Realize Facilitated Targeted Poverty Elimination with Targeted Poverty— Alleviation: A New Anti-Poverty Approach for Rural China
Wang Sangui, Liu Wei*
Realize Facilitated Targeted Poverty Elimination with Targeted Poverty— Alleviation: A New Anti-Poverty Approach for Rural China
Wang Sangui, Liu Wei*
Since the Reform and Opening-up, remarkable achievements in poverty alleviation have been made in China.China’s success in mass poverty reduction can be attributed to its rapid economic growth, large-scale regional poverty alleviation and development, sound social security policies, widereaching farmer-benefiting policies and the equal land allotment system.However, with income inequality on the rise, poverty reduction effect made by the economic growth is declining: More targeted poverty alleviation policies are needed by China.Targeted poverty alleviation aims to improve the effect and efficiency of poverty alleviation through precise identification of poverty-stricken populations and comprehensive supportive measures.To tackle a variety of challenges such as the poor cultivation among povertystricken populations, the complex causes for poverty, and inflexible capital management, China should improve its poverty alleviation mechanism by innovating poverty identification methods, support approaches, capital management and performance assessment.
rural poverty; poverty alleviation policy; precise recognition; targeted support
Through over 30 years of Reform and Opening-up, China has made impressive performance in poverty reduction and significant contributions to the cause of global poverty alleviation and the realization of the UN Millennium Development Goals.However, currently China is still faced with a series of challenges, such as income inequality, a low poverty standard, a large poverty-stricken population, and miss-targeted poverty alleviation and development.Therefore,targeted strategies need to be introduced to further facilitate mass poverty reduction and finish building a moderately prosperous society in all respects by 2020.
1.China’s mass poverty reduction achievements
Since launching the Reform and Openingup in the late 1970s, China has experienced rapid economic growth and made impressive performance in mass poverty reduction.By the World Bank’s international poverty line (USD 1 per capita per day), over the past three decades, China has lifted a total of over 700 million people out of poverty (Chen& Martin, 2010), thus contributing over 90% of the global poverty reduction.In addition, China is the world’s first country to have reduced its povertystricken population by 50%, which was one of the UN Millennium Development Goals.Also, the proportion of China’s poverty-stricken population had been reduced from 60% in 1990 to under 30%in 2002, and to only 4.2% in 2014.China fulfilled 70% of the global poverty reduction task set by the UN Millennium Development Goals (Chang &Zhang, 2015, October 16).China’s mass poverty reduction is clearly demonstrated in Fig.1 (by the Chinese government’s poverty line).In 1984, the National Bureau of Statistics of the PRC set the poverty line at RMB 200 per capita per year, which later experienced multiple adjustments in accordance with commodity price changes.By that poverty line, there was a poverty-stricken population of 250 million in rural China in 1978, indicating a 30.7%poverty incidence.Also by the same poverty line,China’s rural poverty-stricken population reduced by 237 million over three decades to only 13 million in 2008.In 2000, China set its low-income line at RMB 865 per capita per year.By this low-income line, its low-income population reduced from 94.22 million in 2000 to 26.88 million in 2010.In other words, its low-income population reduced by 67.34 million in ten years.In 2011, China significantly raised its poverty line to RMB 2,300 per capita per year.By this updated poverty line, its poverty-stricken population reduced from 122 million in 2011 to 55.75 million in 2015.In other words, its poverty-stricken population reduced by 66.63 million in five years.
