Effect of electroacupuncture at Lower He-Sea points including Yanglingquan (GB 34) on nuclear factor-κB and interleukin-1β in guinea pigs with acute cholecystitis
Ni Wei (倪偉), Zhang Jian (張健)
Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Point, Yanglingquan (GB 34); Point, Lower He-Sea; Interleukin-1 beta; NF-kappa B; Cholecystitis, Acute; Guinea Pigs
Meridian-viscera correlation is one core content of the Zang-fu organs and meridian theory. Discussing the specificity of meridian points based on the Lower He-Sea points has always been a hotspot in the field of acupuncture. Lower He-Sea point refers to a group of meridian points of the three yang meridians of foot where qi of the six Fu organs is gathered and is used in the treatment of disorders of Zang-fu organs[1]. Our previous study found that the intervention effects of Shangjuxu (ST 37, the Lower He-Sea point of the large intestine) and Xiajuxu (ST 39, the Lower He-Sea point of the small intestine) on ulcerative colitis and duodenal ulcer in the model animals were better than those of Quchi (LI 11, the He-Sea point of the Large Intestine Meridian) and Xiaohai (SI 8, the He-Sea point of the Small Intestine Meridian)[2-3], also better than those of other Lower He-Sea points being compared[4-5]. This partially confirmed that the ‘He-Sea points’ in the ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’ should refer to the Lower He-Sea points rather than the He-Sea points in the Five Shu-Transmitting points of the meridians; it also partially explained the relative specificity with the Lower He-Sea points of the large intestine and the small intestine in the treatment of the disorders of corresponding Fu organs. Yanglingquan (GB 34) is the Lower He-Sea point of the Dan Fu (gallbladder), belonging to the Gallbladder Meridian. Clinical studies have also shown that Yanglingquan (GB 34) has a good effect on the cholelithiasis and cholecystitis[6-7]. Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37) and Xiajuxu (ST 39), which are close to Yanglingquan (GB 34) and all located on the Stomach Meridian, have certain relative specificity for the therapeutic effect on the digestive system, especially the internal Fu-organ diseases[4-5]. Therefore, does Yanglingquan (GB 34) have relative specificity in the treatment of Dan Fu (gallbladder) disorders than the Lower He-Sea points belonging to other internal Fu organs? Neither the ancient classics nor modern researches have provided detailed explanations and systematic comparisons. In this study, the acute cholecystitis (AC) model was developed in guinea pigs as the carrier of the Dan Fu (gallbladder) disorder to receive electroacupuncture (EA) at the Lower He-Sea points belonging to the Dan Fu (gallbladder), stomach, large intestine and small intestine. By comparing the expression levels of the serum interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) in AC guinea pigs after EA, and observing the morphological changes of the gallbladder, the current study intended to explore the regulatory effects of EA at Yanglingquan (GB 34) and other Lower He-Sea points on AC guinea pigs, to clarify the correlation between Yanglingquan (GB 34) and Dan Fu (gallbladder) disorders, thus to provide experimental basis for further explaining the connotation of ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animals and groups
A total of 82 guinea pigs, half males and half females, weighing (250±15) g, were provided by the Animal Experimental Center of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (Hunan Animal Quality Certificate No.: 43006700005278) and fed adaptively for 7 d at 20-25 ℃ with a humidity of 50%-70%. The guinea pigs were fasted but with free access to drinking water for 24 h before the experiment, and then randomly divided into 6 groups (half males and half females in each group) according to the random number table method: a blank group, a model group, a Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, a Zusanli (ST 36) group, a Shangjuxu (ST 37) group and a Xiajuxu (ST 39) group, with 12 guinea pigs in the blank group while 14 in the other groups respectively.
1.2 Main reagents and instruments
E. colipowder (Bacterium No.: ATCC 25922, Item No.: BLGW23146, Shanghai Fuxiang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); rabbit anti-NF-κB (Item No.: GH0758), and paraformaldehyde (Item No.: BTN131248), (Sinopharm Shanghai Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China); IL-1β enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Item No.: JL21516, Wuhan Huamei Biological Engineering Co., Ltd., China); secondary antibody DAB color development kit (Item No.: GMS40008, KPL Corporation, USA); chloral hydrate (Item No.: QN0733, Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., China).
Whole set of animal surgical instruments (Hunan Yuanxiang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); THZ-C type constant temperature oscillator (Taicang Qiangle Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd., China); M199-1 slicing machine (Leica, Germany); CX41-72C02 microscope (Olympus, Japan); TGL16M desktop high- speed refrigerated centrifuge (Changsha Kewei Industrial Company, China); filiform needles (0.30 mm in diameter, 25 mm in length) and SDZ-V EA instrument (Suzhou Medical Supplies Factory Company, China).
