The Role of Special Economic Zones in Enhancing Enterprise’s Export Structures: The Perspective of Industry Complexity
Chang Zihao, Lan Wenting
Abstract: Special economic zones (SEZs) help provide the momentum for China’s economic growth. This paper studies the influence of SEZs on enterprise’s export structures from the perspective of production complexity using data from the China Industry Business Performance Database (CIBPD) collected between 2000 and 2007. We found that enterprises in SEZs have a higher export propensity and volume due to more complexity. Also, enterprises with more complexity outside SEZs show a higher export propensity and volume depending on the number of SEZs near them and the radiation effect of the SEZs. Similarly,high and new-tech industrial development zones perform more prominently in this regard.
Keywords: special economic zones, complexity of the production process, export structure
Introduction
SEZs have long been regarded as a powerhouse for the economic growth of a country or region. Through SEZs, many countries and regions have achieved remarkable economic development. Since the 1980s, SEZs have flourished in China and have contributed greatly to China’s economic development miracle.
Owing to the significant role of SEZs in economic development, research in this regard has been constant both at home and abroad, focusing on whether SEZs really promote export and economic growth and if so, how they affect the growth.
Most scholars determined that SEZs do promote export and economic growth of a country or region. Bhatta (2003), analyzed policies, systems and neighboring environments of SEZs in India and pointed out that SEZs can attract capital and technologies to further increase export and boost economic development. Also based on studies in India, Aggarwal (2006) concluded that the implementation of an SEZ system in India can to some extent cope with the country’s lack of infrastructure and complexity in incorporation procedures, and thus attract more foreign investment, increase domestic trade along with financial and tax revenues and thus promote economic growth. Murayama and Yokota (2009)found that after the establishment of SEZs, exports and employment in South Korea, Bangladesh and India witnessed significant increases. As far as China is concerned, Rodrik (2006), Naughton (2007),Alder, Lin, and Zilibotti (2013), Wang and Zhang (2016) determined that China’s SEZs exert a positive influence on the country’s exports and economy. This conclusion was supported by a study done by Wang (2013) based on SEZ data from 1978 to 2008.
Scholars also conducted in-depth studies on how SEZs affect exports and the economy to enable the zones to facilitate national or regional exports and economic growth. Guo and Hao (2005) and Zheng,Gao and Hu (2008) held that technologies and market behaviors of SEZ enterprises would inevitably react with associated factors of local industries, leading to agglomeration effects. On the other hand,agglomeration effects, being important location advantages, will also attract new companies to settle in the zones (Yu and Sun, 2011), resulting in a virtuous circle and higher resource allocation efficiencies in the SEZs (Sheng and Zhang, 2017). Analyzed from the perspective of policies and systems, and three decades of accumulated data about China’s SEZs, Wang (2013) found that SEZs attract foreign direct investment (FDI) through tax reductions or exemptions and favorable land use policies to boost exports and economic growth. Huang, Wu, and Bao (2013) studied export data from customs records in 2006 and found that SEZs exhibit more comparative advantage in terms of contract-based industries and their institutional advantages play a significant role in advancing local export and economic growth. Shen, Gu, and Chen (2017) found that local governments promoted rapid development of some industries by attracting companies to settle in SEZs and formulating relevant industrial policies. As for SEZs’ influence on the economy of the neighboring areas, apart from investigating the influence of agglomeration effects, policies and systems on SEZ enterprise exports, scholars focused on other factors such as company size and per capita productivity. Scholars generally hold that SEZs can promote a country or region’s exports and economic growth mainly through agglomeration effects,policies, systems, and other corporate factors.
With the continuous development of China’s economy, the structure of its export commodities is improving, and the complexity of those commodities is far outdoing countries with similar income levels and getting closer to those of developed countries (Rodrik, 2006; Schott, Fuest & Kevin, 2008).By analyzing cross-country panel data, Hausmann, Hwang, and Rodrik (2007) found that if products with high technology added value take up a greater percentage of export commodities, then trade growth will be faster and economic growth can be realized more rapidly. Jarreau and Poncet (2012)confirmed this conclusion through China’s provincial-level panel data. Costinot (2009) found that for some sophisticated industries, their comparative advantage originates from higher complexity.Chor (2010) also believed that complexity is an important variable for evaluating a country’s export performance. It can thus be seen from the above that complexity plays a significant role in a country or region’s export and economic growth.
At the beginning of its reform and opening-up, China mainly exported low-technology-based products due to comparative advantages in its intensive labor force, as shown in the Heckscher Ohlin model. In recent years, however, not only foreign-invested companies but also domestic enterprises in China have developed a competitive edge in technologies (Yao & Zhang, 2008). China’s export structure has shifted from low-technology-based products to medium level technology-based products while export of products with high technology added values has been increasing (Fan, Guan & Yao,2006). It is undeniable that Chinese enterprises are enhancing the complexity of their production process. Currently, Chinese enterprises have increasingly higher requirements for the quality of their labor force, which shows that their complexity is on the rise and their products show stronger competitiveness (Yu & Zhang, 2017; Li & Wang, 2019) allowing them to develop new comparative advantages for their exported products. With higher complexity in exported technology and increases in education input for laborers’ children (Chen, Wang & Mao, 2014), a solid foundation has been laid for enhancing complexity of the production process in the future so that corresponding complexity of export products can be continuously increased. As a pioneering force for China’s economy, it is natural for SEZs to become a key topic for scholars studying the influence of complexity on the exports of Chinese enterprises.