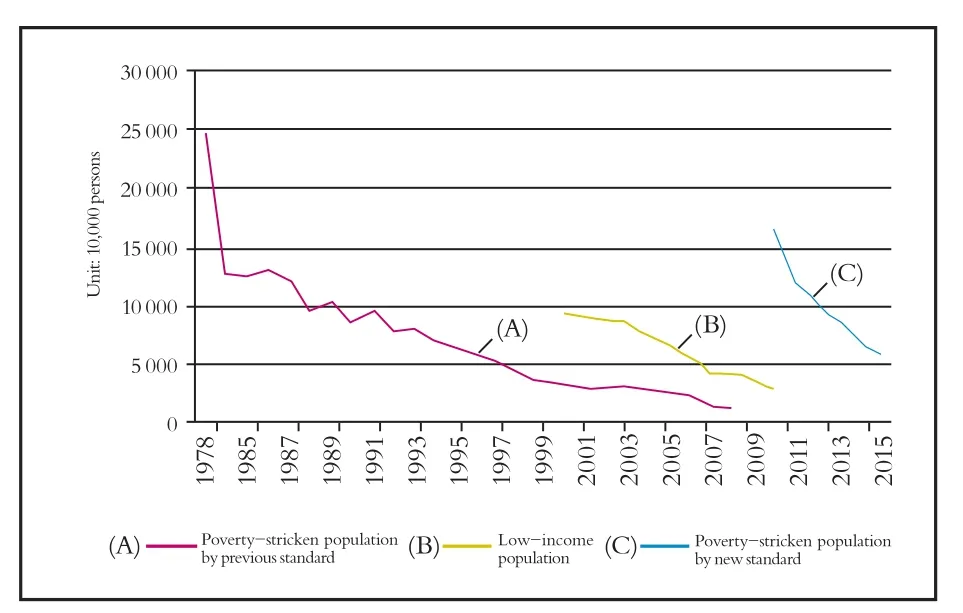
Fig.1 Poverty-stricken population change in rural China(1978-2015)Data source: Based on prevous annual editions of Statistical Communique of the PRC on the National Economic and Social Development and Poverty Monitoring Report of Rural China
China’s sustained mass poverty reduction can be attributed to the joint efforts of multiple factors.First, the sustained rapid growth of the Chinese economy has significantly raised the masses’ income and consumption capacity, which is key to mass poverty reduction.From 1978 to 2014, there was an annual GDP (at current prices) increase of 9.7% and an annual per capita GDP (at current prices) increase of 8.7% (National Bureau of Statistics, 2015).Agricultural growth is of particular importance to poverty reduction.According to the World Bank’s research, the poverty reduction effect of the Chinese agricultural sector is four times higher than those of the secondary and tertiary industries (Martin &Chen, 2007).The mass accumulation of resources such as land, labor force and capital in the secondary and tertiary industries has facilitated the rapid growth of non-agricultural sectors.Even so, ever since the introduction of the Reform and Openingup in 1978, China has maintained a 4.5% growth in primary industry.Agriculture can bring about better effects of poverty reduction and agricultural growth contributes 45% of poverty reduction in rural China.
Second, targeted regional poverty alleviation and development significantly bridges the gap between regions and promotes the social and economic development in poverty-stricken regions.Since the mid 1980s, the Chinese governments at all levels have contributed numerous special funds for poverty alleviation; financial sectors have granted huge amounts of subsidized loans and micro-credits;a variety of social organizations have also actively engaged in poverty alleviation causes.Over 30 years of poverty alleviation has vigorously boosted the economic growth of targeted poverty-stricken regions.During the implementation of the Rural Poverty Alleviation and Development Program(2001─2010), China strove to help 150,000 povertystricken villages and 592 poverty-stricken counties.According to the poverty-monitoring data released by the National Bureau of Statistics of the PRC,the annual growth of rural per capita net income at poverty-stricken village, county and national levels were respectively 8.99%, 8.43% and 7.33%.The income ratio of poverty-stricken villages to rural China was raised from 48% in 2002 to 52% in 2008.The income ratio of poverty-stricken counties to rural China was raised from 53% in 2002 to 55% in 2009.Thus, it can be concluded that those enjoying special national support have had a rapid growth in income and that poverty alleviation and development can effectively bridge the income gap between regions.
Third, in 2007 China began to extend its coverage of social security systems to the rural areas.By means of various security systems such as guaranteed income supplement, new rural cooperative medical care and rural pension insurance, China guaranteed the basic livelihood and public services of rural poverty-stricken populations.As of 2015, a total of 48 million poverty-stricken rural people have enjoyed a guaranteed income supplement (RMB 151 per capita per month)①The “Coverage of Basic Living Allowance System in Rural China above County Level in January 2016” Retrieved from the official website of Ministry of Civil Affairs of the PRC, 2016,3,16.http://www.mca.gov.cn/article/sj/tjyb/dbsj/201603/2016030088352.htm..Some 98% of registered poverty-stricken populations were covered by the new rural cooperative medical care system; 63% of poverty-stricken populations were covered by the rural pension insurance system(Center for Poverty Alleviation Research, Renmin University of China, 2015).
