Survival rate among tuberculosis patients identified in south of Iran,2005-2016
Vahid Rahmanian, Karamatollah Rahmanian, Narges Rahmanian, Mohammad Ali Rastgoofard,Elham Mansoorian
Research Center for Social Determinants of Health, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran
Keywords:Survival rate Tuberculosis Risk factors South Iran
ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the survival rate of tuberculosis (TB) patients and to identify the important factors associated with the survival of these patients in southern Iran. Methods: The present retrospective cohort study extracted and reviewed available medical records of 134 TB patients undergoing TB treatment centre, during 2005 to 2016. The Survival rate of patients for the outcome of the interval from diagnosis until death was plotted using life table and Kaplan-Meier survival curve. Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to examine the simultaneous effect of variables on survival rate. The significance level was considered to be 0.05. Results: In this study, 64.2% of the participants were male, 73.1% had pulmonary TB and 5.22% had HIV. The survival rate of one, five and thirteen years after diagnosis were 93%, 78% and 69%, respectively. The risk of death in patients with extrapulmonary TB (95%CI=1.96-15.83, P=0.001) was 5.58 times higher than in patients with pulmonary TB. The risk of death in smokers with TB (95% CI=1.74-2.46, P<0.001) was 2.07 times higher than in nonsmoker patients, and also the risk of death increased to 1.10 times more for a one-year increase in patient age (95% CI=1.06-1.14, P<0.001). Conclusions: The risk of death in patients with extrapulmonary TB and TB smokers was higher than other patients. Therefore, timely diagnosis and proper treatment of patients with extrapulmonary TB as well as the development and integration of smoking cessation programs are underlined and emphasized in the formulation and implementation of the National Tuberculosis Control Program.
1. Introduction
Tuberculosis (TB) is a life-threatening infectious disease that accounts for a wide range of clinical diseases, which is mainly developed by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; 85% of cases are manifested in pulmonary form and 15% as extrapulmonary[1]. The areas involved in the extrapulmonary type are lymph nodes, pleura,genitourinary system, bone, joints, meninges and peritoneum, and the likelihood of a patient’s death varies according to the illness intensity based on the count of bacteria, the extent of the disease,and anatomical location[2,3]. On the other hand, the clinical symptoms in the type of pulmonary disease are often more specific and include fever, night sweats, weight loss, anorexia and general weakness, and it leads to a cough in 90% of cases that begins with morning coughing and then purulent cough and bloody sputum[4].
Despite global efforts to control TB, the disease remains the most important cause of death among infectious diseases worldwide, and it is estimated that between 8 and 9 million new cases of TB with 2 million deaths annually occur in the world[5].
The TB mortality rate varies from 5% in a few countries to 20%in most African countries, which indicates significant inequalities among countries in access to TB diagnostic services and treatment[6].The TB control is very difficult due to concurrent HIV infection and increased multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB). Extensively drugresistant TB (XDR-TB) has been reported from 49 countries since 2008, with a success rate of 30%[1,6].
In a study in South Korea, the mean survival rate of patients with XDR-TB was significantly lower than in other MDR-TB patients[7].In a study in Iran, the survival rate of patients with concurrent HIV and TB infection at three, five and ten years after the diagnosis of TB, was reported to be 72.0%, 62.5% and 44.3%, respectively[8].
Directly observed treatment, short-course (DOTS, also known as TB-DOTS) is a strategy adopted in TB control, whose treatment success will be 90%-95% if correct and less than 70% if not implemented[9].
More than 80% of TB cases live in 22 Asian and African countries,such as Afghanistan and Pakistan, where are eastern neighbors of Iran. On the other hand, the incidence of TB in Iraq, where is the western neighbor of Iran, is increasing due to political currents and changes in recent years[10].
The incidence rate of smear-positive pulmonary TB is currently the main indicator of measuring the state of TB in Iran[11]. This rate is not the same in all regions of Iran, which is higher in boundary areas such as Sistan Baluchestan, Khorasan, Gorgan and East Azarbaijan and Khuzestan and the southern coasts mainly border with Pakistan,Afghanistan and Iraq, but less prevalent in central provinces[10].