1.3 Model preparation
The model was prepared using the updated method by taking into account the pre-experimental conditions with reference to the relevant literature[8]. Except for the blank group, the guinea pigs in the other groups received peritoneal anesthesia with 10% chloral hydrate at 3.5 mL/(kg·bw), after being fasted while with free access to drinking water for 24 h. Then the ATCC 25922 standardE. coli(8×104bacterium/mL, 0.1 mL/rat) was injected into the gallbladder of the guinea pigs after laparotomy. The guinea pigs had free access to food after surgery. On the 3rd day after modeling, the guinea pigs in the five groups undergoing modeling were mentally depressed with decreased appetite, significantly reduced activities, slouch, lassitude, slack and matted fur, and loose stools. Two guinea pigs were selected from each group (one male and one female, not included in the final statistics) to isolate the entire gallbladder after sacrifice. Macroscopic observation showed that the gallbladder wall was differently thickened; the bile color was dark green and opaque with particles suspended or accumulated. Light microscope observation showed that the submucosal blood vessels of the gallbladder were congested, along with mucosal edema, ulceration, necrosis, shedding, and a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrating in the lamina propria, indicating that the AC model was successfully prepared. Laboratory animal processing complied with the relevant animal ethics standards of theEthical Issue in Animal Experimentation[9].
1.4 Intervention methods
The points were positioned according to the
Experimental AcupunctureScience[10]and the mimetic comparison method in theExperimental Animal Acupuncture Point Atlas[11].
Zusanli (ST 36): About 3 mm under the head of the fibula on the posterolateral side of the knee.
Yanglingquan (GB 34): About 4 mm above and outside to Zusanli (ST 36).
Shangjuxu (ST 37): About 5 mm below Zusanli (ST 36). Xiajuxu (ST 39): About 15 mm below the epicondyle of the tibia on the outside of the knee.
Guinea pigs in each group started intervention on the 4th day after modeling, and were not treated in the blank group. Guinea pigs in the model group did not receive any treatment and were tied up for 30 min every day. After being tied up, the guinea pigs in the Yanglingquan (GB 34), Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37) and Xiajuxu (ST 39) groups were acupunctured daily at bilateral Yanglingquan (GB 34), Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37) and Xiajuxu (ST 39), respectively. The SDZ-V EA instrument was connected to the needle after it was inserted, with a sparse-dense wave, a frequency of 10 Hz/50 Hz, the positive electrode on the left point, the negative electrode on the right point, and a current intensity of 1-3 mA. It is better to show tremors in the limbs. The treatment was performed once a day for 5 d with the needle retaining time of 30 min.
1.5 Sample collection and processing
At the end of treatment, blood was collected using the EP tube from the abdominal aorta in all guinea pigs undergoing successful intraperitoneal anesthesia with 10% chloral hydrate at a dose of 3.5 mL/(kg·bw). Then the supernatant was separated with a desktop refrigerated centrifuge at 4 ℃ and 4 000 r/min for 15 min, and stored in ?70 ℃ refrigerator. After blood sampling, each guinea pig was sacrificed by cervical dislocation and the entire gallbladder was quickly removed. The gallbladder was cut along the longitudinal axis and rinsed with normal saline. The mucosa was spread on the wax board after water was removed from the surface. Then part of the tissue was cut and fixed with 10% formalin solution, embedded in paraffin followed by routine pathological section. After cholecystitis was recorded under light microscope and the inflammatory degree was evaluated in some of the sections, hematoxylin- eosin (HE) staining and NF-κB immunohistochemical detection were performed.
1.6 Test items
1.6.1 Serum IL-1β level
The serum IL-1β level was detected by double antibody sandwich ELISA, strictly following instructions of the manufacturer. After the standard curve was established, 100 μL of serum sample was added into each well, the plate was sealed and incubated in a 37 ℃ incubator for 120 min; after washing the plate for 5 times, 50 μL of the first antibody working solution was added into each well and mixed on the vortex shaker, sealed the plate and set the temperature at 37 ℃ for 60 min; after washing the plate for 5 times, 100 μL of enzyme-labeled antibody working solution was added into each well. After mixing, the plate was sealed and incubated at 37 ℃ for 60 min. After washing the plate for 5 times, 100 μL of substrate solution was added into each well. After mixing, the plate was sealed and incubated at 37 ℃ for 10 min; 50 μL of stop solution was added into each well and mixed. Immediately measured the absorbance at 450 nm and calculated the IL-1β level in the samples with the standard curve.