China has now entered the post-SEZ era with the quantity and quality of SEZs rising remarkably and the gradual polarization of their functions (Zheng, 2008). In a broad sense, China’s SEZs include a variety of development zones or parks such as economic and technological development zones (ETDZs),high and new-tech industrial development zones (HNIDZs), export processing zones, agricultural science and technology demonstration zones, industrial parks, environmental protection-themed industrial parks, and comprehensive parks (Jin, 2013). Among them, ETDZs as well as HNIDZs are the largest in number and size and have the greatest influence (Zhang & Zhao, 2007). These two types of zones differ greatly in the complexity of their resident companies.
Complexity plays an important role in SEZs in China. However this factor has seldom been studied in previous research on how SEZs affect exports and economic growth. Using micro panel data from CIBPD covering 31 provinces and municipalities①Data used in this paper does not cover that of China’s Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan.from 2000 to 2007 and Heckman’s two-stage model, we compared enterprises in and out of SEZs to study the influence of SEZs on export structures to provide additional evidence for theories on the influence of SEZs on national and regional exports and economic growth.
Part 2 of this paper states our theoretical framework and hypotheses; Part 3 covers modeling,variable selection and data description; Part 4 presents our analysis and empirical results, and Part 5 contains our conclusive remarks.
Theoretical Framework and Hypotheses
During the past three decades, China has witnessed great changes in its industrial structure with a continuous decrease in the ratio of its primary industries and its secondary and tertiary industries.Its secondary industries have seen the upgrading of their internal industrial structures, continuous increases in value added manufacturing and a rise in complexity. As the forefront of China’s economic development, SEZs unintentionally play an important role in the upgrading of industrial structures.Li and Shen (2015) held that SEZs effectively promote internal industrial structure changes in urban manufacturing industries. With higher complexity, SEZ enterprises attain stronger export competitiveness in their products and better export structures. For enterprises outside SEZs, SEZs can generate positive spillover so that those companies with high complexity can enjoy export growth as well. This promotes the growth of regionally interconnected development.
SEZs were first launched at the beginning of the 1980s, mainly for addressing China’s lack of capital and backward technologies. From the initial establishment till now, these zones have made great contribution to attracting foreign investments and accelerating technological progress, export and economic growth. ETDZs and HNIDZs were initiated at the end of the 1980s. These developments were the result of China’s learning from Western counterparts and were aimed to bring in high and new-tech industries to advance the internationalization of China’s products and technologies.
Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes the following hypotheses.
Hypothesis 1: If an SEZ enterprise features higher complexity, then it will have higher export propensity and volume.
Hypothesis 2: If a non-SEZ enterprise is somewhat influenced by a SEZ nearby and exhibits higher complexity, then it will have higher export propensity and volume.
Hypothesis 3: Compared with ETDZs, HNIDZs exert more remarkable effects as mentioned in the above two hypotheses.
Modeling, Variable Selection and Data Description
Export Model of SEZs
Modeling
Since not all the enterprises conduct an export business and many of them have zero export volume,selection bias (Heckman, 1979) may arise if only export volume is regressed. Therefore, Heckman’s two-stage model is applied in this paper. At the first stage, a probit model is used to establish a decisionmaking equation of an enterprise’s export behavior. At the second stage, a regression equation is set up for the enterprise’s export scale:
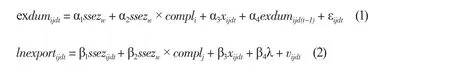
Where: exdum represents two discrete variables regarding the export behavior of an enterprise.If the enterprise exports anything in the year concerned, then the value is taken as 1; if it does not export anything in the year concerned, then the value is taken as 0. export stands for annual export volume of the enterprise (unit: RMB 10,000). ssez and the interaction term between it and compl are key explanatory variables. Vector x is the set of control variables andλis the estimated probability obtained from the probit model of Equation (1) and used as a control variable in Equation (2). It should be noted that exdum with a lag of one phase was added to the probit model to avoid multicollinearity of Equation(2) due to the possibility thatλmay be highly correlated with elements of vector x (Liu, Yi & Shao,2011). exdum with a lag of one phase is a variable that affects export decision-making but has no bias effect on export quotas.
Variable Selection
Key explanatory variables.
They are variable ssez1 of ETDZs, variable ssez2 of HNIDZs, and the interaction term compl×ssez1 between complexity and the fact of being an ETDZ or not, and the interaction term compl×ssez2 between complexity and the fact of being a HNIDZ or not. Although as mentioned above, SEZs in China include a variety of development zones or parks (Jin, 2013). Among them, ETDZs and HNIDZs feature the largest number and size and have far greater influence on China’s economy than any other type of development zone (Zhang & Zhao, 2007). Therefore, only the two types of development zones mentioned are studied in this paper. The two key explanatory variables are binary dummy variables. If variable ssez1 is 1, it means the development zone concerned is an ETDZ; if variable ssez1 is 0, it means it is an area other than a development zone. For variable ssez2, the same principle applies. The two variables are used to determine if exports of a SEZ are affected by any other factor after the control variable is considered. Since data about complexity is not available in China, this paper uses US-based research data referred to by Costinot (2009). The data shows the time to be fully trained and qualified in each industry. The longer the time, the more complexity the job features.
A set of control variables.