The drug-resistant TB in Iran is also becoming a health problem;besides, recent reports indicate totally drug-resistant TB in Iran[12].According to the World Health Organization, the total number of new cases of TB in Iran in 2015 was 10416 cases, of which 170 were MDR-TB and 1 425 were rifampicin-resistance TB; the mortality rate of TB in this year in Iran was 2.03 deaths per 100 000 people[13,14].
By reviewing available literature, there is clearly a research gap in the study of the survival of TB patients in Iran. The present study was conducted to determine the survival rate of TB patients and to identify the important factors associated with the survival of these patients in southern Iran.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study design and sampling methods
The present retrospective cohort study extracted and reviewed available medical records of 134 TB patients undergoing TB treatment centre affiliated to Jahrom University of Medical Sciences,Iran, during 2005 to 2016.
2.2. Data sources/ measurement
A researcher-made questionnaire based on the study objectives was used to collect information. Information contained in the records was noted in the information form, including age, gender,nationality, residence, involved organ, type of disease, incidence time, underlying diseases such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, history of contact with smear-positive pulmonary TB and positive degree of sample. Next, an expert at the TB Center contacted by telephone with all registered patients over a period of six months from March 1 to August 30, 2018, and asked about the current condition of the patient. In case of death, the cause of death and the exact date of death were questioned. Of the 134 registered patients who had the phone number, 22 were excluded due to lack of adequate information from follow-up and survival analysis for reasons such as immigration, change of address and phone number, especially in the foreign citizens group, such as Afghani and Iraqi groups. Eventually,112 patients were followed up for survival analysis. The period of survival was from diagnosis to death, which was calculated by subtracting the date of death from the date of diagnosis of TB. The secondary objective of this study was to determine the risk factors associated with death and to compare the frequency of death among patients with pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB.
In the present study, pulmonary TB was considered in patients with two positive sputum smears or one positive sputum smear plus a positive sputum culture or a chest X-ray. Furthermore, sputumnegative pulmonary TB was considered in patients with two negative sputum smears but with a positive sputum culture or with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB who did not respond to a twoweek broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. Extra-pulmonary TB was diagnosed in patients with positive TB culture and pathological confirmation (caseous necrosis)[10].
2.3. Statistical methods
Mean (±SD) and frequencies (%) were used to describe patients’characteristics in each group. χ2test and Mann-Whitney U test were used to compare categorical and continuous variables between the two groups, respectively.
The Kaplan-Meier test was used to estimate the probability of death and the median time to death after TB diagnosis. The log-rank test was used to compare the median time to death between the two groups of pulmonary and extra pulmonary TB. The Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to determine the chance of death after TB diagnosis by adjusting for confounding factors. The hazard ratio (HR) and its 95% confidence interval (CI) were estimated. All analyses were performed using Stata version 12. A P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.4. Ethical considerations
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Jahrom University of Medical Sciences (Project identification code IR.JUMS.REC.1394.147).
3. Results
Of the 134 patients with TB in Jahrom city in 2005-2016, 64.2%were male and 66.4% were Iranians and the rest were foreign nationals. Concerning the form of TB, 73.1% had pulmonary TB,91.83% of which had positive-smear sputum, and 32.1% of samples in terms of positive grade were above three plus.
According to Table 1, most of the organs involved in extrapulmonary TB were lymph nodes (52.79%), pleura (22.22%),bone (13.89%), skin (5.55%) and meninges (5.55%). The mean age was (50.92±21.39) years in the pulmonary TB patients under study at the time of diagnosis and was (44.03±22.26) years in extrapulmonary TB patients, and this difference was not statistically significant (P=0.104).
During the study period, 27 TB patients died. Out of 27 deceased patients, the cause of death was determined in 21 patients. Of these,the most commonly reported deaths were myocardial infarction, lung infection, TB and lung cancer in 13, 4, 3, and 1 people, respectively.According to life table (Table 2), the one-year survival rate after diagnosis was 93% (95%CI: 87%-96%), five-year survival rate was 78% (95%CI: 69%-85%) and 13-year survival rate was 69%(95%CI: 58%-78%).