1.6.2 NF-κB and IL-1β expressions in the gallbladder
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay was used to detect the NF-κB and IL-1β expression levels in the gallbladder tissues. Paraffin sections were immersed in xylene to dewax, immersed in gradient ethanol to dexylene, immersed in hydrogen peroxide for 10 min followed by antigen repairing for 30 min, blocked with serum for 20 min, incubated with primary antibody against NF-κB or IL-1β for 2 h at 37 ℃ and second antibody at 37 ℃ for 20 min, followed by DAB color development, dehydration, and mounting. Two high- power fields were observed for each slice under the light microscope. Images were analyzed using the Image-Pro-Plus software (Media Cybernetics, USA) and the absorbance values of the positive cells were counted.
1.7 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS version 22.0 statistical software. Normally distributions of all data were tested. The normal distributed serum IL-1β level, and expression levels of NF-κB and IL-1β in the gallbladder tissues were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s), and one-way ANOVA for multiple sets of measurement data was used. The least significant difference (LSD) was used for the serum IL-1β level data with homogeneity of variance; Dunnett's T3 method was used for the average optical density values of NF-κB and IL-1β in the gallbladder tissues with heterogeneity of variance.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2 Results
Ten guinea pigs used for verification of the successful models were not included in the final statistics. The deaths of guinea pigs in each group due to intra- abdominal infection and disease deterioration during the modeling and treatment: 2 in the model group, 1 in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, 1 in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, 3 in the Shangjuxu (ST 37) group, and 2 in the Xiajuxu (ST 39) group. Therefore, 63 guinea pigs were included in the final statistics, including 12 in the blank group, 10 in the model group, 11 in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, 11 in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, 9 in the Shangjuxu (ST 37) group and 10 in the Xiajuxu (ST 39) group.
2.1 Comparison of the results from the gallbladder sections
Pathological (HE staining) results of the guinea pig gallbladder tissues: the gallbladder wall cells were intact without congestion, edema or inflammatory damage in the blank group; the mucosa was severely congested and swelling, the mucosal epithelium was severely necrotic and shed with a large number of diffusely infiltrating inflammatory cells, and piles of neutrophils in the blood vessel lumens in the model group; the mucosa in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group showed no obvious defects and shedding, with mild swelling and congestion, scattered inflammatory cell infiltration, and good tissue recovery; the mucosal epithelium in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, Shangjuxu (ST 37) group and Xiajuxu (ST 39) group was moderately thickened with notable defects, shedding, vasodilation and congestion, more inflammatory cell infiltration, and poor tissue recovery (Figure 1).
2.2 Serum IL-1β level comparison
Compared with the blank group, the serum IL-1β levels in the other groups were statistically significantly higher (allP<0.01); compared with the model group, the serum IL-1β levels in the four groups treated with EA were statistically significantly lower (allP<0.01); compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, the serum IL-1β levels in the other three groups treated with EA were statistically significantly higher (P<0.05 orP<0.01). The serum IL-1β levels in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, Xiajuxu (ST 39) group and Shanjuxu (ST 37) group showed an increased trend, but there were no statistically significant differences among the groups (allP>0.05), (Table 1).
