Clinical characteristics and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations
Yan Zhang, Zheng Wang, Xuezhi Hao, Xingsheng Hu, Hongyu Wang, Yan Wang, Jianming Ying
1Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China;2Department of Pathology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Beijing 100730, China;3Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
Clinical characteristics and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations
Yan Zhang1*, Zheng Wang2*, Xuezhi Hao1, Xingsheng Hu1, Hongyu Wang1, Yan Wang1, Jianming Ying3
1Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China;2Department of Pathology, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology, Beijing 100730, China;3Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
Objective:To investigate the clinical features of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, and the treatment outcomes of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in these patients.
Non-small cell lung cancer; EGFR; uncommon mutation; target therapy
View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2017.01.03
Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common cause of cancer-related death (1,2). The traditional therapy was based on cancer histology. However, since the identification of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in 2004, therapy paradigm has been changed toward molecularly driven strategy based on driver mutations in genes and specific inhibitors of these pathways. EGFR is the product of oncogeneC-erbB-1(HER-1). It is not created equally in different races, with higher mutation incidence in Asian than in Caucasian (30%–60%vs. 10%–20%) (3-5). EGFR mutation is an effective factor of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) treatment response in NSCLC, of which short in-frame deletion in exon 19 (19 del) and L858R substitution account for 90%. These common EGFR mutations are associated with good efficacy of EGFR-TKI, and the objective response rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) are approximately 70% and 10–11 months, respectively (3-6). The remaining 10% of EGFR mutations are generally called uncommon mutation, including a heterogeneous group of molecular alterations within exon 18–21. The clinical characteristics and therapeutic effects of EGFRTKIs on NSCLC with uncommon EGFR mutation subtypes remain unclear. Here we summarized the clinical data of patients who harbored uncommon EGFR mutations in order to perform a retrospective analysis of NSCLC patients with uncommon EGFR mutations and to reveal their association with treatment outcomes after TKI therapy.
Materials and methods
Patients
From January 2010 to December 2015, patients with histologically diagnosed uncommon EGFR mutation by amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS) or direct sequencing in the Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College and Beijing Hospital were enrolled. Uncommon EGFR mutations were defined as all mutations except 19 del, L858R point mutation or acquired T790M mutation. Pathological diagnosis was based on specimens from surgery, percutaneous transthoracic biopsy, transbronchial biopsy, lymph node biopsy, or metastatic tumor biopsy. Patients were eligible for TKI efficacy analysis if they had stage IIIB/IV (American Joint Committee on Cancer AJCC TNM Staging system, 7th edition) NSCLC with uncommon EGFR mutation and had been treated with EGFR-TKIs (gefitinib, erlotinib or icotinib) for more than one month. The type of EGFR TKIs depended on the physicians’ discretion. Patients were given 250 mg of gefitinib daily or 150 mg of erlotinib daily, whereas patients who were treated with nicotine received 125 mg three times daily. Patients received TKI as adjuvant therapy or with other concomitant anticancer therapy were excluded.
Follow-up and effectiveness evaluation of TKI
All enrolled patients were under regular clinical follow-up exams including a physical examination, chest enhanced computed tomography (CT) (including liver and adrenal glands) and routine laboratory test one month after initial treatment and then every 2 months thereafter to evaluate the response to treatment. Baseline assessments were carried out before treatment. The responses were defined as complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PD) according to the criteria of the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, version 1.1 (RECIST 1.1). The treatment response and PFS were determined by review of CT by one chief physician and one attending doctor, and sometimes another one chief physician was needed when different evaluation results occurred. Disease control status comprised CR, PR and SD. The cutoff date was December 31, 2015. PFS was measured from the first day of EGFRTKI treatment until the clinical sign of disease progression or death or cutoff date.
Ethics
This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Board of National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College. Informed consent was exempted by the board due to the retrospective nature of this research. Patient records were anonymized and deidentified prior to analysis.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were carried out by SPSS software (Version 13.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Demographic and clinical data were summarized as medians with ranges for continuous variables, and categorical variables wereexpressed as the means of absolute and percentage numbers. PFS after EGFR-TKI treatment was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method to assess the time to death or progression.
