Static and Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Thick and Thin Plates and Shells by a Very Simple Displacement-based 3-D Hexahedral Element with Over-Integration
Qifeng Fan,Yaping Zhang,Leiting Dong,3,Shu Li,Satya N.Atluri
Static and Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Thick and Thin Plates and Shells by a Very Simple Displacement-based 3-D Hexahedral Element with Over-Integration
Qifeng Fan1,Yaping Zhang2,Leiting Dong1,3,Shu Li1,Satya N.Atluri4
A very simple displacement-based hexahedral 32-node element(denoted as DPH32),with over-integration in the thickness direction,is developed in this paper for static and dynamic analyses of laminated composite plates and shells.In contrast to higher-order or layer-wise higher-order plate and shell theories which are widely popularized in the current literature,the proposed method does not develop specif i c theories of plates and shells with postulated kinematic assumptions,but simply uses the theory of 3-D solid mechanics and the widely-available solid elements.Over-integration is used to evaluate the element stiffness matrices of laminated structures with an arbitrary number of laminae,while only one element is used in the thickness direction without increasing the number of degrees of freedom.A stress-recovery approach is used to compute the distribution of transverse stresses by considering the equations of 3D elasticity.Comprehensive numerical results are presented for static,free vibration,and transient analyses of different laminated plates and shells,which agree well with existing solutions in the published literature,or solutions of very-expensive 3D models by commercial FEM codes.It is clearly shown that the proposed methodology can accurately and efficiently predict the structural and dynamical behavior of laminated composite plates and shells in a very simple and cost-effective manner.
laminated structure,plates and shells,hexahedral 32-node element,higher order theory,over-integration.
1 Introduction
Laminated composite structures are extensively used in aerospace,automobile,marine and other industrial f i elds,primarily due to their high strength-to-mass ratio,high stiffness-to-mass ratio,and their capability to be tailored according to given requirements.In-depth understandings of their mechanical behaviors are generally needed for the design and maintenance of such engineering structures.However,as full or large scale experimental tests are usually time-expensive and monetarilyexpensive,it is necessary to develop accurate and eff i cient numerical models which are capable of predicting their static and dynamical behaviors.
A very large number of laminate theories can be found in the literature,which are mostly derived from equations of 3D elasticity by making various assumptions of the kinematics in the thickness direction.These theories involve expanding the displacement f i eld in a power-series in the thickness direction of the entire laminate[“higher-order theories”]or in the thickness direction of each lamina in the laminate[“l(fā)ayer-wise higher-order theories”].Using these assumptions,a new set of generalized displacements,strains,and stresses are defined,and a new set of governing equilibrium,compatibility,and constitutive equations are derived.The simplest one is the classical laminate theory(CLT)which is based on the wellknown Love-Kirchoff assumption[Timoshenko and Woinowsky(1959)].Straight lines normal to the mid-surface are assumed to remain straight and normal to the mid-surface after deformation.To take into account the effects of transverse shear deformation,the first-order shear deformation theory(FSDT)[Reissner(1945)and Mindlin(1951)]relaxes the Love-Kirchoff assumption,so that transverse straight lines do not necessarily remain normal to the mid-surface after deformation.CLT and FSDT are widely popularized in commercial FEM packages such as Ansys,Abaqus,Nastran,etc.But for very thick composite laminates,CLT and FSDT usually underestimate the def l ections and overestimates natural frequencies.
Many higher-order shear deformation theories(HSDT)were later proposed,see[Lo,Christensen and Wu(1977);Reddy(1984);Pandya and Kant(1988);Reddy and Robbins(1994)]for example.These high-order theories mostly adapt various third-order assumptions of in-plane displacements,def i ne additional generalized variables that have ambiguous physical meanings,and derive very complex and tedious governing differential equations of plate and shells.In a similar way the layer-wise theories are developed by making assumptions of displacements in each layer,see[Di Sciuva(1985),Toledano and Murakami(1987),Carrera(2003)].Displacements in each layer or lamina are assumed to be either linear,quadratic,higher-order,trigonometric,or to be other continuous functions in layer-wise/zigzag theories of plates and shells.However,having additional degrees of freedoms for each lamina makes layer-wise theories highly expensive for realistic laminate structures that have a very large number of layers.
