Combination therapy using evening primrose oil and electrical stimulation to improve nerve function following a crush injury of sciatic nerve in male rats
1 Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, International Branch Aras, Tabriz, Iran
2 Neuroscience Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
3 Immunology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
4 Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
5 Microsystem Fabrication Laboratory, Tabriz University, Tabriz, Iran
6 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
Combination therapy using evening primrose oil and electrical stimulation to improve nerve function following a crush injury of sciatic nerve in male rats
Omid Badri1, Parviz Shahabi2,*, Jalal Abdolalizadeh3, Mohammad Reza Alipour4, Hadi Veladi5, Mehdi Farhoudi6, Mohsen Sharif Zak7
1 Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, International Branch Aras, Tabriz, Iran
2 Neuroscience Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
3 Immunology Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
4 Drug Applied Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
5 Microsystem Fabrication Laboratory, Tabriz University, Tabriz, Iran
6 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
How to cite this article:Badri O, Shahabi P, Abdolalizadeh J, Alipour MR, Veladi H, Farhoudi M, Zak MS (2017) Combination therapy using evening primrose oil and electrical stimulation to improve nerve function following a crush injury of sciatic nerve in male rats. Neural Regen Res 12(3):458-463.
Open access statement:This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Peripheral nerve injuries with a poor prognosis are common. Evening primrose oil (EPO) has beneficial biological effects and immunomodulatory properties. Since electrical activity plays a major role in neural regeneration, the present study investigated the effects of electrical stimulation (ES), combined with evening primrose oil (EPO), on sciatic nerve function after a crush injury in rats. In anesthetized rats, the sciatic nerve was crushed using small haemostatic forceps followed by ES and/or EPO treatment for 4 weeks. Functional recovery of the sciatic nerve was assessed using the sciatic functional index. Histopathological changes of gastrocnemius muscle atrophy were investigated by light microscopy. Electrophysiological changes were assessed by the nerve conduction velocity of sciatic nerves. Immunohistochemistry was used to determine the remyelination of the sciatic nerve following the interventions. EPO + ES, EPO, and ES obviously improved sciatic nerve function assessed by the sciatic functional index and nerve conduction velocity of the sciatic nerve at 28 days after operation. Expression of the peripheral nerve remyelination marker, protein zero (P0), was increased in the treatment groups at 28 days after operation. Muscle atrophy severity was decreased significantly while the nerve conduction velocity was increased significantly in rats with sciatic nerve injury in the injury + EPO + ES group than in the EPO or ES group. Totally speaking, the combined use of EPO and ES may produce an improving effect on the function of sciatic nerves injured by a crush. The increased expression of P0 may have contributed to improving the functional effects of combination therapy with EPO and ES as well as the electrophysiological and histopathological features of the injured peripheral nerve.
nerve regeneration; peripheral nerve injury; sciatic nerve injury; evening primrose oil; electrical stimulation; sciatic functional index; cuff electrode; neural regeneration
Introduction
The peripheral nerve is typically injured by crushing or stretching. Such traumatic neuropathy is usually the consequence of minor traffic accidents, injuries in the workplace, or accidents in the home. Despite advances in medical intervention, traumatic neuropathy is frequent and often has poor prognosis (Ciaramitaro et al., 2010). Trauma created by an operation, called iatrogenic injury, occurs after surgery on the nerve, for example, sciatic nerve injury following hip prosthesis. Traumatic neuropathies are most frequent in young males after traffic accidents, and the quality of life for such patients is worsened. Evening primrose oil (EPO), which is extracted fromOenothera biennis L., is being used in increasing amounts in nutritional and pharmaceutical preparations. A previous study has shown that EPO intake is effective in improving atopic dermatitis and diabetic neuropathy, and EPO may alleviate the chronic disease state (Fan and Chapkin, 1998). EPO is enriched with gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), linolenic acid (LA), and omega 3. In a sample of EPO that was analyzed by the gas chromatography method, approximately 68% GLA was observed (Table 1). Essential fatty acids, such as GLA and LA, play a major role in nerve structure, and they could be useful in the anti-inflammatory mechanisms for autoimmune disease and neuropathy (Keen et al., 1993). Existing evidence demonstrates that GLA can normalize nerve conduction velocity (NCV) and sciatic endoneurial blood flow (Dines et al., 1995).
