Calcifying fibrous tumor of the gastrointestinal tract: A clinicopathologic review and update
Donald Turbivlle, Xuchen Zhang
Abstract Calcifying fibrous tumor (CFT) is a rare mesenchymal lesion that has been documented throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal CFTs may occur at virtually any age, with a predilection for adults and for females. They occur most commonly in the stomach and the small and large intestines. CFTs are most often found incidentally, cured by local resection, and have a low risk of recurrence. Histology shows three characteristic features: Spindle cell proliferations within a densely hyalinized stroma, scattered calcifications, and lymphoplasmacytic inflammation. CFTs are immunoreactive for CD34, vimentin and factor XIIIa, helping to distinguish them from other benign mesenchymal neoplasms. The differential diagnosis of CFTs includes sclerosing gastrointestinal stromal tumor, leiomyoma, schwannoma, solitary fibrous tumor, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, plexiform fibromyxoma, fibromatosis, sclerosing mesenteritis, and reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor. The pathogenesis of CFTs remains unclear, but some have hypothesized that they may be linked to IgG4-related disease, inflammatory myofibroblastic lesions, hyaline vascular type Castleman disease, sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of the spleen, or trauma.
Key Words: Calcifying fibrous tumor; Calcifying fibrous pseudotumor; Gastrointestinal tract; Mesenchymal lesion; Calcification; Pathology
INTRODUCTION
Calcifying fibrous tumor (CFT) is a rare benign mesenchymal lesion that was first described by Rosenthalet al[1]in 1988. Originally, CFTs were considered to primarily be tumors of soft tissue sites. Since that time, CFTs, also described as calcifying fibrous pseudotumors, have been documented at a variety of anatomic sites including the pleura, mediastinum, heart, lung, neck, mandible, spine, back, arm, thigh, as well as oral, inguinal, paratesticular, and intrascrotal locations[2]. Recently, CFTs arising from the gastrointestinal tract have been documented, with CFTs reported in the small bowel, large intestine, stomach, esophagus, and appendix[3]. Previously thought to be rare in the gastrointestinal tract, improved clinical recognition of this entity has led to the observation that the majority of these tumors may in fact arise in the gastrointestinal tract[2,4]. The occurrence of CFTs in the gastrointestinal tract presents a diagnostic dilemma, firstly due to the rarity of the lesion, and secondly, due to the occurrence of a variety of other stromal lesions in the gastrointestinal tract with histologic features that overlap with CFT. Here we provide a review and update of the clinical and pathologic features of CFTs, as well as a description of other stromal lesions to consider in the differential diagnosis of CFT.
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
CFTs of the gastrointestinal tract are rare lesions with nonspecific clinical features. The tumor has a predilection for adults with a median age of 49.2 years and occurs slightly more often in females[2,3]. CFTs have been reported in the stomach, small intestine, colon, and appendix, with one documented case arising in the esophagus[2-5]. Previous studies have shown the most common sites to be the stomach and small bowel, however, a recent large case series found a higher frequency of CFTs in the large bowel than in the stomach[2,3,6]. CFTs are most commonly asymptomatic and discovered incidentally[2]. When present, symptoms are non-specific and most commonly include abdominal pain and discomfort[2,3]. Additional symptoms include lack of appetite, fever, weight loss, fatigue, dyspepsia, flatulence, halitosis, nausea, vomiting, red blood per rectum, and altered bowel habits[2]. CFTs are occasionally associated with more severe manifestations including gastric ulcers, obstruction, intussusception and volvulus[3,6].
Imaging findings show evidence of a mass lesion but are not specific for CFT. The clear border, coarse calcification on conventional ultrasound and peripheral hypoenhancement without central enhancement on contrast-enhanced ultrasound may help to distinguish CFT from other lesions[7].
Computerized tomography scan typically shows a well-circumscribed, homogenous mass with mild enhancement and calcification[6]. Magnetic resonance imaging examination may show isosignal intensity on gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted imaging and hyposignal intensity on T2-weighted imaging[8].