(1) lnlabor: the number of laborers, which is defined as the logarithmic value of the average number of laborers in the enterprise in the year concerned. Favorable policies generally enable an enterprise to expand its scale, which is often manifested by an increase in the number of laborers. Therefore,the variable can control the factor of policies. (2) lninvestment: investment, which is defined as the logarithmic value of investment amounts in the enterprise. It is also an indicator of company scale to control the factor of policies. (3) lnvcount: total output of a certain industry in the area to be explained.It is defined as the logarithmic value of total output of all the enterprises in each industry in the area to be explained and is used to measure agglomeration effects. It is inevitable that technologies and market behaviors of enterprises in the area to be explained would interact with associated factors of local industries to generate agglomeration effects. Under such effects, spillover is bound to occur in terms of technology, management and markets within the industry chain to further promote exports and economic growth (Guo and Hao, 2005; Zheng, Gao & Hu, 2008). Therefore, such spillover needs to be controlled as well. (4) lnprodu: per capita productivity, which is defined as the logarithmic value of average productivity per person of the enterprise. Enterprises with higher productivity are often more inclined to conduct an export business. (5) lntime: years after establishment, which is defined as the logarithmic value of the years after the enterprises are established. A new company often pays more attention to overseas markets so that it may have more export business. (6) gy: whether state-owned.It is a binary discrete variable, for which 1 is taken if the company concerned is state-owned and 0 is taken if the company concerned is not state-owned. As state-owned enterprises play an important role in China’s economy, they generally focus more on the domestic market. (7) foreign: foreigninvested enterprises. Since SEZs attract the inflow of abundant FDI, the differences between foreigninvested enterprises and domestic companies should not be ignored. With comparative advantage due to its expertise in technologies and management, an enterprise with a medium level of product cost would choose to sell a certain product in the domestic market while a company with a lower level of product cost would choose to export to gain access to bigger markets (Melitz, 2003). Foreigninvested enterprises often outperform domestic companies in technology. Therefore, export of the latter mainly involves low-end products (Zhang, Zhang & Huang, 2010). The variable is also a binary discrete variable, for which 1 is taken if the company concerned is foreign invested and 0 is taken if the company concerned is a domestic enterprise. (8) lnlxzhch: interest expense of the enterprises, which is defined as the logarithmic value of such expenditures.
Data Description
The the panel data used came from Chinese Industrial Enterprises Database, covering a wide range of relevant factors about enterprises in 31 provinces and municipalities①Data used in this paper does not cover China’s Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan.from the period 2000 to 2007,including export volumes and decision-making, interest expenses, years after establishment, and per capita productivity of enterprises, whether state-owned, being foreign-invested or not, and the type and number of SEZs in the neighboring areas,②The number of SEZs in the neighboring areas refers to the number of SEZs in the city and adjacent cities.number of laborers, investment amounts, total output of the industry in the same area. Descriptive statistics results are shown in Table 1.
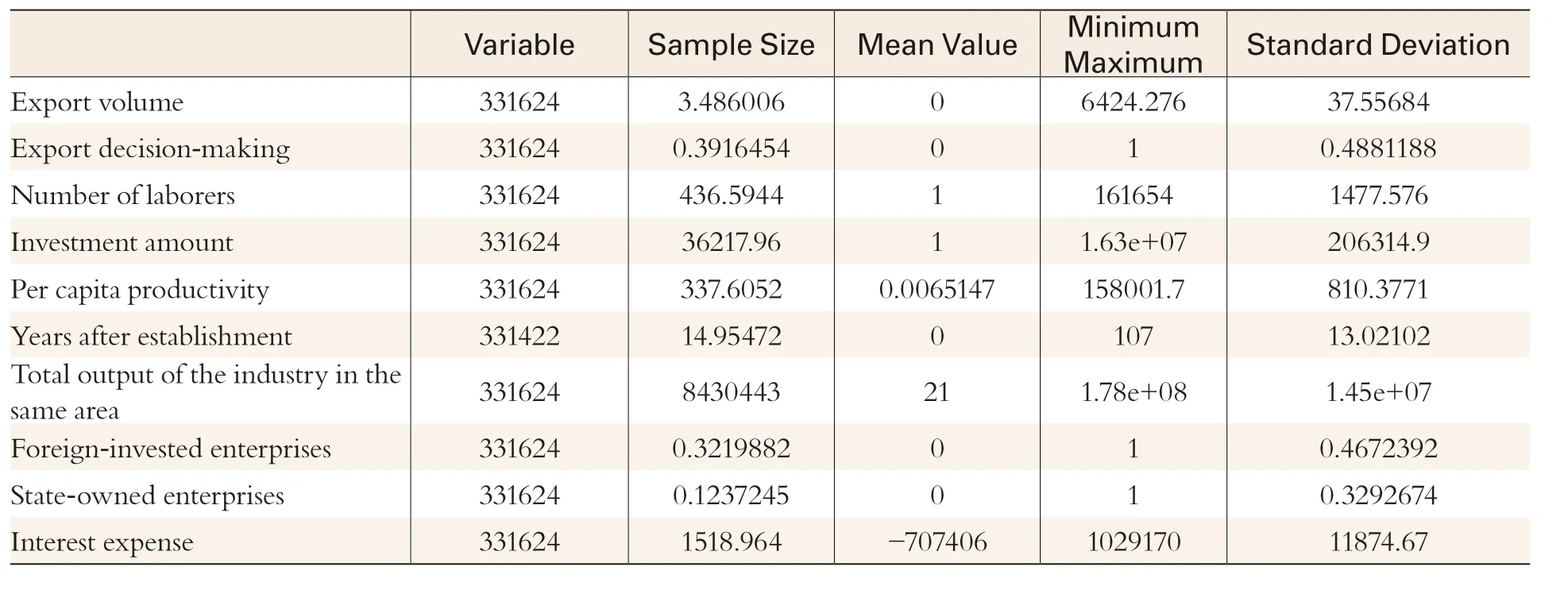
Table 1 Descriptive Statistics of Samples
Exports of enterprises in HNIDZs are higher than those in ETDZs, and much higher than those in non-SEZs. Export volumes in all three zones increased from 2000 to 2007 while the two types of SEZs witnessed the faster growth rate.
It should be noted that the data of complexity is based on the US research data used by Costinot (2009).A matching process was conducted between Industrial Classification for National Economic Activities in 2002 and Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes. For instance,the category 4721 (railway, road, tunnel and bridge engineering construction) in the former is considered to correspond to the category covering bridge, tunnel and elevated highway in SIC1622. Among others, the top four industries in terms of complexity are optical and health services supplies, aircraft and parts, drugs and medicines, and construction and material handling machines. See Table 2.