Moreover, the survival rates of 1, 5 and 13 years were 96% (95%CI:8%9-98%), 83% (95%CI: 72%-90%) and 72% (95%CI: 59%-82%) in the patients with pulmonary TB and 86% (95%CI: 68%-94%), 69% (95%CI: 49%-82%) and 65% (95%CI: 44%-79%) in the patients with extrapulmonary TB; this difference was not statistically significant (P=0.223) (Figure 1).
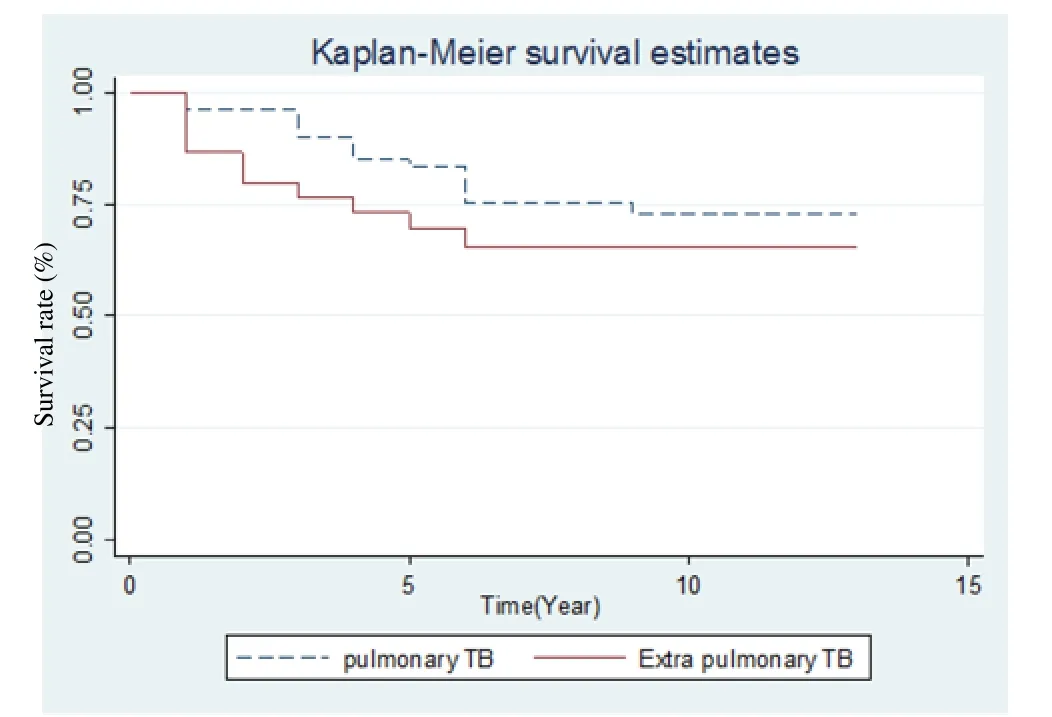
Figure 1. Survival rate between pulmonary and extra pulmonary TB.
In the next step of data analysis the Cox proportional hazard model was used to determine the chance of death after TB diagnosis by adjusting for confounding factors. The factors in this model included gender, weight, type of TB, Smoking, co-infected with HIV/AIDS,Diabetes mellitus, and Residence place (Table 3). We found thatextra pulmonary TB was associated with a higher probability of death (HR=5.58, 95% CI=1.96-15.83, P=0.001); that is, patients who did extra pulmonary were 5.58 times as likely to die compared with patients pulmonary TB. The other risk factors associated with a higher probability of death were smoking (HR=2.07, 95% CI=1.74-2.46, P<0.001) and age (HR=1.10, 95% CI=1.06-1.14, P<0.001).