PATHOLOGIC FINDINGS
The gross examination of gastrointestinal CFTs reveals a well-circumscribed, unencapsulated, spherical to lobulated mass with variable calcifications. Sectioning reveals a homogenous, partially gritty, grey-white cut surface that is firm to rubbery (Figure 1A and B). The average size is 2.6 cm with a range in size of less than 1 to greater than 10 cm[9].
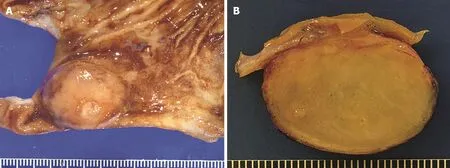
Figure 1 Gross findings of calcifying fibrous tumor. A: Partial gastrectomy showing a submucosal calcifying fibrous tumor mass lesion; B: Cut surface of calcifying fibrous tumor showing a well-circumscribed, unencapsulated, firm mass with variable calcifications.
The histologic features that characterize CFTs include well-circumscribed, unencapsulated hypocellular spindle cell proliferations embedded within abundant hyalinized collagen. The collagen may be arranged in a haphazard or whorled pattern (Figure 2A). The spindle cells exhibit bland, ovoid, vesicular nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (Figure 2B). Atypia and mitotic figures are rare with less than 1 per 10 high power field. Necrosis is universally absent. Scattered calcifications are common and may be psammomatous or dystrophic. A lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate is virtually always present (Figure 2C), and may occasionally form lymphoid follicles (Figure 2D), which in turn may have germinal centers. A lymphoplasmacytic cuff may be noted at the periphery of the tumor. Entrapment of nerves or adipocytes is only rarely observed[3,6].
Immunohistochemically, the spindle cells stain positively for CD34, vimentin and factor XIIIa. Smooth muscle actin, muscle specific actin, ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase), desmin, S100, cytokeratin, DOG1 (discovered on gastrointestinal stromal tumors protein 1) and c-kit immunostains are typically negative[6,10].
PATHOGENESIS
Currently, the pathogenesis of CFT is uncertain. Possible etiologies include previous infection, trauma or surgical intervention. The plasma cells in CFT may stain positively for IgG and IgG4, which has raised the possibility that CFT may be a manifestation of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD)[9]. IgG4-RD leads to formation of pseudotumors, most commonly in the pancreas[11]. Similar to CFT, IgG4-RD gives rise to inflammatory mass lesions that are clinically benign. However, IgG4-RD giving rise to mass lesions in the stomach is remarkably rare, although such cases have been reported[12]. Histologically, IgG4-RD shows storiform fibrosis, lymphoplasmacytic inflammation, and obliterative phlebitis[11]. CFT similarly shows a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, and the dense fibrosis seen in CFT frequently shows a vaguely but not classic storiform pattern[13]. Cases of CFT with increases in IgG4-positive plasma cells have been reported, occasionally with elevated serum IgG4[9,14,15]. However, cases of CFT in patients with other manifestations of IgG4-RD such as autoimmune pancreatitis type I are often lacking. Histologic evidence of obliterative phlebitis, a major criterion of IgG4-RD, has not been convincingly demonstrated in CFT. Furthermore, the finding of variably increased IgG4-positive plasma cells is nonspecific, and may be seen in a variety of inflammatory conditions[16].
It has been hypothesized that CFT may represent a late sclerosing (“burnt-out”) phase of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT). This hypothesis was formed due to the observation that CFT and IMT may co-exist in close proximity in the same patient[17]. Late-stage IMTs are paucicellular with dense collagenous fibrosis and are occasionally associated with calcification. Studies showing the presence of ALK rearrangements in IMT, which are not present in CFT, have suggested that CFT is a distinct neoplastic process[18]. However, genome-wide methylation analysis has shown overlapping methylation patterns of CFT and IMT, suggesting that both lesions may represent a spectrum of the same disease, irrespective of gene fusion analysis[19].