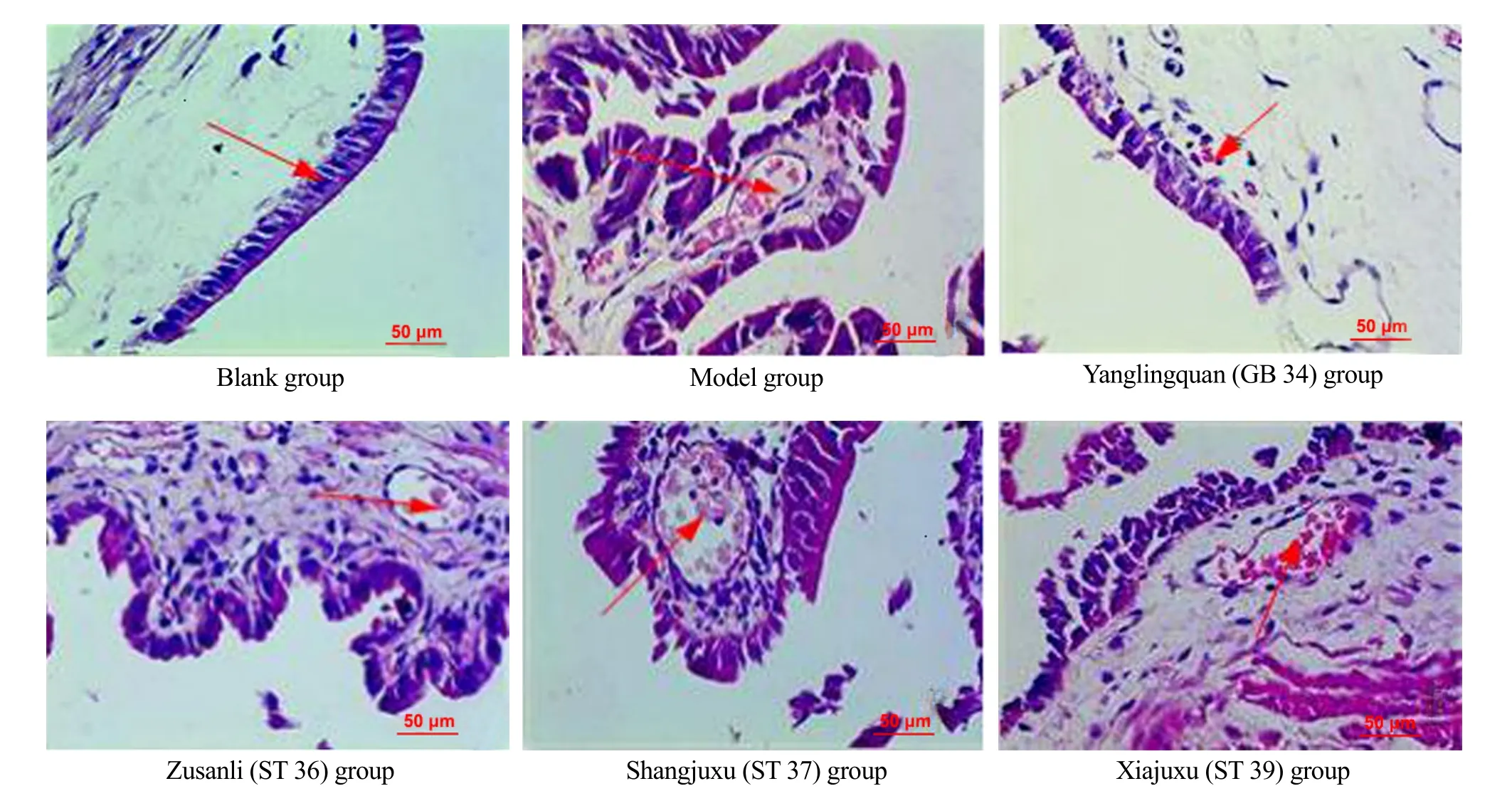
Figure 1. Observation of guinea pig gallbladder slices in each group (HE, ×400)
Table 1. Comparison of the serum IL-1β level among groups (±s, pg/mL)
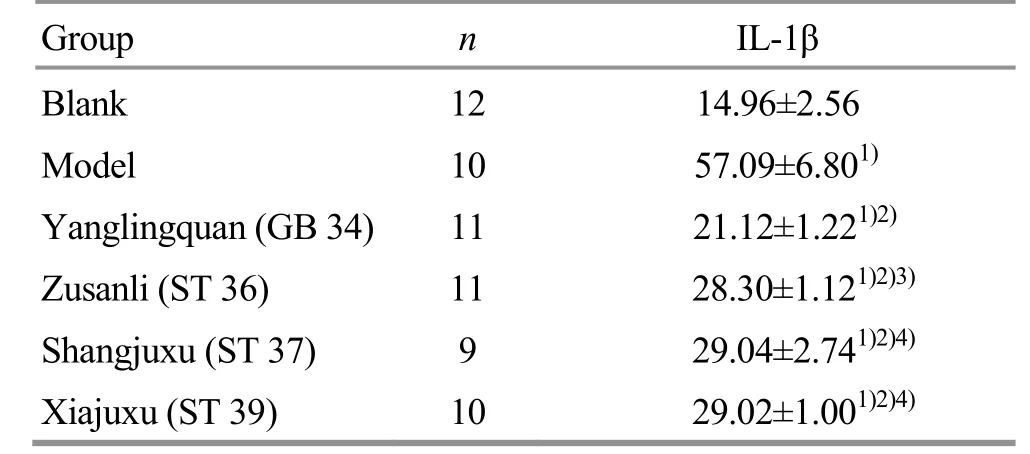
Table 1. Comparison of the serum IL-1β level among groups (±s, pg/mL)
Note: Compared with the blank group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01; compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, 3) P<0.05, 4) P<0.01
Group n IL-1β Blank 12 14.96±2.56 Model 10 57.09±6.801) Yanglingquan (GB 34) 11 21.12±1.221)2) Zusanli (ST 36) 11 28.30±1.121)2)3) Shangjuxu (ST 37) 9 29.04±2.741)2)4) Xiajuxu (ST 39) 10 29.02±1.001)2)4)
2.3 Comparison of the IL-1β expression level in gallbladder tissues
Compared with the blank group, the IL-1β expression level of the gallbladder tissues in the model group was statistically significant increased (P<0.01), and those in the 4 groups treated with EA were high but without significant difference (allP>0.05). Compared with the model group, the IL-1β expression levels in the gallbladder tissues were statistically significantly lower in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group and Xiajuxu (ST 39) group (bothP<0.01), and the Zusanli (ST 36) group and Shangjuxu (ST 37) group (bothP<0.05). Compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, the IL-1β expression levels in the gallbladder tissues of the other three groups receiving EA were statistically significantly higher (allP<0.01), (Table 2).