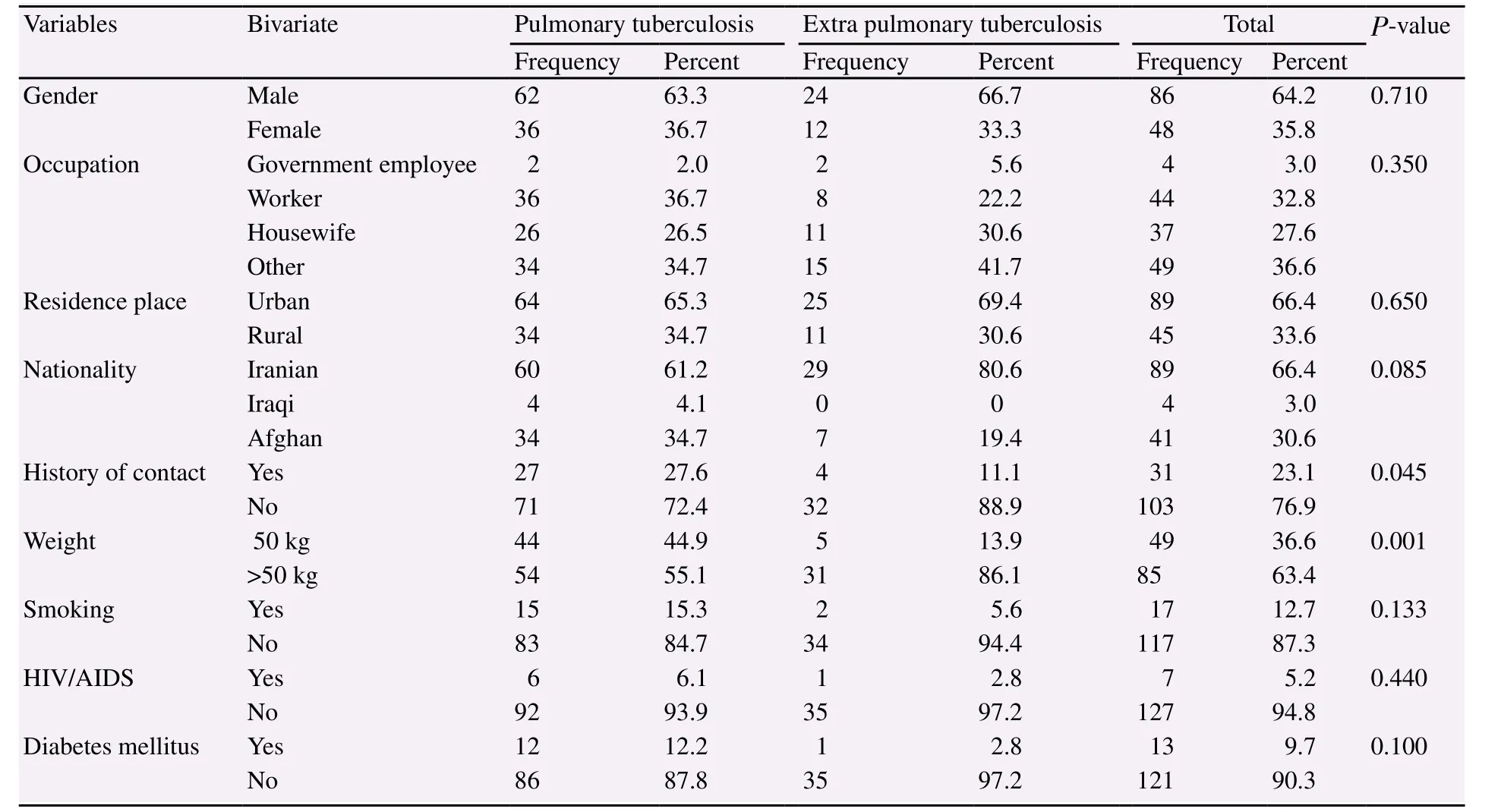
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of patients in groups of pulmonary and extra pulmonary tuberculosis.
