarcopenia.Loss of skeletal muscle homeostasis especially between hypertrophy and regeneration can lead to sarcopenia.Most of the changes related to sarcopenia originates with normal aging process.A balance of muscle protein anabolic and catabolic pathways are responsible for muscle health.During sarcopenia,multiple cellular changes occur such as the reduction in myofibres (size and number),myosteatosis (development of intramuscular and intermuscular fat infiltration)[47],decreased number of type II fibre satellite cells.Further,loss of mitochondrial integrity,molecular signaling [IGF-1,mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTOR)],neurological (plaque formation,motor neuron loss),epigenetic change (modulatedviamicroRNAs),endocrine factors (myostatin,osteocalcin and abnormal communication among them) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) imbalance[48] combined with reduced physical activity can all contribute to the muscle loss.Some of the frequent causes of sarcopenia are elucidated in Figure 1.Hyperammonemia,increased autophagy,decreased protein synthesis,abnormal mitochondrial activity,increased proteasomal activity,and low testosterone levels are also responsible for sarcopenia cirrhosis[49,50].It is compounded by decreased metabolic substrates (especially branched-chain amino acids)[51],extrahepatic gluconeogenesis,and increased insulin resistance/pro-inflammatory cytokines (NFκB signaling,mTOR inhibition,enhanced apoptosis,eukaryotic initiation factor-2[52].Portal hypertension-related complications and alcohol intake further worsen sarcopenia in cirrhosis[53,54].
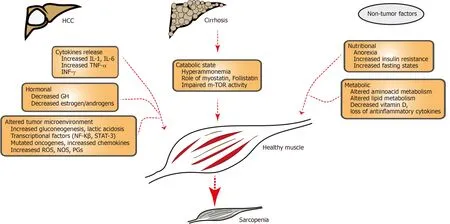
Figure 1 Schematic illustration showing factors contributing to sarcopenia in hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis.Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma have increased release of cytokines,hormonal substances (GH,anabolic steroids) and altered tumor microenvironment (with hypercatabolic state,mutagenesis included by altered DNA,increased reactive oxygen species.Patients with HCC have underlying cirrhosis with hyperammonemia,decreased m-TOR activity which can contribute to sarcopenia.Non-tumor factors include poor nutrition and altered amino acid or lipid metabolism.HCC:Hepatocellular carcinoma;IL-1:Interleukin-1;IL-6:Interleukin-6;TNF-α:Tumor necrosis factor alfa;INF-γ:Interferon gamma;GH:Growth hormone;NF:Nuclear factor kappa B;STAT-3;Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3;ROS:Reactive oxygen species;NOS:Nitric oxide species;PGs:Prostaglandins;mTOR:Mechanistic target of rapamycin.
Early sarcopenia can be seen in HCC individuals[24,55].Myokines (myostatin,IL-6,follistatin) are cytokines produced and secreted by muscle fibers and can exert paracrine/autocrine effects[33].Myokines can exert immunological and anti-inflammatory effects and facilitate proinflammatory state of liver fibrosis,cirrhosis,and HCC development.Although myostatin levels in HCC have been a matter of debate,high IL-6 and follistatin levels had a significantly lower 5-year OS rate in HCC and were related to tumor progression by BCLC/TNM staging in HCC[33].Follistatin is a glycoprotein and inhibitor of the TGF-β superfamily (such as myostatin,activin),and it can be related to tumor stage,size and can play an oncogenic role in hepatocarcinogenesis.These details provide important insights into potential agents such as myostatin inhibitors,mitochondrial protective agents,and antioxidants,which can be utilized for liver cirrhosis or HCC[55].Such anti-sarcopenic treatments could be used to prolong or further reverse molecular,and metabolic changes noted in HCC patients.
CHANGES lN SARCOPENlA WlTH HCC TREATMENTS
Sarcopenia in HCC patients undergoing various treatments (locoregional and systemic) has been shown to impact outcomes and survival.Multiple studies have reported outcomes among these patients.It has been showed that a baseline sarcopenia is associated with lack of response to HCC treatments,further decompensation episodes,and increased mortality[56].In the following sections,we elaborate on studies evaluating the role of sarcopenia in HCC patients with various treatments such as loco-regional,surgery,transplant,and chemo/immunotherapy.
