Novel molecular targets in hepatocellular carcinoma
Ariel Ka-Man Chow,Simon Wing-Lung Yau,School of Nursing and Health Studies,The Open University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong,China
Lui Ng,Department of Surgery,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong,China
Abstract
Key words:Hepatocellular carcinoma;Prognosis;Arginine deprivation;Cancer stem cells;Glypican-3;Hedgehog signaling pathway;Histone deacetylases;Personalized medicine;Molecular targeted therapy;Notch signaling pathway;Polo-like kinase 1;Tumourassociated antigens
INTRODUCTION
Cancer of the liver is the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide,and is responsible for 4.7% of all new cancer cases and 8.2% of all cancer-related deaths[1].Although the five-year survival rate of liver cancer have improved from an abysmal 3% four decades ago to 18%,it is still significantly lower than the survival rates observed in many other solid cancers with a high global incidence,including breast(90%),colorectal (65%),and prostate (98%) cancers[2].Three quarters of liver cancer patients present with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC);while the other subtypes include cholangiocarcinoma,angiosarcoma,hepatoblastoma,and other non-cancerous liver diseases.The most common cause of HCC is hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection which is responsible for more than 90% of HCC cases in developing countries and nearly half the number of cases in developed countries[3].Other risk factors include aflatoxin B1consumption,alcoholic liver disease,nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,smoking,autoimmune hepatitis,hemochromatosis,obesity,and diabetes.Importantly,in countries endemic for HBV,the introduction of a new universal vaccination program aided by mass screening has been shown to significantly reduce the rate of HBV-induced HCC in children and young adults[4,5].Nevertheless,patients with early HCC are always asymptomatic or develop nonspecific complaints such as abdominal pain,enlarged abdomen,jaundice,and weight loss which results in HCC being initially undetected.Consequently,the management of high risk groups using routine serum α-fetoprotein monitoring and abdominal ultrasonography is important for better control over disease progression[6].For the management of early and intermediate HCC,liver resection,orthotopic liver transplantation,thermal ablation including radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation,transarterial therapies including,radioembolization with yttrium-90 and transarterial embolization with chemotherapeutic agents,and selective internal radiotherapy are potentially curative[6-8].Although a 5-year survival rate of 50%-75%can be achieved,these curative therapies are only applicable for HCC patients with a smaller tumour size and adequate liver function[7,9-13].Moreover,for patients presenting with advanced HCC,neoadjuvant and adjuvant systemic therapies are prescribed to reduce the rate of recurrence or the development of extrahepatic metastases;however,systemic chemotherapy has been reported to have a low tumour response rate and is commonly associated with the development of chemoresistance in advanced HCC[14-17].
The most actively used first-line systemic therapeutic agent approved for patients with nonresectable advanced HCC is sorafenib,an oral multikinase inhibitor targeting Raf,epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR),vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR),platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR),FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3 and c-kit[18,19].At least two large-scale,randomized,placebo-controlled drug trials independently confirmed the effectiveness of sorafenib treatment in inhibiting tumour growth and angiogenesis in advanced HCC;although,the median increase in the overall survival period of HCC patients treated with sorafenib was just under 3 mo as compared to the placebo group[20,21].Moreover,prolonged exposure of HCC cells to sorafenib has been shown to induce resistance,caused by activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway,resulting in enhanced tumour growth and the development of distant metastases[22,23].Considering this predicament in managing HCC using sorafenib alone,it is essential to explore alternative options such as investigating potentially druggable molecular targets or the administration of alternative drug regimens,to achieve an improved disease outcome.Recently,the FDA approved lenvatinib (Lenvima) as an alternate first-line therapeutic agent demonstrated a non-inferior role in improving the overall survival of HCC patients relative to sorafenib[19,24].Furthermore,for HCC patients not benefitting from sorafenib,regorafenib or nivolumab and ipilimumab are the approved second-line therapeutic agents[25,26].Treatment with lenvatinib was found to have improved secondary endpoints including a higher objective response rate,longer progression-free survival and longer time to progression than patients treated with sorafenib alone[19],HCC patients not responding to first-line sorafenib treatment were found to have a better overall survival following the administration of second-line drugs[25,27,28].Due to the limited options available for the systemic treatment of HCC patients,there is an immediate requirement to develop novel therapeutic compounds with high efficacy to improve disease management.In this review,we explore some of the novel molecular targets currently known in HCC.Emphasis will also be paid to the development and clinical application of personalized molecular targeted therapies as powerful therapeutic strategies to improve prognosis in HCC.