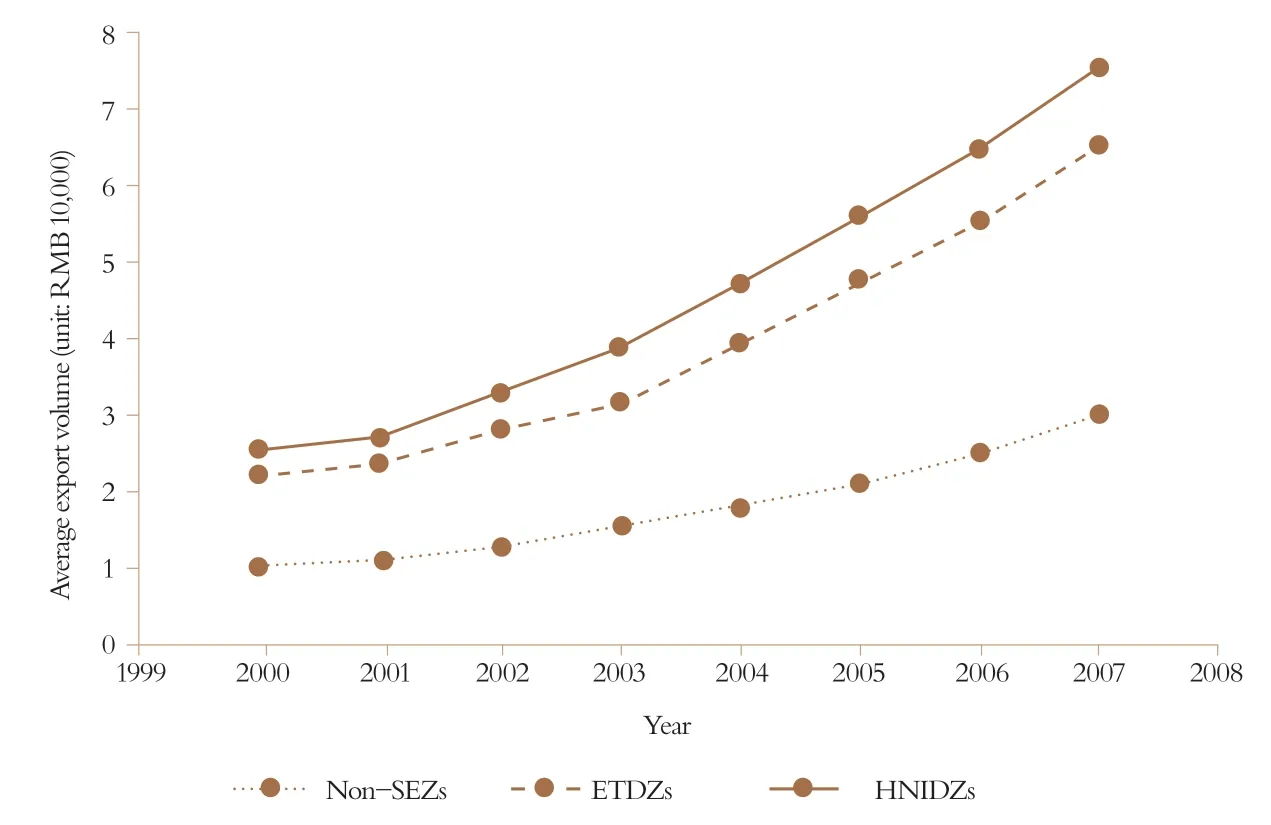
Figure 1 Change Tendency of Enterprise Exports

Table 2 Top Four Industries by Complexity
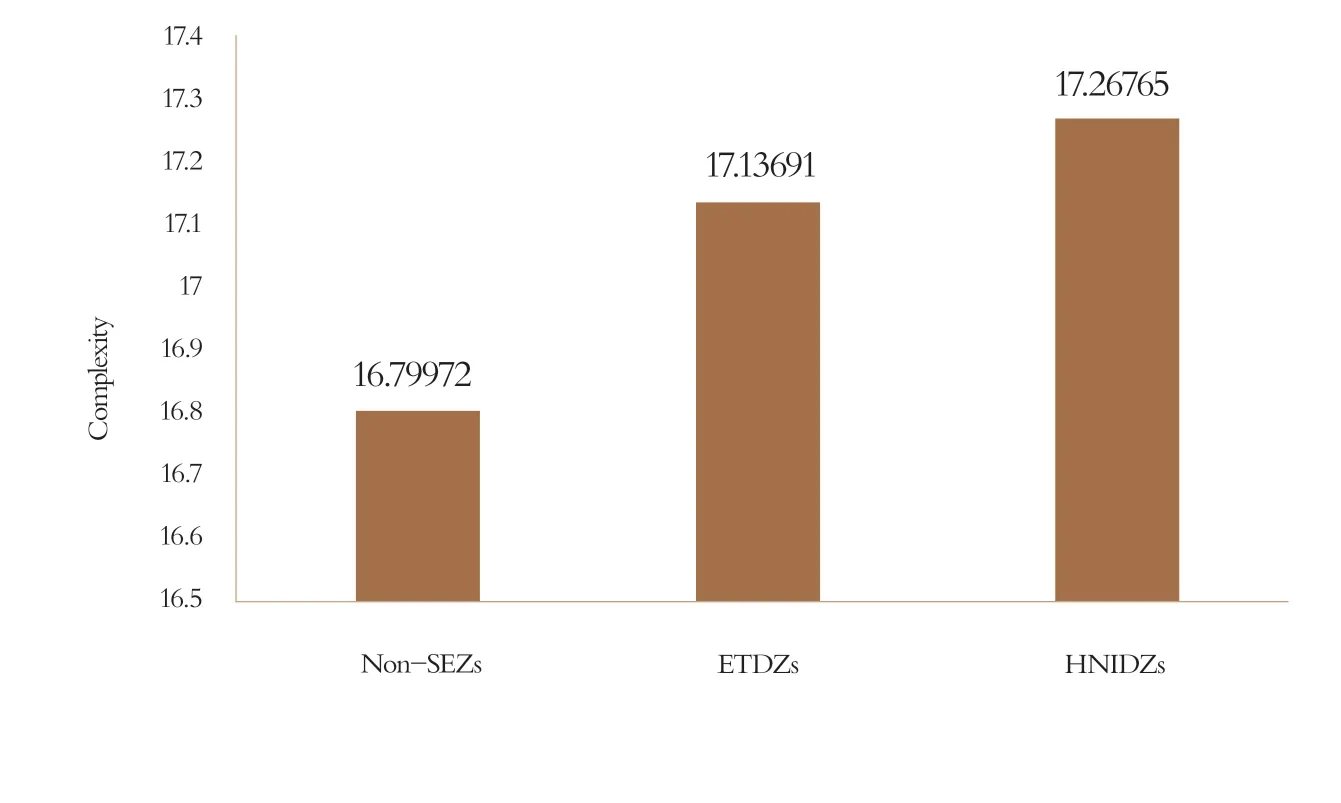
Figure 2 Comparison of Enterprises’Complexity
Enterprises in HNIDZs have higher complexity than those in ETDZs, and far higher complexity than those in non-SEZs, as shown in Figure 2.