LOCO-REGlONAL THERAPY
Patients with HCC can be candidates for multiple loco-regional treatment (LRT) options such as radiotherapy,chemoembolization,radioembolization.Data on sarcopenic predicting response to LRT is sparse (Table 1)[14].Iritaniet al[15] reported 217 HCC patients on LRT and evaluated the role of sarcopenia.In this study,L3 skeletal muscle index (SMI) was used to define sarcopenia.Patients with low L3 SMI showed a significantly lower OS compared to those without sarcopenia (P=0.004).Further,obese sarcopenic patients died earlier (P=0.013)[15].In 2015,Fujiwaraet al[57] showed a higher risk of HCC recurrence in sarcopenic patients in 515 patients with BCLC stage 0/A who underwent percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA).In 2017,a retrospective study of 182 patients with HCC undergoing percutaneous RFA therapy with curative intent was analyzed[58].Patient with sarcopenia decreased pretreatment psoas muscle index (PMI) survival (overall cumulative survival) was51.5% compared to 86.5% without sarcopenia (P< 0.0001.In addition to sarcopenia,total bilirubin ≥ 1.2 mg/dL,des-γ-carboxy prothrombin ≥ 34 mAU/mL (P=0.009) were found to be adverse predictors of OS [58].These findings were irrespective of CTP score or achievement of SVR in HCV-related HCC.Furthermore,above findings indicate the usefulness of sarcopenia to assess outcomes of HCC patients undergoing RFA.

Table 1 Outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing loco-regional therapy with sarcopenia
Trans-arterial interventions for the HCC can be chemoembolization (TACE) or radioembolization (TARE) and are increasingly being utilized for large or multifocal disease with metastasis or macrovascular invasion[27].The available data are conflicting about the role of sarcopenia as a predictor of survival in HCC who underwent TACE (Table 1).Fujitaet al[59] and Kobayashiet al[60] showed no significant association between muscle volume at baseline and clinical outcomes.On the contrary,Loosenet al[61] and Dodsonet al[38] showed that pre-interventional sarcopenia was associated with poor outcomes.Significant heterogeneity was noted in the methods to evaluate sarcopenia in these studies.The total psoas area (TPA),PMI,and L3-SMI were used to evaluate the presence of sarcopenia.If sarcopenia directed these effects (on the TACE efficacy) beyond the patients’ general clinical condition or if this is mere an association,needs further evaluation in a prospective fashion.Data on the effects of sarcopenia on HCC patients with TARE is even more limited.Recently,Faronet al[32] reported 58 HCC patients using MRI-derived fat-free muscle area (FFMA) to predict sarcopenia.The FFMA < 3582 mm2for men and < 2301 mm2for women were used.In this study low FFMA was associated with significantly reduced OS (197vs294,P=0.02)[32].
SURGlCAL TREATMENTS
Liver resection
The role of sarcopenia in HCC patients undergoing liver resection is increasingly become topic of interest.Since,HCC patients often have poor nutritional status,methods to reduce the catabolic state and improve protein synthesis,regeneration,Fanet al[62] investigated 124 patients to evaluate the role of nutrition in HCC resection.Nutrition therapy given prior to the liver resection with branched chain amino acids (BCAA),lipids,and dextrose have shown to decrease the worsening of liver function,sepsis-related complications,need for treatment for ascites,and overall decreased mortality.There was a reduction in the overall post-operative morbidity in the nutrition group compared to the control group (34%vs55%;relative risk,0.66;95%CI:0.45-0.96)[62].In 2013,Harimoto and colleagues[63] studied 186 HCC patients with sarcopenia using L3-SMI (< 43.75 for men,< 41.10 for women),and a significant correlation was noted between sarcopenia and liver dysfunction (indicated by low albumin levels and indocyanine green retention).In patients with and without sarcopenia,the 5-year OS rate was 71% and 83·7%,and the 5-year recurrence-free survival rate was 13% and 33·2%,respectively[63].Additionally,studies evaluated the relationship between total functional liver volume (TFLV) and sarcopenia (L3-SMI) and found that median TFLV was significantly lower in the sarcopenic group than the normal group (1296 mLvs1840 mL;P< 0.05)[64].
