Mesenchymal stromal cells as potential immunomodulatory players in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection
Panagiotis Mallis,Efstathios Michalopoulos,Theofanis Chatzistamatiou,Catherine Stavropoulos-Giokas,Hellenic Cord Blood Bank,Biomedical Research Foundation Academy of Athens,Athens 11527,Greece
Abstract
Key words:SARS-CoV-2;COVID-19;Respiratory syndrome;Cytokine storm;Mesenchymal stromal cells;Immunoregulation;Lungs;Th2 response;Dendritic cells;Natural killer cells
INTRODUCTION
In December 2019,a new highly transmitted coronavirus,which was provisionally named 2019-novel coronavirus,was spread in Wuhan,China[1].In March 2020,the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) has renamed it as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)[2].The zoonotic transmission in a seafood market of Wuhan is speculated until now as the initial route of transmission to humans[2,3].By the time that this publication is prepared,more than 7258842 cases have been reported,and more than 411879 deaths have been occurred worldwide.Due to the global transmission of SARS-CoV-2,the World Health Organization recognized it as a serious public health issue and in January 2020 declared coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) as pandemic[1].Despite the fact that China was initially affected by COVID-19,accounting more than 80000 cases and 77000 deaths,the United States is now the leading country in confirmed SARS-CoV-2 cases[4].It is estimated that more than 1979893 people have been infected in the United States[4].The European Union,Italy,and Spain have been stricken hard by COVID-19,accounting for more than 32500 deaths[4].
Epidemiological studies have shown that SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease severity vary between the two genders.Currently,it has been reported that males are more susceptible to COVID-19 infection than females[5,6].In addition,SARS-CoV-2 can affect all group ages,while 15% of patients may suffer from the severe form of this disorder[3].Moreover,the probability for severe disorder occurrence increases dramatically in those aged over 65 years[3,5,7].The average mortality of COVID-19 is under 3%,however,in highly affected countries such as Italy,Spain and France,the mortality rate may exceed 6%[4].Additionally,mortality rate can be varied and is dependent on underlying disease and age[3].Recently,a mortality rate of 10%-27% was reported in patients aged over 85 years,3%-11% in ages of 65-84 years,1%-3% in ages of 55-64 years,and below 1% in ages of 20-54 years[3,5,7].
SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for inducing severe acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS) in infected patients,which promotes further lung damage and tissue fibrosis[8,9].Its pathophysiology is related with elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-2,IL-6,IL-7,GSCF,IP10,MCP1,MIP1A,and TNF-α,an event which is known as “cytokine storm”[9-11].Except for lung damage,SARS-CoV-2 may infiltrate other organs such as heart,kidney,and brain,causing cardiomyopathy,arrhythmias,kidney failure,and encephalitis,respectively[3,12,13].Also,the placental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from mothers to their fetuses is currently being investigated[13,14].In the study of Schwartz[13],no SARS-CoV-2 intrauterine transmission from infected mothers to their fetuses was reported.Additionally,no maternal deaths from SARS-CoV-2 has been reported to date,which is in contrast to previous related viruses such as SARS and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)[13-15].
Until now,several treatments have been tested,including prophylactic hydroxychloroquine and colchicine administration,antiviral agents,monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2,and transfusion of convalescent plasma[16-19].The majority of the above treatments have Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for their application to other diseases,while their use in COVID-19 patients is still under investigation.Remdesivir,an experimental drug to treat Ebola,has been tested in clinical trials for its efficacy in SARS-CoV-2 infection,while globally a great effort has been performed for the production of satisfactory vaccines against the current virus[19-24].Recently,remdesivir was approved by the FDA for application in COVID-19 patients.
Knowing that COVID-19 can cause significant modifications to the patient’s immune system,alternative strategies should also be tested.In this way,the mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs),a mesodermal cellular population originated mostly from bone marrow (BM),Wharton’s Jelly tissue (WJ-tissue),and adipose tissue(AT),could be potentially applied in COVID-19 patients[25-28].MSCs are known for their immunoregulatory/immunosuppressive properties,which are exerted in several ways[25].MSCs are currently applied in severe autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis (MS),amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS),Crohn’s disease,diabetes mellitus,etc.,thus reducing disease manifestations[29].In this way,MSCs can be applied mostly as cotherapy in combination with the above pharmaceutical agents to reverse the severe manifestations induced by SARS-CoV-2 infections.In this review,we will highlight the specific immunomodulation aspects of MSCs and their potential application in patients infected by SARS-CoV-2.Furthermore,the immune response against COVID-19,MSCs origin,immunoregulatory properties,and their possible application in COVID-19 will be presented.For the purposes of the current review article,we searched initially over 300 published articles focused on COVID-19 pathogenesis and MSC biology.During the eligibility process,166 studies were excluded and the remaining 134 articles were finally included in this review.Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses flow diagram describes the methodological framework that was followed in the current article (Supplementary Figure1).Based on the above data,the scientific community might consider the broad use of MSCs in critically ill patients,improving their overall condition.
INVASION MECHANISM OF SARS-COV-2
SARS-CoV-2,according to the ICTV,is placed within theCoronaviridaeand specifically is a member of the subgenusSarbecovirus[2,30].SARS-CoV-2 consists of four structural proteins,spike (S),envelope (E),membrane (M),and nucleocapsid (N),and its diameter is approximately 50-150 nm[31,32].It is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus (++ssRNA),while its genome contains 29903 bases[33].The use of molecular methods has revealed that SARS-CoV-2 (Genbank accession No.NC_045512) is similar to bat -SL-CoVZC45 (88% similarity,Genbank accession No.MG772933.1) and bat-SLCoVZXC21 (89% similarity,Genbank accession No.MG772934.1)[33-35].Also,it is related more with the original SARS-CoV (80% similarity,Genbank accession No.FJ588686)than the MERS coronavirus (MERS-CoV,50% similarity,Genbank accession No.NC_019843)[36].
The infection of SARS-CoV-2 begins with its proper adaption to the angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 receptor (ACE2),a process where the S protein is involved[17].Zhouet al[37]showed with the use of reverse genetics that ACE2 is the main receptor that SARS-CoV-2 uses for its fusion with the cellular membrane.Moreover,Wrappet al[38,39]showed that SARS-CoV-2 can bind ACE2 with higher affinity than the original SARS-CoV.Furthermore,the entrance of the virus to host cells is performed by the S protein primed by transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2)[40].TMPRSS2 is a cysteine-rich protease domain,and its expression is regulated by androgenic hormones[41].Overexpression of TMPRSS2 is mostly observed in prostate cancer[41].Its relation with the pathophysiological mechanism of SARS-Cov-2 led researchers to associate possibly its function with lung damage severity and tumorigenesis.
ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are mostly found in alveolar type II cells[42].Additionally,capillary endothelial cells (ECs) of other tissues such as heart,liver,kidney,and intestine also express the above proteins[43].For this reason,patients suffering from COVID-19,besides pneumonia,which is the most common manifestation,may exhibit other disorders such as cardiomyopathy,impaired liver and kidney function,and encephalitis.
IMMUNE SYSTEM AND COVID-19
After the infiltration of SARS-CoV-2 to the host cells,a specific series of events occur.COVID-19 is characterized by three-phase immunopathology,where the patient’s immune system has a central role.Among patients,fever (92.8% of the patients),cough(69.8%),dyspnea (34.5%),myalgia (27%),headache (7%),and diarrhea (6%) were the most common symptoms[3].Additionally,there is an increasing tendency that younger persons (ages <20-years-old) can be asymptomatic carriers of SARS-CoV-2,who can transmit effectively the virus to others[5,7].