POTENTIAL DRUGGABLE MOLECULAR TARGETS IN HCC
An important aspect of cancer therapeutics is the development of targeted therapy that makes use of chemical compounds designed to regulate the activity of specific molecular targets involved in critical oncogenic signaling pathways that ultimately govern the proliferation,growth,survival and distant metastatic dissemination of cancer cells.Consequently,targeted therapy has the advantage of delivering focussed and powerful suppression of cancer development and progression,albeit with a lower toxicity to non-malignant cells;which is a common pitfall associated with systemic chemotherapy and radiotherapy.With an increase in our understanding of the molecular biology of HCC,many such druggable molecular targets associated with HCC genesis and progression have been identified.Key targets include:(1)Intracellular signaling proteins such as those involved in the PI3K/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway,ras/raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK) pathway,Janus kinase (JAK)/Signal transducer and activator of transcription(STAT) pathway and Wnt/β-catenin pathway;(2) Angiogenic factors such as VEGF,fibroblast growth factor (FGF),angiopoietins,platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor (PD-ECGF),heparanase,matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs),PDGFR,and COX-2;(3) Peptide growth factors and their receptors such as EGF and its receptor (EGFR),hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor (c-Met),insulin-like growth factor(IGF) and its receptor (IGFR) and transforming growth factor-alpha (TGF-α);(4) Cell cycle regulators such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs);and (5)Transcription factors such as nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein 2.The details of these targets have been comprehensively reviewed elsewhere[29-36].Examples of the therapeutic agents against these molecular targets,currently in phase II/III clinical trials for the treatment of HCC are summarized in Table 1.However,the antitumour activity as well as the primary outcome measures,such as time to progression and overall response rate and safety level,exhibited by most of these compounds are either equivalent or significantly less than the effectiveness of sorafenib in HCC[37-40].Consequently,it is important to identify novel molecular targets that are druggable in HCC.Table 2 summarizes potential pipeline compounds targeting novel targets that are a part of oncogenic signaling pathways in several cancers,including HCC.Given the importance of these oncogenic pathways in HCC development,these pipeline compounds hold promise as novel therapeutic strategies in HCC treatment.Hence,the following section specifically focuses on these targets to understand their role in HCC pathogenesis.
Hedgehog signaling pathway
The Hedgehog (Hh) pathway is an evolutionarily conserved signaling cascade that plays a critical role in early embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis.Under normal circumstances,the adult liver does not manufacture the Hh protein unless the organ is undergoing regeneration after a partial hepatectomy[41].However,recent evidence suggests that dysregulation of Hh signaling contributes to the development of HCC[42-44].In its oncogenic role,the Hh protein impairs the inhibitory activity of patched homolog-1 (Ptch),resulting in the release of the proto-oncoprotein smoothened (Smo) from Ptch[42].The released Smo subsequently induces the nuclear translocation of glioma-associated oncogene homolog (GLI) transcription factor,resulting in increased transcription of regulatory genes such as,cyclins and β-catenin which promote cell cycle progression,a higher rate of cell proliferation and an associated tumour growth in HCC.Moreover,activation of the Hh signaling pathway also enhances the metastatic potential of HCC cells through focal adhesion kinase(FAK)/AKT and ERK-mediated production and activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9[45,46].In addition to the Hh protein,mRNA levels of Ptch and GLI were found to be overexpressed in HCC and have been reported to serve as potential biomarkers to determine disease recurrence and overall survival following curative surgery[47].In addition,blocking of the Hh signaling pathway by a Smo inhibitor (Vismodegib) has been found to exert anti-proliferative effects in HCC cells[42,48],suggesting that targeting the Hh signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic option for HCC patients.