An injury that influences axons initiates a high degree of depolarization, which travels back to the soma. Vigorous spiking activity is then triggered, sustaining depolarization that initiates signaling pathways for axon regeneration. Tus, electrical activity plays an important role after an injury to the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Previous studies have shown that electrical stimulation (ES) facilitated peripheral nerve recovery in rats after a crush injury (Al-Majed et al.,2000a; Lal et al., 2008). The low intensity of ES increased the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and improved nerve regeneration (Zhang et al., 2013). One study showed that ES could improve diabetic neuropathy (Yao et al., 2012), and Lu et al. (2008) determined the positive and negative effects of ES on neural improvement after a crush injury. In the abovementioned studies, choosing the best pattern for the stimulation of the nerve made it a challenge to avoid any side effects and to achieve the most effective impact. Subthreshold electrotonic stimulation was used in the current study to minimize the side effects of ES on nerve regeneration.
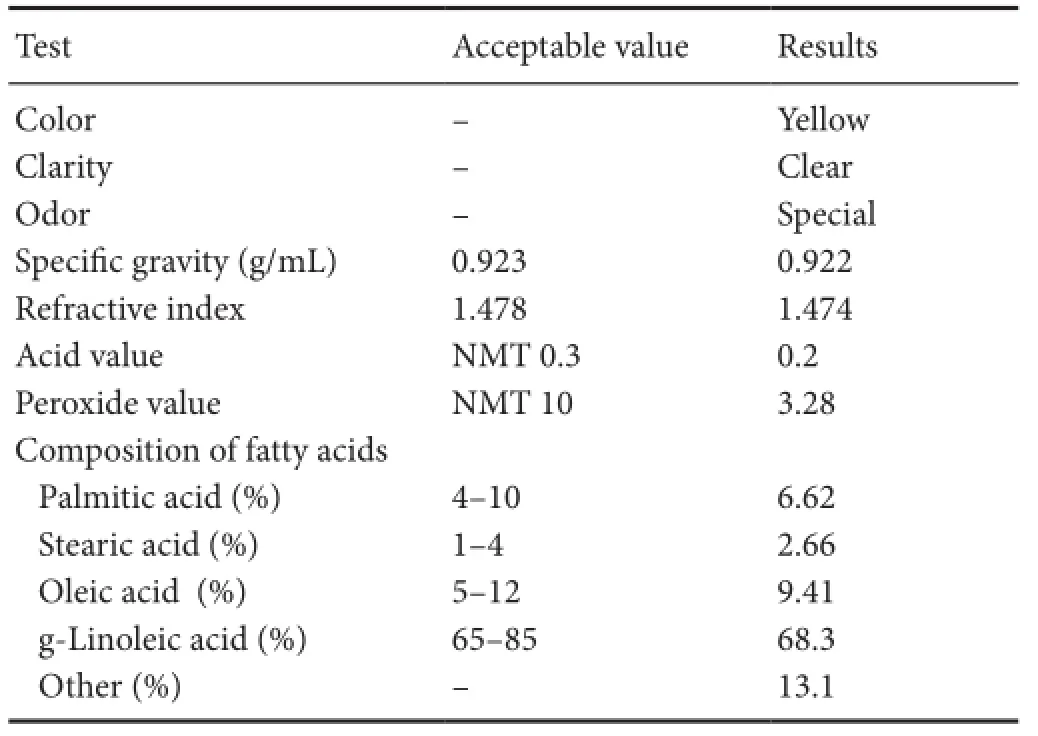
Table 1 Analysis for fatty acid of evening primrose oil
In this study, we investigated the effects of EPO in combination with ES on nerve function and histological changes following a sciatic nerve injury.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Tirty-six healthy adult male Wistar rats weighing 200-250 g were used in the present study. The rats were maintained in groups of six per cage in a 12-hour light-dark cycle at a controlled ambient temperature (22 ± 0.5°C) with free access to food and water. All experiments were conducted between 12:00 and 19:00. All research and animal care procedures were approved by the veterinary ethics committee of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran (approval number: 93/1-1/1) and were performed according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Chemicals
The chemicals used in the present study, including EPO, were purchased from Barij Essence Pharmaceutical Co., Kashan, Isfahan, Iran.
Treatment groups
All included rats were randomly divided into the following six groups (n= 6 in each group):
(1) Normal control (control) group: Rats were intact and received no intervention.
(2) Sham-surgery group: The sciatic nerve was exposed, but it was not crushed.
(3) Injury group: The sciatic nerve was exposed and then crushed, but rats received no intervention.
(4) Injury + EPO group. Rat sciatic nerve was exposed and EPO (450 mg/kg, intragastrically) was administered for 4 weeks.
(5) Injury + ES group: Rat sciatic nerves were exposed and crushed. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-covered stimulation electrodes were implanted 2 mm away from the injury site and leftin situ. The injured sciatic nerves were daily stimulated by the implanted electrodes connected to the WinLTP system (version 2.1; WinLTP Ltd., Bristol, UK) using the stimulation parameters including 0.1 ms duration, 20 Hz frequency, 60 μA intensity, 1 hour per day for 4 weeks.