Fourth, preferential rural policies extensively benefit the rural population.In 2003, China launched the project for conversion of cropland to forest in poverty-stricken regions, granting corresponding subsidies to affected farmers.In 2006, it abolished the agricultural tax nationwide and at the same time introduced a comprehensive subsidy policy in the agricultural sector.In 2008, it began to implement the 9-year free comprehensive education nationwide.Some 71% of registered poverty-stricken populations enjoyed a variety of subsidies.In 2013, the per rural household subsidy reached RMB 1,780 (Center for Poverty Alleviation Research, Renmin University of China, 2015).
Fifth, the basic land system and business practices ensure poverty-stricken population’s benefits from agricultural growth.The contract responsibility system (also known as the household responsibility system) is the basic land system of rural China.This system features collective ownership of rural land and farmers’ long-term right to use and manage rural land.In the early 1980s,rural land was distributed to agricultural community members on an equal footing, which ensured poverty-stricken households’ benefits from land and agricultural development by institutional means.
2.The challenges facing China’s future poverty reduction
While enjoying over 30 years of rapid economic growth, China is also suffering from an intensifying income inequality.China’s Gini coefficient increased from 0.288 in 1981 to 0.469 in 2014.Regional poverty alleviation and development has significantly boosted the economic growth of poverty-stricken regions and bridged the gap between them and other regions.However, within those poverty-stricken regions, relatively better-off families have benefited more, thus widening the internal income gap.During the implementation of the Rural Poverty Alleviation and Development Program (2001─2010), in targeted poverty-stricken counties, the income gap among different income groups kept widening.The ratio of the highestincome group to the lowest-income group dropped from 21.59% in 2002 to 17.38% in 2010.On the other hand, the higher income a group enjoyed, the faster its rural per capita income increased.From 2002 to 2010, by the constant price of 2002, the lowest-income group had a 7.7% annual increase in rural per capita income while the highest-income group had a 10.66% annual increase in rural per capita income.The higher income a group enjoyed,the faster its rural per capita income increased.The economic growth in poverty-stricken regions significantly benefited high-income farmers (see Table 1).From 2002 to 2009, the average income growths of poverty-stricken rural households, rural households in major poverty-stricken counties and all Chinese rural households were respectively 2.75%, 11.76% and 11.04%.The income growth of poverty-stricken rural households was 9% lower than that of rural households in major povertystricken counties.The proportion of poverty-stricken households’ income in national rural residents’income declined, dropping from 1/3 in 2002 to 1/5 in 2009.

Table1 Rural household income growths of different income groups in poverty-stricken counties (2002-2010)
This intensifying income inequality can be attributed to several factors.First, China was transforming its labor-intensive agriculturaldominated structure to a manufacturing and service-dominated one, which intensified its income inequality.In the primary industry, the equal distribution of land helped to bridge the agricultural income gap.By contrast, the capital and technologyintensive secondary and tertiary industries featured much more prominent income inequality.Second,the labor flow between rural and urban areas gave rise to income inequality.Affected by a range of factors such as poor education, low comprehensive competence, insufficient capital and limited access to information, poverty-stricken farmers had a lower chance than well-off farmers to work in urban China, which in turn widened the income gap between the two groups.Third, although the poverty alleviation and development in poverty-stricken regions significantly improved local infrastructure and other production and living conditions, the poverty-stricken population, with limited human capital and competence, still found it difficult to utilize such infrastructure to increase their incomes, as opposed to their well-off counterparts’capability to make the most out of such production improvements to substantially raise their incomes.Fourth, the poverty-stricken population had little access to effective financial services, which hampered their income growth.
The slowing economic growth and widening income gap meant the previous growth-driven regional development path became less and less feasible for poverty reduction.Under such circumstances, more targeted and precise support strategies were needed.
