Clinical characteristics and risk factors for liver injury in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan
Hu Zhang, Yu-Sheng Liao, Jing Gong, Jing Liu, Heng Zhang
Abstract
Key words: COVID-19; Liver injury; Clinical characteristics; Risk factors
INTRODUCTION
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an emerging infectious respiratory disease, has become a worldwide pandemic. The clinical features of COVID-19 are complicated and varied. In addition to lung injury, liver injury has been reported to occur during the course of the disease[1-3]. Similarly, previous studies have shown that patients infected by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus may develop different degrees of liver injury. Nevertheless, the specific mechanism of liver injury is not clear. It has been confirmed that SARS-CoV uses angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as the receptor for cell entry[4]. Chaiet al[5]found that both liver cells and bile duct epithelial cells express ACE2. Whether the liver injury may be associated with the significant expression of ACE2 in liver or bile duct epithelial cells requires further research. The Central Hospital of Wuhan, China, is a major tertiary teaching hospital assigned to the treatment of COVID-19. We retrospectively investigated the clinical characteristics and risk factors for liver injury in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
Clinical data were extracted from electronic medical records of COVID-19 patients at the Central Hospital of Wuhan from January 14, 2020 to March 3, 2020 and analyzed retrospectively. All patients were diagnosed according to the 7thversion of the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Novel Coronavirus issued by the National Health Commission of China[6]. A confirmed case was defined as nucleic acidpositive for 2019-nCoV. This study was approved by the institutional ethics board of the Central Hospital of Wuhan Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Informed consent was not required due to the retrospective design of the study.
Data collection
The enrolled patients were divided into either a liver injury group or a normal liver function group. Liver injury was defined as one or more of the following: Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) > 40 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > 35 U/L, total bilirubin (TBil) > 20.4 μmol/L, alkaline phosphatase > 150 U/L, or γ-glutamyl transferase (GGT) > 45 U/L. Patients not meeting these criteria were classified as the normal liver function group. The liver injury group was further classified as severe (severe and critical) or non-severe (mild and moderate) subgroup.
The clinical data collected included sex, age, coexisting illness, maximum temperature before admission, complete blood count, C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin, D-dimer, liver function tests, and coagulation function tests. The coexisting illnesses included chronic lung diseases, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic kidney diseases, chronic liver diseases, cerebrovascular diseases, and malignancies.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with SPSS version 25.0 (International Business Machine Corp., Armonk, New York, United States). Continuous variables with a normal distribution are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and were compared by the Student’sttest. Continuous variables not following a normal distribution were compared by the Mann-WhitneyUtest. Categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and were compared using theχ2test. A logistic regression model was used to analyze the independent risk factors for the severe cases.P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Epidemiologic features
Data were extracted and analyzed for 505 COVID-19 patients, and 287 cases were excluded due to unavailable or negative 2019-nCoV results. Finally, 218 cases were included in the study, with 79 (36.2%) patients in the liver injury group and 139 (63.8%) in the normal liver function group (Table 1). The mean age for all patients was 50.1 (range, 22-91) years. The mean age in the liver injury group was significantly higher than in the normal liver function group (57.94 ± 16.57 yearsvs45.66 ± 17.82 years,P< 0.001). There was a significantly higher frequency of patients older than 60 years in the liver injury group. There were 94 (43.1%) male patients, with significantly more males in the liver injury group than in the normal group [54 (68.4%)vs40 (28.8%),P< 0.001].
There were 79 patients with at least one coexisting illness, including 52 (23.9%) with hypertension, 22 (10.1%) with diabetes, 21 (9.6%) with coronary diseases, 16 (7.3%) with chronic lung diseases, 12 (5.5%) with cerebrovascular diseases, 7 (3.2%) with malignancies, 5 (2.3%) with chronic renal diseases, and 3 (1.4%) with chronic liver diseases. Patients with liver injury were more likely to have at least one coexisting illness than those with normal liver function (48.1%vs27.3%,P= 0.002). As shown in Table 1, the proportion of patients with coexisting illnesses such as hypertension, coronary diseases, and chronic lung diseases was significantly higher in the liver injury group than in the normal liver function group. In addition, a higher frequency of coexisting illness was observed in the severe liver disease group compared to the non-severe disease group.