(6) Injury + EPO + ES group: Rat sciatic nerves were exposed and crushed. Rats received both intragastrical administration of EPO and ES treatment for 4 weeks.
Surgery
Rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of ketamine (60 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg). The area above the left lower thigh was shaved and sterilized with betadine. An incision (2 cm) was made over the lateral aspect of the hind limb, and the muscle was separated in order to expose the sciatic nerve. The nerve was crushed at 0.5 cm proximal to its trifurcation point using small haemostatic forceps, and the jaw was covered with Teflon tubing to provide a smooth surface. Ten, the nerve was crushed for 60 seconds with an estimated pressure of 0.5-1 kg/mm2, as determined by a dynamometer (Lutron Digital Force Gauge, USA). The crushed zone was approximately 2-3 mm2, and it was uniformly transparent for several minutes thereafter (Tamaddonfard et al., 2013). The muscle layers were re-approximated using 4/0 chromic gut sutures, and the skin was closed with 3/0 silk sutures.
Sciatic functional index (SFI)
Evaluation based on the SFI was performed one day before the surgery and on days 7, 14, 21, and 28 following the surgery. The rats were held by the chest, and their hind paws were pressed down onto a water pad. Ten, the rats were immediately allowed to walk along a confined walkway, 7.5 cm wide by 60 cm long, with a dark shelter at the end of the corridor, leaving their footprints on paper that was dipped in a solution of bromophenol blue, which was yellow when it was dry and blue when it became wet (Lowdon et al., 1988). Each animal was individually trained to walk on the track before the footprints were recorded. Once the rats were able to walk quickly toward the shelter, their hind paws were soaked in water, and they were allowed to walk on the strip of previously prepared paper.
The following measurements were taken from the footprints: (1) the distance from the heel to the third toe, that is, the print length (PL); (2) the distance from the first to the fifth toes, that is, the toe spread (TS); and (3) the distance from the second to the fourth toes, that is, the intermediary toe spread (ITS). All three measurements were taken from the experimental (E, undergoing sciatic nerve crush) and normal (N) limbs. The three factors that comprised the SFIscores were calculated as follows: (1) print length factor (PLF) = (EPL - NPL)/NPL; (2) toe spread factor (TSF) = (ETS -NTS)/NTS; (3) intermediary toe spread factor (ITF) = (EIT - NIT)/NIT. Using these data, the SFI scores, which indicated the differences between the injured and the intact contralateral paws, were calculated by the following formula (Bain et al., 1989): SFI = -38.3[(EPL-NPL)/NPL] + 109.5[(ETSNTS)/NTS] + 13.3[(EIT-NIT)/NIT]-8.8.
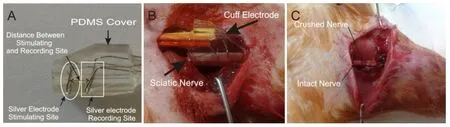
Figure 1 Cuff electrode with two sites for nerve stimulation and two sites for recording.
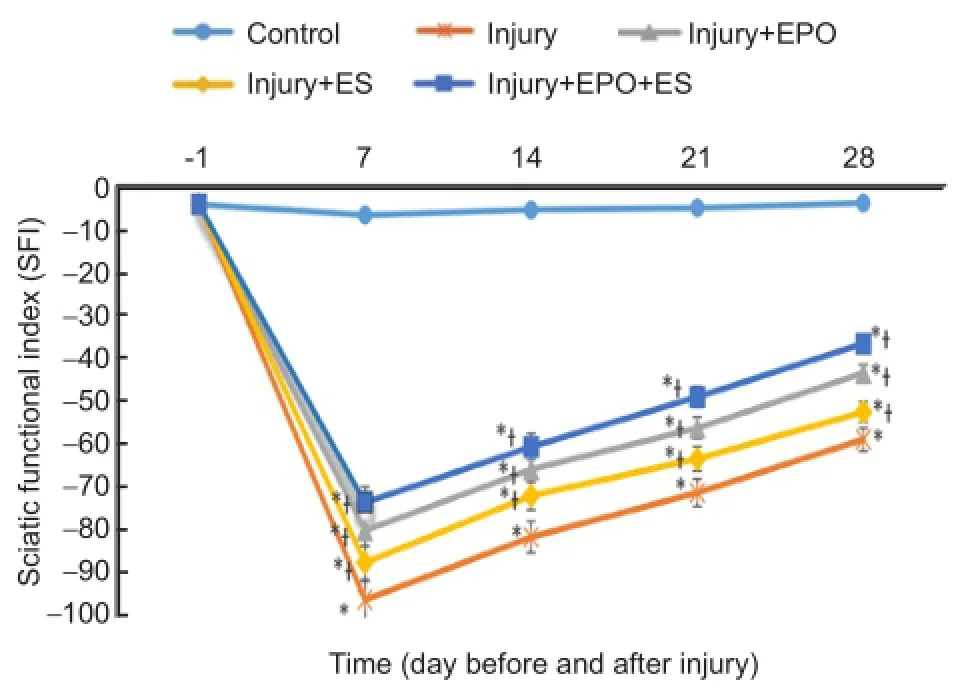
Figure 2 The effects of evening primrose oil (EPO) and electrical stimulation (ES) on the sciatic functional index (SFI) in rats with crushed sciatic nerves.