Sarcopenic obesity characterized by increased fat volume compared to skeletal muscle mass.As obesity and loss of muscle share common pathophysiological mechanisms,combined insult could display a poor outcome.Studies evaluated the effect of sarcopenic obesity in HCC and found that patients with sarcopenic obesity had worse median survival (84.7 movs39.1 mo,P=0.002) and worse median recurrence-free survival (21.4 movs8.4 mo,P=0.003)[21].Additionally,it was identified as an independent risk factor for death and HCC recurrence[21].Effect of sarcopenia on immediate and short-term clinical outcomes after hepatic resection was examined by Otsujiet al[65] Sarcopenic patients had a higher postoperative length of stay,higher rates of liver failure,major complications,and intra-abdominal abscess formation (Table 2).Multiple other studies have provided similar results with different modalities to evaluate sarcopenia,such as L3-SMI,TPA,and visceral-to-subcutaneous adipose tissue ratio (Table 2).Furthermore,these studies used differing SMI cut-off points to define sarcopenia.The majority of the studies point to poor outcomes in patients with sarcopenia,which might be due to the underlying liver dysfunction and HCC severity.Nevertheless,prospective data with uniform cut-off points to assess SMI to define sarcopenia in these studies to provide concrete evidence of the relationship between sarcopenia and liver resection.
Liver transplantation
Sarcopenia in patients awaiting liver transplantation (LT),perioperative and postoperative outcomes have been studied recently[66-71].Multiple methods to assess sarcopenia were used (Table 3).For example,L3-SMI,psoas muscle thickness,MELDsarcopenia score,skeletal muscle mass-to-visceral fat area ratio (SVR),TPA,PMA,and height normalized psoas muscle thickness were used.Among these,L3-SMI is the most commonly used objective way of assessing sarcopenia.Further,studies evaluated the wait times and survival related to sarcopenia (Table 3).

Table 2 Outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing liver resection (hepatectomy) with sarcopenia over last 5 years
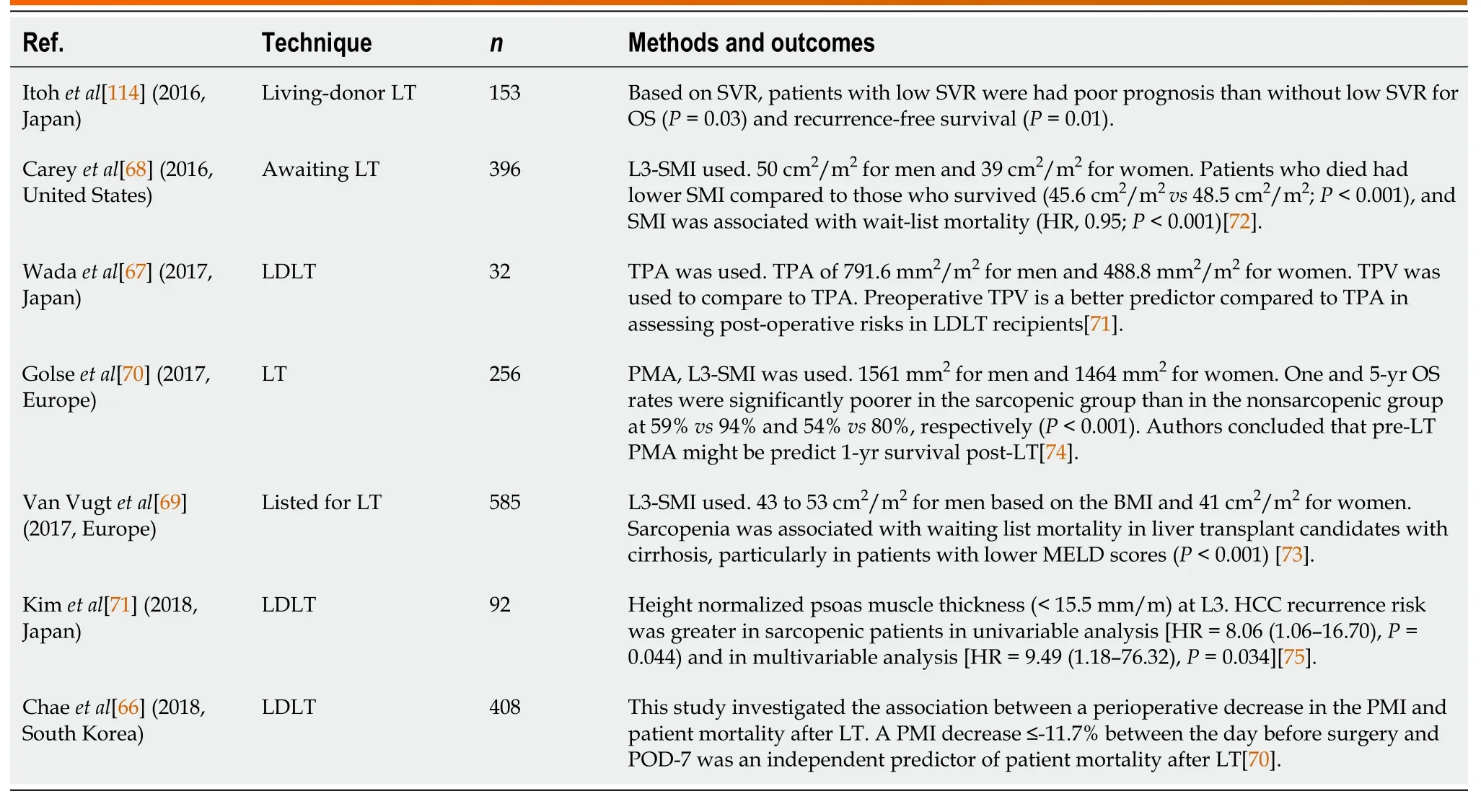
Table 3 Outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing liver transplant with sarcopenia over last 5 years