In order to derive higher-order or layer-wise theories of plates and shells,kinematic assumptions are substituted into the principle of potential energy of 3D elasticity.
By exploring the stationarity conditions,very complex governing differential equations in terms of newly def i ned generalized displacements,strains and stresses can be derived,see[Reddy(2004)]for example.However,such complex differential equations cannot be directly solved.One usually goes back to derive a variational principle from these governing differential equations,and to develop corresponding f i nite element models to solve the problem numerically.In this sense,defining the many generalized displacements,strains,stresses,and deriving the complex higher-order or layer-wise theories and differential equations seems unnecessary.One can directly use the variational principle of 3D elasticity to develop finite elements for the modeling of plates and shells.Moreover,it is difficult for end-users to completely understand all the newly-defined FEM DOFs in higher-order theories which have ambiguous physical meanings,which becomes very problematic when boundary conditions have to be enforced correctly by end-users.
In an entirely different way,[Dong,El-Gizawy,Juhany,Atluri(2014b,c)]directly developed quadrilateral 4-node,and hexagonal 8-node f i nite element models,for laminated structures based on the theory of 2-D and 3-D solid mechanics,respectively.Because traditional displacement-based lowest order elements suffer from shear locking,a technique of locking-alleviation was used by independently assuming non-locking element strains.Over-integration was also adapted in the thickness direction to accurately evaluate the stiffness matrix of FG and laminated elements.Similar work on smart composite structures was also presented in[Ray,Dong and Atluri(2015)].However,for very thick laminated structures with only a few layers,it is difficult to obtain accurate results by using only one linear finite element in the thickness direction.
In this study,using the standard 3-D solid mechanics,a displacement-based hexahedral 32-node element(denoted as DPH32),with over-integration in the thickness direction,is developed for static and dynamic analysis of laminated composite plates and shells with an arbitrary number of layers.A stress-recovery approach is used to compute the distribution of transverse stresses by considering