SFI analysis was determined as follows: an SFI that equaled -100 indicates significant impairment whereas an SFI oscillating around 0 showed normal function.
Histopathological evaluation
At 28 days after sciatic nerve injury in all groups, the sedated rats were euthanized, and the injured segments of the sciatic nerve and gastrocnemius muscle were removed and fixed in 10% formalin in buffered saline. The formalin fixed muscle was routinely processed for paraffin embedding, while thin (4-5 μm) transverse sections from the muscle were cut and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for light microscopic observations. The evaluation of gastrocnemius muscle atrophy severity was based on pathological changes on a scale from normal (0) to severe (3) (Tamaddonfard et al., 2013).
Immunohistochemistry
Protein zero (P0) is a marker for PNS myelination (Li et al., 2010). At 28 days after re-exposing the sciatic nerve, the nerve specimens were dissected and fixed in 10% formalin for 12 hours. The tissue samples were embedded in the paraffin and cut into 5-μm thick sections. The slides were allowed to dry for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by 1 hour in an incubator at 60°C. After deparaffinization and rehydration, the slides were washed with the distilled water. Ten, the slides were covered for 5 minutes with 3% H2O2to block endogenous peroxidase.
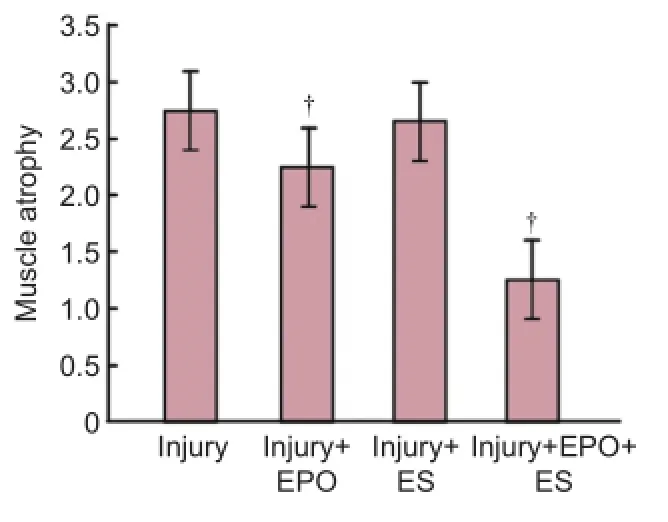
Figure 4 The effects of evening primrose oil (EPO) and electrical stimulation (ES) on gastrocnemius muscle atrophy severity in rats with crushed sciatic nerves.
Antigen retrieval was achieved by steaming the tissue sections in a citrate buffer for 20 minutes (BioGenex antigen retrieval citra). Non-specific immunoreaction was blocked, and the sections were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature and washed three times by the PBS buffer. Ten, the sections were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. As a primary antibody, anti-rat myelin P0 (Abcam, 1:100 dilution) was used as the myelination marker of the PNS for all groups. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat and anti-rabbit IgG was added to the sections as a secondary antibody at 25°C for 1 hour. After that, the diaminobenzidine substrate was added, and the slides were dehydrated and analyzed qualitatively (Choi et al., 2005).
Electrophysiological study
On the day of the operation and 28 days after that, the animals in each group were subjected to electrophysiological studies using the WinLTP system (UK, Version 2.1). During the test, the rats’ body temperature was kept between 36.5-37°C. After the intraperitoneal injection of ketamine and xylazine, the right sciatic nerve was exposed, and the dis-tance between cuff electrodes in between stimulating and recording sites was 3 mm, cuff electrodes were placed around the sciatic nerve (Figure 1). All stimulations were conducted by 60 μA and then recorded. Waves were analyzed by the WinLTP system to determine the NCV.