3.Realize facilitated targeted poverty elimination with targeted poverty alleviation: approaches, challenges and ideas
3.1 The definition of targeted poverty alleviation
In November 2013, General Secretary Xi Jinping proposed the notion of targeted poverty alleviation on a visit to western Hunan province.In 2015,targeted poverty alleviation was identified as the general strategy for China’s rural poverty alleviation cause.The core of targeted poverty alleviation is to identify poverty-stricken populations and poverty causes, and utilize various approaches to offer targeted support, eliminate a range of poverty causes facing households and individuals, and enhance poverty-stricken households’ development initiative and capacity in a bid to achieve sustainable poverty elimination.In short, targeted poverty alleviation should be oriented towards individuals and households, instead of remaining at the regional poverty alleviation or regional development levels.Targeted poverty alleviation mainly includes precise recognition, targeted support, targeted management and targeted assessment.More specifically, precise identification refers to the adoption of democratic appraisal and multi-dimensional poverty indicators to identify poverty-stricken households and individuals and make corresponding registrations.Targeted support refers to the adoption of comprehensive aid measures based on the actual conditions and needs of poverty-stricken households and individuals to improve their development capacity and condition.Targeted management includes the registration of all poverty-stricken households and individuals, the management of aid measures, as well as the tracking and continual support of registered households already lifted out of poverty to ensure poverty elimination.Moreover, targeted management also includes the management of poverty-alleviation projects and funds in accordance with the specifications of targeted support.Targeted assessment comprises two aspects.First, an assessment and review of the poverty alleviation effect is conducted in accordance with the requirements of “no shortage of food and clothing” and “guarantee of compulsory education,basic medical care and safe housing” to prevent falsification (such as “data fabrication-facilitated poverty alleviation”).Second, an assessment of the overall poverty alleviation of a given region is conducted to ensure an orderly removal of povertystricken county/village titles.
3.2 Precise identification and registration
The effective implementation of targeted poverty-alleviation strategies and the smooth lifting of the remaining 55.75 million poverty-stricken people out of poverty by 2020 require a precise identification of poverty-stricken individuals so as to “target the right group.” Currently, democratic appraisal is a preferred approach, which further subdivides tasks to provincial, county, township and village levels based on the National Bureau of Statistics’ estimation of poverty-stricken populations,and commissions the village-level CPC committees and villagers’ autonomous committees to identify poverty-stricken households and individuals by means of democratic appraisal and indicators-based rating under the guidance of government authorities at township and county levels.Since 2013, China has identified a total of 29.48 million poverty-stricken households containing 89.62 million povertystricken people and registered them in its national poverty-alleviation information system.In this way,it manages to record the family structure, resources,revenue sources and poverty causes of every poverty-stricken household.Starting from the end of 2015, a review of the abovementioned registration work and a re-identification of poverty-stricken households and individuals has been conducted.The review and re-identification conclude that there are a total of over 19 million registered povertystricken households and 56.23 million povertystricken people.①The Central Government advocates continual support to the population newly getting out of poverty to ensure their stable position above the poverty line.Ever since the introduction of poverty registration system in 2013, a total of 32.17 million people have been raised out of poverty and another 1.22 million inaccurately registered people have been identified in low-level poverty and placed on record.Those registered poverty-stricken populations will be the primary target of the povertyalleviation efforts during the 13th Five-year Plan.
The biggest challenge facing precise identification and registration lies in the inconsistency in poverty identification indicators and methods between the National Bureau of Statistics and local government authorities.The former identifies poverty-stricken households and populations in accordance with internationally accepted economic welfare indicators (consumer spending and income) and the poverty line.The latter, however, due to a lack of reliable consumer spending and income data, mainly identifies poverty-stricken households and populations in accordance with the Central Government’s policies of “no shortage of food and clothing” and “guarantee of compulsory education, basic medical care and safe housing,” rather than relying solely on relevant standards of consumer spending and income①Apart from the data of over 70,000 rural households covered by National Bureau of Statistics’sampling survey, there are very limited accesses to rural households’income and consumption data..Given that the policies of “no shortage of food and clothing” and “guarantee of compulsory education,basic medical care and safe housing” cover a range of areas, poverty-stricken population figures collected based on such standards is inevitably larger than the population figure collected in accordance with a single economic standard.Based on the National Bureau of Statistics’ estimation, the poverty data collection task is assigned to lower-level administrative units in the hierarchy.This move inevitably prevents households beyond the coverage of the abovementioned policies from being identified as poverty-stricken households and populations②In fact, the result of National Bureau of Statistics’sampling survey can only demonstrate the provincial-level progress and cannot accurately reflect the distribution of poverty-stricken population in administrative units below the provincial level.Therefore, there is bound to be certain deviation when the poverty alleviation task is further subdivided to counties, townships and villages..This is why many administrations complain about an insufficient poverty-alleviation quota and the failure to extend policy support to all povertystricken populations.
We believe that policy support should cover a poverty-stricken population much larger than the National Bureau of Statistics’ estimation.Only by doing so can the poverty-stricken population beyond the coverage of the abovementioned policies enjoy due support and the objective of poverty elimination by 2020 be fulfilled.So far, there seems to be only one feasible solution: To keep the poverty quota(a registered poverty-stricken population of 88.40 million) unchanged; identify those already steadily above the poverty line from that registered povertystricken population and gradually reduce support to them; and timely have those newly emerged povertystricken households and individuals identified and registered and offer them corresponding support.Dynamic management is needed to echo the actual change in poverty-stricken populations and ensure full support to those in real need.Only through constant and dynamic support can poverty be truly eliminated.