Table1 Summary of current molecular targeted compounds under phase II/III clinical studies for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma

EGFR:Epidermal growth factor receptor;FGFR:Fibroblast growth factor receptor;Flt-3:FMS-like tyrosine kinase-3;HCC:Hepatocellular carcinoma;MEK1:Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase;PDGFR:Platelet-derived growth factor receptor;TACE:Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization;VEGF:Vascular endothelial growth factor;VEGFR:Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
Notch pathway
The Notch cell-cell signaling cascade is highly conserved and regulates cell fate,cell proliferation and cell death in several developmental and physiological processes[49].Four Notch proteins are found in mammals and they are transmembrane proteins composed of a large extracellular domain for ligand binding and a cytoplasmic Notch intracellular domain (Nicd) for signal transduction.Mammalian Notch ligands include Delta-like ligand (DLL)1,DLL3,DLL4,Jagged1 and Jagged2 which are also membrane-bound.Therefore,activation of the Notch signaling pathway is mediated by ligand-receptor interaction between adjacent cells which leads to a conformational change in Notch receptors.After γ-secretase-induced cleavage of the Notch receptor,cytoplasmic Nicd is released and then translocated to the nucleus.Nuclear Nicd functions as a transcription factor to cause the transcription of its target genes including,HES-family members p21 and c-Myc[50].
Dysregulation of the Notch signaling pathway is observed in several types of cancers,including HCC.Aberrant expression of Notch receptors and its ligand Jagged1 has been detected in HCC tissues when compared with the adjacent nonmalignant mucosae[51-54].Activation of Notch signaling has also been reported to induce HCC tumour formation in mice[55].Moreover,Notch signaling also contributes to enhancement of the oncogenic effects of HBV and HCV in HCC pathogenesis[56-58].Several studies have verified that targeting critical members of the Notch signaling pathway represents a potential therapeutic avenue for HCC treatment.Giovanniniet al[59]demonstrated that selective ablation of the Notch protein in combination with chemotherapeutics such as doxorubicin results in increased DNA damage,cellular apoptosis,and a concurrent decrease in cell cycle progression in HCC cells.Treatment with γ-secretase inhibitors (GSI) was found to inhibit growth of HCC cellsin vitro[60,61].Zhou and colleagues inhibited the Notch signaling pathway using DAPT which suppressed the invasion of HCC cells by impacting signaling of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2),thereby repressing the activity of MMP2,MMP9 and VEGF[62].Active clinical studies on the use of GSIs such as MK-0752 and RO4929097 demonstrated a significant anti-tumour effect in different cancer models[63-66],which suggests its therapeutic potential in treating HCC.
Polo-like kinase 1
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is a serine/threonine kinase with peak expression during the mitotic phase of the cell cycle[67].Plk1 functions as a cell cycle regulator promoting mitosis by modulating the activities of cell division cycle 25 homolog C (Cdc25C) and CDK1/Cyclin B[68,69].Overexpression of Plk1 overrides the mitotic checkpoint which results in immature cell division and genetic instability leading to aneuploidies and tumour development[70].In HCC,activation of Plk1 by HBx,a hepatitis B viral protein,was found to impair the DNA damage checkpoint and DNA repair pathways causing increased genetic instability and malignant transformation[71].Consequently,Plk1 has been reported to be upregulated in numerous cancers,including HCC.In addition,a higher expression of Plk1 was found to predict poor prognosis in HCC[72-74].Silencing Plk1 inhibited proliferation of HCC cellsin vitroandin vivoby inducing G2/M arrest and enhanced apoptosis[75-77],suggesting that targeting Plk1 with small molecule inhibitors is a potential strategy for the treatment of HCC.Gilmartinet al[78]described a reversible ATP-competitive Plk1 inhibitor with a very high selectivity for Plk1 relative to other Plk subtypes or a panel of 48 other kinases that included CDK2/Cyclin A,MEK and serine/threonine kinase NEK2.Moreover,the authors demonstrate that the inhibition of Plk1 resulted in a dose-dependent arrest of cell cycle progression,leading to cell culture growth inhibition and tumour regression in xenograft models;while the toxicity of the drug in slow dividing non-cancerous cells was minimal.Therefore,GSK461364 offers the feasibility to overcome the limitation of traditional chemotherapy.Other phase I/II clinical studies of Plk1 inhibitors also demonstrated an anti-tumour effect by causing tumour regression and inhibition of tumour growth[79-82].These studies suggest that Plk1 may be a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of HCC.