Results
Characteristics of NSCLC patients with uncommon EGFR
From January 2010 to December 2015, excluding 19 del, L858R point mutation or acquired T790M mutation, 128 patients with driver oncogene detection were enrolled. Among these patients, 59.4% were women, 62.5% were never smokers, and the median age was 58 years old. Eleven patients were non-adenocarcinoma, including squamous carcinoma (3.9%), adenosquamous carcinoma (2.3%), large cell carcinoma (0.8%), and composite neuroendocrine carcinoma (1.6%) (Table 1).
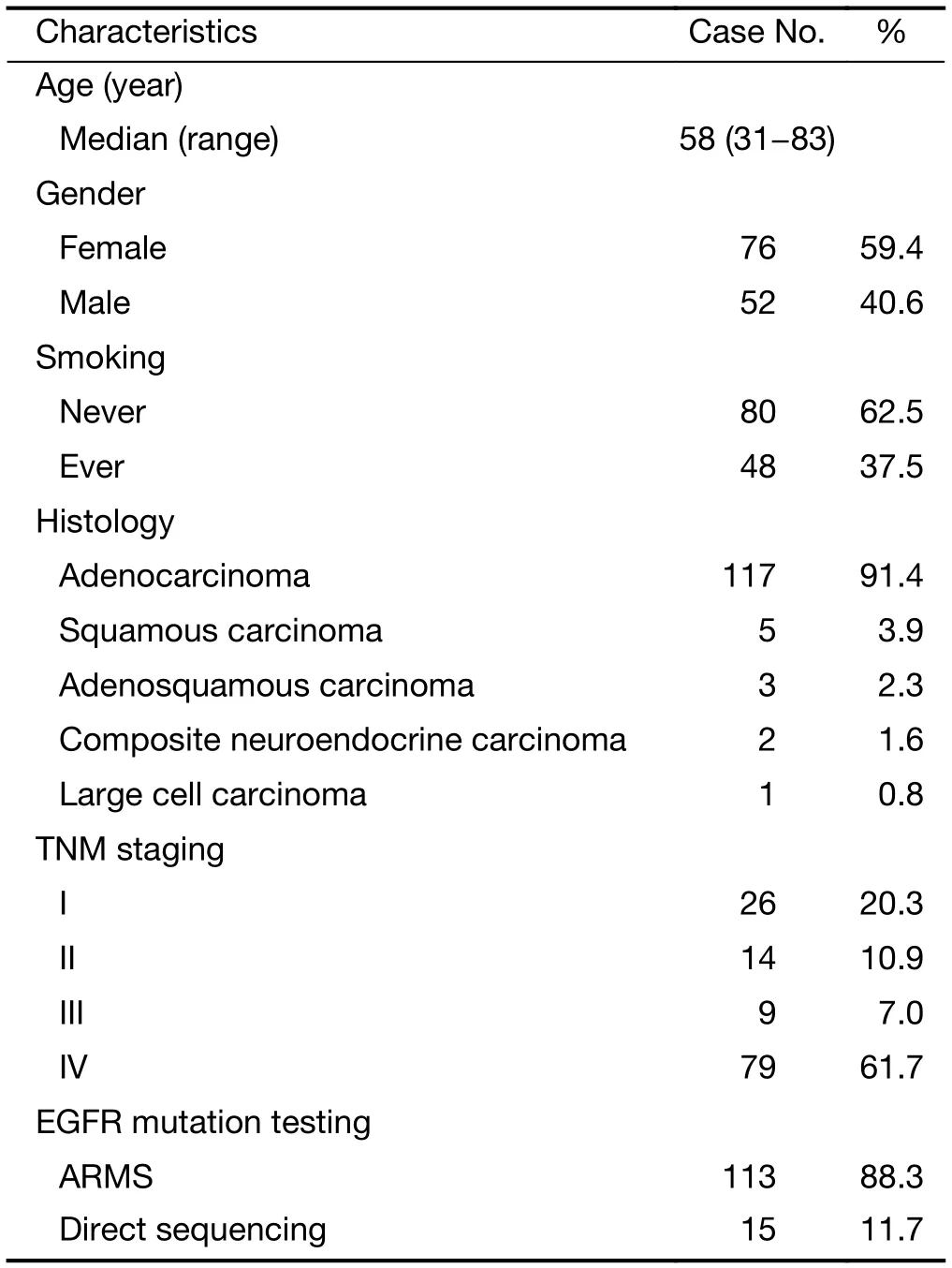
Table 1 Clinicopathological features of patients with NSCLC (N=128)
Types of EGFR uncommon mutation
Of all 128 patients, single mutations account for 75.0% (96/128), including G719X (29.7%), S768I (18.0%), 20 exon insertion (13.3%), L861Q (12.5%),De novoT790M (0.8%), and T725 (0.8%). Complex mutations were detected in 32 patients: L858R + 19 del in 2 patients, L858R/19 del + uncommon mutation in 15 patients, and uncommon + uncommon mutation in 15 patients (Table 2).