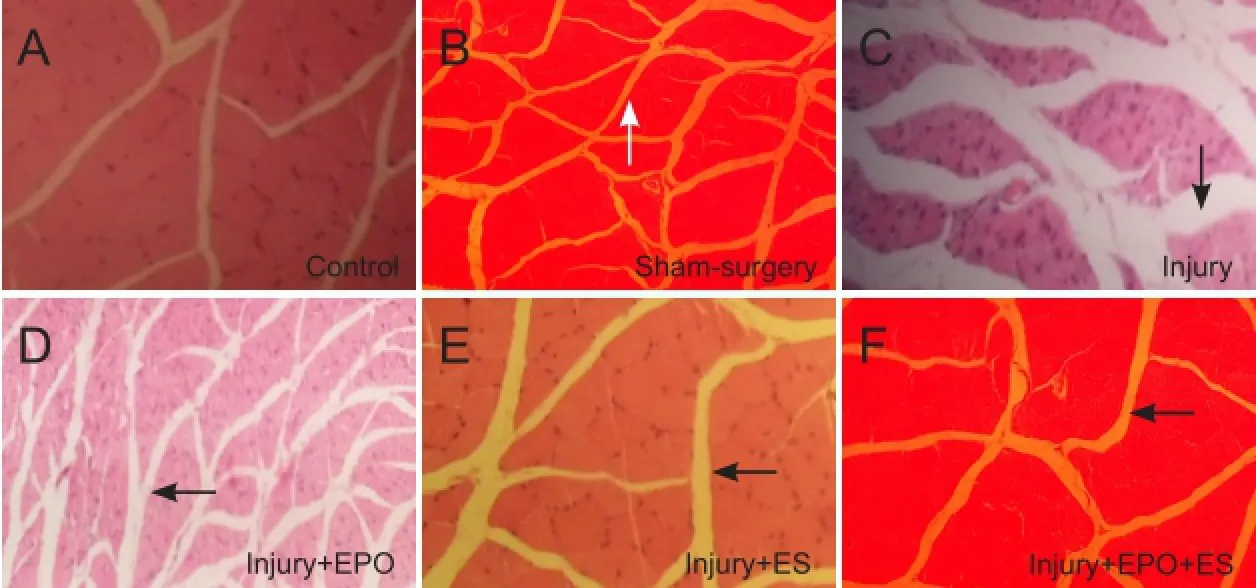
Figure 3 Effects of evening primrose oil (EPO) and electrical stimulation (ES) on gastrocnemius muscle fibers in rats with crushed sciatic nerves.

Figure 5 Electrophysiological recordings of NCV of the sciatic nerve.
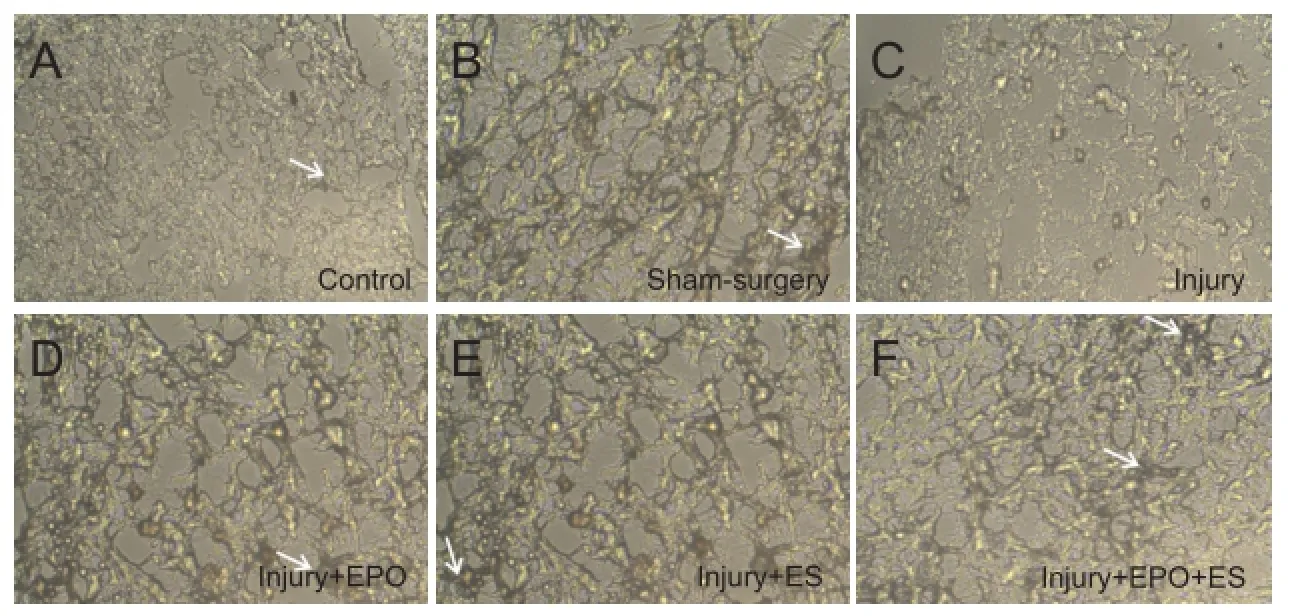
Figure 6 Immunohistochemistry analysis of remyelinated nerve distal to the transected site of the sciatic nerve (original magnification, × 400).