Table 2. Comparison of the IL-1β expression level in gallbladder tissues (±s)
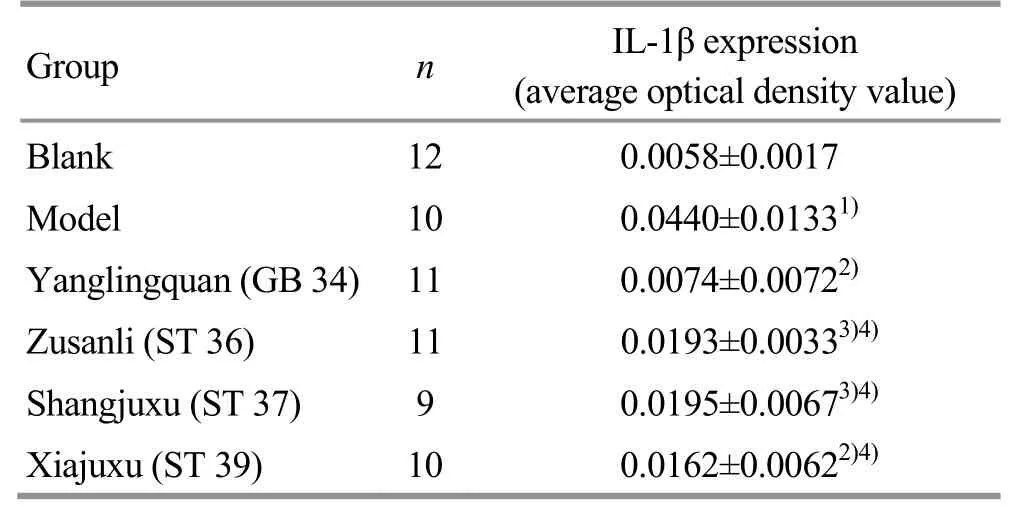
Table 2. Comparison of the IL-1β expression level in gallbladder tissues (±s)
Note: Compared with the blank group, 1) P<0.01; compared with the model group, 2) P<0.01, 3) P<0.05; compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, 4) P<0.01
Group n IL-1β expression (average optical density value) Blank 12 0.0058±0.0017 Model 10 0.0440±0.01331) Yanglingquan (GB 34) 11 0.0074±0.00722) Zusanli (ST 36) 11 0.0193±0.00333)4) Shangjuxu (ST 37) 9 0.0195±0.00673)4) Xiajuxu (ST 39) 10 0.0162±0.00622)4)
The IHC results of IL-1β expression in the gallbladder tissues are shown in Figure 2. The brown particles in the cytoplasm of the gallbladder wall are positively expressed IL-1β. The IL-1β expression level in the gallbladder tissues was low in the blank group, while significantly increased in the model group; more expressions were found in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, Shangjuxu (ST 37) group and Xiajuxu (ST 39) group, and the expression was significantly lower in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group than in the other three groups receiving EA treatment (Figure 2).