Table 2 Types of EGFR uncommon mutation (N=128)
EGFR TKI effectiveness and survival in patients with uncommon EGFR mutation
Forty advanced patients receiving EGFR TKI treatment were eligible for TKI effectiveness analysis. Gefitinib was administered in 26 patients, and erlotinib and icotinib were administered in 7 patients respectively. EGFR TKIs were used as first-line treatment for 21 patients, second line for 15, and third or later lines for 4 patients. By the time of cutoff date, 8 patients still had cancer remained controlled.The ORR in those 40 patients was 20.0%, the disease control rate (DCR) was 85.0% and the PFS was 6.4 [95% confidence interval (95% CI), 4.8–7.9] months (Figure 1).
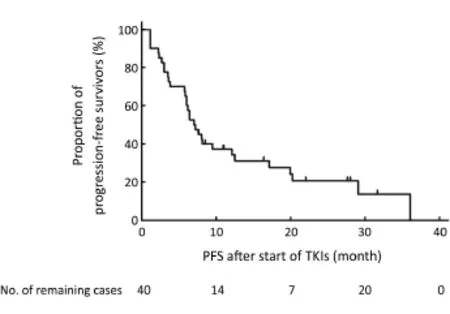
Figure 1 The PFS analysis of patients with EGFR uncommon mutations treated with EGFR-TKIs. PFS, progression-free survival; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
In the subset analysis, 2 patients with L858R + 19 del achieved PR, and PFS was 6.0 months and 6.2 months, respectively. Two patients with 20 exon insertion mutation experienced rapid disease progression after one-month treatment.De novoT790M occurred concurrently with sensitive mutations, L858R (2/3) or exon 19 deletion (1/2). Two patients withDe novoT790M + L858R mutation had rather limited benefit from EGFR-TKI, with one having progressed disease after one month of TKI therapy and the other one suffering SD with PFS only 2.7 months. However, the PFS of the patient withDe novoT790M + 19 del reached as long as 8.1 months. The exploratory analysis of tumor response and PFS in 33 patients with G719X/S768I/L861Q subtypes showed the DCR was 93.9% (31/33), ORR was 21.2% (7/33), and PFS was 7.6 (95% CI, 5.8–9.4) months. The subset analysis of G719X/S768I/L861Q subtype is demonstrated inTable 3.
Remarkably, a 64-year-old Chinese male, with 20 packyears smoking history, was detected with S768I mutation. Nicotine was given 125 mg three times a day as second-line therapy. The tumor still maintained SD at the time of cutoff date, totally 31 months of TKI treatment.
Discussion
As the efficacy of EGFR TKIs for the treatment of patientswith uncommon mutations has not yet been fully elucidated, more research and data should be encouraged to share for clinical practice. In this study, we reported the clinical data of 128 NSCLC patients with uncommon EGFR mutations diagnosed in the Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College and Beijing Hospital. We observed that uncommon EGFR mutations were harbored not only in adenocarcinoma, but also in squamous carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma, large cell carcinoma and carcinoid. Forty patients received EGFR-TKIs, the ORR was 20.0% and the PFS was 6.4 (95% CI, 4.8–7.9) months. Both results were inferior to the patients with common EGFR mutations in previous reports (5,6).