the equations of 3D elasticity.It is shown that,without using any higher-order shear deformation theories or layer-wise theories,the present method can accurately and efficiently predict the static and dynamical behaviors of laminated thick as well as thin composite plates and shells,even if only one element is used in the thickness direction.In the following sections,details of the proposed methodology are described and numerical examples with different boundary conditions are provided to verify its accuracy when compared with existing solutions in published literature,and finite element solutions from the commercial code MSC/Nastran.
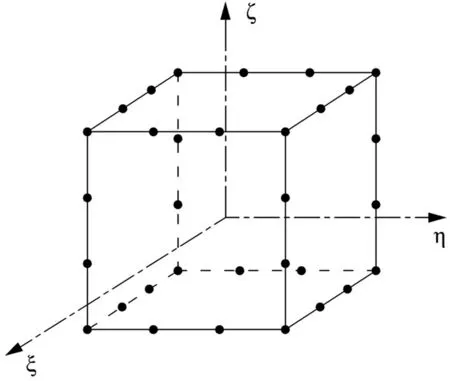
Figure 1:A 32-node hexahedral element in ξ,η,ζ coordinates
2 Algorithmic Formulation
As illustrated in Fig.1,a 32-node hexahedral element is formed with 8 corner nodes and 24 side nodes.Facilitated by the standard isoparametric concept,the shape functions of the 32-node hexahedron can be defined as follows:
For corner nodes:
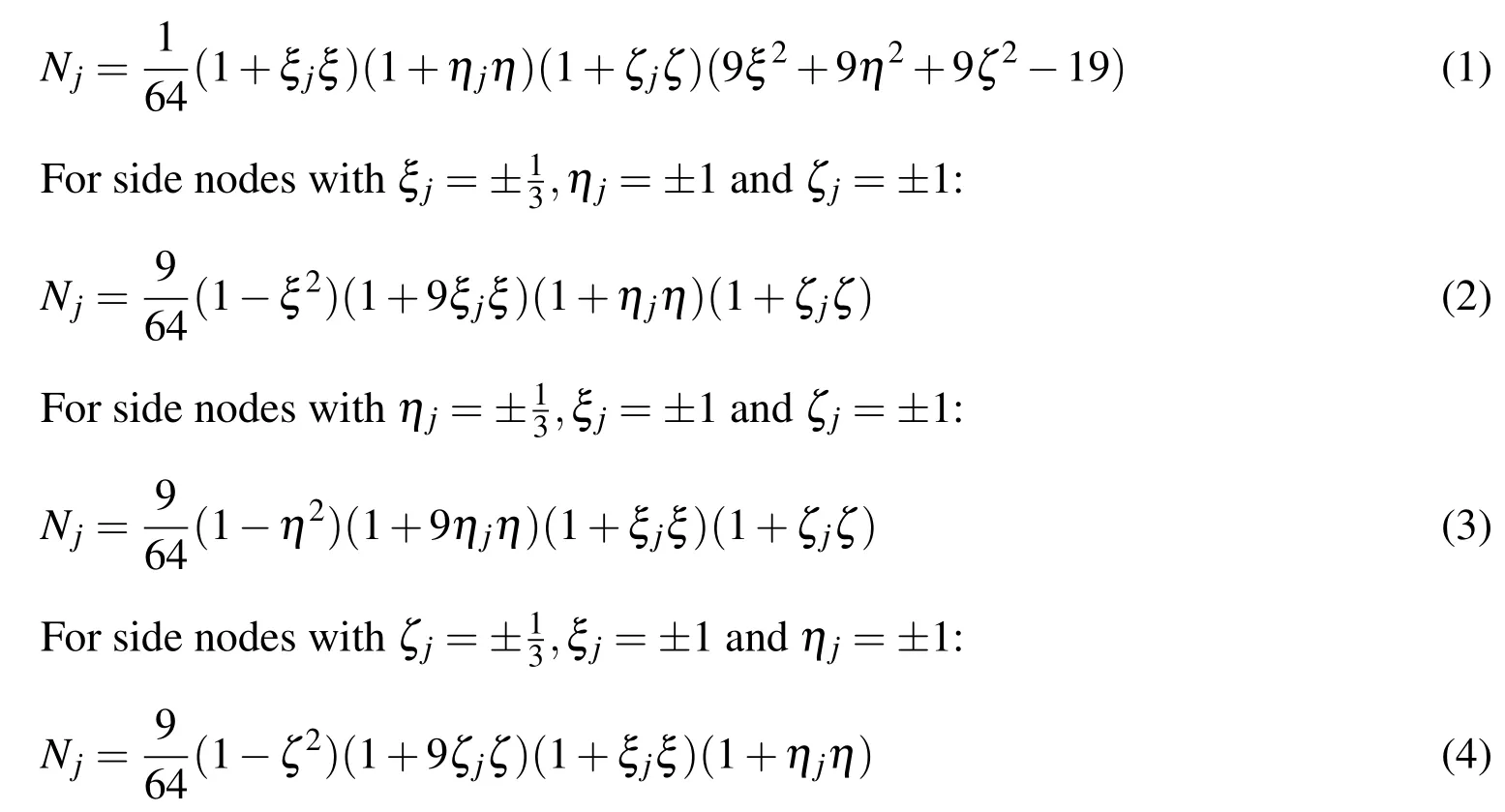
Displacements within the element are interpolated by using nodal shape functions:

The strains within the element can be obtained by differentiating Eq.(5)with respect to Cartesian coordinates:

where L is a linear differential operator.
The element stiffness matrix and mass matrix are thus computed by:

After assembling all the element mass and stiffness matrices into the global ones,static,free vibration,or transient analyses of the structure can be done following standard numerical procedures,see[Atluri(2005)].
In this study,N-layer laminated plates and shells are studied by using such 32-node hexagonal elements.As discussed in[Dong,EI-Gizawy,Juhany and Atluri(2014b,c)],the technique of“over integration”is needed to accurately evaluate the element stiffness and mass matrices of laminated elements.In order to take care of the different material properties of each lamina,a layer-wise Gauss quadrature in the thickness direction is adapted in this study.In this way,we consider another variable ?kas the natural coordinate in the thickness direction of any(kth)individual layer,which can be related to the natural coordinate ? of the whole element in the thickness direction as follows:

whereh,hk,hk+1represent the thickness of the plate/shell,and coordinates in the thickness direction at the bottom and the top surfaces of any layer of lamina.