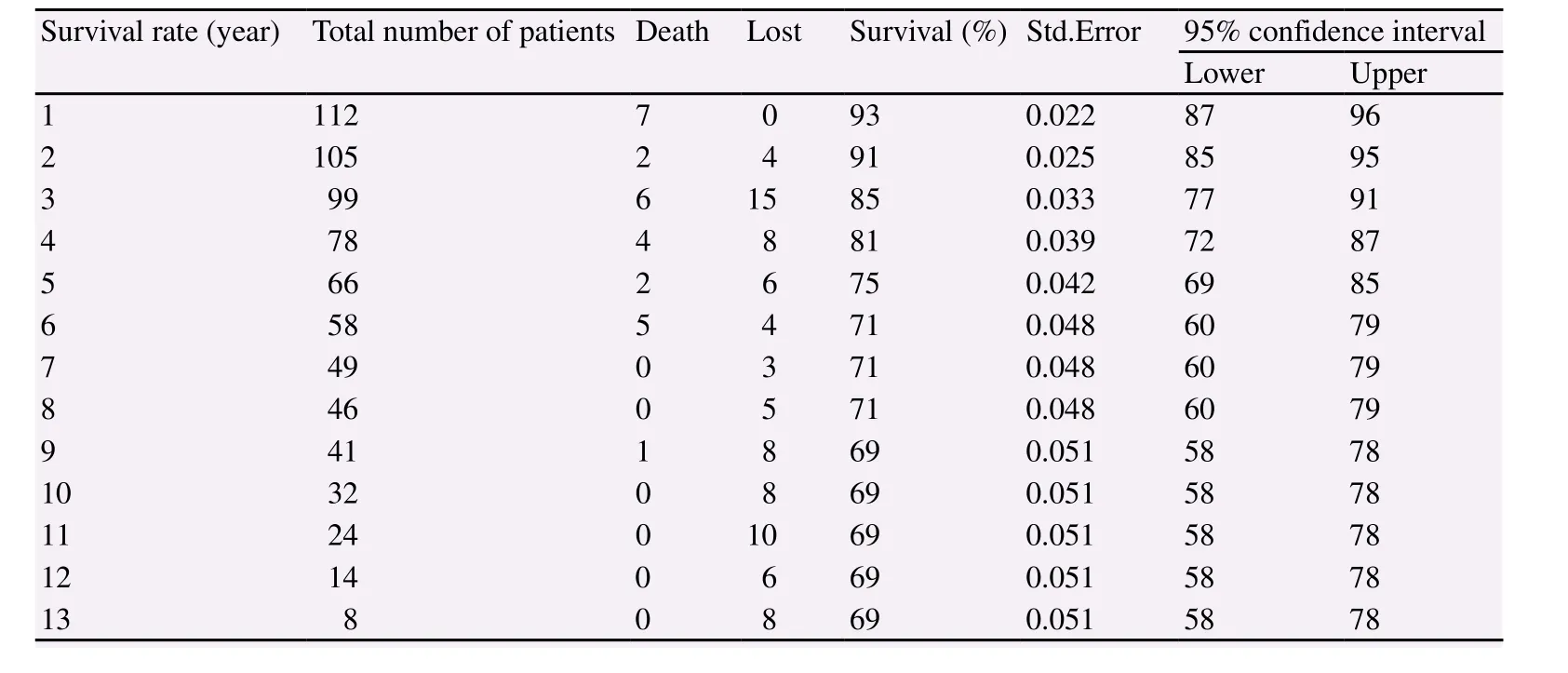
Table 2 Survival rate from diagnosis to death in tuberculosis patients in Jahrom during 2005-2016.