The first phase is the incubation – non-severe stage,where the virus is recognized by the immune system[5,44].In this way,the innate immune response is performed to limit the virus infection.If the virus escapes the host’s defense,then the second phase is initiated[44,45].For this reason,immunocompromised patients or patients with underlying disorders characterized by impaired immune function,may have increased probabilities for severe disease occurrence.Chenet al[5]showed that the most common underlying diseases,which were related with the severe outcome,were cardiovascular disease,hypertension,and diabetes mellitus.
In the second phase,the virus induces severe damage to the infected cells through its replication cycle[46].This event leads to the activation of dendritic cells (DCs),epithelial cells,and macrophages,which are producing IL-1β,IL-2,IL-6,IL-8,interferon (IFN)-α/β,TNF-α,C-C motif chemokine 3 (CCL3),CCL5,CCL2,and IP-10.These inflammatory molecules can efficiently stimulate T helper cell (Th)1,Th2,and Th17 responses.Indeed,the overactivation of CXCR3+CD4+T cells,CXCR3+CD8+T cells,and CXCR3+natural killer (NK) cells has been observed in COVID-19[47].These cells are responsible for the production of inflammatory cytokines.Previous studies in COVID-19 patients have shown increased levels of IL-1B,IL-1RA,IL-7,IL-8,IL-9,fibroblast growth factor,granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF),IFN-γ,G-CSF,IP10,MCP1,MIP1A,platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF),TNFα,vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)[48].Among them,IL-2,IL-6,IL-7,G-CSF,IP10,MCP1,MIP1A,and TNF-α were significantly higher in severely conditioned patients[9-11,47,49].In addition,thrombocytopenia,lymphopenia,respiratory failure,pneumonitis,shock,and organ failure have been observed in COVID-19 patients[11].In addition,Wanet al[50]reported that COVID-19 patients were characterized by overactivated lymphocytes despite the occurred lymphocytopenia that was evident in the peripheral blood.This study showed that CD8+T cells were reduced at a percentage of 28.4% and 61.9% in mild and severe group patients,respectively.Also,NK cell reduction was evident in both groups (34.1% in mild,47.6% in severe)[50].These findings were accompanied by significantly high IL-6 levels in both mild and severe groups.Additionally,Xuet al[51]reported the substantial reduction of CD4+and CD8+T cells in peripheral blood of COVID-19 patients,although it appeared that lymphocytes were overactivated due to high expression of human leukocyte antigen DR-isotype(HLA-DR) (34.7%) in CD4+and CD38 (39.4%) in CD8+T cells[51].
The third phase involves the prolonged lung damage that can cause severe ARDS.These patients must enter the intensive care unit (ICU),followed by connection to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in order to survive[46].It has been reported in COVID-19 patients that hyaluronan (HA) is produced due to the “cytokine storm”,thus promoting pneumonia accompanied by pulmonary ground-glass opacity[52].Indeed,IL1 and TNF-α can strongly induce the HA production through overactivation of HA-synthase-2 of CD31+cells and lung alveolar epithelial cells.A series of studies showed that damaged lungs are infiltrated mostly by macrophages,monocytes,and giant cells,while few overactivated CD4+and CD8+T cells were present[52,53].Furthermore,inflammatory cytokines can activate fibroblasts,which in turn can overproduce collagen,promoting even more lung fibrosis[53,54].
Currently,the satisfactory administration of COVID-19 is a great challenge.Th1 and Th2 responses are playing a central role in disease severity of SARS-CoV-2 in the same way as MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV.Moreover,from previous experience,it is known that most neutralizing antibodies are against the S and E proteins[11,55].However,the manufacturing of COVID-19 specific drugs and vaccines is still an ongoing process.Alternative strategies should also be tested for the suppression of the hyperacute immune response,which can lead to patient survival.To date,a great number of pharmaceutical agents,including antiviral agents,monoclonal antibodies against inflammatory cytokines,and convalescent plasma,are under investigation for COVID-19 (Table1).The majority of these agents have current FDA approval for other diseases,including treatment of hepatitis C and rheumatic disease,while they are under evaluation for the safety,tolerability,and efficacy in COVID-19 patients.Most of these pharmaceutical agents have specific targets (e.g.,S protein,IL-6R,and IL-6)but also are accompanied by adverse reactions.Moderate adverse effects may be observed in patients,including fever,headache,nausea,skin rash,diarrhea,and impairment of liver function.In addition to the use of pharmaceutical agents,it has been suggested that MSCs can effectively suppress the patient’s overactivated immune system by utilizing their immunoregulatory properties.MSCs have been used extensively in a wide number of registered clinical trials,supporting their tolerability,safety,and efficacy[56].No severe adverse reactions have been observed after MSCs infusion to patients.In this way,MSCs could be employed as an alternative therapeutic strategy or as cotherapy in severely conditioned COVID-19 patients.
ORIGIN AND PROPERTIES OF MSCS
MSCs,a mesodermal multipotent cellular population,can mostly be derived from BM,WJ-tissue,umbilical cord blood,AT,amniotic fluid (AF),and dental pulp[57].MSCs also have been isolated from solid organs such as the liver,lungs and kidney.Friedenstein,40 years ago,was the first to isolate a fibroblastic-like cell population from BM with plastic adherent and differentiation properties[58].In 2006,the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT) provided the minimum criteria for the proper identification of MSCs[59].Based on ISCT,the following criteria must be fulfilled to define MSCs:(1)Spindle-shaped plastic adherent cells;(2) Expression of specific antigens.Specifically,positive expression (≥ 95%) of CD73,CD90,CD105,and low expression (≤ 2%) of CD34,CD45,CD11a,CD19 and HLA-DR;and (3) Mesodermal multilineage differentiation abilities towards “osteocytes”,“adipocytes”,and “chondrocytes”.
Additionally,ISCT proposed the term “multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells” be used when this cellular population is applied in experimental approaches[59].In 2019,the ISCT’s MSC committee reported that “mesenchymal stromal cells” have specific secretory,immunomodulatory,and homing properties and are distinguished from“mesenchymal stem cells”,which have restricted properties focused on self-renewal and differentiation[60].
Until date,BM is the most common source for MSCs isolation,estimating that MSCs represent 0.01%-0.001% of total nucleated cells[25].BM-MSCs are located to the abluminal surface of sinusoidal blood vessels in BM.These cells represent the stroma,where can efficiently regulate the differentiation of the resident hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)[25].Specifically,MSCs support HSC differentiation through the expression of c-Kit,CXCR4,and Tie2.It has been shown in the literature that CXCR4/CXCL12,and CXCR7/CXCL12 interplay has a significant impact on the regulation of HSC homing and differentiation[61].Additionally,the Notch-Delta,Wnt,Shh signaling pathways have been reported to be involved in this differentiation process[61].
Unlike BM harvesting,MSCs can be non-invasively isolated from other sources,including the umbilical cord’s WJ-tissue,a discarded material after gestation[62].In recent years,there is a tendency to use MSCs derived from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of liposuction aspirates or subcutaneous AT in regenerative medicine applications[63].Typically,MSCs represents 1%-10% of AT resident cells,making AT a greater source than BM.MSCs originated from AT are known as adipose derived stem cells or adipose derived MSCs (AD-MSCs) and exhibit similar immunophenotypic,differentiation potential and immunoregulatory properties as MSCs from other sources[63].