3.3 Targeted support and the “five-batch poverty alleviation” strategy
Once poverty-stricken populations and poverty causes are identified, household/individual-specific measures are needed to provide targeted support.Aware of the complex reason of poverty, the Chinese government has introduced a comprehensive support strategy—the “five-batch poverty alleviation”strategy, which covers a range of fields, including industrial development, employment, migration &relocation, ecology, education, medical treatment,and social security.
For poverty-stricken populations, sustainable income-generating ability is the key to overcoming poverty and permanently staying above the poverty level.After all, poverty-stricken individuals tend to be poorly educated and are faced with a variety of restrictions.They hardly have any awareness of the market economy or the ability to utilize market mechanisms for industrial development.Besides, they also lack necessary funds, technology and market insights, making it very difficult for them to run a business independently.Given that,poverty alleviation through industrial development should be individually specific.There are some households without any labor capacity, for which they cannot run a business independently.Under such circumstances, assets income-based support measures are needed to enable poverty-stricken households to make profits out of their own assets and poverty-alleviation funds with the help of modern business entities.For households with labor capacity, however, the key to poverty alleviation through industrial development lies in the integration of poverty-stricken households into the modern industry chain.More specifically, relevant business entities (enterprises, cooperatives and individual businesses) should help the poverty-stricken individuals solve market and technical problems and provide corresponding services before, during, and after business production, while poverty stricken individuals only need to participate in relatively simple production activities.This approach can significantly lower the risks facing poverty-stricken households engaged in business activities.When it comes to poverty alleviation through employment,priority should be given to improving povertystricken households’ comprehensive competence and expertise through training.Meanwhile, employment information and judicial assistance should be offered to reduce their employment concerns and obstacles.
As we know, there are poverty-stricken individuals living in remote and harsh regions,where they cannot rely on local resources to make a living.And some poverty-stricken individuals dwell dispersively, bringing about excessive costs of infrastructure construction and public services.Regarding these individuals, migration and relocation is the most effective approach to lift them out of poverty.Judging from previous migration and relocation experience, there are mainly two challenges.One is the high relocation costs borne by poverty-stricken households.The other is a lack of a post-relocation life guarantee.During the 13th Fiveyear Plan period, this poverty alleviation-oriented migration and relocation campaign concerns a population of 10 million, which is even larger than the total relocated poverty-stricken population over the previous 30 years.It therefore matters a lot to control the relocation costs, formulate a rational cost-sharing system, and identify an appropriate relocation approach based on actual situations.These are vital to the fulfillment of the “affordable relocation and stable living” target.To satisfy the relocation project’s capital needs, the Chinese government, in collaboration with state-owned non-commercial banks (policy lenders), has raised a special fund of RMB 600 billion, most of which fall into the categories of policy-based loans and financial bonds.To prevent poverty-stricken families from acquiring heavy debt, the Central Government and government authorities at all levels should be responsible for repaying most debts and the relocated households should bear only part of the house construction costs.Considering the differences in household family structures and capacities, a“gradient relocation” strategy should be introduced to better adapt to local conditions.Those capable of finding a stable job in urban areas can be relocated there and equipped with necessary techniques and jobs.For those who do not have sufficient work skills and can only live on agriculture, centralized settlements are preferred; meanwhile, regionspecific agricultural and non-agricultural supports need to be provided.
Poverty-stricken individuals in ecological reserves and restoration areas should be helped in the form of subsidies concerning eco-compensation and conversion of croplands to forests.While improving the poverty-stricken area’s environment and ecofunction, relevant government authorities should also focus on increasing the asset income and wages of poverty-stricken individuals in ecological reserves and restoration areas based on the principles of“those who benefit must compensate” and “rational transfer payments.” It is now imperative to formulate an operable eco-compensation scheme, estimate and set a compensation standard, and identify a corresponding compensation mode and mechanism.Those moves are expected to lift residents out of poverty by means of eco-compensation and at the same time inspire them to protect and improve the local eco-environment.