Table 3 Tumor response and PFS in G719X/S768I/L861Q subtypes
Mutations on G719X/S768I/L861Q constituted a major part of uncommon EGFR mutations, accounting for nearly 6% of EGFR mutations (7). One hundred and sixty-one patients with stage IIIB/IV lung adenocarcinoma bearing G719X/S768I/L861Q mutations were enrolled in a study from Taiwan, China. After receiving EGFR-TKI treatment, patients with those uncommon mutations exhibited a significantly inferior tumor response rate (41.6%vs. 66.5%; P<0.001) and PFS (median, 7.7vs. 11.4 months; P<0.001) than patients with common mutations in the controlled group (8). The exploratory analysis of G719X/S768I/L861Q subtypes in our study showed thatthe PFS was 7.6 (95%CI, 5.8–9.4) months, which was consistent with the previous research.
G719X in exon 18 was found with the highest incidence in our cohort. The frequency of exon 18 mutations was about 5%, among which G719X accounted for the majority. Anin vitrostudy had indicated that the affinity of G719X mutation with ATP was lower than that of L858R but higher than that of wild type (9). A six-fold higher concentration of gefitinib was required to inhibit the growth of cells expressing G719X compared with cells expressing L858R (10). A previous study reported patients with G719X single mutation or compound mutations had a median PFS of 8.1 months and a median OS of 16.4 months (11). After receiving EGFR-TKI treatment in our study, patients with G719X single mutation or compound ones exhibited an ORR of 22.7% and a median PFS of 7.6 months. Therefore, first-generation EGFR-TKIs were active in G719X mutations though less effective than in common mutations. However, a preclinical and clinical study demonstrated that second-generation EGFR-TKI afatinib may be an optimal choice for G719X mutations, with a median PFS of 13.8 months (12). Additionally, E709X, S720P, V689M and insertion mutations in 18 exon were also rarely reported in previous studies. In our study, one of two patients with G719X + E709A received EGFRTKI and experienced a PFS of 6.3 months. It was less effective than single G719X mutation due to E709A reducing the sensitivity of G719X to EGFR-TKI as demonstrated in anin vitrostudy (13,14).
In our current study, another uncommon mutation with high incidence was S768I. The frequency of mutation in exon 20 differed in diverse population, ranging from 1% to 17% (15-17). The efficacy of EGFR-TKI in S768I mutation was controversial. Kanchaet al. showed in preclinical study that the IC50value of gefitinib or erlotinib in S768I was higher than that of G719X and L861Q. In other words, S768I may be resistant to EGFR-TKI (10). However, a clinical study demonstrated similar response in S768I compared with 719X and L861Q (8). In our population, S768I mutation had favorable response (ORR, 27.3%; DCR, 90.9%) and survival (PFS, 8 months). Additionally, one patient harbored S768I with icotinib treatment as second-line therapy experienced 31 months of TKI treatment at the time of cutoff date and still maintained SD. Similarly, Masagoet al. also reported the case of a patient harboring S768I with gefitinib as secondline therapy had a PFS as long as 15 months. Although National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guidelines have not recommended it as drug-sensitive mutation, S768I indeed seemed to be sensitive to EGFRTKIs (18,19).
The mutation of L861Q accounted for approximately 2% of EGFR mutations (20). The response of L861Q to EGFR-TKI in previous reports was inconsistent. A number of studies demonstrated that first-generation EGFR-TKI was active in patients with L861Q mutations though less effective than in those with common mutations, with a PFS of 8.9 months and an OS up to 21.98 months (7,10,21). Therefore, L861Q was recommended as TKI-sensitive mutation in NCCN Guidelines. However, there was a study elucidated first-generation EGFR-TKIs might be an ineffective treatment option for this patient population (22). In current study, the PFS of patients with L86IQ was 5.7 (95%CI, 1.6–9.8) months. Thus, cancers with L861Q mutation were probably heterogeneous and associated with different EGFR TKIs treatment responses.
EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation (approximate 10% of all EGFR mutations) was generally associated with insensitivity to available TKIs (23). Consistent with the previous study, patients with exon 20 insertion in our cohort suffered progressed disease one month after TKI therapy. However, it was reported that the effectiveness of EGFR-TKI in exon 20 insertion mutation depended on the type and location of the insertion, for instance, the specific EGFR-A763 Y764ins alteration was associated with a high DCR (13). Therefore, EGFR-TKI was not recommended as the first-line therapy for EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation in clinical practice.