MSCs have been used in a great number of approaches,including tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications,graftvshost disease (GvHD),cotransplantation with HSCs,and administration of autoimmune disorders such as MS,ALS,and Crohn’s disease[64-66].MSCs can exert their functions through the production of cytokines,chemokines,exosomes,and miRNAs,which can act in a paracrine manner on targeted cellular populations[25].Moreover,MSCs have proven their regenerative properties when applied to injured lungs,liver,kidney,and heart[67].Recently,it is under evaluation the beneficial regenerative effect of MSCs in erectile dysfunction[68,69].MSCs,due to their plasticity,have been differentiated successfully to ECs,vascular smooth muscle cells,hepatocytes,insulin-producing cells,etc.Much effort has been put into the transdifferentiation of MSCs to ectodermal cell lineages,such as neurons,by utilizing the induced pluripotent stem cell technology[70].
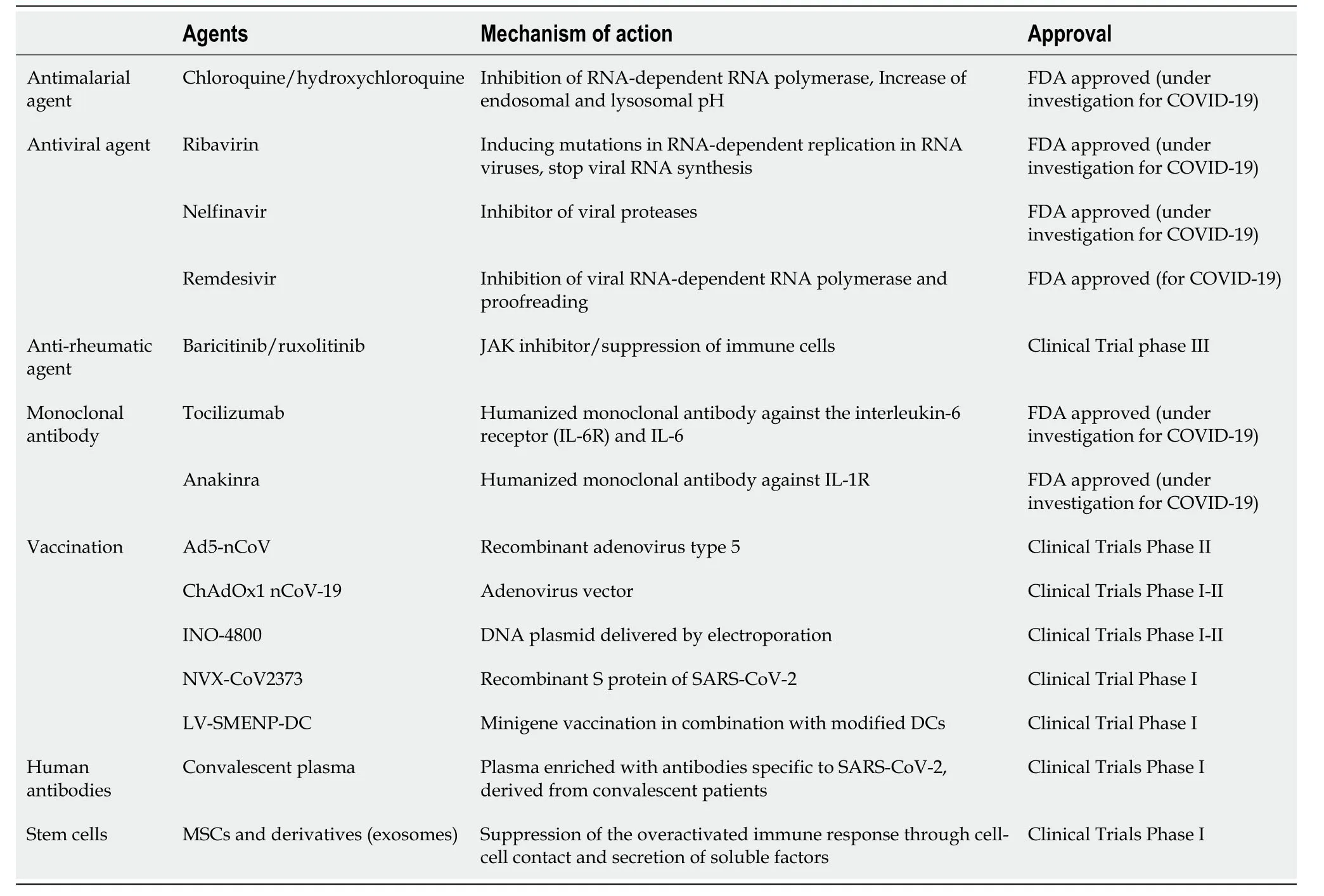
Table1 Most common therapeutic compounds used for the treatment of coronavirus disease-19
MSCs are immune privileged cells,and thus can be used either allogeneically or autologously in large scale clinical trials.Most often,a great number of clinical grade MSCs is required,which has been proven a quite demanding task.In this way,the autologous isolation and expansion of MSCs in significant numbers may be hampered by an individual’s characteristics,such as age and disease severity.On the other hand,allogeneic pooled MSCs may be a better option for regenerative medicine approaches.Le Blancet al[71]have reported that MSCs expressed low levels of HLA class II intracellularly,which can be presented to their membrane surface after IFN-γ induction.However,MSCs do not express the costimulatory molecules B7-1,B7-2,CD40,and CD40L.Studies in non-human primates have revealed that MSCs escape T cell recognition and are well tolerated[71,72].Besides the above properties,MSCs have unique immunoregulatory properties.Specifically,there is evidence that MSCs have a role in the antigen presentation process and are actively involving in organism homeostasis[29].
IMMUNOMODULATORY PROPERTIES OF MSCS
Despite the therapeutic potential of MSCs in regenerative medicine applications,these cells have shown promising results in the regulation of immune responses[25,29].MSCs can act both in immune activation and immune suppression,depending on the microenvironment stimuli (Figure1).The significant immunoregulatory/immunosuppressive abilities of MSCs have been exploited for therapeutic applications in autoimmune disorders and GvHD[65,66].Taking into account that SARS-CoV-2 can induce significant alterations to innate and adaptive immune responses,leading to the“cytokine storm”,the transfusion of MSCs to COVID-19 patients may be beneficial.