The only three patients with chronic liver disease had a history of chronic hepatitis B, with no active virus at present. No other cases had a history of chronic liver disease, such as viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, alcohol related liver disease, autoimmune liver disease, or hereditary liver disease. The incidence of liver injury showed a positive correlation with the clinical classification of COVID-19. A significantly higher frequency of liver injury was observed in the severe patients when compared to the non-severe patients (P= 0.007).
Clinical manifestations
The most common symptom was fever (166 patients), including 63 (38.0%) with lowgrade fever, 76 (45.7%) with mild-grade fever, and 27 (16.3%) with hyperthermia at admission. There were 92 cases (42.2%) with dry cough, 77 (35.3%) with fatigue, 73 (33.5%) with a sense of heaviness in the chest, 59 (27.1%) with expectoration, 43 (19.7%) with shortness of breath, and 42 (19.3%) with myalgia. Atypical symptomsincluded diarrhea (33 cases, 15.1%), poor appetite (32 cases, 14.7%), dizziness (20 cases, 9.2%), headache (19 cases, 8.7%), pharyngalgia (13 cases, 6.0%), nausea (10 cases, 4.6%), abdominal pain (6 cases, 2.8%), nasal discharge (6 cases, 2.8%), and vomiting (3 cases, 1.4%). Among all the symptoms, the incidence of fever (87.3%vs69.8%,P= 0.003) and shortness of breath (29.1%vs5.0%,P= 0.009) was significantly higher in the liver injury group.
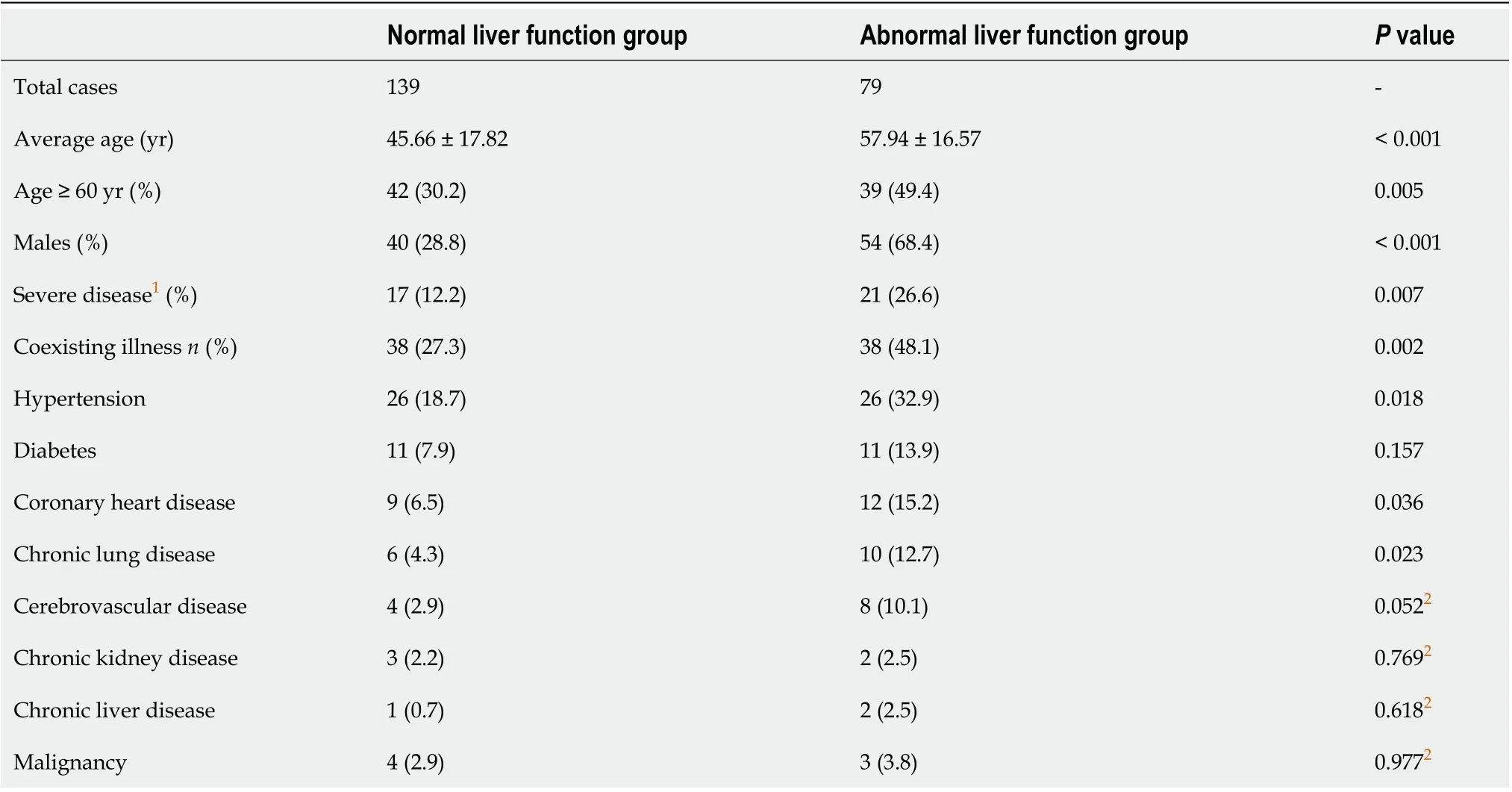
Table 1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
Laboratory parameters
Liver function tests: There were 79 (36.2%) cases with elevated ALT, AST, GGT, or TBil at admission. Elevated GGT was present in 45 (57.0%), and 86.7% of these had GGT < 135 U/L [3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN)]. Elevated AST and ALT were seen in 42 (53.2%) and 36 (45.6%) cases, respectively. Serum level of AST was significantly higher in patients with severe COVID-19. An elevated AST level was observed in 13.9% of patients with non-severe disease and 44.7% of patients with severe disease, while an elevated ALT level was observed in 16.1% of patients with non-severe disease and 18.4% of patients with severe disease. These data suggest that liver injury is more prevalent in severe cases