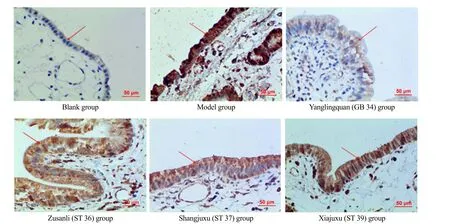
Figure 2. IL-1β expression level in the gallbladder (IHC, ×400)
2.4 Comparison of the NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues
Compared with the blank group, the NF-κB expression level of the gallbladder tissues in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group was increased without statistically significant difference (P>0.05); while statistically significantly increased in the other groups, (P<0.05 orP<0.01). Compared with the model group, the NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group was statistically significantly lower (P<0.01), while only a decreasing trend without statistical significance was showed in the other three groups receiving EA (allP>0.05). Compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, the NF-κB expression levels in the gallbladder tissues in the other three groups receiving EA were statistically significantly higher (P<0.05 orP<0.01), (Table 3).
The IHC results of NF-κB expression in the gallbladder tissues are shown in Figure 3. The brown particles in the cytoplasm of the gallbladder wall are positive NF-κB expression. The NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues in the blank group was low, while the expression was significantly increased in the model group; more NF-κB was expressed in the Zusanli (ST 36) group, Shangjuxu (ST 37) group and Xiajuxu (ST 39) group. The NF-κB expression in the gallbladder tissues in the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group was significantly reduced compared with the other three groups receiving EA treatment.
3 Discussion
Ling Shu(Spiritual Pivot) regards the Lower He-Sea point as important points for the treatment of the Fu-organ disorders, and the clinical application of acupuncture and moxibustion based on the ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’ theory has a significant therapeutic effect on the intestinal diseases[12]. Therefore, it is of clinical significance to study the relative specificity of Lower He-Sea points in the treatment of Fu organs disorders based on the theory of ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’.
Table 3. Comparison of the NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues among groups (±s)
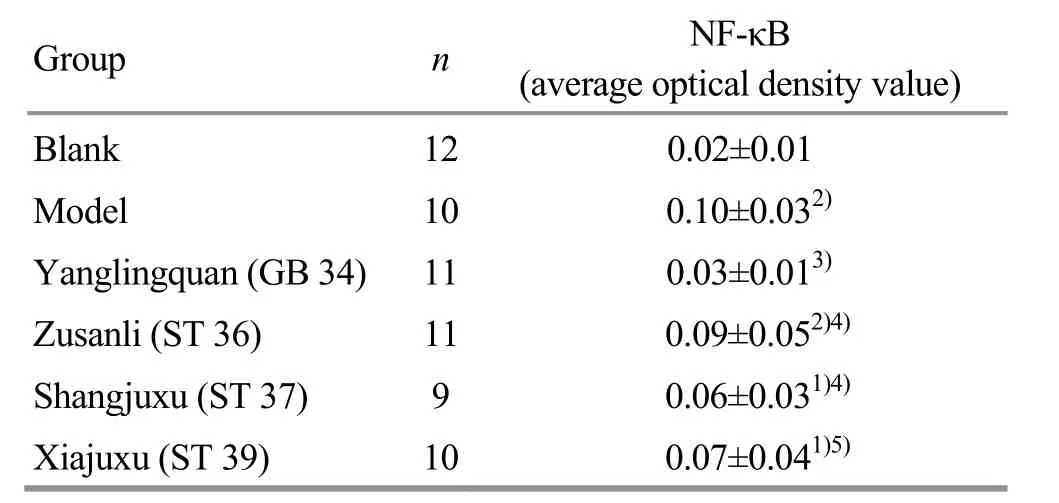
Table 3. Comparison of the NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues among groups (±s)