EGFR T790M was considered as the most common mechanism of resistance to first-generation EGFR-TKIs. But before exposure to EGFR TKIs, patients with baseline EGFR T790M were detected by standard molecular analysis in our study. The incidence of primary T790M ranged from 1% to 25% depending on the detection method and the population tested (24). Generally,De novoT790M occurred concurrently with sensitive mutations as observed in our research (25). Proved by previous and current studies,De novoEGFR T790M mutations had limited benefit from EGFR-TKIs and reduced the sensitivity of classical active mutations (24).
According to previous studies, 3.19%–15% of patients with EGFR mutations had complex mutations (26,27). In this study, most complex mutations contained the 19 del or L858R mutations, and the result suggested that the concomitant occurrence of 19 del and L858R might be a strong predictive factor in terms of the efficacy of EGFRTKIs. Earlier studies showed that patients with 19 del + L858R mutations had a median PFS of 9.53–16.5 months after TKI treatment (21,28). Furthermore, 19 del or L858R + rare mutations also seemed to be strong predictors of sensitivity. In current study, 2 patients with L858R + 19 del achieved PR and PFS of 6.0 months and 6.2 months, respectively. Consistent with previous studies, patients in our study who had a T790M mutation in addition to an L858R or 19 del mutation failed to demonstrate a superior response to EGFR TKI therapy, although contained an L858R or 19 del mutation. Therefore, first-generation TKIs such as erlotinib, gefitinib and icotinib maybe the optimal choice of therapy for patients with complex mutations containing 19 del or L858R mutations but not T790M.
The major limitation of this study is its retrospective design. Besides, uncommon EGFR mutations are heterogeneous and should be analyzed separately. However, due to its low incidence, the sample size in each subgroup is rather small. We therefore had to integrate the diverse mutations into one group and made conclusions combining with previous literature.
Conclusions
Uncommon EGFR-mutant NSCLC is a group of rare diseases with heterogeneity, and EGFR-TKIs can have different efficacy in specific subtypes. Thus, further individual assessment is required for each case.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the funding from Chinese Geriatric Oncology Society (CGOS) (No. H08151).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:7-30.
2.Chen W, Zheng R, Zuo T, et al. National cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2012. Chin J Cancer Res 2016;28:1-11.
3.Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2009;361:947-57.
4.Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with nonsmall-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:121-8.
5.Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2011;12:735-42.
6.Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:239-46.
7.Shi Y, Li J, Zhang S, et al. Molecular epidemiology of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology – Mainland China subset analysis of the PIONEER study. PLoS One 2015;10:e0143515.
8.Chiu CH, Yang CT, Shih JY, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment response in advanced lung adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/S768I mutations. J Thorac Oncol 2015;10:793-9.
9.Yun CH, Boggon TJ, Li Y, et al. Structures of lung cancer-derived EGFR mutants and inhibitor complexes: mechanism of activation and insights into differential inhibitor sensitivity. Cancer Cell 2007;11:217-27.
10.Kancha RK, von Bubnoff N, Peschel C, et al. Functional analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations and potential implications for EGFR targeted therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2009;15:460-7.
11.Wu JY, Yu CJ, Chang YC, et al. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:3812-21.
12.Yang JC, Sequist LV, Geater SL, et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: a combined post-hoc analysis of LUXLung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol 2015;16:830-8.
13.Beau-Faller M, Prim N, Ruppert AM, et al. Rare EGFR exon 18 and exon 20 mutations in non-smallcell lung cancer on 10,117 patients: a multicentre observational study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT network. Ann Oncol 2014;25:126-31.
14.De Pas T, Toffalorio F, Manzotti M, et al. Activity of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring rare epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J Thorac Oncol 2011;6:1895-901.
15.Wu JY, Wu SG, Yang CH, et al. Lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 mutations is associated with poor gefitinib treatment response. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:4877-82.
16.Yasuda H, Kobayashi S, Costa DB. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol 2012;13:e23-31.
17.Oxnard GR, J?nne PA. Power in numbers: metaanalysis to identify inhibitor-sensitive tumor genotypes. Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:1634-6.