Empirical Result and Analysis
SEZ Enterprises
The empirical process involved two types of samples: ETDZs and non-SEZs; HNIDZs and non-SEZs. Table 3 shows the differences of the two types of SEZs in export propensity and volume.Estimated coefficients of variables (ssez1, ssez2) of ETDZs and HNIDZs are significantly positive at the confidence level of 1% or 5%. This means that both types of SEZs can promote export growth.Estimated coefficients of the interaction terms (compl×ssez1, compl×ssez2) between complexity and being in a SEZ or not show the same result. This means that the higher the complexity an SEZ enterprise features, the higher its export propensity and volume are. Table 3 also indicates that export propensity and volume of enterprises in ETDZs and HNIDZs are higher than those of enterprises in non-SEZs,and enterprises in HNIDZs, have much higher export propensity and volume.

Table 3 Estimated Results of SEZ Enterprises
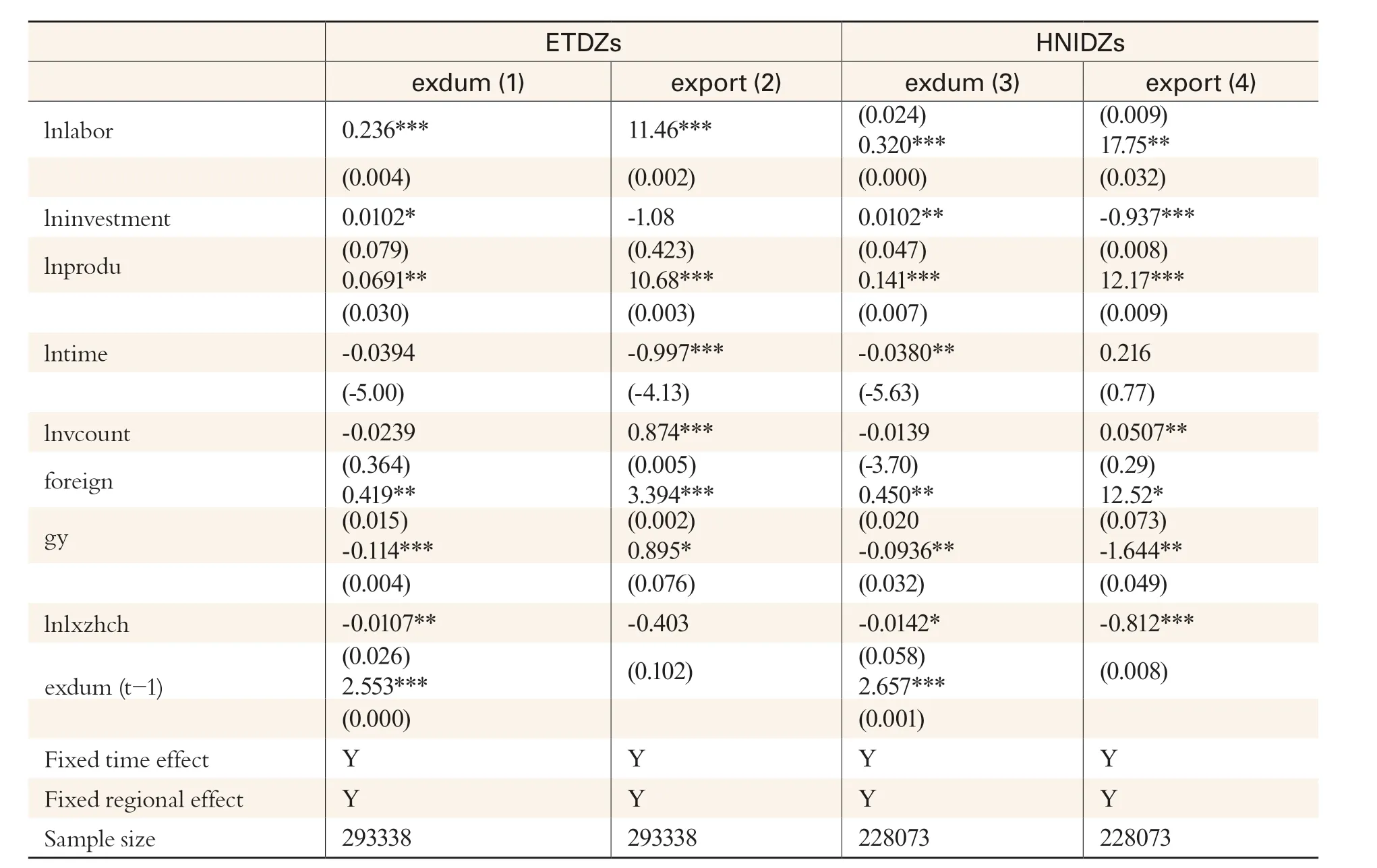
Note: *, **, *** represent statistical significance of 10%, 5%, and 1% respectively.