Poverty alleviation through education is conducive to most poverty-stricken households.In the short run, it helps poverty-stricken household to cut education costs and subsequently improve livelihood; in the long run, it stops the intergenerational transmission of poverty.The biggest challenge facing poverty alleviation through education lies in the fact that poverty stricken children do not have equal access to education, let alone quality education.Possible solutions to this problem include popularizing pre-school education in poverty-stricken regions and preventing those children from falling behind at the starting line.Not covered by the Chinese compulsory education system, pre-school education is not the item that most poverty-stricken households can afford.Therefore, it is imperative to introduce a special subsidy to ensure poverty-stricken children’s preschooling right.In this regard, China can draw on the overseas experience of conditional cash transfer payments, and offer free pre-schooling services to poverty-stricken children and certain cash subsidies to their families.At the elementary education stage,China’s primary task is to cut related schooling costs, such as the “parent’s companionship costs.” To this end, village-level schools need to be resumed.At the secondary education stage, China should provide free high-school education and professional& vocational education for poverty-stricken students and grant them living allowances in a bid to enhance their competitiveness in the labor market.To improve the education quality in poverty-stricken regions and bring quality education to povertystricken students, China can extensively adopt new teaching technologies and methods (such as distance teaching) while fostering competent teachers locally.
For poverty-stricken households without any labor capacity and households tormented by prolonged illness, comprehensive social security measures should be taken as a major means of poverty alleviation.Those measures include the already widely implemented system of guaranteed income supplement, the new rural cooperative medical care system, the critical illness insurance &aid system, chronic disease subsidies, the pension insurance fund, etc.By 2020, all households below the poverty line will be lifted out of poverty through the guaranteed income supplement system.In short,China strives to ensure the full basic health care coverage of its poverty-stricken population and find a once-and-for-all solution to its prevalent illnesscaused poverty.
3.4 Targeted management and fund integration
In terms of poverty-alleviation fund management, China should prioritize the reform of its fund management system (particularly the integration of various poverty-alleviation funds controlled by different government authorities).In the meantime, it should transfer the power of fund distribution, use and management to countylevel governments and let them decide the range and ways of fund application to satisfy the specific capital needs of different household-targeted poverty alleviation projects.Only in this way can our poverty alleviation work truly be individual and household specific.In April 2016, the General Office of the State Council issued the Opinions on Supporting Poverty-stricken Counties to Launch the Pilot Program on Integrated Use of Agricultural Funds.In 2016, the Pilot Program was launched in 1/3 of the povertystricken counties.In 2017, it has been implemented in 832 poverty-stricken counties, involving 20 types of the “three rural issues” related funds.Through fund integration, the power of capital distribution and program approval is transferred to the governments of poverty-stricken counties, which strive to build a new poverty alleviation structure featuring “multiple fund-raising channels and one fund-allocation outlet.” When it comes to countylevel fund integration, the major concern now is how to effectively use the allocated funds to serve the given purposes.To this end, while offering fund-use access, China should also enhance the assessment of those funds’ effect on poverty reduction, and transform the existing process-centered supervision and management mechanism to a result-oriented mechanism.Meanwhile, it should also monitor the fund use via multiple channels and prevent the use of poverty alleviation fund for non-poverty alleviation purposes.
3.5 Targeted assessment and targeted poverty elimination
The ultimate purpose of targeted poverty alleviation is to achieve targeted poverty elimination,which requires definite standards and an assessment mechanism.In terms of poverty elimination for poverty-stricken households and individuals,corresponding standards include the policies of“no shortage of food and clothing” and “guarantee of compulsory education, basic medical care and safe housing,” and the stipulation of per capita net income at or above the national poverty line (RMB 2,855 in 2015).At the village level, the removal of a poverty-stricken village title requires the reduction of poverty incidence to a level below 2% (below 3%in western China) and comprehensive improvement in infrastructure, basic public services, industrial development, a village’s collective income, and so on.At the county level, the removal of a povertystricken county title requires the reduction of poverty incidence to a level below 2% (below 3%in western China).At present, the primary task for China is to improve the specification of relevant standards and the access to data.In this regard, the abovementioned policies of “no shortage of food and clothing” and “guarantee of compulsory education,basic medical care and safe housing” merely serve as general requirements, whose fulfillment needs to be assessed with more concrete indicators.Such an assessment should be supported by reliable data.However, the grass-roots government authorities in general lack access to such reliable data concerning revenue, consumption and public services.A possible solution to this problem is to extensively draw support from sampling survey systems run by third-party institutions or statistical authorities.Such systems evaluate the effectiveness of povertystricken title removal and poverty elimination at reasonable costs.