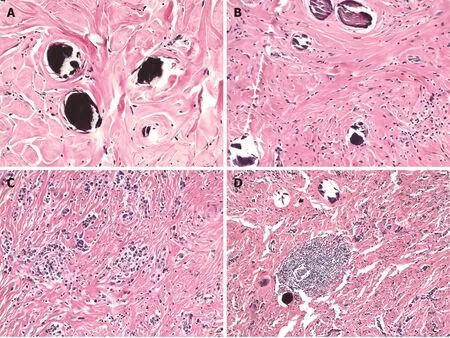
Figure 2 Histologic features of calcifying fibrous tumor. A: Haphazard or whorled pattern hyalinization admixed with calcifications (original magnification 200 ×); B: Dense hyalinization admixed with spindle cells and psammomatous calcification (original magnification 200 ×); C: Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in a background of dense hyalinization (original magnification 200 ×); D: Lymphoid follicle in a background of dense hyalinization and scattered calcification (original magnification 100 ×). Hematoxylin-eosin stain.
CFT has also been associated with hyaline vascular type Castleman disease, although such an association appears to be remarkably rare. Castleman disease is a benign lymphoproliferative disorder that may occur in a single (unicentric) or in multiple (multicentric) lymph nodes. The hyaline vascular type is characterized by germinal centers surrounded by concentric rings of mantle zone lymphocytes and a hyalinized vascular proliferation between follicles[20]. Six cases have been reported from 1999 to 2019 in which CFT was found in association with hyaline vascular type Castleman disease[21-26]. In some cases, both CFT and hyaline vascular type Castleman disease were found to co-exist within the same lymph node tissue[21,22,25,26], while in other cases, patients with gastrointestinal CFTs were found to have hyaline vascular type Castleman disease in adjacent lymph nodes[23,24]. The etiology of this association remains unclear and raises the possibility that both entities may represent different stages of the same reactive disease process. It has been suggested that CFT-like features in lymph nodes of patients with hyaline vascular type Castleman disease are the result of fine needle aspiration-induced trauma, supporting the notion that CFTs may be reactive proliferations resulting from trauma[21,22]. Further supporting this theory are reports of patients developing soft tissue CFTs within a few months of sustaining trauma at the same anatomic site[27]. However, many cases of CFTs in the gastrointestinal tract are not associated with a prior history of trauma or acute tissue injuries such as peptic ulcers or perforations, suggesting that gastrointestinal tract CFTs may be the result of chronic tissue injury, rather than acute trauma, or may have a different pathogenesis altogether. The passage of food contents conceivably exposes the gastrointestinal tract to localized tissue injury that may induce an inflammatory sclerotic reaction, ultimately giving rise to CFTs, and potentially accounting for the relatively high frequency of CFTs in the gastrointestinal tract.
An additional rare association has been made between CFT and sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of the spleen (SANT). SANT refers to a splenic non-neoplastic vascular proliferation of unknown etiology, histologically characterized by nodules with vascular spaces lined with plump endothelial cells interspersed with ovoid or spindle cells, surrounded by concentric collagen fibers[28]. Rare cases of SANT co-existing with disseminated abdominal CFTs have been described[29,30], and suggest a possibly common reactive mechanism. Additionally, increased IgG4-positive plasma cells have been observed in SANT and in associated CFTs, suggesting that both processes may be pathophysiologically associated with IgG4-RD[29].
Ultimately, the pathogenesis of CFTs remains unclear, although emerging evidence has suggested that these lesions may be pathophysiologically associated with other inflammatory lesions such as IgG4-RD, IMT, hyaline vascular type Castleman disease, or SANT. CFTs may represent a late-stage manifestation of any one of these lesions. Alternatively, CFTs may simply represent an end-stage manifestation of a variety of inflammatory and sclerotic processes, without regard to a specific etiology. This may account for the association of CFT with such a variety of other lesions. Other genetic and/or environmental factors, such as trauma, may contribute to formation of CFTs, and etiologies may differ based upon anatomic site. More studies are needed to further elucidate the pathogenesis of CFT.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
CFT, with a hypocellular spindle cell proliferation, abundant hyalinized collagen, scattered calcifications, and variable degree of lymphoplasmacytic inflammation, lends itself to a myriad of differential diagnostic considerations. The differential diagnosis for CFT of the gastrointestinal tract includes gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), schwannoma, leiomyoma, solitary fibrous tumor, IMT, plexiform fibromyxoma, fibromatosis, sclerosing mesenteritis, and reactive nodular fibrous pseudotumor (RNFP).