18.Masago K, Fujita S, Irisa K, et al. Good clinical response to gefitinib in a non-small cell lung cancer patient harboring a rare somatic epidermal growth factor gene point mutation; codon 768 AGC > ATC in exon 20 (S768I). Jpn J Clin Oncol 2010;40:1105-9.
19.Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Akerley W, et al. NCCN Guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, Version 4.2016. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2016; 14:255-64.
20.Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J 2010;277:301-8.
21.Xu J, Jin B, Chu T, et al. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring uncommon EGFR mutations: A real-world study in China. Lung Cancer 2016;96:87-92.
22.Hsieh MH, Fang YF, Chang WC, et al. Complex mutation patterns of epidermal growth factor receptor gene associated with variable responses to gefitinib treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006;53:311-22.
23.Yasuda H, Park E, Yun CH, et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci Transl Med 2013;5:216ra177.
24.Yu HA, Arcila ME, Hellmann MD, et al. Poor response to erlotinib in patients with tumors containing baseline EGFR T790M mutations found by routine clinical molecular testing. Ann Oncol 2014;25:423-8.
25.Peng L, Song ZG, Jiao SC. Efficacy analysis of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on rare non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring complex EGFR mutations. Sci Rep 2014;4:6104.
26.Kobayashi S, Canepa HM, Bailey AS, et al. Compound EGFR mutations and response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Thorac Oncol 2013;8:45-51.
27.Liu Y, Wu BQ, Zhong HH, et al. Screening for EGFR and KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung carcinomas using DNA extraction by hydrothermal pressure coupled with PCR-based direct sequencing. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013;6:1880-9.
28.Keam B, Kim DW, Park JH, et al. Rare and complex mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor, and efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 2014;19:594-600.
Cite this article as: Zhang Y, Wang Z, Hao X, Hu X, Wang H, Wang Y, Ying J. Clinical characteristics and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Chin J Cancer Res 2017;29(1):18-24. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2017.01.03
10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2017.01.03
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Yan Wang. Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China. Email: wangyanyifu@126.com; Jianming Ying. Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China. Email: jmying@hotmail.com.
Methods:We retrospectively analyzed the data of 128 NSCLC patients pathologically diagnosed with uncommon EGFR mutation in the Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College and Beijing Hospital from January 2010 to December 2015, including 40 advanced patients who received EGFR-TKI.
Results:Among the total 128 patients, 11 patients were non-adenocarcinoma, including squamous carcinoma (3.9%), adenosquamous carcinoma (2.3%), large cell carcinoma (0.8%), and composite neuroendocrine carcinoma (1.6%). Single mutations accounted for 75.0% (96/128), including G719X (29.7%), S768I (18.0%), 20 exon insertion (13.3%), L861Q (12.5%), De novo T790M (0.8%), and T725 (0.8%). Thirty-two patients harbored complex mutations. Forty advanced patients received EGFR-TKI, the objective response rate (ORR) was 20.0%, the disease control rate (DCR) was 85.0%, and the progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.4 [95% confidence interval (95% CI), 4.8–7.9] months. The exploratory analysis of tumor response and PFS in 33 patients with G719X/S768I/L861Q subtypes showed that ORR was 21.2% (7/33), the DCR was 93.9% (31/33), and PFS was 7.6 (95% CI, 5.8–9.4) months. Patients with exon 20 insertion mutation and De novo T790M experienced rapid disease progression with PFS no more than 2.7 months.
Conclusions:Uncommon EGFR-mutant NSCLCs are heterogeneous, EGFR-TKIs can have different efficacy in this specific subtype, and thus further individual assessment is required for each case.
Submitted Sep 13, 2016. Accepted for publication Feb 10, 2017.
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2017年1期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2017年1期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in treatment of gastric cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis
- PEG-asparaginase in BFM-90 regimen improves outcomes in adults with newly diagnosed lymphoblastic lymphoma
- Extranodal involvement in young patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: distribution, prognostic value and treatment options
- Upregulation of kazrin F by miR-186 suppresses apoptosis but promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition to contribute to malignancy in human cervical cancer cells
- Prognostic factors for transarterial chemoembolization combined with sustained oxaliplatin-based hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy of colorectal cancer liver metastasis
- Influencing factors of inpatient expenditure pattern for cancer in China, 2015