Among control variables, estimated results of the numbers of laborers are significantly positive while those of investment amounts are not. With higher productivity per capita, export propensity and volume would rise accordingly. This is in line with the theory of comparative advantage. Estimated results of the years after establishment are significantly negative, meaning that newly established enterprises often attach more importance to their export business. Estimated results of total output of a certain industry within the two types of SEZs are significantly positive, meaning that agglomeration effects exist and interactions between enterprises in the same industry promotes their export business.Moreover, state-owned enterprises conduct less export business than other enterprises while foreigninvested enterprises have more. Interest expense causes heavier burdens on enterprises so that they tend to be too conservative to export.
It can be seen from the above estimated results that enterprises with high complexity in SEZs have higher export propensity and volume and estimated results of those in HNIDZs are even more conspicuous. The results are consistent with statements in the theoretical hypotheses.
Non-SEZ Enterprises
Previous studies (Combes, Duranton & Gobillon, 2010; Bao and Tang, 2016) have demonstrated that a radiation effect may arise in regional economic growth. As for enhancing the export structure of SEZs, it is very likely for such an effect to spread from SEZs to non-SEZs.
Since such an effect decreases with the increase in geographic distance, we selected the SEZs in a city and its adjacent cities as key explanatory variables. nssez indicates whether there are ETDZs or HNIDZs in adjacent cities or not. nssez1 means one to three ETDZs or HNIDZs are there in the neighboring areas; nssez2 means four or more ETDZs or HNIDZs are there in the neighboring areas.The interaction terms between the two variables and complexity were also added while other control variables remain unchanged.
It can be seen from Table 4 below that estimated coefficients of variables of ETDZs or HNIDZs in the neighboring areas are generally significantly positive at the confidence level of 1% to 10%,meaning that SEZs can really boost the exports of non-SEZ enterprises in the neighboring areas. In addition, the interaction terms are significantly positive at the confidence level of 1% to 10%, which means that SEZs have great influence on export propensity and volume of non-SEZ enterprises with higher complexity in the neighboring areas, and HNIDZs in particular, exert an even more conspicuous influence.
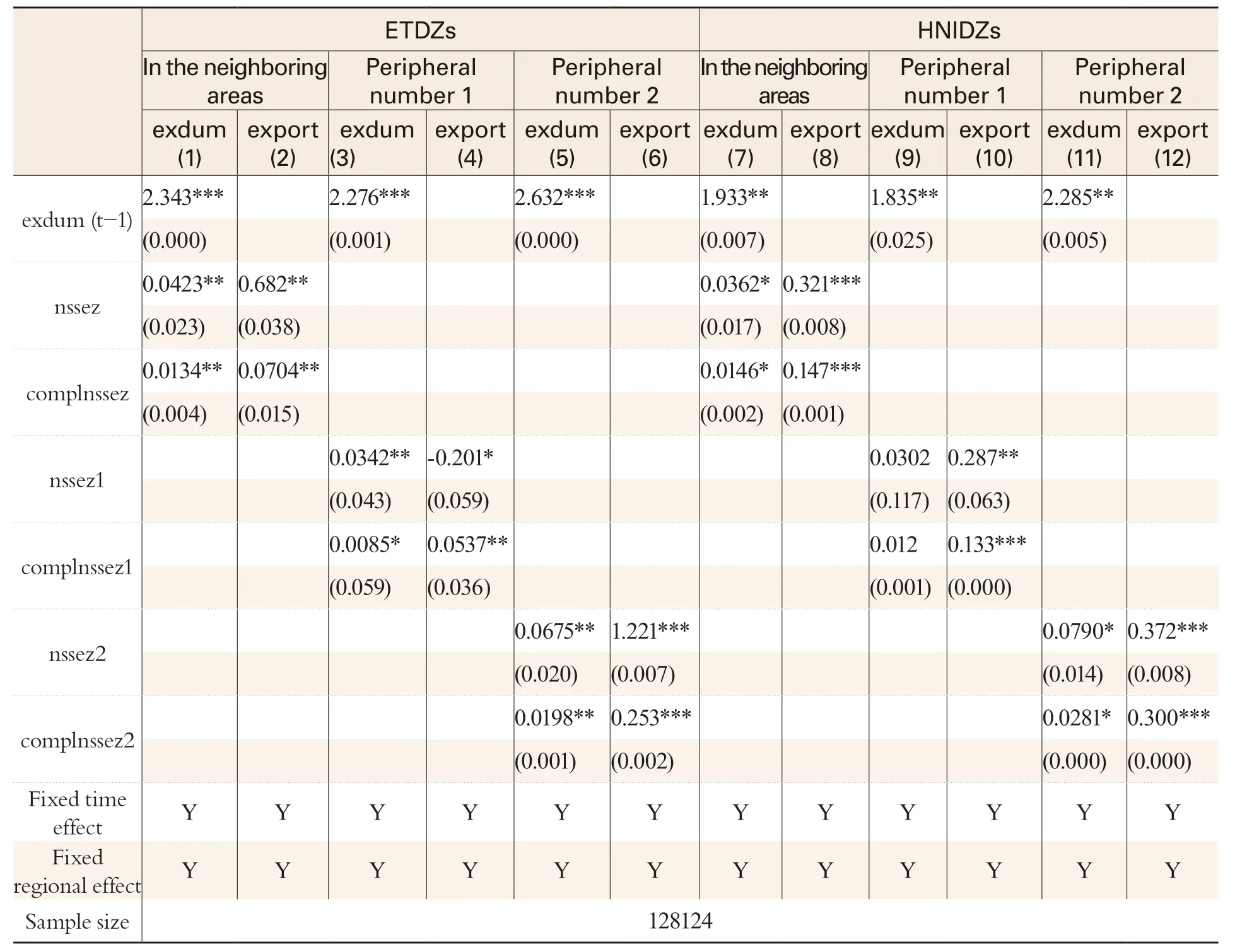
Table 4 Estimated Results of Non-SEZ Enterprises
Estimates by Regions
SEZs in China’s eastern, central and western regions are not evenly distributed due to the imbalance in economic development and geographical conditions between these regions. Liu and Cheng(2018) studied state-level economic development zones (SEDZs) and found that their contribution to promoting the rationality of the industrial structure of their regions varied with the difference between Tier 1 and 2 cities. Take the number of SEDZs as an example. By 2017, there were 111 SEDZs in the eastern region, 66 in the central region, and 42 in the western region. There were also differences in company scale and state of operation between regions. Take small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)as an example, Lin and Guan (2004) found based on survey data that the competitiveness of SMEs in the eastern region was much higher than in the central and western regions.