Spindle cell GIST consists of a uniform, bland spindle cell population arranged in short fascicles[31]. The sclerosing subtype of GIST shows extensive collagen deposition with relatively low cellularity, and frequently shows calcifications, complicating distinction of this entity from CFT[32]. Features that, when present, would favor CFT over sclerosing GIST include psammomatous calcification and a prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Immunohistochemically, the spindle cells of GIST stain diffusely positive for c-kit and DOG1, while these stains are negative in CFT. CD34 immunostaining is positive in both entities, however, positivity is typically variable and focal in CFT and diffuse in GIST[3,31]. The mutations of c-kitandPDGFRAcommonly seen in GIST were not identified in gastric or colonic CFTs, and can be used to differentiate these two entities at the molecular level[13,33].
Gastrointestinal schwannomas are most commonly found in the stomach and consist of spindle cells with “wavy” nuclei and tapered ends that are arranged in a microtrabecular pattern[34]. A peripheral lymphoid cuff is characteristic of schwannoma and may be a confounding factor with CFT. A microtrabecular pattern and scattered atypical cells assists in distinguishing schwannoma from CFT. However, definitive exclusion of schwannoma is best accomplished by S100 staining, which is diffusely positive in schwannoma and negative in CFT.
Leiomyomas typically arise in the stomach, sigmoid colon, rectum and esophagus and consist of spindle cells with elongated, cigar-shaped nuclei and abundant red-pink cytoplasm[35]. Similar to CFTs, leiomyomas may have a hyalinizing stroma, and mitoses and nuclear atypia are rare. Unlike in CFTs, immunohistochemistry in leiomyomas shows positivity for smooth muscle actin and desmin, and negativity for CD34[36].
Solitary fibrous tumors (SFTs) consist of spindle-shaped cells with thick bands of hyalinized collagen, with hemangiopericytoma-like (staghorn) vessels, and perivascular hyalinization[37]. Like CFTs, solitary fibrous tumors show extensive hyalinization and an absence of atypia or mitotic figures[3,37]. However, SFTs typically lack lymphoplasmacytic inflammation[37]. Solitary fibrous tumors stain positively for CD34 (95%), CD99 (70%), BCL-2, EMA (20%-30%), and show nuclear expression of STAT-6[38].
IMT is a myofibroblastic spindle-cell proliferation with a predominantly lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and abundant background blood vessels. The inflammatory infiltrate occasionally contains neutrophils, eosinophils and/or foamy histiocytes. IMT demonstrates variable cellularity and typically shows a myxoid background. Unlike CFT, IMTs only rarely contain calcifications[39]. Positive immunohistochemical stains for smooth muscle actin and ALK are typically seen in IMT, but are negative in CFT[39].
Plexiform fibromyxoma (also known as plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor) is a benign tumor occurring in the stomach that generally forms a submucosal or transmural mass ranging from 0.3 cm to 17 cm[40]. The tumor shows a plexiform multinodular growth pattern with a hypocellular proliferation of bland spindle cells, myxoid stroma, and prominent network of small blood vessels[41]. Plexiform fibromyxomas are positive for smooth muscle actin and negative for CD34, DOG1, S100, and c-kit[40,42].
Desmoid tumor (fibromatosis) commonly involves the abdominal wall or mesentery and is characterized by sweeping fascicles of bland spindle cells with an infiltrative growth pattern. Isolated mass-forming desmoid tumors involving the stomach and gastroesophageal junction have been reported[43,44]. Desmoid tumor is occasionally associated with keloid-like fibers. Unlike CFT, desmoid tumor is not characterized by prominent lymphoplasmacytic inflammation or calcifications, and it shows strong immunoreactivity for nuclear b-catenin[45].