than in mild cases of COVID-19. However, the ALT and AST levels were only mildly elevated (1-3 times the ULN) in 86.1% and 92.9% of the cases, respectively. Only two (2.5%) patients had ALT or AST levels greater than five times the ULN. Elevated TBil was seen in only 12 (15.2%) patients, and 83.3% of these had mildly elevated TBil (1-1.5 times the ULN). Of 100 patients with test results available, only one patient had elevated alkaline phosphatase.
There were 23 (29.1%) cases with simultaneous elevations of both ALT and AST and 15 (19.0%) with simultaneous elevations of ALT, AST, and GGT. Only two (2.5%) cases had simultaneous increases in TBil, ALT, AST, and GGT. More than 85% of abnormal transaminase levels were mildly elevated, and only one case had a very high level of aminotransferases.
The level of serum albumin decreased in 108 (50%) of 216 patients. The incidence of decreased serum albumin level was significantly higher in severe COVID-19 patients than in non-severe patients (76.3%vs44.4%,P< 0.001). There were 55 patients with a decreased serum albumin level who had ALT, AST, TBil, and GGT in the normal range.
Hematology and coagulation: Leukocytes were normal in most of patients (74.8%), with 19.2% having a decreased and 6.0% having an increased count. Lymphopenia was found in 62.0% of patients with liver injury. Other laboratory findings in the liver injury group included high CRP (79.5%), neutrophil percentage (48.1%), D-dimer (47.2%), serum procalcitonin (32.9%), fibrinogen (11.8%), and white blood cell count (10.1%).
Risk factors for liver injury
We compared patients in the two groups to identify possible risk factors for liver injury in patients with COVID-19. Univariate analysis of epidemiological, clinical, and laboratorial variables identified age ≥ 60, male sex, severe disease, coexisting illness, fever, shortness of breath, albumin, globulin, white blood cell count, neutrophils, leukomonocytes, CRP, prothrombin time, prothrombin activity, fibrinogen, and Ddimer as significant risk factors for liver injury in patients with COVID-19 (Table 1 and 2). Multivariate logistic regression analysis further revealed that male sex, high Ddimer level, and neutrophil percentage were significantly associated with the incidence of liver injury (Table 3).