Note: Compared with the blank group, 1) P<0.05, 2) P<0.01; compared with the model group 3) P<0.01; compared with the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, 4) P<0.05, 5) P<0.01
Group n NF-κB (average optical density value) Blank 12 0.02±0.01 Model 10 0.10±0.032) Yanglingquan (GB 34) 11 0.03±0.013) Zusanli (ST 36) 11 0.09±0.052)4) Shangjuxu (ST 37) 9 0.06±0.031)4) Xiajuxu (ST 39) 10 0.07±0.041)5)
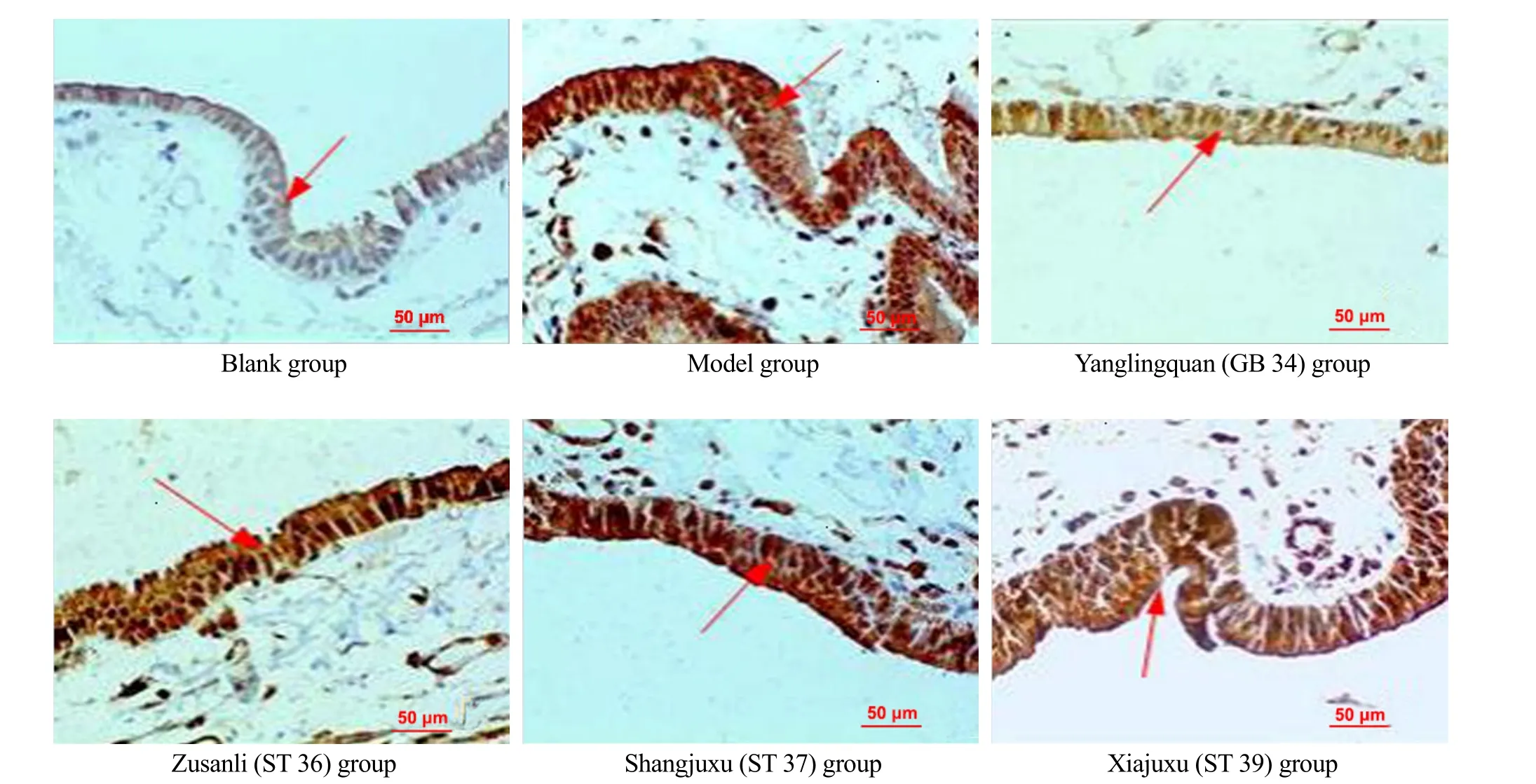
Figure 3. NF-κB expression level in gallbladder tissues (IHC, ×400)
Cholecystitis is a common digestive system disease. AC is an inflammatory reaction of the gallbladder caused by blockage of the cystic duct and bacterial invasion. The onset is faster and the disease progresses quickly, which can cause severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting[13]. In this experiment, AC guinea pigs were used as a model of gallbladder disease to observe whether there is relative specificity in the treatment of gallbladder diseases with Yanglingquan (GB 34), the Lower He-Sea point, so as to make a useful attempt to reveal the theoretical connotation of ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’. IL-1β has various biological activities and acts on different tissues and organs in the body, which is recognized as one of the strongest inflammatory mediators produced by the mononuclear macrophage and an important inflammatory mediator produced by the human monocytes with the stimulation of endotoxin, showing the pro-inflammatory activity[14]. IL-1β can activate neutrophils and monocytes-macrophages to enhance their phagocytosis and killing function, promote their release of inflammatory mediators and inflammatory proteins, trigger the immune and inflammatory reactions, and play an important role in the development of inflammation[15]. Studies have found that IL-1 level was gradually increased with the extension of common bile duct obstruction time, which was consistent with the macroscopic and microscopic pathological changes of gallbladder tissues. After removal of the obstruction of the common bile duct, IL-1 level was significantly decreased compared with the obstruction group on the corresponding days, and the inflammation of the gallbladder was also significantly reduced, indicating that the increased IL-1 may mediate the occurrence of gallbladder inflammation[16].