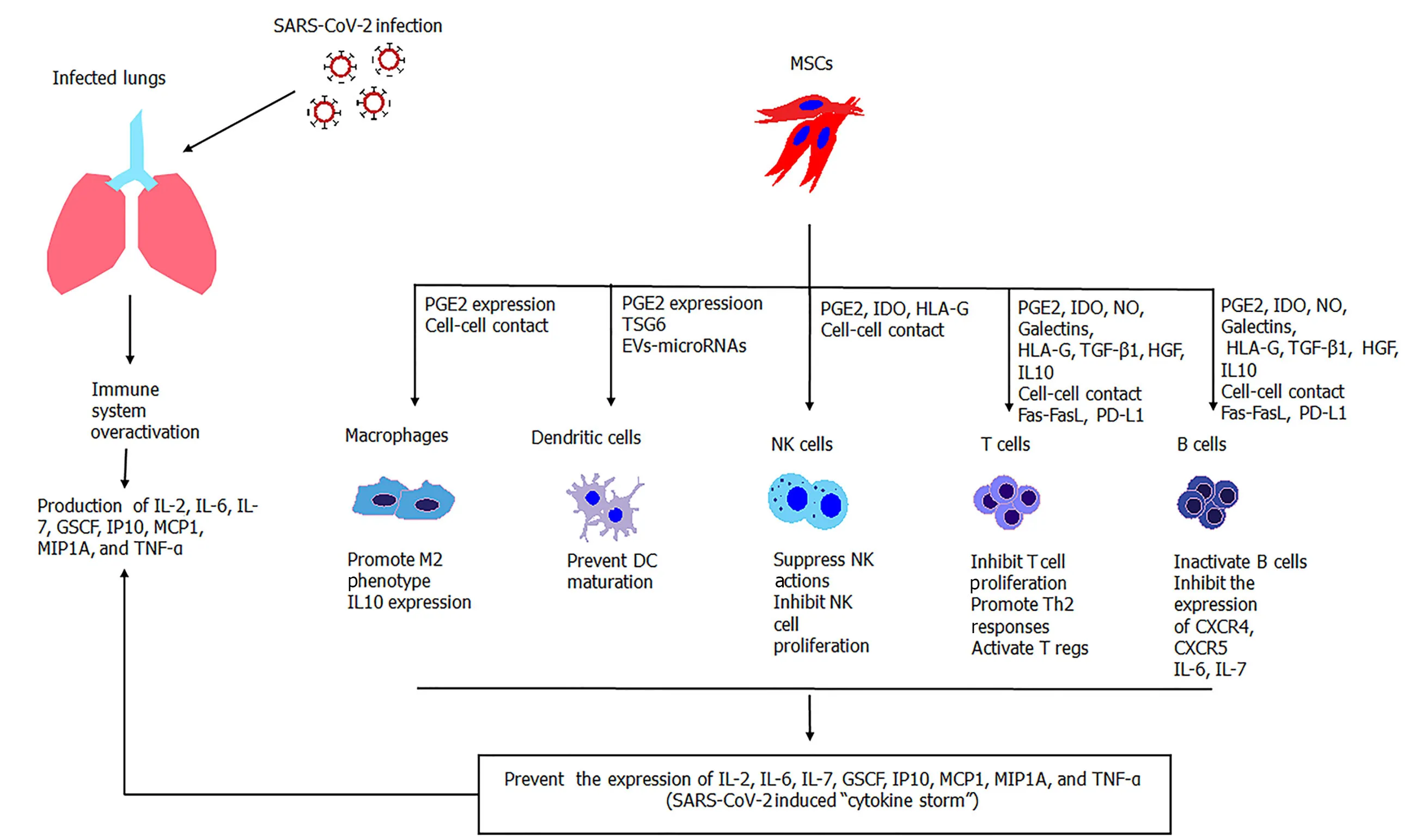
Figure1 Immunomodulatory properties of activated MSCs against overactivated immune cells during SARS-CoV-2 infection.MSCs efficiently suppress the immune responses through the secretion of soluble molecules or cell-cell contact interactions.MSCs have a broad effect on the immune responses exerted by macrophages,dendritic cells,natural killer cells,and T and B cells.SARS-CoV-2:Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2;MSCs:Mesenchymal stromal cells;NK cells:Natural killer cells;NO:Nitric oxide;IDO:Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase;EVs:Extracellular vesicles.
It has been described in the literature that MSCs can effectively modulate DC maturation,T cells (na?ve and effector T cells – Th1/ Th2/ Th17 cells),and NK cell responses[25,29].In the presence of low IFN-γ levels,MSCs can translocate the intracellular HLA class II to their membrane,thus playing a role in innate immunity.On the other hand,high IFN-γ levels can induce MSCs to exert their immunoregulatory properties,mostly through paracrine signaling pathways.In addition,there is evidence that MSCs under specific circumstances may act as antigenpresenting cells[25].The immunomodulation abilities of MSCs can be exerted by delivered soluble factors (cytokines,chemokines,growth factors,modulators of enzyme function),direct cell-cell contact,or a combination of those (Table2)[29].
Interplay between MSCs and macrophages
MSCs can effectively modulate the responses of neutrophils and macrophages.Both cells are playing central roles to the antigen presentation process to DCs,leading to specific immune responses by the cells of innate immunity[73].Macrophages are distinguished to M1 (classically activated) and M2 (alternatively activated)macrophages[29].M1 macrophages are responsible for pathogen phagocytosis and presentation of antigen epitopes to DCs.In this process,a set of inflammatory cytokines are produced by M1 macrophages,such as TNF-α,ΙL-1α/β,IL-6,and IL-12,thus activating and promoting Th1 responses.On the other hand,M2 macrophages promote Th2 responses and are considered immunosuppressive cells[74].These cells exhibit low expression of inflammatory cytokines and high production of antiinflammatory IL-10,which is associated with tissue remodeling,wound repair,and clearance of apoptotic cells[74].It has been reported that MSCs can modulate the M1/M2 macrophage phenotype through cell-cell or paracrine interactions[29,75].
論侵害知識產權的裁量性判賠..............................徐聰穎 11.19
Activation of MSCs with IFN-γ leads to the production of TNF-α,MCP1,and IL-1β,which can further promote the M1 macrophage phenotype.Alternatively,MSCs,through the expression of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2),can induce M2 macrophage phenotype switch[29].Further evidence for the role of MSCs in promoting the M2 macrophage phenotype arises from the study of Wahnonet al[76].Specifically,they reported that signal transducer activators of transcription-3 (STAT3) is activated through cell-cell interactions between MSCs and macrophages[76].Moreover,the same study showed that the STAT3 transcription factor is responsible for IL-10 production by macrophages and DCs,promoting further their immunosuppressive functions[76].

Table2 Immunomodulation mechanisms of mesenchymal stromal cells
Regulation of DC maturation
Immature DCs (imDCs),the immune sentinels of the periphery,can be activated after inflammatory cytokine production by macrophages.Cleaved antigenic epitopes are loaded to HLA molecules of imDCs,followed by the presentation to T cells of the draining lymph nodes[77].Then,DCs undergo maturation,which can induce specific Th1 and Th2 responses against specific antigenic epitopes.It has been found that TNFα,IL-1β,and IL-6,produced either by M1 macrophages or IFN-γ activated MSCs,can drive DC maturation[78].The prevention of DC maturation is of great importance,especially when this leads to prolonged T cell responses,causing host cell and tissue damage.Several studies have shown that MSCs can interfere with DCs maturation through the production of soluble factors[29,78,79].Mostly,it has been suggested that secreted PGE2 by activated MSCs plays an important role in the inhibition of DCs maturation[29].This has been confirmed by results from co-culture studies using MSCs and DCs[80].These studies,were characterized by low expression of CD38,CD80,CD86,IL-6,and IL-12,which are significant molecules for T cell activation[81].Moreover,DCs exhibited low migratory ability,exerted by CCR7-CCL21 interaction.Liuet al[82]suggested that the production of TNF-α-stimulating gene 6 by MSCs can suppress DCs maturation though the inactivation of signaling cascades mediated by mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB).
The inhibitory effect of MSCs in DC maturation can be increased by the production of specific miRNAs,including miR-21-5p,miR-142-3p,miR-223-3p,and miR-126-3p[83].In this process,extracellular vesicles (EVs) of MSCs are enriched with the above miRNAs,suggesting an additional way of regulating DC maturation[84].
MSCs and T cell responses
Immunomodulation of T cell responses can be exerted by MSCs in several ways.MSCs secrete a set of molecules that can act either positively or negatively to the T cell responses.Also,inhibition of T cell proliferation can be performedviacell-cell contact with MSCs[85].