Poverty elimination is a systematic project with a tough mission.Therefore, the Central Government has reiterated the fight against poverty alleviationrelated fraud and data falsification.On the premise of existing definite poverty-stricken standards,appropriate procedures of poverty-stricken title removal and effective supervision mechanisms are important guarantees for targeted poverty elimination.The removal of poverty-stricken household titles involves the procedures of household survey; result publicity; verification (by the villagelevel CPC committee, the villagers’ autonomous committee and the residency working group); and the recognition from the poverty-stricken households themselves.The removal of poverty-stricken village titles involves the procedures of sampling surveybased poverty incidence calculations; verification of village-level infrastructure, public services and the collective economy; and assessment of local independent development.The removal of povertystricken county titles involves the procedures of provincial-level assessments; third-party special assessments led by the poverty-alleviation leading groups under the State Council; and the approval of title removal from provincial-level governments.During the whole process of targeted poverty elimination and assessment, social supervision and third-party review play a key role.Regarding the third-party assessment, an entrusted party and source of funds should be specified at the beginning so as to avoid conflicts of interests during the assessment process.The following measures are adopted to ensure the impartiality and independence of thirdparty assessments.The first measure is government authority-commissioned third-party assessment of a subordinate unit.The third-party assessment of a county-level administration should be commissioned by its corresponding provincial-level government;the third-party assessment of a provincial-level administration should be commissioned by the Central Government.The second measure is institutional norms.In other words, specific assessment procedures and a corresponding management system should be established to“l(fā)egitimize” the third-party assessment.The third measure is improved professionalism.Relevant assessment agencies should enhance their selfcultivation and work harder on assessment theory,methodology and technology.The fourth measure is the extensive application of assessment results,which should be accessible to more institutions and individuals to enhance social supervision.
(Translator: Wu Lingwei; Editor: Yan Yuting)
This paper has been translated and reprinted with the permission of Journal of South China Normal University (Social Science Edition), No.5, 2016.
Center for Poverty Alleviation Research, Renmin University of China.(2015).Data analysis report on the registration of national poverty alleviation and development .Chang Hong & Zhang Zhida.(2015, October 16).Over 70% contributions to global poverty reduction: “China Miracle” benef i ts the entire world.Retrieved from http://world.people.comcn/n/2015/1016/c1002-27703507.htm.
Chen Shaohua & Ravallion Martin.(2010).The developing world is poorer than we thought, but no less successful in the fi ght against poverty.Quarterly Journal of Economics, 125(4), 1577-1625.
National Bureau of Statistics.(2015).2015 China statistical yearbook.Beijing: China Statistics Press.
Ravallion Martin & Chen Shaohua.(2007).China's uneven progress against poverty.Journal of Development Economics, 82(1), 1-42.
World Bank.An update to the World Banks’ estimates of consumption poverty in the developing world 2012.Retrieved from http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTPOV-CALNET/Resources/Global-Poverty_Update_2012_02-29-12.pdf.
*Wang Sangui, professor and doctoral supervisor at School of Agricultural Economics and Rural Development, Renmin University of China; director and professor at Center for Poverty Alleviation Research, Renmin University of China; associate dean at Institute of Sustainable Development and Institute of Rural Economy and Finance, Renmin University of China.Liu Wei, currently a PhD student at Center for Poverty Alleviation Research, Renmin University of China.
*Foundation item: This paper is included in“Studies in the Mechanism and Policies on Targeted Poverty Alleviation and Elimination”(15ZDC026)—a major program of the National Social Sciences Fund.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2017年5期
Contemporary Social Sciences2017年5期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- New Forms, Trends and Problems of Cultural and Creative Industries in China Today
- On the Cross-border E-commerce Development Strategy in the Context of the Belt and Road Initiative
- Development and Protection:Reshaping Cultural Policies— A Study of the UN’s Advancement of Cultural and Creative Industry in Developing Countries
- A Study on the Influence of Local Top Leaders’ Corruption— An Empirical Analysis Based on the Municipal Party Committee Secretaries Sacked after the Eighteenth National Congress of the Communist Party of China
- A Philosophical Review of China’s Eco–Countryside Construction
- Re–innovation on Thought and Mode of Poverty Alleviation in Rural Areas of Western China Under the Goal of Finishing Building a Moderately Prosperous Society in All Respects