DISCUSSION
A high level of serum aminotransferase is believed to be a major biochemical manifestation of liver injury. A recent study on COVID-19 has shown that the incidence of liver injury ranges from 14.8% to 53%[7]. In this study, liver injury occurred in 36.2% (79/218) of COVID-19 patients, and most abnormal transaminase levels were mildly elevated, similar to previous reports[1,8]. We found that 86.1% of the abnormal ALT levels and 92.9% of the abnormal AST levels were mildly elevated (1?3 times the ULN). Serum ALT and AST levels in severe COVID-19 patients were significantly higher than those in the non-severe patients. These data suggest that more than 85% of abnormal transaminase levels were mildly elevated at admission.
Multivariate regression analysis showed that male sex, high D-dimer level, and high neutrophil percentage were predictive risk factors for liver injury in patients with COVID-19. Liet al[9]found that male sex was associated with the severity of disease in COVID-19, and men were likely to have more severe disease than women. Sex differences in clinical findings among severe patients may be due to estrogen effects. The higher estrogen level in females may help to protect these patients from liver injury[10,11]. Our data showed similar findings to the above study, suggesting that male sex may be closely related to severe COVID-19. In our study, 28.2% (57/202) of COVID-19 patients presented with increased D-dimer. Serum levels of D-dimer in severe COVID-19 patients were significantly higher than those in the non-severe patients. Further, the proportion of patients with an elevated D-dimer level was significantly higher in severe patients than in non-severe patients, which is also similar to previous reports[2,12]. In severe patients, D-dimer increases were considered to be related to advanced age, long-term bedridden status, and comorbid cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that older patients often have comorbidities, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which may also result in the liver injury. With aging degenerative changes, older patients, especially those with underlying diseases, are more susceptible to the attack of SARS-CoV-2. It may be related to the low immunity of the body. Yuet al[13]studied an age-related rhesus macaque model of COVID-19 and found that viral load in the nasopharyngeal swabs, anal swabs, and the lung was more higher in old monkeys after infection, and SARS-CoV-2 caused more severe pneumonia in old monkeys.
It is particularly worth noting that we found higher GGT levels in 45 (57.0%) of 79 patients, and 86.7% of them had GGT < 135U/L (3 × ULN). As the patients’ clinical status deteriorated, the serum GGT levels progressively elevated. However, serum alkaline phosphatase level was in normal range in both mild and severe COVID-19 cases.
Currently, the specific mechanism of liver injury caused by SARS-CoV-2 is still unclear. It has been shown that SARS-CoV2, like SARS-CoV, uses ACE2 as its entry receptor[14]. Chaiet al[5]found that ACE2 expression is much higher in bile duct epithelial cells than in liver cells. Bile duct epithelial cells are known to play important roles in immune response and liver regeneration[15]. These results suggest that liver injury could be caused by SARS-CoV-2 as a result of the damage to bile duct epithelial cells in COVID-19.
Furthermore, liver injury may be related to the cytokine storm syndrome. In our study, lymphocytes decreased in patients with COVID-19. As the clinical status deteriorated, the lymphocytes progressively decreased. Previous studies have shownthat over-activated lymphocytes secrete a large number of cytokines, resulting in systemic inflammatory response syndrome, which causes inflammation and damage of the liver[16].