Dependent on the microenvironment stimuli,MSCs can effectively inhibit T cell proliferation through the production of PGE2,indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO),TGF-β,and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)[25,29].The effect of PGE2 inhibition of T cell proliferation was reported for the first time in 1971[86].Several years later,the specific mechanism of action by which PGE2 can exert its immunosuppressive effects on T cells was revealed.PGE2 is a prostanoid,which is synthesized by arachidonic acid through the action of cycloxygenase-1[87].PGE2 is responsible for the production of cAMP in activated T cells.CAMP plays a key role in the downregulation of IL-2 and IL-2R expression and abrogation of Ca2+after T cell receptor (TCR) activation.Also,PGE2 negatively regulates the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol and the production of diacylglycerol and inositol phosphate (IP),resulting in T cell inactivation[87].Recently,it was reported that PGE2 may be involved in T cell polarization,promoting further Th2 responses.In addition,PGE2 produced by MSCs can orchestrate the CD4+CD25+FOXP3 T reg responses,influencing even more the immunosuppression of hyperactivated T cells[29].
IDO also is a strong immunosuppressive agent of T cell responses[85].Specifically,IDO blocks the metabolism of tryptophan to kynurenine in T cells.Kynurenine is an essential amino acid for the cell cycle of T cells,and its absence leads to G0/G1 cell cycle arrest.In addition,Ryanet al[88]reported that IFN-γ activated MSCs can produce TGF-β1 and HGF and,in combination with IDO,can significantly suppress alloreactive T cell proliferation.MSCsviathe secretion of nitric oxide (NO) can inhibit T cell proliferation[89].NO is another potent immunosuppressive agent that can effectively downregulate immune responses.Specifically,NO is responsible for the suppression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 phosphorylation,which further results in the inhibition of TCR-mediated T cell proliferation and inflammatory cytokine production.Additionally,it was found that galectins 1 and 3 secreted by MSCs can effectively suppress T cell proliferation by preventing TCR clustering through a crosslink interaction mechanism[89].
Additionally,MSCs can exert their immunosuppressive properties through T cell apoptosis mediated by cell-cell interactions[90].In this way,the Fas/Fas ligand death signaling pathway can induce apoptosis to T cells,through downstream activation of Fas-associated death domain and caspases.It has been found that MSCs,upon inflammatory stimuli,can express the Fas ligand,binding in this way to Fas receptor of hyperactivated T cells[90,91].Another potential activator of Fas-associated death domain is the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/death receptor (DR)signaling pathway.IFN-γ activated MSCs produce high amounts of TRAIL,which binds to DRs expressed in T cells,thus leading to their apoptosis.Also,MSCs can reduce T cell proliferationviaprogrammed death ligand-1 (PD-L1)/programmed death-1 (PD-1) interaction.Specifically,PD-L1 expressed by MSCs binds to the inhibitory checkpoint molecule PD-1 of T cells,followed by Src-homology 2 domaincontaining protein tyrosine phosphatases (SHP)-1 and SHP-2 phosphorylation.Finally,inhibition of MAPK is performed,which leads to inhibition of cellular proliferation.The PD-L1 can inhibit cellular proliferation and may have a broad effect on T cell subpopulations,including CD4+,CD8+,and Th17 cells[91].Remarkably,Luz-Crawfordet al[92]showed that the PD-L1/PD-1 interaction also could induce inhibition of Th17 cellsviacell-cell contact.On the other hand,this mechanism has a positive association with CD4+CD25+FOXP3 T reg proliferation.
MSCs and B cell responses
Similarly,to T cell modulation,B cell responses can be regulated by MSCsviathe secretion of soluble factors and through cell-cell contact interactions.IDO and PGE2 alongside the production of TGF-β1 and HGF can lead to cell cycle arrest of B cells(G0/G1)[93].Additionally,direct cell contact interactions,mostly utilizing the Fas/Fas ligand,TRAIL/DR death signaling,and PD-L1/PD-1 pathways,can promote apoptosis in B cells[94,95].Recent evidence also showed that coculture of MSCs with B cells resulted in downregulation of CXCR4 and CXCR5,thus preventing the migratory ability and homing of B cells towards CXCL12 and CXCL13 chemoattractant agents.It has been shown that BM-MSCsviasecretion of GM-CSF can inhibit the production of CXCR4,CXR5,IL-6,and IL-7 by activated B cells[95].Indeed,the MSC interaction with plasma B cells results in impaired secretion of immunoglobulin (Ig)M,IgG,and IgA by plasma B cells.However,MSCs cannot downregulate the expression of the costimulatory molecules CD80,CD86,and HLA-DR in activated B cells[96].Additionally,MSCs did not cause any negative effect on IFN-γ,TNF-α,IL-4,and IL-10 expression by B cells[96].
Modulation of NK responses
A remarkably complex interplay between NK cells and MSCs has been reported[99].Indeed,NK cells can exert cytolytic actions against MSCs due to the low expression of HLA class I[100].Alternatively,activation of MSCs with IFN-γ leads to upregulation of HLA class I expression,which can strongly interact with KIRs,inhibiting in this way the MSCs cytolysis mediated by NK cells[100].In this context,toll-like receptors (TLRs),presented in MSCs,seem to play a significant role.Activation of TLR3 in MSCs leads to increased immunosuppression against NK cells[101].
Further immunosuppression of NK cells is mediated by the secretion of soluble factors from MSCs[29].Indeed,IDO and PGE2 can inhibit IL-2 induced NK responses,while TGF-β1 and HGF act cooperatively with the above-described molecules[29,102].Depending on the microenvironment stimuli,MSCs can either activate or inhibit the action of NK cells.It has been shown that WJ-MSCs can stimulate the proliferation of NK cellsviathe production of inflammatory cytokines,including TNF-α,IL1α / β,ΙL-6,and others[103].More research is required regarding the interplay of MSCs and NK cells in order to understand better their association.
HLA-G and immune responses
The HLA system has an essential key role in immune responses[104].The HLA system includes the HLA class I and class II molecules,which are located within chromosome 6p21[105].In this complex system,the HLA class I involves the classical A,B,and C genes and the non-classical genes E,F,and G,while the HLA class II involves the genes DP,DQ,DM,DO,and DR.Both,HLA class I and II are expressed in all cells,particularly in immune cells,and thus play a significant role in antigen recognition and presentation.On the other hand,the exact role of non-classical HLA genes has not yet been completely elucidated.Among them,HLA-G seems to share key immunoregulatory properties[104,105].
For the first time,the role of HLA-G was investigated in pregnancy.The placental and fetus region of the umbilical cord express significant amounts of HLA-G,thus preventing the rejection of the semi-allogeneic fetus by the mother[104,106].HLA-G involves the non-secreted membrane bound isoforms HLA-G1-4 and the soluble isoforms HLA-G5-7.It is speculated that HLA-G5 occurs after specific cleavage of membrane-bound HLA-G1 mediated by metalloproteinase-2.It seems that HLA-G exerts its anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory properties in a wide variety of immune cells,including monocytes,DCs,NK cells,and T cells[104].