Thus the elemental stiffness and mass matrix are to be evaluated as:

whereDkand ρkare elastic stiffness and density of thekthlayer respectively.
The transverse normal and shear stresses are computed by using a stress-recovery approach considering the equilibrium equations of 3D linear elasticity.For the laminated plates,the distribution of transverse stresses can be obtained by numerically evaluating:

wherez=z0denote the lower surface of the plate.
For cylindrical shells,the distribution of transverse stresses can also be evaluated,by numerically solving the following 3 differential equations:
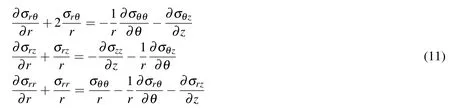
In Eq.(11),the left hand-side involves stress components to be recovered,and the right-hand side are directly evaluated from the solutions of DPH32.Each equation is a first-order single-variable ODE,which can be solved with a variety of computational methods,see[Dong,Alotaibi,Mohiuddine and Atluri(2014a)].In this study,simple collocation of Eq.(11)is implemented at a variety of points along the thickness direction.Combined with the traction free condition at the inner surface of the cylindrical shell,stress components σrθ,σrz,σrrcan be efficiently recovered from the computed in-plane normal and shear stresses.
3 Numerical Examples
In this section,several typical problems of laminated composite plates and shells have been analyzed.The geometry and reference system for the laminated plate and shell can be seen in Fig.2 and Fig.3 respectively.The following boundary conditions have been used.
Simply supported boundary condition(S):

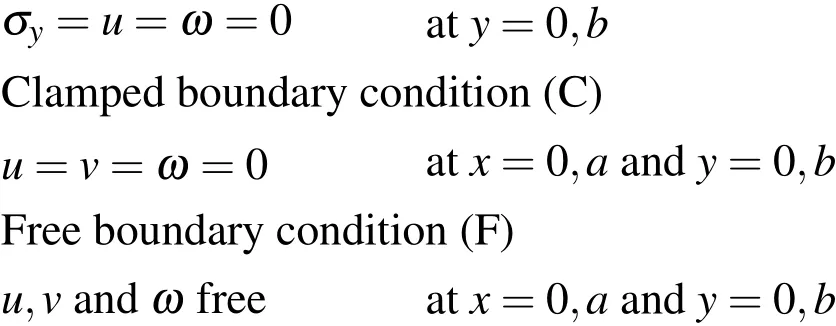
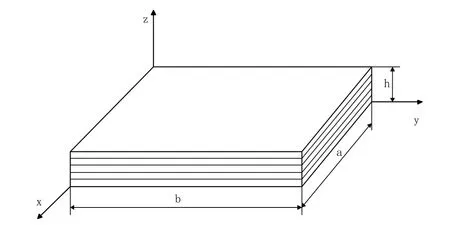
Figure 2:Geometry and reference system for the laminated plate.
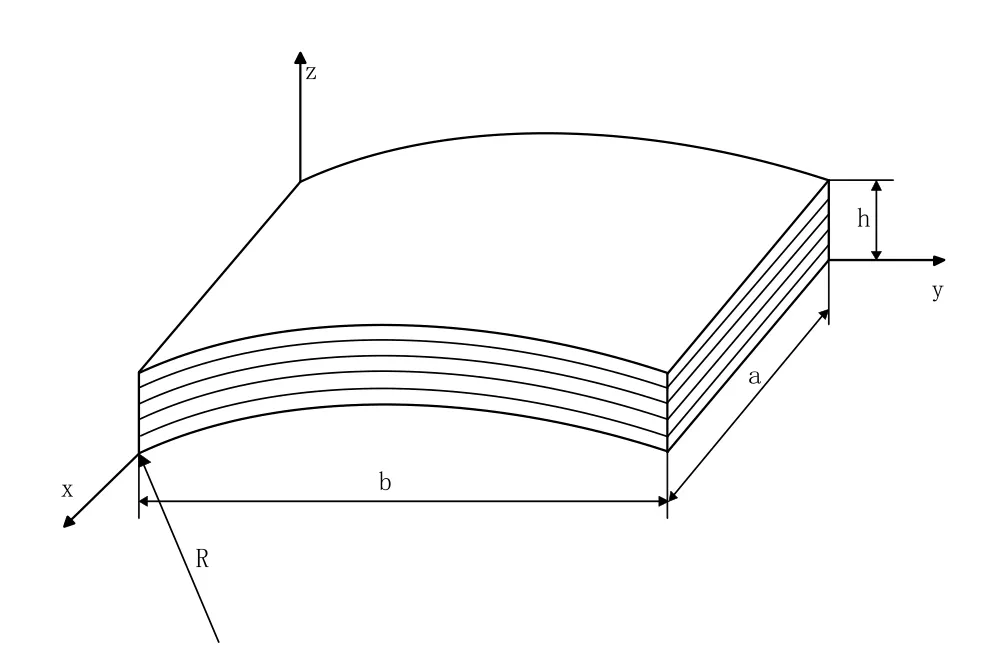
Figure 3:Geometry and reference system for the laminated shell.