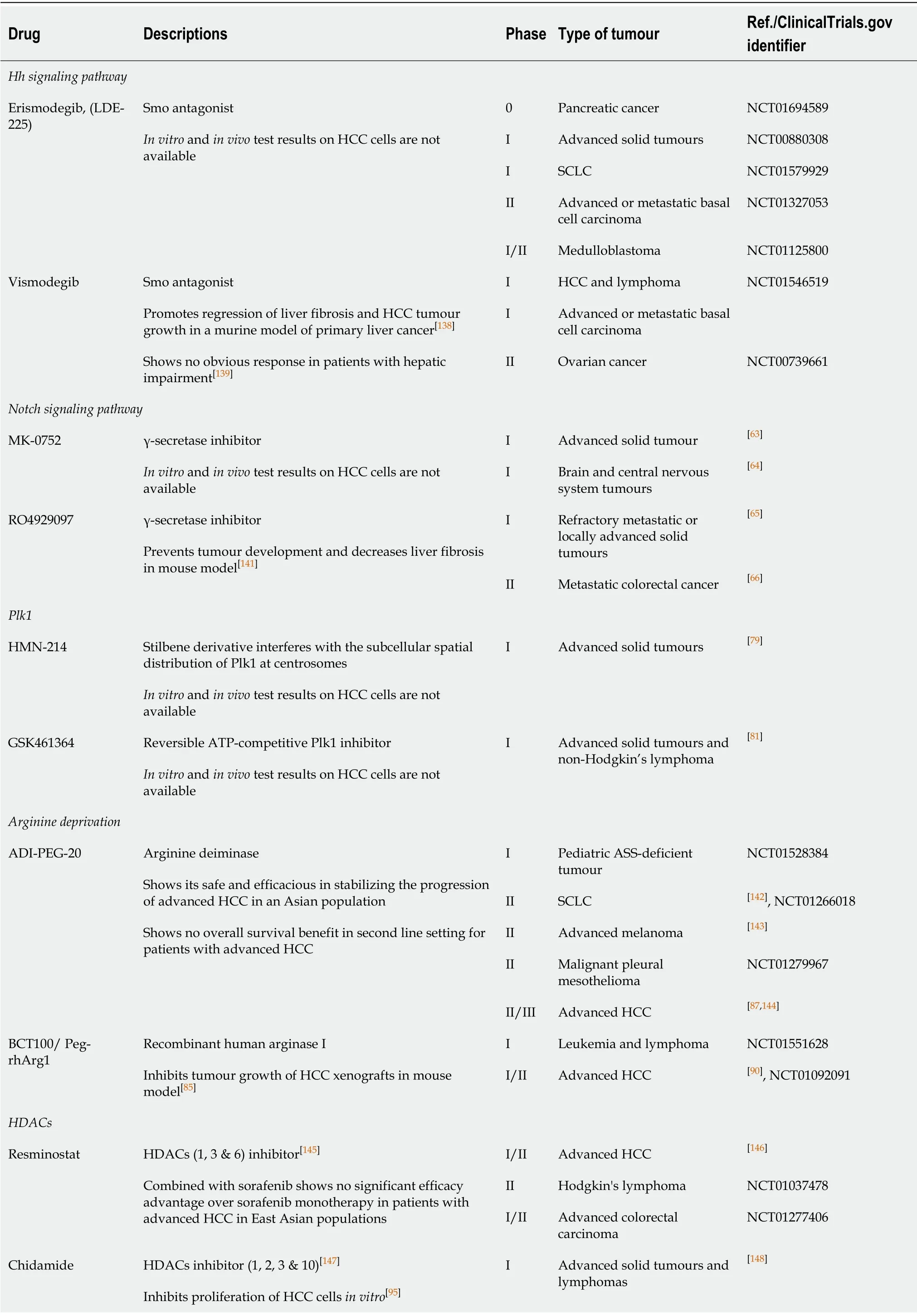
Table2 Summary of potential pipeline compounds targeting novel molecular targets in several cancers
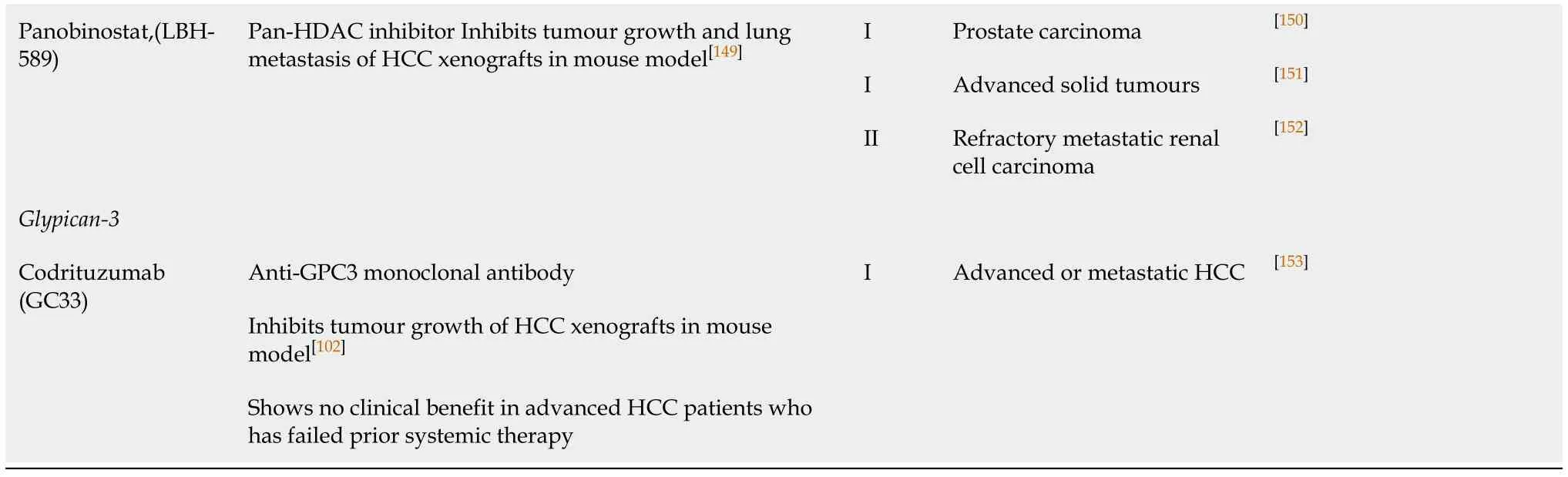
HCC:Hepatocellular carcinoma;HDAC:Histone deacetylase;Plk1:Polo-like kinase-1;SCLC:Small cell lung cancer;Smo:Proto-oncoprotein smoothened.
Arginine deprivation in arginine-driven HCC
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid biosynthesized from citrulline in the urea cycle through the action of argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS-1),argininosuccinate lyase(ASL) and ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC)[83].HCC is auxotrophic for arginine as it lacks the expression of ASS-1,ASL and/or OTC[84,85].Therefore,enzymes capable of removing arginine can function as potential therapeutic agents in HCC.ADI-PEG-20 is an arginine deiminase (ADI) which has been shown to induce HCC regression through arginine depletion in ASS-deficient tumours[86,87].For ASS-positive but OTC-deficient HCC,a recombinant human arginase I (rhArg1) has been shown to be potent in inhibiting HCC tumour growth[84,88-90].A recent study by our group demonstrated that treatment with a pegylated rhArg1,BCT100,inhibits proliferation of HCC cells through an enhanced caspase-dependent apoptosis and induction of S-phase cell cycle arrest[85].Moreover,the drug also inhibited xenograft tumour growth in a dosedependent manner.At the molecular level,arginine deprivation was observed to inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways with a concurrent downregulation of survivin and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) expression[85].Therefore,human recombinant arginase may be a potential agent in arginine-driven tumours such as HCC.