Importantly,the HLA-G isoforms can interact with leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor B1 (LILRB1,ILT2/CD88j),LIRB2 (ILT4/CD85d),and KIR2DL4 (CD158d),which are expressed in monocytes,DCs,T cells,and NK cells[104,107].Indeed,the interaction of HLA-G with LILRB1 and LIRB2 induces the phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-base inhibitory motifs,followed by activation of SHP phosphatases,which lead to downregulation of MAPK and inhibition of cell proliferation[107].Alongside IDO and IL10,HLA-G can suppress the proliferation of hyperacute T cells and can prevent the differentiation of monocytes to DCs[80,85].In this way,the secreted cytokines,including TNF-α,ΙL1-α,β,IL-6,IL-7,IL-8,IL-9,GM-CSF,and IFN-γ,can be blocked indirectlyviathe HLA-G mediated inhibition of DCs and T cells.In a high inflammatory environment,HLA-G interactions can mediate the recruitment and the expansion of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+T cells (T reg),which in turn can inhibit effectively the proliferation of allocytotoxic T cells.Additionally,soluble HLAG5-7 isoforms,can induce the secretion of IL-10 and TGF-β1,which further promotes the inhibition of CD8+T cell proliferation[104,108].Several reports have indicated that HLA-G can influence the Th2 response,leading to increased production of antiinflammatory cytokine IL-10,TGF-β1,and HGF.HLA-G can also modulate the function of NK cells by interacting with KIR2DL4.It has been described in the literature that endocytosis of soluble HLA-G with KIR2DL4 is required for the inhibition of NK cells and cytokine production[109].On the other hand,it has been reported that HLA-G homodimers are required for the secretion of TNF-α,ΙL-4,and IL-6[110].This specific set of cytokines is required for successful trophoblast implantation.In this way,more experiments must be performed in order to elucidate better the interplay between HLA-G and NK cells.
MSCs,as part of their immunomodulation,are capable of producing both the membrane bound and soluble HLA-G isoforms.MSCs can be derived efficiently from placental and WJ-tissue,which is located within umbilical cord.Also,it has been shown that placental and WJ-MSCs may exert advanced immunoregulatory/immunosuppressive properties compared to BM or AD -MSCs due to their embryonic origin[106].Evidence from our previous work confirmed the expression of HLA-G isoforms by WJ-MSCs[106].Moreover,HLA-G expression was retained after long term storage of WJ-MSCs with the vitrification approach.Vitrified WJ-MSCs after 1 year of storage at -196 °C successfully inhibited monocyte proliferation in mixed lymphocyte reaction studies[106].In this way,MSCs can be isolated,expanded and stored long term without any negative effect to their immunomodulatory properties.Thus,they can be ready for use on demand.
MSCS AND COVID-19
Until date,MSCs have been applied in large scale cell based therapies,where safety and treatment efficacy have been well documented[56].Their unique role in immune modulation led to the use of MSCs as potential treatment in immunological based diseases,including GvHD,MS,ALS,SLE,etc[25,29].Currently,no specific drugs against COVID-19 exist,while the development of satisfactory vaccines is a challenging process.Therefore,a safe and effective treatment is still under investigation.Taking into consideration that SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for an extended immunomodulation,caused by “cytokine storm”,the administration of MSCs may have a considerable therapeutic benefit,especially in patients with increased COVID-19 severity[8,9].In addition,MSCs are negative for ACE2 receptor and TMPRSS2,and thus cannot be a target for SARS-CoV-2,making their application even safer[47].
Currently,over 30 clinical trials,where MSCs can be potentially applied in COVID-19 as therapeutic agents,have been officially registered (www.clinicaltrials.gov)[111].The majority of the clinical trials involve intravenous administration of MSCs to COVID-19 patients,but most of them are currently under the recruitment phase(Table3 ).
Among them,a study of Lenget al[47]showed promising results in severe diseased COVID-19 patients.This study was conducted in a great number of hospitals,mostly in China,and was approved by the National Health Commission of China.In this study,clinical grade MSCs were intravenously infused in seven patients diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2.Importantly,one patient was in critical condition and entered the ICU,four patients exhibited severe type of the disease,and the last two were in better condition.Also,a placebo group was used,consisting of three severe type patients.The MSCs were administrated in a number of 1 × 106cells/kg with an infusion rate of 40 drops/min.After 2-4 d of MSC administration,the severe symptoms,including fever,oxygen saturation,and cough,were improved,and the majority of the patients were discharged.Also,the critically severe patients exited the ICU and successfully recovered.On the other hand,one patient from the placebo group was died,one developed ARDS,and one was in stable condition[47].
Lenget al[47]showed that MSCs exerted their immunoregulatory properties and were capable of tolerating the hyperacute immune responses of patients,thus improving significantly the patients’ overall condition (Figure1).Indeed,the levels of C-reactive protein in the study group were declined,accompanied by a decrease in the TNF-α concentration.Mass cytometry analysis revealed that the overactivated CXCR3+CD4+T cells,CXCR3+CD8+T cells,and CXCR3+NK cells disappeared and that the CD14+CD11c+CD11bmidDCs reversed to normal conditions.Leukopenia was also reversed in all patients within 1 or 2 wk after MSCs administration.Furthermore,the ground glass opacity of lungs seemed to have subsided in patients[47].
Another important issue that should be mentioned is the time point of MSC administration to COVID-19 patients.The exact time point for MSC administration varied among the studies.In a number of clinical trials,the MSCs are infused at specific time points (0,2,6,10,14 wk) after disease onset.In other studies,MSCs are infused in severe conditioned COVID-19 patients as a co-therapy alongside with theirprimary therapeutic protocol.Severe COVID-19 condition is established through the determination of specific clinical manifestations.Severe clinical manifestations include fever,respiratory distress (respiratory rate ≥ 30/min),low oxygen saturation (≤ 93% at rest state),low arterial partial pressure of oxygen/fraction of inspiration O2 ≤ 300 mmHg,while respiratory failure (connection of patients to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation),shock,and organ failure compromise the critically severe manifestations.The cytokine levels of IL-2,IL-6,IL-7,G-CSF,IP10,MCP1,MIP1A,and TNF-α are also determined and were mostly found to be elevated when patients are suffering from the severe manifestations and critically severe manifestations.