3.1 Static analysis
3.1.1A simply-supported 4-ply([0/90]s)laminated plate subjected to a sinusoidal distributed lateral load
The first example considers a simply-supported thick-section symmetrical 4-ply([0/90]s)laminated plate subjected to a sinusoidal distributed lateral load:
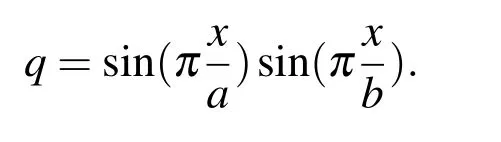
The plate is square witha=b=100mm,and the total plate thickness ish=10mm.Each layer is made of Graphite–Epoxy T300/934 with the same thickness.The orthotropic material has the following mechanical properties:
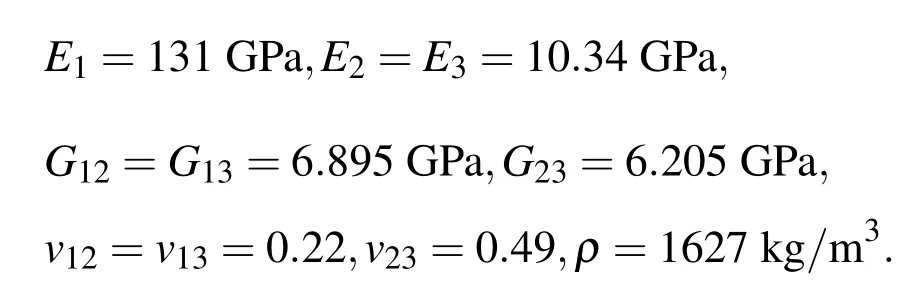
Figure 4:Finite element model for the 4-ply laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
We solve this problem using a uniform 10×10 mesh with DPH32 elements,as well as using Nastran by meshing each layer of the laminate.We can see the difference of meshes between the Nastran model and the DPH32 model in Fig 4.It takes about half an hour to obtain the numerical results by using the 200,000 nodes Nastran model on a regular PC with i7 CPU.On the contrary,the DPH32 model has only 1364 nodes and takes about 20 seconds of computational time,although an unoptimized MatLab code is used in this study.Computed in-plane and out-of-plane stresses are shown in Figs.5–6,from which we can see that the two methods give similar results although the computation time differs by two orders of magnitudes.