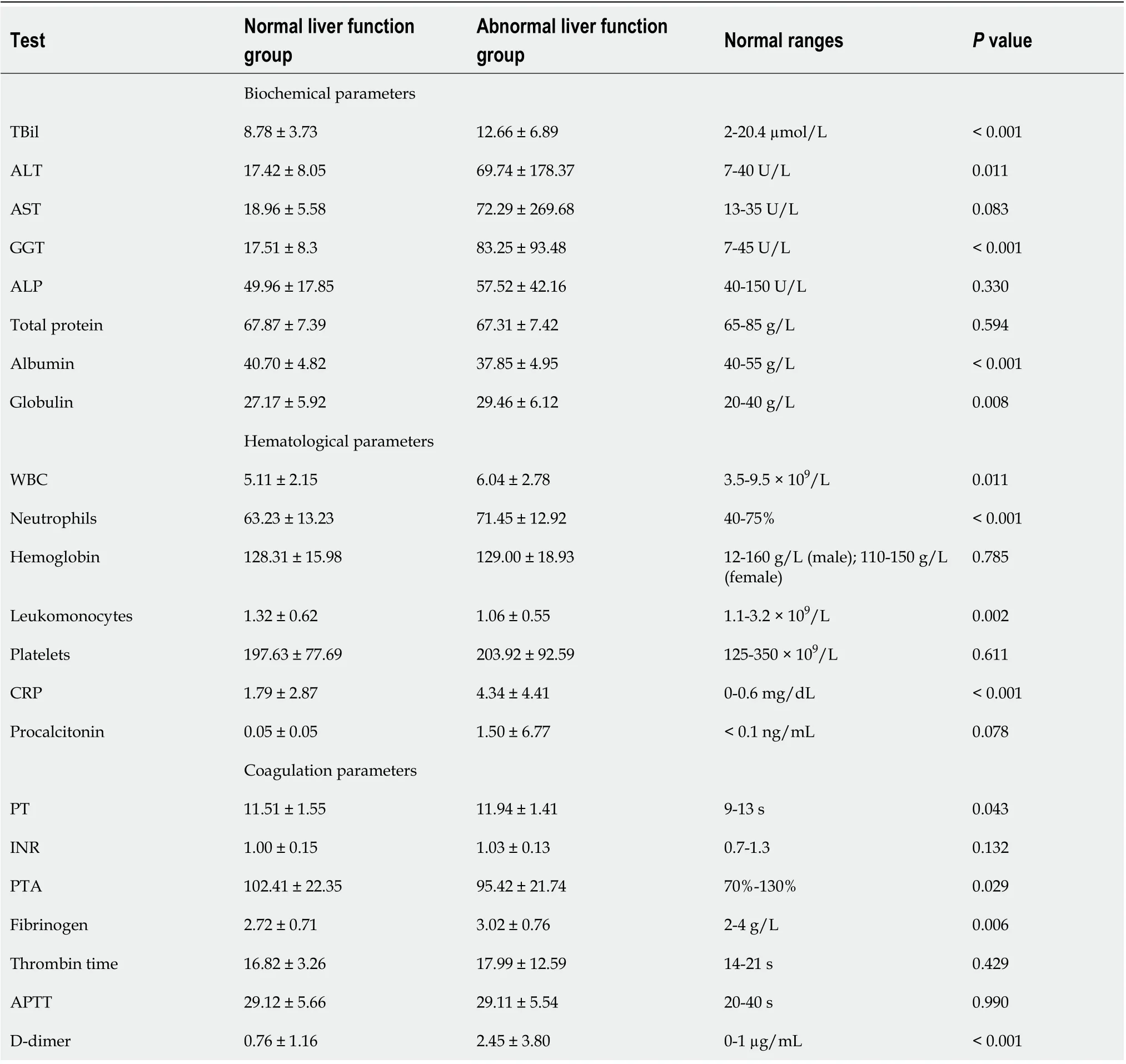
Table 2 Comparison of laboratory parameters between the two groups
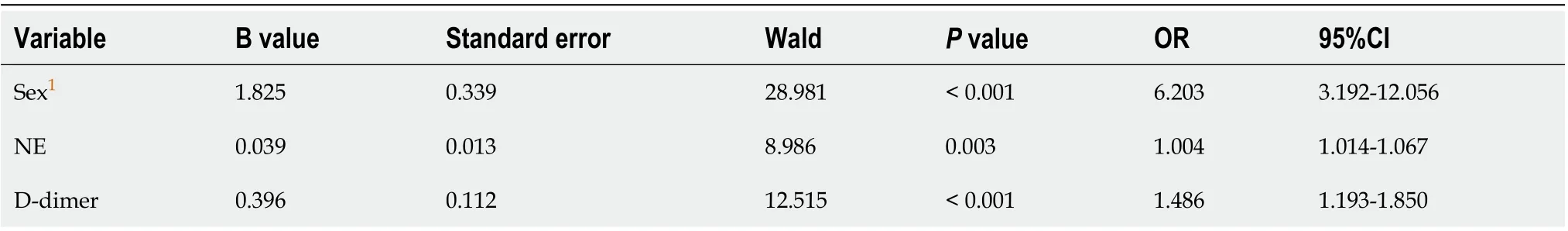
Table 3 Logistic regression analysis of liver injury in patients with coronavirus disease 2019
In addition, patients with hypoxic saturation have extensive pulmonary inflammation, which leads to tissue ischemia and hypoxia, resulting in the internal environment disorder and multiple organ dysfunction[17], including liver dysfunction. One study reported that serum interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, and IL-10 levels in patients with liver injury were higher than those in patients with normal liver function[18]. In this study, the serum CRP levels and neutrophil percentage increased significantly in patients with liver injury, while the leukomonocyte count decreased. These data suggest a possible correlation between liver injury and the inflammatory responses induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Last, liver injury may be drug-induced. Although there is no effective antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2, interferon-α, lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin, and chloroquine phosphate have been used for treatment of COVID-19[6]. These drugs may result in liver injury, yet whether this results in liver damage in COVID-19 patients remains to be investigated.