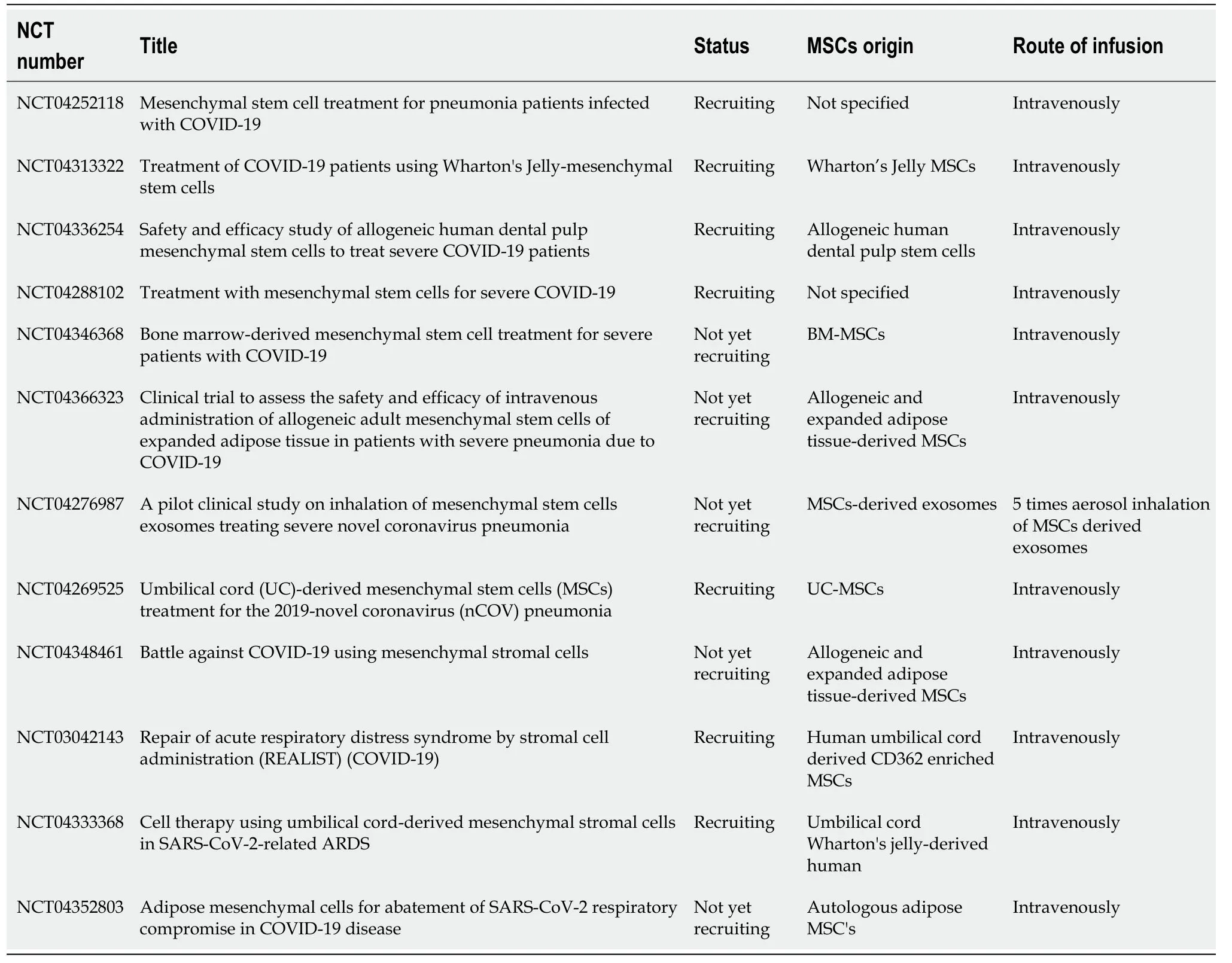
Table3 Clinical trials associated with the use of mesenchymal stromal cells in coronavirus disease-19
MSCs can exert their immunoregulatory properties by activating inflammatory cytokines,including IL-1,IL-6,IFN-γ and TNF-α.At disease onset,patients are not characterized by increased alveolar epithelium damage due to the low virus replication.On the other hand,when virus load is high,severe alveolar epithelium damage can occur due to the production of inflammatory cytokines and the initiation of “cytokine storm”.MSCs can now be activated (by inflammatory cytokines),which can lead to immunoregulation of the overactivated immune system.Besides these facts,MSCs could also have a prophylactic effect,and this could be the primary reason for their use at disease onset.Taking into consideration the above data,the specific time point for the administration of MSCs should be established that leads to patients’condition improvement.
Similar results regarding the immunomodulatory benefits of MSCs have been reported by other research groups around the world.Indeed,in the study of Petrouet al[112]the ALS severity score was decreased in all patients after MSCs infusion,while the treatment was proven safe and well tolerated.
In this way,MSCs can modulate effectively a series of immune responses,including macrophages,DCs,NK,T,and B cells.Especially in COVID-19,the latest evidence supports that IL-6 is the main inflammatory cytokine for the immune system overactivation,and MSCs may be used as potential immunoregulatory players and inhibitors of IL-6 production[113].MSCs can secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines,including IL-10.In addition,MSCs can induce apoptosis to overactivate T and B cells,promote Th2 responses,and activate M2 macrophages,regulating even more the inflammation.
Besides its well documented immunoregulatory properties,MSCs may exert key regenerative properties towards damaged alveolar epithelium and lung fibrosis[114].In previous studies,it has been shown that MSCs accumulate in lung capillary vessels after intravenous injections[115].MSCs engraft to the injury site in a chemokine-gradient dependent manner.Upon chemokine detection (CXCL12,SDF-1,CXCL12L),MSCs can upregulate CD44 and ανβ1integrins,and through the interaction with P/E selectins,vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) can perform the rolling adhesion to endothelium surface until reaching the injury site[25].Then,transendothelial migration of MSCs occurs in a process mediated by junctional adhesion molecules,platelet-EC adhesion molecule-1,and cadherins(Figure2).MSCs produce several growth factors,such as TGF-β1,VEGF,HGF,EGF,and IGF,that could induce the differentiation of alveolar epithelial cells from progenitor cells,attracting the M2 macrophages while reducing the scar tissue formation process[25].This has been further confirmed by evidence regarding the reversion of ground glass opacity in lungs of COVID-19 patients after MSC infusion[47].
The safe and tolerability of allogeneically infused MSCs have been reported in the past.There was evidence that intravenously infused MSCs could be accumulated in capillary vessels of lungs,thus raising the possibility of pulmonary embolism occurrence.In a phase I clinical trial performed by Iacobaeuset al[115],no long-term engraftment of MSCs was performed in patients with MS.MSCs were further cleared from the circulation through the secondary lymphoid organs[115].In another phase I clinical trial evaluating the possible treatment of ARDS,allogeneic BM-MSCs were well tolerated by the patients,and no infusion or treatment related adverse events were reported[116].Moreover,Matthayet al[117]reported that intravenous injection of MSCs in a number of 10 × 106cells/kg was safe in patients with moderate ARDS.In both studies,after MSC infusion,the levels of IL-6 and IL-8 and the in-hospital mortality of patients were critically decreased,promoting even more the therapeutic potential of MSCs[47,117].In recent years,AD-MSCs have gained significant interest by the scientific society for their regenerative and immunoregulatory properties.Recently,Gentileet al[26,27]reported that AD-MSCs exert key immunosuppressive propertiesviathe secretion of TGF-β1,HGF,and IFN-γ and remarkable regenerative properties through the secretion of VEGF and PDGF[26,27].Indeed,besides their immunosuppressive properties,AD-MSCs can secrete pro-angiogenic factors such as VEGF and PDGF,which can stimulate the ECs,promoting in this way the vascularization and the regeneration of damaged lung tissue[26-28].Moreover,a phase I clinical trial using autologous or allogenic AD-MSCs was conducted since April 2020 in COVID-19 patients,determining the safety and tolerability of these cells[26].
Moreover,MSCs,upon environmental stimuli,are able to secrete EVs containing biomolecules,which effectively can promote key function processes,such as local immunomodulation and tissue regeneration[118].EVs are composed of lipid bilayer membranes and can be classified into exosomes (microvesicles (MVs) with diameter of 30-100 nm),apoptotic bodies,and the recently described nanovesicles with diameter of 8-12 nm[119,120].MVs mostly contain mRNAs,microRNAs,cytokines,and chemokines that can regulate a wide number of biological processes,including the function and homing of immune cells[121,122].It has been shown that MVs derived from BM-MSCs suppress the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α and can promote the conversion of Th1 to Th2 responses[120,123].Also,MVs contain the miRNAs miR-145,miR-146,and miR-155,which can effectively suppress the expression of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 and IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 1,followed by down-regulation of NF-κB p65 phosphorylation[120,122,124].These events further lead to the impaired production of TNFα,ΙL-1β,and IL-6 and is accompanied by inhibition of proliferation of M1 macrophages[120,122].To date,a clinical trial that involves the application of inhaled exosomes derived from MSCs in patients with COVID-19 has been registered(NCT04276987).Moreover,MSC derived exosomes have been used as therapeutic agents in lung inflammatory diseases and tissue protection from fibrosis.In this context,WJ-MSCs derived exosomes significantly suppressed TGF-β1 expression and its downstream signaling pathway involving the inactivation of SMAD4 and SMAD5,leading to decreased collagen production and attenuation of scar tissue formation[120,125].Exosomes can be produced under large scale good manufacturing practices (GMPs) conditions and could act beneficially in COVID-19 patients.