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. The significanceof the SFI scores between groups was assessed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s test for multiple comparisons. Values for the degree of muscle atrophy severity were also analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s test for multiple comparisons. Significance atP< 0.05 was receptive in all tests. SPSS 16.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for this analysis.
Results
SFI results
There were no post-operative deaths or clinical evidence of wound infections. There was no significant difference in SFI between control and sham-surgery groups. Results belonging to the sham-surgery group are not shown inFigure 2. SFI significantly decreased on the first day post-surgery in injury, injury + ES, injury + EPO, and injury + EPO + ES groups. SFI was increased on the last day of the examination compared to that on the first day of the examination in the injury + EPO + ES group, and SFI was significantly higher in the injury + EPO + ES, injury + ES, injury + EPO groups than in the injury group ( allP< 0.05;Figure 2). There was no significant difference in SFI between injury + ES and injury + EPO groups. The SFI in the injury group was reduced to nearly -100 on day 7 after operation. In contrast, EPO administration in the injury + EPO + ES group significantly altered the SFI in a progressive pattern, but the differences between ES and EPO groups were not significantly different (P> 0.05).
Recovering SFI to the control group level in the injury + EPO + ES group was accelerated than that in the other groups, but difference in SFI between injury + EPO + ES group and injury + ES or injury + EPO group was not significant (P>0.05).
Gastrocnemius muscle atrophy results
Figure 3shows the effects of EPO and ES on muscle atrophy severity in the sciatic nerve induced by a crush injury. In the intact and sham-surgery groups, no muscle atrophy was observed (Figure 3A,BandFigure 4). In the injury group, severe atrophy in the gastrocnemius muscle was seen (Figures 3C,Eand4). However, EPO and ES both produced significant, positive effects on gastrocnemius muscle atrophy (Figures 3D,Eand4). Combination therapy using EPO and ES and admininstration of ES alone significantly prevented muscle atrophy (P< 0.05) (Figure 3Fand4).
NCV
On day 28, NCV in the injury + ES, injury + EPO, and injury + EPO + ES groups was statistically different from that in the injury group (P< 0.05). However, NCV was not significantly different between injury + ES and injury + EPO groups on day 28, but NCV in the injury + EPO + ES group was significantly different from that in the injury + ES and injury + EPO groups (P< 0.05). Changes in electrophysiological recordings of the sciatic nerves are shown inFigure 5.
Immunohistochemistry
On day 28 after operation in the injury + EPO + ES group, the P0 expression zone was extensively visible in cross-sections taken from the midpoint, indicating myelinated axons in the crushed sciatic nerve. In the injury + EPO + ES group, the formation-regenerated axons were similar to those of the normal axons (Figure 6).
Discussion
In the present study, the effects of EPO and ES on the remyelination of the sciatic nerve in adult male rats were evaluated, and our data showed that the combination therapy of EPO and ES accelerated the recovery of nerve function and the histopathological features of the nerve, preventing against gastrocnemius muscle atrophy. A previous study has shown the positive effect of EPO on peripheral nerve conduction in the diabetic rat (Ford et al., 2001). Another study showed that the anti-inflammatory features of an EPO component could modulate the immune system, which was useful for treating patients with multiple sclerosis (Rezapour-Firouzi et al., 2013b). Tus, the effects of EPO administration on nerve injury in the present study were consistent with findings from a previous study (Halat and Dennehy, 2003).
EPO used in this study was enriched with a myelin precursor, which might have accelerated the remyelination process in the crushed sciatic nerve (Rezapour-Firouzi et al., 2013a). There have been conflicting results from previous studies on the effects of ES on injured peripheral nerves (Al-Majed et al., 2000b). Enhanced PNS remyelination, which was in agreement with the results reported by Al-Majed et al. (2000b), was seen by the use of ES in the injury + EPO + ES group in the present study. Yet, several previous studies showed that ES impaired early functional recovery and exacerbated skeletal muscle atrophy after a sciatic-nerve crush injury in rats (Baptista et al., 2008; Lu et al., 2008; Gigo-Benato et al., 2010). Another study revealed that ES promoted axon regeneration at the expense of decreasing the fidelity of muscle reinnervation, resulting in unchanged functional recovery (Hamilton et al., 2011). Based on these findings, the subthreshold ES was more effective for nerve regeneration without negative effects (Gordon et al., 2008; Vivo et al., 2008; Asensio-Pinilla et al., 2009). Since subthreshold ES could preserve the signaling of regeneration in the crushed nerve without the disadvantages of high-intensity stimulation, this pattern was used in the current study for nerve stimulation in the injury + ES and injury + EPO + ES groups. If used in combination therapy, EPO and ES could be complementary interventions that facilitate each other.