A subset of sclerosing mesenteritis is now considered to be a manifestation of IgG4-RD[46]. The disease involves the small bowel mesentery and, similar to CFT, is characterized by a paucicellular, fibrotic spindle cell proliferation with a prominent lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Additionally, sclerosing mesenteritis may show variable focal calcifications, although prominent calcifications are not a classic feature[46]. Sclerosing mesenteritis surrounds and entraps fat and classically is associated with fat necrosis, helping to distinguish this entity from CFT. Additionally, the presence of obliterative phlebitis in IgG4-related sclerosing mesenteritis may help to distinguish this entity from CFT.
RNFP is a rare fibroinflammatory lesion of the gastrointestinal tract which histologically closely resembles CFT. Similar to CFT, RNFP is composed of a paucicellular proliferation of fibroblasts within a hyalinized collagenous stroma, associated with a sparse lymphocytic inflammatory infiltrate[47]. However, CFT is typically more cellular, the fascicles of the spindle cells are more regular, and the inflammatory infiltrate consists of granulocytes and plasma cells as well as lymphocytes. The presence of dystrophic or psammomatous calcification in CFT assists in distinguishing these two entities. By immunohistochemistry, RNFP shows positive staining for vimentin, smooth muscle actin, and desmin, and is negative for CD34. In contrast, CFT is negative for smooth muscle actin and desmin, but shows positive staining for CD34[47].
MANAGEMENT AND CLINICAL OUTCOMES
CFTs are benign lesions and are most commonly treated by local surgical resection[2]. Few cases of complete resection by endoscopic submucosal dissection have been reported and have not been associated with recurrence[48,49]. While complete excision appears appropriate for large tumors, some have suggested that long-term follow-up is sufficient for patients with small, asymptomatic gastrointestinal CFTs[50]. The local recurrence rate for CFT has been estimated to be approximately 10%[51], and some authors have recommended follow-up for patients following excision of CFT[52]. However, no guidelines for follow-up have been established. Furthermore, the rate of recurrence in gastrointestinal CFTs as opposed to CFTs arising at other sites remains unclear. Some authors have suggested that gastric CFTs, for example, have no tendency for local recurrence compared to soft tissue CFTs[51]. While multifocal CFTs in the gastrointestinal tract have been reported, true recurrence or metastatic disease has not been shown[18,50]. To date, there are no reported cases of malignant transformation of CFT or of metastatic disease. No deaths due to CFT have thus far been reported in the literature.
CONCLUSION
The gastrointestinal tract is a common site of involvement by CFT. CFTs are histologically characterized by a spindle cell proliferation with a densely hyalinized stroma, calcifications, and variable degree of lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Distinction of this entity from other stromal lesions of the GI tract is important as management and prognosis may differ. The most important entity to consider in the differential diagnosis is GIST, which is considerably more common, and which may have aggressive behavior. Similarly, IMT often has a worse prognosis and must be excluded. Further studies are needed to clarify the pathogenesis of CFTs. The relationship between CFT and IgG4-RD remains unclear, and could have important implications for management and prognosis. IgG4-RDs are treated with steroids, while CFTs are currently managed with local resection. Furthermore, IgG4-RD is a systemic illness, and establishing CFT as an IgG4-RD would necessitate increased surveillance for other IgG4-RDs in patients with CFT. It is possible that only a subset of CFTs may arise in the context of either IgG4-RD or IMT. Additional larger studies with molecular characterization of CFTs could help to clarify these relationships. Further studies are needed to clarify the recurrence rate of CFTs in different anatomic sites in the gastrointestinal tract. Such studies could drive guidelines for management of patients with CFT, as certain populations may be amenable to close follow-up without the need for an invasive procedure. However, current data suggest that local resection is typically curative.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年37期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年37期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Artificial intelligence technologies for the detection of colorectal lesions: The future is now
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in cirrhosis: An exhaustive critical update
- Abernethy syndrome in Slovenian children: Five case reports and review of literature
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the treatment of pancreaticopleural fistula in children
- Risk prediction rule for advanced neoplasia on screening colonoscopy for average-risk individuals
- Endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle biopsies of pancreatic lesions: Prospective study of histology quality using Franseen needle