NF-κB is a transcription factor that regulates the expression of many inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators. In the complex cytokine network of inflammatory response, NF-κB activation may be a central link to involve in the inflammatory reactions, the immune responses and the cell proliferation, transformation, apoptosis and other important pathophysiological processes[17].
In recent years, many animal experiments and clinical studies have shown that NF-κB is very closely related to AC[18-19]. NF-κB is highly activated in inflammatory diseases, which induces a large number of transcriptions and release of pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-1. After NF-κB activation, the gene expressions of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, and others, induce the synthesis and release of the corresponding inflammatory mediators, and stimulate the inflammatory response[20]. The IL-1β has a κB binding site, which not only induces NF-κB activation, but also regulates its transcription through NF-κB activation[21]. NF-κB activation enhances the transcription of IL-1β gene, increases the production and release of IL-1β, and then further activates NF-κB[22], thus strengthening the inflammatory response. Therefore, this experiment aimed to explore whether Yanglingquan (GB 34) and other Lower He-Sea points have relative specificity to AC by observing the above items, thus to provide experimental basis for revealing part of the connotation of ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’ based on the inflammatory mediators and transcription factors.
The results of this experiment showed that the serum IL-1β level and NF-κB expression level in the gallbladder tissues in the model group were higher than those in the blank group, indicating that a large amount of inflammatory factors were released into the serum of AC guinea pigs with the transcription of immune- regulatory factors, indicating that the AC model was successfully prepared. Compared with the model group, the four groups receiving EA treatment showed differently improved gallbladder inflammation, and significantly reduced serum IL-1β levels (allP<0.01), indicating that EA at the above-mentioned Lower He-Sea points effectively reduces serum inflammatory factors and inflammation in the AC guinea pigs; however, except for the Yanglingquan (GB 34) group, the NF-κB level in the gallbladder tissues in the other three groups receiving EA only had a lower trend without statistical significance compared with the model group, indicating that Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37), and Xiajuxu (ST 39) had a limited inhibitory effect on the AC inflammation; the effects of Yanglingquan (GB 34) on reducing serum IL-1β and gallbladder NF-κB, and on gallbladder morphology were significantly better than those of Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37) and Xiajuxu (ST 39), indicating that Yanglingquan (GB 34) has a certain relative specificity for the treatment of AC of the Dan Fu (gallbladder) disorders, which is consistent with the related research[23]and clinical practice[6].
The results of this study indicate that EA at the Lower He-Sea point related to the Fu organs (gallbladder, stomach, large intestine and small intestine) of the digestive system produces a certain effect on the AC guinea pigs; the therapeutic efficacy of Yanglingquan (GB 34) was superior to that of Zusanli (ST 36), Shangjuxu (ST 37) and Xiajuxu (ST 39) in guinea pigs, suggesting a certain relative specificity of Yanglingquan (GB 34) in treatment of AC. The mechanism of EA at Yanglingquan (GB 34) in AC treatment may be to inhibit the inflammatory factors and immune responses by regulating IL-1β and NF-κB, thus to the reduce inflammation and improve gallbladder tissue damage. The results of this study partially confirmed that the Lower He-Sea points should be the points in the ‘He-Sea points treating the internal Fu organs’, and can be used to treat the corresponding intestinal diseases; however, the specific mechanism still needs further investigation from different perspectives.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by National Natural Science Foundation of China (國家自然科學(xué)基金項目, No. 81173327); Li Jia-bang’s Inheritance Studio Construction Project of National Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (國家中醫(yī)藥管理局全國老中醫(yī)藥專家李家邦傳承工作室建設(shè)項目).
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria.
Received: 28 December 2019/Accepted: 22 January 2020
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年4期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2020年4期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Clinical observation of Zhen’ai needling method in Nei Jing (Classic of Internal Medicine) for children with allergic rhinitis accompanied by adenoid hypertrophy
- Clinical observation of tuina manipulations for tic disorders in kids
- Clinical observation on muscle regions of meridians needling method in improving upper limb function for children with cerebral palsy of spastic hemiplegia type
- Electronic moxibustion apparatus and traditional moxibustion in treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial
- Clinical observation on filiform fire-needling plus continuous passive motion therapy for frozen shoulder
- Clinical study on auricular point sticking plus Western medicine for moderate gastric cancer pain