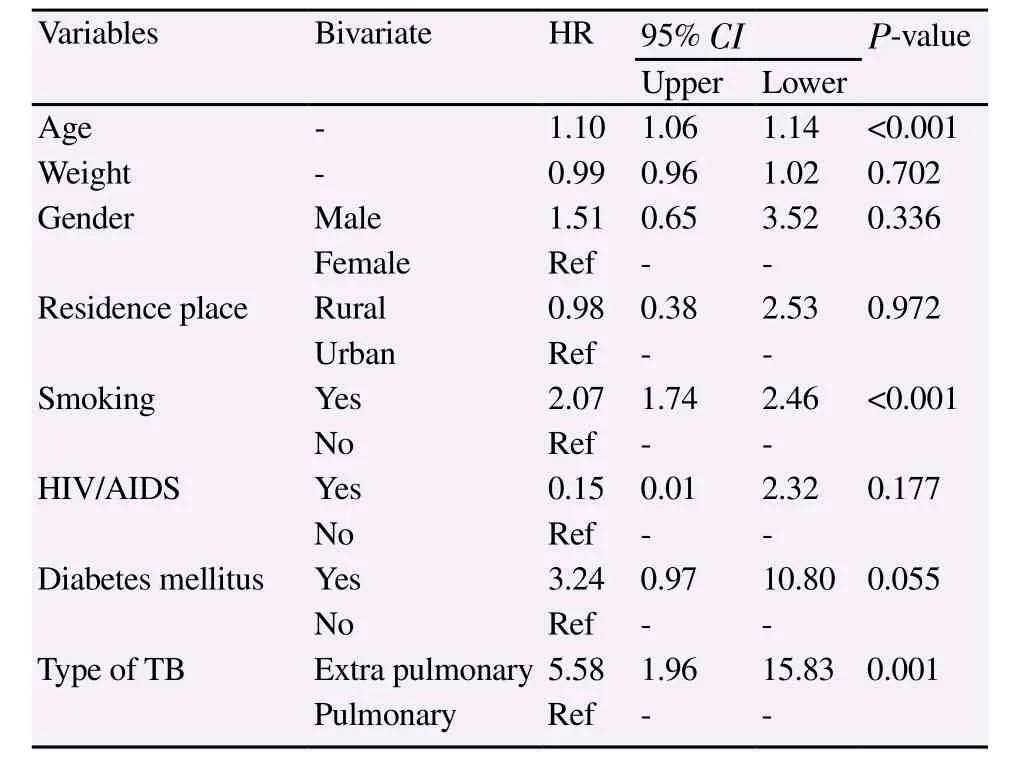
Table 3 Cox regression of possible risk factors for mortality in TB patients.
4. Discussion
Based on the life table, the results of this study showed that the survival rates of one, five and 13 years in the patients with TB under study were 93%, 78% and 69%, respectively. On the other hand, the survival rates were 83%, 96% and 72% in the patients with pulmonary TB, and 86% 69% and 65% in the patients with extrapulmonary TB, but the log-rank test was not significant(P=0.223).
Kim from South Korean compared the survival rate of patients with XDR-TB and other MDR-TB, and showed that 80-month survival was 45% in the patients with XDR-TB and 80% in other MDR-TB, and XDR-TB was the strongest predictor of both allcause and TB-related mortality[7].
Roshanaei et al. evaluated survival rates among patients with coinfected HIV/TB in Tehran, Iran, and showed that the survival probability of patients with a period of infection onset to TB after 3, 5 and 10 years of post-diagnosis of HIV was 72.0%, 62.5% , and 44.3% respectively[8]. Another study in Thailand investigated the survival rate among HIV/TB-coinfected patients with and without antiretroviral therapy. The survival rates at 1, 2 and 3 years were 96.1%, 94.0% and 87.7% in ART+ group and 44.4%, 19.2% and 9.3% in ART- group (log-rank test, P> 0.001)[15]. Further, Catala et al. in Spain reported that the 10-year survival rate of patients with concurrent HIV and TB infection was 47.4%[16].
Based on the results of this study, 73.1% of the cases were pulmonary TB and the remaining cases were extrapulmonary, and the most cases of TB in Jahrom are pulmonary TB, which is in line with the results of the studies by Biranvand et al. in the southwest of Iran[17], MohamadiAzni et al. in the city of Damghan in Iran[18],Ebrahimzadeh et al. in Birjand in Iran[19], Culqui et al. in Spain[20]and Abdallah et al. in Sudan[21].
In the present study, there was no significant difference in the forms of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in terms of gender,nationality, residence and occupation (P>0.05). These results were consistent with the results of Ebrahimzadeh et al. in Birjand[19],Saghafipour et al. in Qom[22], but inconsistent with the results of the Yazdani et al. in Lorestan[23]. Additionally, there was a significant difference between the forms of TB and the history of contact with the cases and the weight of the patient (P<0.05).