Moreover, for the above samples, the numbers of SEZs in the eastern, central and western regions are not uniform, and since enterprises in the three regions have different competitiveness levels, the influence of complexity on SEZ enterprise export structures may vary from region to region. Our estimates for SEZs in the three regions were based on the above factors. The division of the three regions was made by reference to the criteria applied by He Canfei (He and Liang, 2004): the eastern region covers Liaoning, Hebei, Beijing, Tianjin, Shandong, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Zhejiang, Fujian,Guangdong, Guangxi, and Hainan; the central region consists of Heilongjiang, Jilin, Inner Mongolia,Shanxi, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Anhui, and Jiangxi; the western region includes Xinjiang, Ningxia,Gansu, Shaanxi, Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, and Yunnan.
As handled in the empirical model, the samples were divided into two types: ETDZs and non-SEZs; HNIDZs and non-SEZs. Table 5 shows that enterprises with high complexity in the eastern and central regions exhibit significantly higher export propensity and volume at the confidence level of 1%or 5% while such a case is not so conspicuous for the western region.
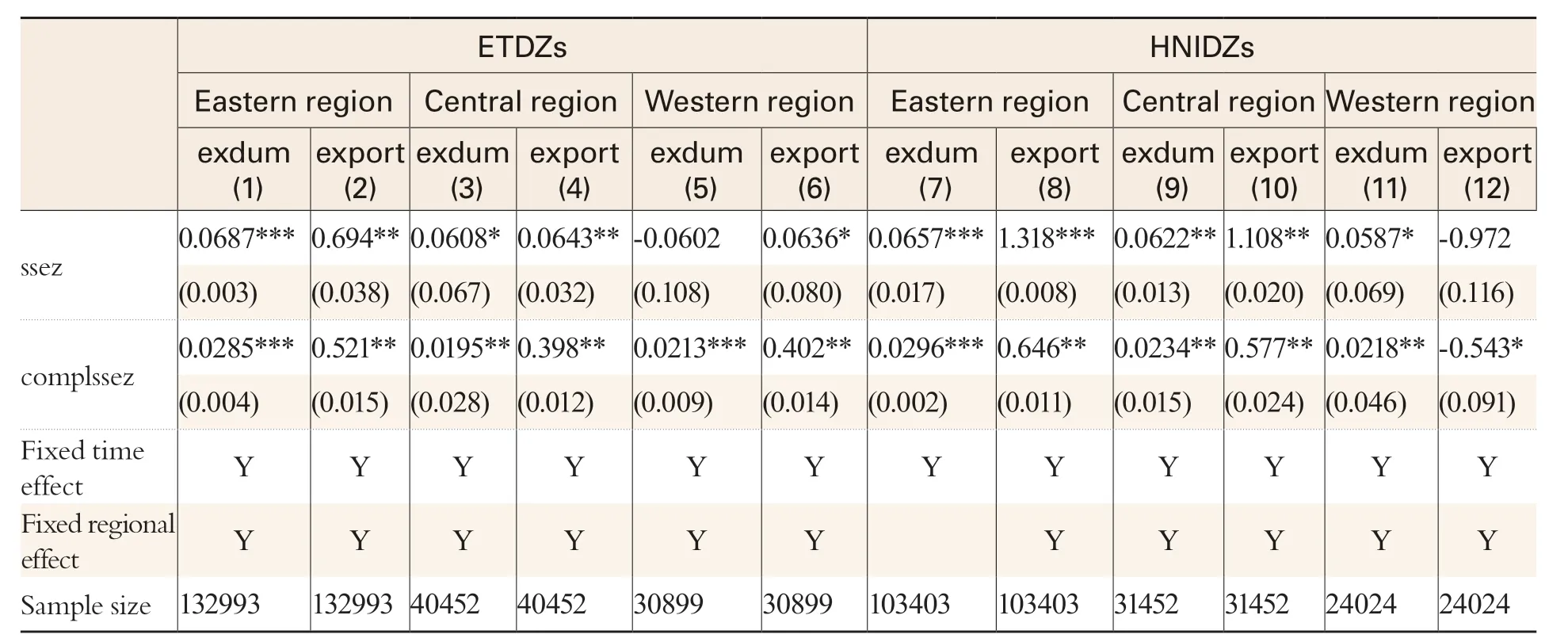
Table 5 Estimates by Regions
Analysis of Steadiness: Selecting Resident Enterprises
The agglomeration effects and policy advantages of SEZs will attract many enterprises outside the SEZs to move into an SEZ and operate there so that the following situation may happen: SEZs have not made efforts to boost export propensity and volume of enterprises with high complexity, yet such enterprises take the initiative to apply for settling there, leading to improvement in export structure of SEZs. Therefore, this paper selected enterprises which have not moved out of their original places during the observation period of this empirical analysis.