This study has several limitations. First, inflammatory and immune indicators such as IL-6, ferritin, blood sedimentation, immunoglobulin series, and lymphocyte subsets are closely related to liver function. Due to the limited medical conditions surrounding the pandemic, these factors could not be adequately analyzed. Therefore, it is necessary to further analyze the relationship between these indicators and liver injury in COVID-19. Moreover, in view of possible drug-induced liver injury, patients’ preadmission medication information should be noted in detail. In this study, it is impossible to exclude the influence of pre-admission medication on liver injury. Finally, the retrospective design of this study may decrease its credibility and there may have been bias due to the small number of samples.
In summary, liver injury is common in COVID-19, and most patients with abnormal transaminase had mildly elevated levels. Elevated D-dimer and neutrophil percentage and male sex may be important independent risk factors for liver injury. COVID-19 may be associated with a mild elevation of aminotransferase levels during the early stage of the disease in Wuhan. While further studies are needed to clarify these findings, they will provide reference for the management and treatment of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an emerging infectious respiratory disease, has become a worldwide pandemic. The clinical features of COVID-19 are complicated and varied. In addition to lung injury, liver injury has been reported to occur during the course of the disease[1-3]. Similarly, previous studies have shown that patients infected by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus may develop different degrees of liver injury. Nevertheless, the specific mechanism of liver injury is not clear.
Research motivation
COVID-19 has become a worldwide pandemic. We investigated the clinical characteristics of and risk factors for liver injury in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan by retrospectively analyzing the epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory data for 218 COVID-19 patients and identifying risk factors for liver injury by multivariate analysis.
Research objectives
To investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors for liver injury in COVID-19 patients in Wuhan.
Research methods
The 218 patients included 94 males (43.1%), aged 22 to 94 (50.1 ± 18.4) years. Elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were present in 42 (53.2%) and 36 (45.6%) cases, respectively, and 79 (36.2%) patients had abnormally elevated transaminase levels at admission. Patients with liver injury were older than those with normal liver function by a median of 12 years, with a significantly higher frequency of males (68.4%vs28.8%,P< 0.001) and more coexisting illnesses (48.1%vs27.3%,P= 0.002). Significantly more patients had fever and shortness of breath (87.3%vs69.8% and 29.1%vs14.4%, respectively) in the liver injury group.
Research results
The early stage of COVID-19 may be associated with mildly elevated aminotransferase levels in patients in Wuhan. Male sex and high D-dimer level and neutrophil percentage may be important predictors of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.
Research conclusions
Male sex and high D-dimer level and neutrophil percentage may be important predictors of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.
Research perspectives
While further studies are needed to clarify these findings, they will provide reference for the management and treatment of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We sincerely thank all the front-line medical staff of Wuhan Central Hospital North and South Hospital and Support Hospital and their families for fighting COVID-19.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年31期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年31期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- COVID-19 pandemic: Pathophysiology and manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract
- Risk of malignancy in Caroli disease and syndrome: A systematic review
- Mucosal-associated invariant T cells in hepatitis B virus-related liver failure
- Prognostic value of pretreatment contrast-enhanced computed tomography in esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma: A multicenter follow-up study
- Impact of interval between neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery in rectal cancer patients
- Feasibility and efficacy evaluation of metallic biliary stents eluting gemcitabine and cisplatin for extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