As demonstrated in the present study, the signaling of regeneration can be preserved by a subthreshold pattern of ES, and the substances needed for remyelination can be made available for Schwann cells by EPO administration. Also, the results revealed that the use of EPO and ES significantly enhanced peripheral nerve remyelination. Following the crush injury of the sciatic nerve in rats, gastrocnemius muscle weight loss and atrophy were reported (Liu et al., 2007). However, based on our results, EPO in combination with ES produced a protective effect on gastrocnemius muscle atrophy.
The SFI is reported to be a useful tool to determine thefunctional recovery of the sciatic nerve of rats in experimental groups (Varej?o-Silva, 2001). Functional recovery of the sciatic nerve following a crush injury in groups treated with ES and EPO could be determined by SFI measurement. According to our results, EPO and ES administration had positive effects on the functional recovery of crush-injured sciatic nerve. There is evidence that NCV depends on axon diameter, myelination, and intermodal distance (Brown et al., 1991). Despite the damage to a large number of remaining fibers, a nerve might have a few fibers that can still conduct effectively. For this reason, NCV might be used to evaluate the fastest and, healthiest fibers rather than the total nerve function (Kanaya et al., 1996). According to our results, NCV was enhanced by day 28 after operation. This finding showed that remyelination and regeneration of the nerve fiber were accelerated.
In conclusion, the present study showed that a combined treatment with EPO and ES might have increased the remyelination of rats with crushed sciatic nerves, contributing to recovery of sciatic nerve function.
Acknowledgments:The present research was financially supported by the Neuroscience Research Center of the Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran.
Author contributions:OB designed this study and performed all experiments. PS guided the study. JA and MSZ were responsible for immunohistochemistry. MRA, HV and MF performed electrical stimulation and statistical analysis. All authors approved the final version of this paper.
Conflicts of interest:None declared.
Plagiarism check:This paper was screened twice using CrossCheck to verify originality before publication.
Peer review:This paper was double-blinded and stringently reviewed by international expert reviewers.
Al-Majed AA, Brushart TM, Gordon T (2000a) Electrical stimulation accelerates and increases expression of BDNF and trkB mRNA in regenerating rat femoral motoneurons. Eur J Neurosci 12:4381-4390.
Al-Majed AA, Neumann CM, Brushart TM, Gordon T (2000b) Brief electrical stimulation promotes the speed and accuracy of motor axonal regeneration. J Neurosci 20:2602-2608.
Asensio-Pinilla E, Udina E, Jaramillo J, Navarro X (2009) Electrical stimulation combined with exercise increase axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol 219:258-265.
Bain JR, Mackinnon SE, Hunter DA (1989) Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg 83:129-138.
Baptista AF, Gomes JR, Oliveira JT, Santos SM, Vannier-Santos MA, Martinez AM (2008) High- and low-frequency transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation delay sciatic nerve regeneration after crush lesion in the mouse. J Peripher Nerv Syst 13:71-80.
Brown CJ, Evans PJ, Mackinnon SE, Bain JR, Makino AP, Hunter DA, Hare G (1991) Inter- and intraobserver reliability of walking-track analysis used to assess sciatic nerve function in rats. Microsurgery 12:76-79.
Choi BH, Zhu SJ, Kim BY, Huh JY, Lee SH, Jung JH (2005) Transplantation of cultured bone marrow stromal cells to improve peripheral nerve regeneration. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 34:537-542.
Ciaramitaro P, Mondelli M, Logullo F, Grimaldi S, Battiston B, Sard A, Scarinzi C, Migliaretti G, Faccani G, Cocito D (2010) Traumatic peripheral nerve injuries: epidemiological findings, neuropathic pain and quality of life in 158 patients. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15:120-127.
Dines KC, Cameron NE, Cotter MA (1995) Comparison of the effects of evening primrose oil and triglycerides containing gamma-linolenic acid on nerve conduction and blood flow in diabetic rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ter 273:49-55.
Fan YY, Chapkin RS (1998) Importance of dietary gamma-linolenic acid in human health and nutrition. J Nutr 128:1411-1414.
Ford I, Cotter MA, Cameron NE, Greaves M (2001) The effects of treatment with alpha-lipoic acid or evening primrose oil on vascular hemostatic and lipid risk factors, blood flow, and peripheral nerve conduction in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Metabolism 50:868-875.
Gigo-Benato D, Russo TL, Geuna S, Domingues NR, Salvini TF, Parizotto NA (2010) Electrical stimulation impairs early functional recovery and accentuates skeletal muscle atrophy after sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Muscle Nerve 41:685-693.