Histone deacetylases
One of the key regulatory mechanisms of gene expression isviaepigenetic posttranslational modifications of histone proteins.Among other covalent modifications,acetylation of the histones is a critical physiological process that is regulated by a balance between the activities of histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases(HDACs).Contrary to the acetyltransferases,HDACs work by removing acetyl groups from the lysine amino acid on the histone protein to increase the net positive charge on the histone tails,resulting in high-affinity binding between the histones and the DNA backbone.High HDAC activity results in a condensed and a transcriptionally inactive chromatin[91].Moreover,aberrant expression of HDAC family members has been observed in multiple steps of cancer development including,cell proliferation,autophagy and cell cycle progression (HDAC 1,2,3 and 8),apoptosis (HDAC 1 and 2),differentiation (HDAC 3,4,5,and 8),angiogenesis (HDAC 4,6,7 and 10),migration(HDAC 6),and chemosensitivity (HDAC 1).The functional roles played by each family member of HDACs have been reviewed elsewhere in greater detail[92].Dysregulated expression of HDACs has been found to correlate with a poor disease outcome in several cancers including HCC[92-94].Specifically,upregulation of HDAC 3 and 5 mRNA expression was observed to be associated with DNA copy number gains in HCC[93].Several HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) have been shown to have an antiproliferative effect on HCC cellsin vitroandin vivo.Panobinostat,a pan-HDAC inhibitor,has been found to enhance apoptosis and inhibit tumour growth in HCC cells through down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic protein survivin[93].Chidamide,a benzamide type inhibitor of HDAC 1,2,3 and 10 subtypes,inhibits HCC cell growth by inducing cell cycle arrest at G0/1 phase by the up-regulation of p21[95].Although most of the studies of HDACi in HCC are still at the pre-clinical stage,HDACi in HCC therapy has great potential.
Glypican-3
The glypican (GPC) family represents a group of cell-surface heparan sulphate proteoglycans which interact with growth factors,act as a co-receptor and modulate growth factor activity.Glypican-3 (GPC3),a carcinoembryonic antigen,promotes cell proliferation by modulating fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) activity[96]and canonical Wnt signaling[97].Interestingly,GPC3 is a transcriptional target of c-Myc,while the expression of c-Myc is under the regulation of GPC3[98].This positive feedback loop between GPC3 and c-Myc also determines the oncogenic behaviour of GPC3.GPC3 is a diagnostic marker for HCC which is over-expressed in 70% of cases,while its expression is correlated with a poor outcome[99,100].Silencing GPC3 in HCC cells induced apoptosisviathe Bax/Bcl-2/cytochrome c/caspase-3 signaling pathway[101].An antibody against GPC3 has also been developed,and it has been shown to cause antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in HCC cells[102].In addition,due to its highly specific expression in HCC tumours,but not in the normal hepatocytes or benign hepatocellular mass lesions[103],GPC3 serves as a tumour-associated antigen which is an ideal target for immunotherapy.Tumour immunotherapy is the use of the host tumour-specific immune response to selectively target the tumour-associated antigens present on tumour cells.A phase I trial of a GPC3-derived peptide vaccine demonstrated measurable immune response and antitumor efficacy which correlated with overall survival in advanced stage HCC patients[104].
CANCER STEM CELLS AS THERAPEUTIC TARGETS FOR HCC TREATMENT
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a subpopulation of cancer cells possessing stem cell-like properties.Briefly,CSCs are tumour-initiating cells in the bulk of tumours that are capable of self-renewal and can divide and differentiate into multiple cell lineages.Markers of CSCs in HCC include ALDH,CD13,CD44,CD90,CD133,CD326(EpCAM),and OV6,and a side population (SP) determined through an adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-binding cassette (ABC) membrane transporter[105,106].CSCs also play a crucial role in tumour recurrence,metastasis and chemoresistance.A recent study reported that circulating CD45-CD90+CD44+CSCs can predict post-hepatectomy HCC recurrence[107].Importantly,while systemic chemotherapy is effective in killing differentiated,fast-growing cancer cells,it induces chemoresistance and enriches the population of CSCs which significantly increases the risk of disease recurrence and metastasis.Maet al[108]reported a CSC population in HCC characterized by their CD133 phenotype which were shown to survive chemotherapy of doxorubicin and fluorouracil with preferential expression of survival proteins involved in the AKT and Bcl-2 pathway.The authors further demonstrated that treatment with an AKT1 inhibitor significantly reduced the expression of these survival proteins,thereby enhancing the chemosensitivity of CD133+CSCs.In a different study,CD133+ cells were also observed to contribute to radio-resistance in HCC in a mouse xenograft model[109].Other molecular pathways including TGF-β,Wnt,Notch and Hh,that are deregulated in HCC were also found in CSCs[105,110,111].Therefore,molecular therapy that is targeted towards CSCs can assist in preventing tumour-initiation,recurrence,metastasis or even chemoresistance in HCC.
