Rare primary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the renal pelvis
Shi-Cong Lai, Samuel Seery, Tong-Xiang Diao, Jian-Ye Wang, Ming Liu
Shi-Cong Lai, Tong-Xiang Diao, Jian-Ye Wang, Ming Liu, Department of Urology, Beijing Hospital, Beijing 100730, China
Shi-Cong Lai, Tong-Xiang Diao, Jian-Ye Wang, Ming Liu, National Center of Gerontology,Beijing 100730, China
Shi-Cong Lai, Tong-Xiang Diao, Jian-Ye Wang, Ming Liu, Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
Shi-Cong Lai, Jian-Ye Wang, Ming Liu, Graduate School of Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China
Samuel Seery, School of Humanities and Social Sciences, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China
>Tong-Xiang Diao, Peking University Fifth School of Clinical Medicine, Beijing 100730, China
Abstract
Key words: Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma;Prognosis;Radical nephroureterectomy;Upper urinary tract;Treatment;Case report
TO THE EDITOR
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma (LELC) is a rare, malignant epithelial tumour which can arise within the upper urinary tract (UUT)[1,2].Due to its rarity, little is known about this malignant neoplasm.We recently published a systematic review and cumulative analysis of all the 28 previously published UUT-LELC cases in an effort to support clinicians identifying and treating this disease[3].We found that administering a radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) treatment was associated with better disease-free survival, although our tentative recommendations were based on only a modicum of evidence.Therefore, we hope to share a new renal pelvis LELC case in our hospital with long-term follow-up, and to develop the existing evidencebase for clinicians treating this rare malignant disease.
In this instance, a 75-year-old woman with an history of hypertension presented at our urology department in February 2011 having experienced two weeks of gross haematuria.A 1 cm × 1.2 cm hypoechoic mass in the left renal pelvis was found through ultrasound;however, no malignant cells were detected through cytological urine tests.The patient was sent for abdominal magnetic resonance imaging, which identified a slightly enhanced mass in the left renal pelvis although there was no evidence of lymph node metastasis (Figure 1A).Ureteroscopic tumor biopsy suggested the existence of urothelial carcinoma, hence, laparoscopic radical left nephroureterectomy with bladder cuff excision was performed.
Microscopic examination confirmed abundant lymphoid stroma surrounding the large polygonal tumour cells (Figure 1B).Immunohistochemical staining of polygonal tumour cells were returned positive for cytokeratin 7 (Figure 1C).Further, analysis of lymphoid stroma also yielded positive results for CD3 and CD20, although, Epstein-Barr virus immunostaining was negative (Figure 1D).This histological picture is compatible with the criteria for lymphoepithelial carcinoma and eventually the pathological stage was determined to be pT3N0M0.In view of this patient’s age and through a shared-decision making process which involved communicating the associated potential complications, we agreed to administer no additional therapy.Follow-up assessments including abdominal computed tomography scans and cystoscopies were taken during outpatient consultations.This lady remains in relative good health, without evidence of postoperative tumour recurrence at 93 mo.
This current case presented with similar characteristics to those previously published which commonly describe gross hematuria as the initial symptom and negative Epstein-Barr Virus testing[1,4,5].However, pathological testing revealed two distinct histologic patterns, consisting of large predominant LELC and focal urothelial carcinoma in this case.Of note, the identified urothelial carcinoma was aggressive and may play a critical role in prognosis;although, previous literature suggests that predominant or pure subtype LELC have a relatively favorable prognosis compared to focal LELC[3,6,7].Even though the pathological stage was pT3N0M0, which would usually require chemotherapy, through discussion with our patient we decided not to administer this intervention after RNU.Follow-up examinations provided no evidence of disease recurrence or metastasis.