Gordon T, Brushart TM, Chan KM (2008) Augmenting nerve regeneration with electrical stimulation. Neurol Res 30:1012-1022.
Halat KM, Dennehy CE (2003) Botanicals and dietary supplements in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Am Board Fam Pract 16:47-57.
Hamilton SK, Hinkle ML, Nicolini J, Rambo LN, Rexwinkle AM, Rose SJ, Sabatier MJ, Backus D, English AW (2011) Misdirection of regenerating axons and functional recovery following sciatic nerve injury in rats. J Comp Neurol 519:21-33.
Kanaya F, Firrell JC, Breidenbach WC (1996) Sciatic function index, nerve conduction tests, muscle contraction, and axon morphometry as indicators of regeneration. Plast Reconstr Surg 98:1264-1271, discussion 1272-1264.
Keen H, Payan J, Allawi J, Walker J, Jamal GA, Weir AI, Henderson LM, Bissessar EA, Watkins PJ, Sampson M, et al. (1993) Treatment of diabetic neuropathy with gamma-linolenic acid. The gamma-Linolenic Acid Multicenter Trial Group. Diabetes Care 16:8-15.
Lal D, Hetzler LT, Sharma N, Wurster RD, Marzo SJ, Jones KJ, Foecking EM (2008) Electrical stimulation facilitates rat facial nerve recovery from a crush injury. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 139:68-73.
Li FQ, Fowler KA, Neil JE, Colton CA, Vitek MP (2010) An apolipoprotein E-mimetic stimulates axonal regeneration and remyelination after peripheral nerve injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ter 334:106-115.
Liu M, Zhang D, Shao C, Liu J, Ding F, Gu X (2007) Expression pattern of myostatin in gastrocnemius muscle of rats after sciatic nerve crush injury. Muscle Nerve 35:649-656.
Lowdon IM, Seaber AV, Urbaniak JR (1988) An improved method of recording rat tracks for measurement of the sciatic functional index of de Medinaceli. J Neurosci Methods 24:279-281.
Lu MC, Ho CY, Hsu SF, Lee HC, Lin JH, Yao CH, Chen YS (2008) Effects of electrical stimulation at different frequencies on regeneration of transected peripheral nerve. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 22:367-373.
Rezapour-Firouzi S, Arefhosseini SR, Farhoudi M, Ebrahimi-Mamaghani M, Rashidi MR, Torbati MA, Baradaran B (2013a) Association of expanded disability status scale and cytokines after intervention with co-supplemented hemp seed, evening primrose oils and hot-natured diet in multiple sclerosis patients. BioImpacts: BI 3:43.
Rezapour-Firouzi S, Areftosseini SR, Mehdi F, Mehrangiz EM, Baradaran B, Sadeghihokmabad E, Mostafaei S, Fazljou SM, Torbati MA, Sanaie S, Zamani F (2013b) Immunomodulatory and therapeutic effects of Hot-nature diet and co-supplemented hemp seed, evening primrose oils intervention in multiple sclerosis patients. Complement Ter Med 21:473-480.
Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Ahmadian E, Hamidhoseyni A (2013) Crocin enhanced functional recovery after sciatic nerve crush injury in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16:83-90.
Varej?o-Silva MA (2001) Meteorologia e climatologia: Inmet.
Vivo M, Puigdemasa A, Casals L, Asensio E, Udina E, Navarro X (2008) Immediate electrical stimulation enhances regeneration and reinnervation and modulates spinal plastic changes after sciatic nerve injury and repair. Exp Neurol 211:180-193.
Yao CH, Chang RL, Chang SL, Tsai CC, Tsai FJ, Chen YS (2012) Electrical stimulation improves peripheral nerve regeneration in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 72:199-205.
Zhang X, Xin N, Tong L, Tong XJ (2013) Electrical stimulation enhances peripheral nerve regeneration after crush injury in rats. Mol Med Rep 7:1523-1527.
Copyedited by Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
*Correspondence to: Parviz Shahabi, Ph.D. in physiology, parvizshahabi@gmail.com.
orcid: 0000-0001-5594-5544 (Parviz Shahabi)
10.4103/1673-5374.202927
Accepted: 2017-02-03
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Anesthetic considerations for patients with acute cervical spinal cord injury
- Transplantation of autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the subarachnoid space for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a safety analysis of 14 patients
- Anatomical distributional defects in mutant genes associated with dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type C in an adenovirusmediated mouse model
- Mechanisms responsible for the inhibitory effects of epothilone B on scar formation after spinal cord injury
- The mechanism of Naringin-enhanced remyelination after spinal cord injury
- Estrogen affects neuropathic pain through upregulating N-methyl-D-aspartate acid receptor 1 expression in the dorsal root ganglion of rats