Figure2 Transendothelial migration of intravenously infused MSCs in COVID-19 patients.Proposed mechanism of MSCs trafficking towards to chemokine stimuli produced from affected cells.MSCs perform endothelial rolling through interactions of CD44 and ανβ1 with intercellular cell adhesion molecule and vascular cell adhesion molecule.Transendothelial migration of MSCs is mediated through interactions of junctional adhesion molecular,platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule PECAM,and cadherins.Upon arrival to their destination,MSCs exert their immunomodulatory and regenerative potential to the damaged tissue.COVID-19:Coronavirus disease-19;ICAM:Intercellular cell adhesion molecule;MSCs:Mesenchymal stromal cells;VCAM:Vascular cell adhesion molecule;PECAM:Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule;JAM:Junctional adhesion molecular;ECs:Endothelial cells.
CURRENT LEGISLATION DESCRIBING THE USE OF MSCS
The use of MSCs in COVID-19 patients is categorized as stem cell-based therapies,and therefore the guidelines of International Society for Stem Cell Research must be strictly followed[126].Moreover,International Society for Stem Cell Research released the “The Guidelines for the Clinical Translation of Stem Cells”,which involves the current standards for the development of stem cell-based therapies,leading to proven therapeutic potential for the patient[126].
To promote the therapeutic outcome for the patients,MSC based therapies must overcome a great number of challenges,including expansion time,required cell number-dosage,cell cultivation,and cell exposure to animal-derived products,which can affect significantly the safety and efficacy.Furthermore,prolongedin vitrocultured stem cells may lose their key function characteristics such as stemness and plasticity,or even more could undergo malignant tumorigenic transformation[126].
According to the “Guidance of Human Somatic Cell therapy and Gene Therapy”established for human cells,tissues,and cellular,tissue-based products (HCT/Ps),stem cell-based products must be developed under GMPs conditions.Also,additional regulations exist depending on the cell manipulation or either if HCT/Ps are intended to be used in homologous or allogeneic setting[126].FDA has defined the minimal manipulation as the process,which is not altering the biological characteristics of stem cells.Moreover,processes including density-gradient separation,cell selection,centrifugation,and cryopreservation are defined as minimal manipulation HCT/Ps[126].
All other processes involving cell cultivation,expansion,exposure to animal derived substances,activation,and gene modifications are considered as more-than-minimalmanipulated HCT/Ps[126].Furthermore,the use of MSCs in allogeneic setting must fulfill donor eligibility (donor screening and testing for communicable diseases),Quality Assurance program (GMPs conditions and Quality Control system),proper storage conditions (long-term stem cell stability under cryopreserved conditions),and distributing–release criteria.The aforementioned information must be specifically defined in Standard Operation Procedure documentation in order to reduce the risk occurrence for the patient.Trials regarding the homologous or allogeneic use of MSCs must be approved by the corresponding national health commission[126].
All MSC based therapies performed in United States must be registered to the FDA.Accordingly,the European Medicines Agency and the Therapeutic Goods Administration is responsible for the cell-based therapies performed in Europe and in Australia,respectively.According to Committee for Advanced Therapies,which has been established by the European Medicines Agency,all MSC-based products in the European Union will be defined as Advanced Therapeutical Medicinal Products,with the only exception being the aforementioned minimally manipulated stem cells[126].The above requirements and the developed authorities make the MSC based therapies even safer for the patients,bringing stem cell based therapy one step closer to broad clinical utility.
CONCLUDING REMARKS
The above evidence clearly indicate that MSCs could be used as potential therapeutic agents in patients suffering from COVID-19.MSCs can modulate effectively the overactivated immune responses caused by SARS-CoV-2 through inactivation of macrophages and NK,T,and B cells,while at the same time could promote the Th2 response and the activation of M2 macrophages[25,29].In addition,MSCs could have a beneficial regenerative effect in damaged lungs and alveolar epithelial cells,reversing in this way the ground glass opacity in patient’s lungs[67].
Until now,several treatment protocols have been proposed,such as the administration of remdesivir,hydrochoriquine,colchicine,and vaccination of high risk patients[20,22].However,most of these treatments are accompanied by significant adverse reactions,limiting their application to patients.The induced “cytokine storm”by SARS-CoV-2 infection has attracted the attention of the scientific society.This phenomenon,and specifically IL-6,may be responsible for the immune system overactivation and also is associated with poor prognosis in critically ill patients.
On the other hand,MSCs,which are negative for ACE2 receptor and TMPRSS2,could be effective in regulating the “cytokine storm”[47].Moreover,WJ-MSCs may possess better immunoregulatory properties through the elevated expression of HLAG,the existence of longer telomeres,and fewer epigenetic modifications compared to MSCs from the other sources[106].AD-MSCs that are extensively used in a great series of personalized regenerative medicine applications,including breast reconstruction with fat graft,androgenic alopecia,etc,exhibited similar properties as the MSCs from other sources[127-133].
Recently,the application of AD-MSCs as immunoregulatory agents in COVID-19 patients is gaining day by day more attention by the scientific society,worldwide[26,27].AD-MSCs can be efficiently isolated in great quantities from SVF or subcutaneous AT,expanded under clinical grade GMP conditions,and applied through intravenously infusion to critically-ill COVID-19 patients[26,27].AD-MSCs exert equal immunoregulatory properties as MSCs from BM and WJ tissue through secretion of soluble factors or cell–cell contact interactions,as has been described previously[26,27].Furthermore,AD-MSCs can be efficiently differentiated towards “chondrogenic” and“osteogenic” lineages and can produce significant amounts of proangiogenic factors,indicating their significant regenerative potential[26,27,127].These regenerative properties of AD-MSCs may prove to be of great importance in restoration of lung alveolar epithelium and reversion of ground-glass opacity in critically-ill COVID-19 patients.Taking into account the above data,AD-MSCs may also represent a safe and effective therapeutic strategy for COVID-19 patients,and may be the best cellular population option when a great number of MSCs are required for immediate use.
CONCLUSION
MSCs can be potentially applied in COVID-19 as co-therapy without having severe adverse reactions.The exact time point of MSCs administration should be established in order to obtain the best outcome for patients[134].It has been shown in literature that MSCs can suppress the overactivated immune system of severe and critically severe patients.Simultaneously,MSCs may also possess a prophylactic effect if used at disease onset.Existing evidence suggest that MSCs are important immunoregulatory players,but more research is needed,in order to obtain safer conclusions.The ultimate goal will be to decrease the COVID-19 mortality rate,and this is where MSCs can assist significantly.
 World Journal of Stem Cells2020年8期
World Journal of Stem Cells2020年8期
- World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Practical choice for robust and efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells
- Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer's disease
- Exosomes derived from stem cells as an emerging therapeutic strategy for intervertebral disc degeneration
- Off-the-shelf mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord tissue can significantly improve symptoms in COVID-19 patients:An analysis of evidential relations
- Human embryonic stem cells as an in vitro model for studying developmental origins of type 2 diabetes
- Autophagy in fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells and bone remodeling