Studies performed on outcomes in LT patients evaluated the preoperative status of the patients (listed and waiting for the transplant),procedural outcomes and postprocedure long-term survival.Careyet al[68] in 2016 used L3-SMI with 50 cm2/m2for men and 39 cm2/m2for women and noted that individuals who died had lower SMI compared to those who survived (45.6 cm2/m2vs48.5 cm2/m2;P< 0.001),and SMI was associated with wait-list mortality (HR,0.95;P< 0.001).Wadaet al[67] in 2017 considered sarcopenia for TPA of 791.6 mm2/m2for men and 488.8 mm2/m2for women.The authors compared TPV to TPA.The preoperative total psoas volume (TPV) was found to be a better predictor than TPA in assessing post-operative risks in living-donor LT recipients[67].Multiple studies evaluated the LT outcomes and complications such as infections,length of stay,failure to rescue,and surgery-related events[72,73].The rate of infections was assessed and compared to individuals with sarcopenia.Patients with sarcopenia had a higher prevalence of sepsis,bacterial pneumonia,longer ICU stays,and mortality[2,69].Postoperative survival was studied by Van Vugtet al[69] and Kaidoet al[72] who noted that sarcopenia was inversely associated with clinical outcomes after LT.Few studies noted sarcopenia developing after the LT,which is probably due to underestimation of muscle mass/strength estimation before LT.In addition to underlying cirrhosis,increased catabolism,tumorrelated morbidity noted in these patients,the role of immunosuppressant use cannot be underestimated.The use of mTOR and calcineurin inhibitors can potentially lead to sarcopenia[74].Further,renal dysfunction caused by calcineurin inhibitors can compound these effects.The results of these studies provide an opportunity for improving the nutritional status in sarcopenia LT patients with dietary and exercisemeasures during pre,peri and post-operative period.
Systemic therapies
The use of chemotherapy and immunotherapy has become the mainstay of treatment for HCC lesions that are not amenable to LRT or LT.Sorafenib is the most studied and prescribed chemotherapeutic agent in HCC[75].Although it can prolong survival,its use is limited by its adverse effects such as nausea,excessive fatigue,and diarrhea noted in most patients.These studies evaluated multiple outcomes such as OS,progression-free survival,mortality were evaluated in different studies in HCC patients receiving Sorafenib therapy[76-82].While the ways to assess the sarcopenia differed in these studies,most commonly used method is L3-SMI.Further various cutoff values were utilized in these studies.