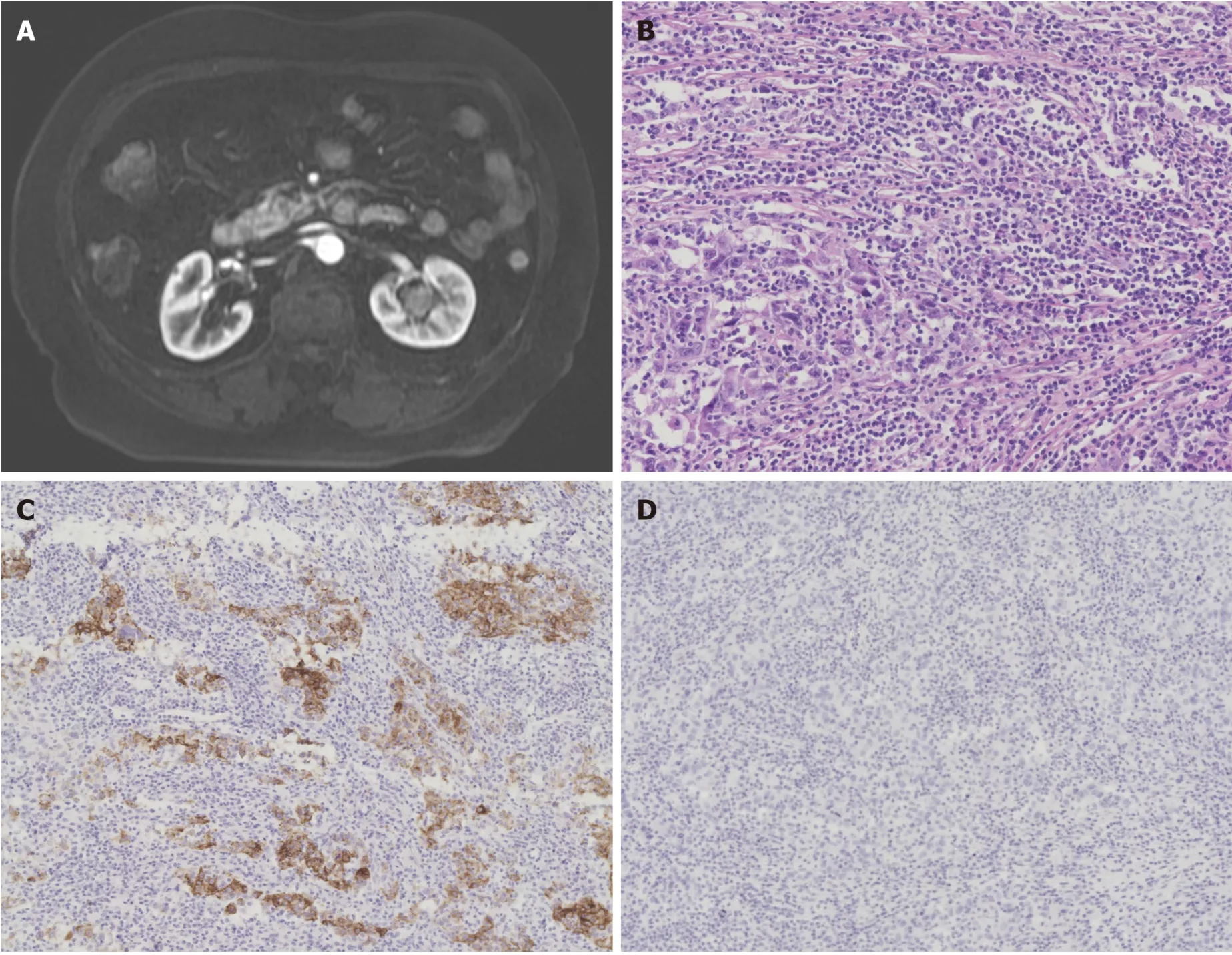
Figure 1 Clinical imaging and pathological features.
This experience adds to this small but growing evidence base.Despite the sparsity of available data to guide decisions, favorable prognosis can be achieved with RNU based therapy which is evidence-based[3,8,9].Having said that, there remains insufficient data on renal pelvis LELC to distinguish differences, therefore we encourage urologists to record and report these rare cases with longer follow-up.It remains of paramount importance to further assess the biologic behavior of these tumors and to identify the optimal management regimen and particularly disease prognostics.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年9期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年9期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Portal hypertension in a patient with biliary hamartomas:A case report
- Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix with rare lung metastases:A case report and review of the literature
- Endoscopic ultrasonography elastography in the diagnosis of intrapancreatic ectopic spleen:A case report
- Giant ventral hernia simultaneously containing the spleen, a portion of the pancreas and the left hepatic lobe:A case report
- Application of curved ablation in liver cancer with special morphology or location:Report of two cases
- COVlD-19 managed with early non-invasive ventilation and a bundle pharmacotherapy:A case report