Other results of the present study showed that the risk of death in the patients with extrapulmonary TB is 5.58 times higher than the risk of death in patients with extrapulmonary TB. Most of the organs involved in extrapulmonary TB were lymph nodes(52.79%), pleura (22.22%), bone (13.89%) skin (5.55%) and meninges (5.55%), while a study by the Ministry of Health of Iran in 2006 reported that the most common involvements in the extrapulmonary TB were the lymph nodes (26.8%), pleura (20.8%)and spinal cord (17.7%). The prevalence of extrapulmonary TB in Iran is higher than what the World Health Organization offers[24],perhaps due to an increase in HIV infection or a mistake in detecting extrapulmonary TB and exaggeration in diagnosis.
Other results of this study showed that smoking increases the risk of death to 2.07 times in people with TB. Several studies have shown the role of smoking as a risk factor in pulmonary diseases,including lung cancer[25,26], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD)[27,28], asthma[29], emphysema[30], and TB[31].
A study in Masih Daneshvari Hospital as a referral center for treating TB cases in Iran showed that the odds ratio of smokers with TB was 4 times higher than non-smokers[32]. This result indicates the severity of pulmonary and non-pulmonary damage in patients with TB. According to various studies, smoking has been shown to have a major impact on pulmonary immunity. Tomito et al. found that alveolar macrophages in smokers have a significant increase in relation to COPD and apoptosis[33]. Zappacost et al.demonstrated that smoking with horseradish peroxidase inhibited luminal oxidation, which inhibited the strong chemiluminescence of the polymorphonuclears. They showed that the secretion of macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP-1α) and TNF- (IL-6MM,IL-1B, IL-10 and IL-2) in smokers[34].
Other findings of this study revealed that diabetes increased the risk of death in patients with TB by 3.24 times, but this was not significant (P=0.055). Several studies have reported the concurrent TB and diabetes, and found diabetes as a serious risk factor in activating the latent TB and the incidence of active TB[35].Although most of the studies indicate concurrent TB and diabetes,they have been unable to pinpoint these two diseases; in other words, they could not determine whether diabetes is a cause of TB or vice versa. Overall, a 40-year study by researchers confirms the impact of diabetes in increasing the risk of TB[36]. The results of review study by Jeon and Murray on 17 research articles from 2007 to 1983 on 700 000 people, of whom approximately 18 000 were infected with TB, indicated that the diabetes increased the risk of developing TB by three times, and researchers in various studies estimated this risk up to 7.83-0.99 times more[37].
There are limitations in this study. A valid prospective cohort study was needed to estimate the survival rate, while the results of this study were derived from a retrospective cohort study and from data recorded in the TB treatment center. In addition, information about the patient’s condition during the follow-up period, cause and date of death were obtained by telephone from the patient or the family, as the error of attained information may affect the quality and the accuracy of the study results. On the other hand,so far, no study has evaluated the survival rates of TB patients in Iran. This casts the inability to compare the results with other study results.
According to the results of this study, the survival rates of one,five and 13 years in the patients with TB were 93%, 78% and 69%,respectively. The risk of death in patients with extrapulmonary TB and TB smokers was higher than other patients. Therefore, timely diagnosis and proper treatment of patients with extrapulmonary TB as well as the development and integration of smoking cessation programs are underlined and emphasized in the formulation and implementation of the National Tuberculosis Control Program.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Acute Disease2018年5期
Journal of Acute Disease2018年5期
- Journal of Acute Disease的其它文章
- CORRIGENDUM
- False negative diffusion weighted imaging in an acute onset double vision patient with isolated internuclear ophthalmoplegia from ischemic origin
- A case of human acute otoacariasis caused by Rhizoglyphus sp, the first report from Iran
- Intracranial hematoma development following thrombolysis inpatients suffering with acute myocardial infarction: Management strategy
- Think muscle; Think rhabdomyolysis
- Inhibiting effect of immunoeffector cells induced by denderitic cells vaccine on growth of PC3 and BEL7402