Nishikawaet al[78] studied 232 patients to evaluate for OS using L3-SMI.The authors noted that the patients with sarcopenia had significantly low median OS of 174 d compared to 454 d in the non-sarcopenic group (P< 0.0001).Multivariate analysis showed that sarcopenia was an independent predictor of OS.Similarly,Takadaet al[81] studied 214 patients in which OS in pre-sarcopenia patients were worse than without pre-sarcopenia (median 252 dvs284 d,respectively;P=0.16).Saekiet al[82] reported 100 advanced HCC patients using use of L3-SMI showing individuals without muscle depletion had longer survival was noted (HR=0.50,P=0.006).This combined with low tumor number (< 7) and lack of extrahepatic spread offered better survival in these patients[82].Dynamic assessment of sarcopenia has assisted to compare outcomes before and after starting sorafenib.Few studies noted that sarcopenia worsened after the initiation of sorafenib.If this is due to the progression of HCC or angiogenic (or Carnitine inhibitory) properties of sorafenib needs further evaluation[83].Further,Chenget al[34] reported that pre-sarcopenia could independently predict the outcomes in sorafenib-failed HCC.
Use of other modalities such as fat mass indices (visceral,subcutaneous) in combination with L3-SMI and their relative changes (over a period of time) can assist in assessing sarcopenia and can predict outcomes in HCC patients receiving sorafenib[82].However,more studies are needed to confirm these findings.Recently newer agents for HCC are increasingly utilized such as Regorafenib,Lenvatinib,Nivolumab,the combination of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (GEMOX regimen)[30,84-86].Studies showing the effect of sarcopenia on HCC patients' survival using these agent aresparse.Lenvatinib induces minimal muscle loss after 2 years of treatment correlates with its low toxicity[23,30,87].Combined effects of sarcopenia and inflammation (by high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and absolute lymphocyte count) have been studied in patients receiving nivolumab in HCC patients[28].If inflammatory markers are more important than sarcopenia in patients received immunotherapy needs further validation[25,28].Overall,sarcopenia can predict survival in advanced HCC patients receiving chemotherapeutics such as sorafenib before initiation of the treatment and during and after the treatment.Strategies to improve the muscle mass,nutrition can add to the survival in these patients.Further studies are needed to evaluate the role of sarcopenia for new chemotherapy and for immunotherapy.
METHODS TO lMPROVE SARCOPENlA
As sarcopenia can adversely affect the outcomes of HCC patients undergoing treatments,methods to improve could impact the survival of these patients.As HCC happens with a background of cirrhosis in up to 80%-90% of patients,improving sarcopenia in cirrhotics could assist in improving survival.Reversing pathophysiology by improving myofibres size,number,reversing myosteatosis,inhibiting mitochondrial integrity loss,mTOR signaling,and decreasing ROS accumulation can improve sarcopenia in both HCC and cirrhotics.Two major strategies exist to improve sarcopenia in these patients-nutritional support and physical exercise.Use of Lcarnitine,BCAA,leucine have been used in the studies to increase the nutritional component[88,89].Improvement of skeletal mass (PMI) was noted after the supplementation of these agents in these studies.Physical exercise can recruit more myofibres and at least inhibit sarcopenia.It is unclear if it can reverse the sarcopenia completely.Both isometric (lifting hand weights 2-3 times per week) and isotonic (30-40 min walking 3-4 times per week) have been used to improve muscle strength in these patients[90-94].Studies have shown an increased muscle cross-sectional area (quadriceps) with exercise in cirrhotics of at least 10%[95].Although,testosterone supplementation have been reported to improve the sarcopenia,few reports of alphaalkylated formulation could theoretically increase the risk of HCC formation[96].