The empirical process also involves two types of samples: ETDZs and non-SEZs related to the resident enterprises; HNIDZs and non-SEZs related to the resident enterprises. It can be seen from Table 6 that estimated coefficients of variables (ssez1, ssez2) of ETDZs and HNIDZs are significantly positive at the confidence level of 1%. This means that both types of SEZs can promote export growth for resident enterprises. Estimated coefficients of the interaction terms (compl×ssez1, compl×ssez2)between complexity and being in an SEZ, or not, are also significantly positive at the confidence level of 1% or 5%. This means that the higher complexity a resident SEZ enterprise features, the higher its export propensity and volume are. In this regard, the above conclusion is not affected by an enterprise’s voluntary migration.
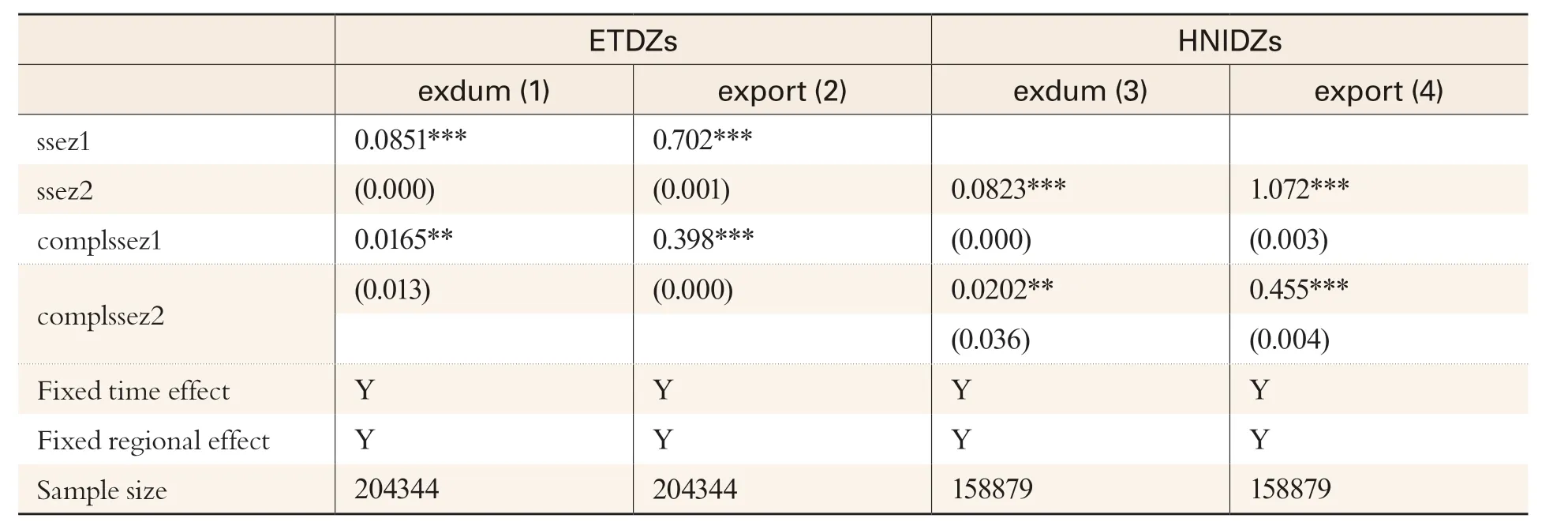
Table 6 Estimates of Resident Enterprises
Conclusive Remarks
As the main powerhouse of China’s export and economic development, SEZs have made tremendous contributions to regional and national economic growth over the past three decades.Through an empirical research on micro panel data from CIBPD which included 31 provinces and municipalities from 2000 to 2007, we found that with the development of SEZ, they enable enterprises with high complexity to have higher export propensity and volume. This effect is not affected by enterprise migration and is applicable to both SEZ and non-SEZ enterprises, and HNIDZs perform even better in this aspect.
With continuous upgrading of China’s industrial structure and constant improvements in complexity by enterprises, our comparative advantage of export products will step onto a higher technological level. It should be noted, however, that there is still a huge gap between complexity of goods made in China and in western developed countries and an economic growth mode based on exporting low-end products in huge quantities cannot promote China’s economic development in the long run. It is recommended that the government take various measures to further strengthen infrastructure construction favorable for the production of enterprises with high complexity, and further improve policies for encouraging technological innovation to attract such enterprises to establish factories and undertake the tasks for upgrading China’s industrial structure in a bid to enhance the overall product quality of Chinese enterprises.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2019年6期
Contemporary Social Sciences2019年6期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Measurement of Urban Economic Gravity of China’s Three Major Agglomerations and Its Implications for the Coordinated Development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region
- The Social Security Miracle of China: Development Mechanism and Institutional Transformation
- A Brief Introduction of Sichuan Academy of Social Sciences
- A Brief Introduction to the English Periodical of Contemporary Social Sciences
- Requirements for contribution
- A Critical Analysis of the Legality of Fan-subbing in Copyright Law