PERSONALIZED AND COMBINED MOLECULAR TARGETED THERAPIES IN HCC
Development of HCC is a multi-step process and the mechanisms involved in the initiation,progression and metastasis are not completely understood.Recent studies have demonstrated the role of multiple signaling pathways that contribute to the pathogenesis of HCC.Although no single pathway is deemed dominant,the inhibition of a single pathway may induce a feedback mechanism within an alternate pathway resulting in a low response rate to monotherapy.For example,rapamycin up-regulates the expression and phosphorylation of PDGFRβ and the subsequent activation of the AKT and MAPK pathway through the PDGFRβ-dependent feedback loop results in rapamycin resistance[112].Therefore,emphasis is focussed on a personalized and combined molecular targeted therapy as an ideal therapeutic strategy for HCC.
Anin vitrostudy demonstrated that the level of EGFR expression predicts the cell line response to sorafenib treatment and the addition of gefitinib or erlotinib (EGFR inhibitors) or cetuximab (a monoclonal antibody against EGFR) significantly enhances the efficacy of sorafenib and a synergistic anti-proliferative effect is also demonstrated[113].Therefore,by screening the EGFR status,we can predict the tumour’s response to sorafenib treatment,and the addition of an EGFR inhibitor may help sensitize the tumour’s response to sorafenib.However,anin vivoorthotopic model failed to demonstrate a synergistic anti-tumour effect of combination treatment with erlotinib and sorafenib[114].A recent press release also reported that a large scale phase III clinical trial on the efficacy of combining erlotinib with sorafenib treatment in HCC (SEARCH trial,NCT00901901) failed to demonstrate any additional benefit on the overall survival of patients with unresectable HCC over sorafenib treatment alone[115].Although these studies failed to show a clinical impact of one combined treatment in HCC,presently several clinical studies are evaluating alternate combination based molecular targeted therapies,examples of which are summarized in Table 3.Importantly,the success of personalized therapies in HCC heavily depends on the identification of novel biomarkers that provide critical information pertaining to the progress of the disease.As small tissue biopsy or fine-needle aspiration biopsy specimens are easily obtained,evaluation of biomarkers associated with crucial signaling pathways within these specimens can provide indications for treatment of these patients with drug combinations with/without locoregional therapies to maximize tumour response and survival rates.
CONCLUSION
HCC has been a cause of concern for a long time owing to a high rate of mortality and an overall poor outcome associated with the disease.Molecular investigations have indicated the dysregulation of several critical signaling pathways that contribute to the genesis and progression of HCC.Hence,the role of molecular therapy targeting pivotal members within these signaling pathways is undisputed.While monotherapy is frequently associated with a low tumor response rate and chemoresistance events,there is a need to explore and develop personalized and combined molecular targeted therapies as a powerful therapeutic strategy in HCC.Additionally,an increase in the discovery and clinical application of novel biomarkers that can speak volumes about the developing tumor would provide important information for guiding the clinician on the usage of appropriate personalized therapies in HCC.

Table3 Clinical study of combined molecular targeted therapy based on sorafenib treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Dr.Deepak Iyer for editing this manuscript.
 World Journal of Clinical Oncology2020年8期
World Journal of Clinical Oncology2020年8期
- World Journal of Clinical Oncology的其它文章
- Intravascular lymphoma with hypopituitarism:A case report
- Proton beam therapy of periorbital sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma:Two case reports and review of literature
- Concurrent renal cell carcinoma and hematologic malignancies:Nine case reports
- Management of neuroblastoma in limited-resource settings
- Mutational analysis of Ras hotspots in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder
- Effectiveness of a novel,fixed dose combination of netupitant and palonosetron in prevention of chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting:A real-life study from India