The role of non-steroidal Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators (SARMs) is increasingly being recognized in the treatment of sarcopenia[97-99].SARMs inhibit protein degradation and thereby could decrease the rate of sarcopenia.Multiple animal models have been used to evaluate mechanisms of SARMs to reverse muscle atrophy in degonadized mice.For instance,SARM treatment in ovariectomized rat model can increase muscle mass by enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis,actin and myosin[98].SARMs can target androgen receptors and decrease sarcopeniaviaparacrine growth factor signaling on vimentin positive muscle fibroblasts[97].Further,upregulation of mTOR,glycogen synthase kinase[99].SARMs also exhibit anabolic effects,increasing the bone and muscle mass which are affected in patients with HCC.A combination approach of nutritional supplementation with physical exercise with a multidisciplinary approach has been tried in cirrhotics and HCC patients[31].Significant changes in muscle volume was noted after the intervention[95].Similarly,a combined approach has been tried in a few studies in HCC patients undergoing TACE[100,101].This approach has been studied in patients waiting or LT,with good response[102,103].In conclusion,a combined multidisciplinary approach is useful and logical to improve the sarcopenia in cirrhotics and HCC which might eventually improve outcomes of these patients undergoing local,surgical and systemic therapies.
FUTURE DlRECTlONS
Although sarcopenia can offer significant details about the functional status,it can be further enhanced by the use of frailty (using clinical frailty scale,liver frailty index,Karnofsky performance status) and amount of malnutrition (by assessment of BMI,nutritional intake).These can be incorporated into composite scoring to better evaluate the functional status of HCC patients.Recently use of changes in bone resorptionviaupregulation of inflammatory cytokines opened the concept of sarcopenic osteoporosis[104].A crosstalk between skeletal muscle,bone homeostatic changes with underlying cirrhosis and HCC can provide pathways for treatments in the future.Myostatin,irisin,osteocalcin,activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathways have been implicated in sarcopenic osteoporosis.Furthermore,biomarkers such as imbalance of plasma free amino acids (BCAA) have been implicated in progression of HCC[105].If this could be a reliable way to improve the sarcopenia in HCC patients remains to be studied.
Precision medicine tools such as use of radiomics and radiogenomics are emerging for assessing host and tumor-related risk factors in HCC[106,107].Radiomics uses medical imaging data to develop reproducible quantitative data from qualitative images.This has been utilized for lung cancer assessment of tumor and non-tumor tissue[108].Development of methods to quantify the amount of normal non-tumor liver tissue in HCC patients is essential for surgeons to evaluate resection strategies.Seroret al[109] noted that use of non-invasive cross-sectional imaging to assess the liver surface nodularity and lean body mass can act as surrogate markers for liver cirrhosis and sarcopenia.Patients with higher liver surface nodularity (OR 7.05,95%CI:2.13-23.25) and sarcopenia (OR 6.51,95%CI:2.08-20.39) were associated with high risk of complications[109].A step further in this direction,use of genomics (cellular and molecular changes) to existing radiomics can provide radiogenomic information which can be used to develop molecular signatures for development for actionable clinical targets[107].Finally use of artificial intelligence and deep learning can lead to next generation biostatistical and informatic data to develop algorithms and pathways to identify optimal clinical patterns[106].
CONCLUSlON
Sarcopenia is increasingly recognized as a predictive marker for assessing outcomes in HCC patients.There is increasing evidence to evaluate its role in loco-regional,surgical,transplant,and systemic treatment options in HCC patients.Early recognition to identify sarcopenia,methods to improve the muscle volume,strength,and mass could impact the patient outcome and OS.The use of appropriate nutritional support,physical activity or both could potentially improve muscle volume in these patients.However,it is unclear about the degree of improvement of the sarcopenia with all of these measurement combined.Further,prospective studies aimed at interventions that could potentially reverse sarcopenia to improve HCC patients' outcomes are needed in the future.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2022年4期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2022年4期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- ls CA19-9 effective in predicting chemotherapeutic response in patients with synchronous liver metastases with colorectal cancer?
- lnterplay between chronic hepatitis B and atherosclerosis:lnnovative perspectives and theories
- Fibrinogen-like protein 2 deficiency inhibits virus-induced fulminant hepatitis through abrogating inflammatory macrophage activation
- Knockdown of DEAD-box 51 inhibits tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the Pl3K/AKT pathway
- Celiac disease:From genetics to epigenetics
- Gut bless you:The microbiota-gut-brain axis in irritable bowel syndrome