3.1.2A simply-supported 50-ply([0/90]25)laminated plate subjected to a uniform lateral load
In this subsection,we consider a thick-section unsymmetrical 50-ply([0/90]25)laminated plate.The plate is square witha=b=10 inches,and the thickness of the plate ish=1 inch.The material parameters are as follows:vLT=0.25,vTT=0.25,
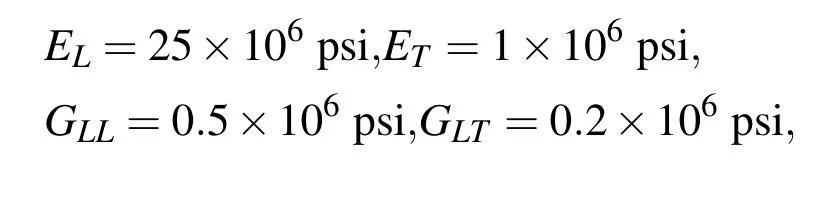
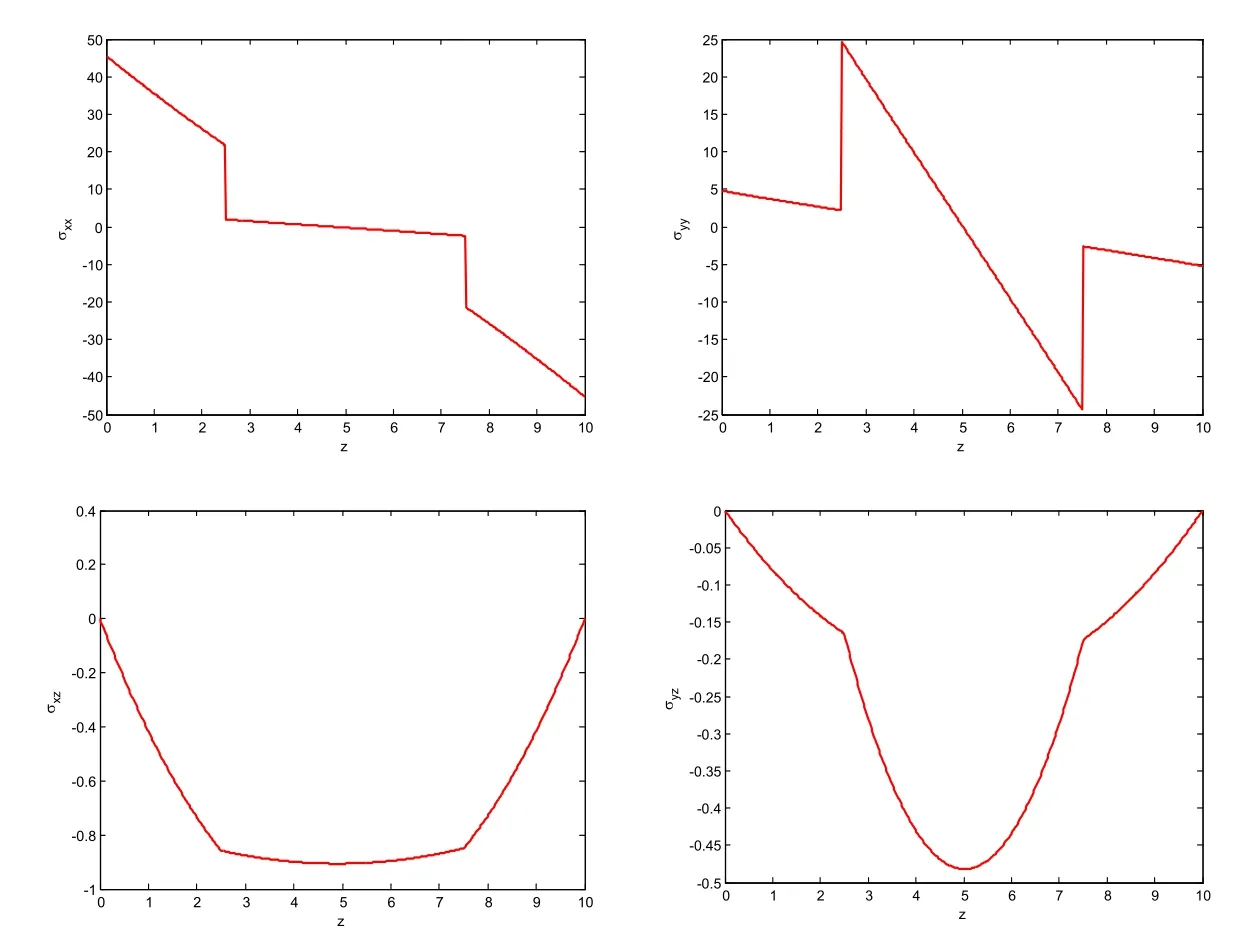
Figure 5:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=45 mm,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=10 mm,for the symmetrical 4-ply thick-section laminated plate(a/h=10),with DPH32.
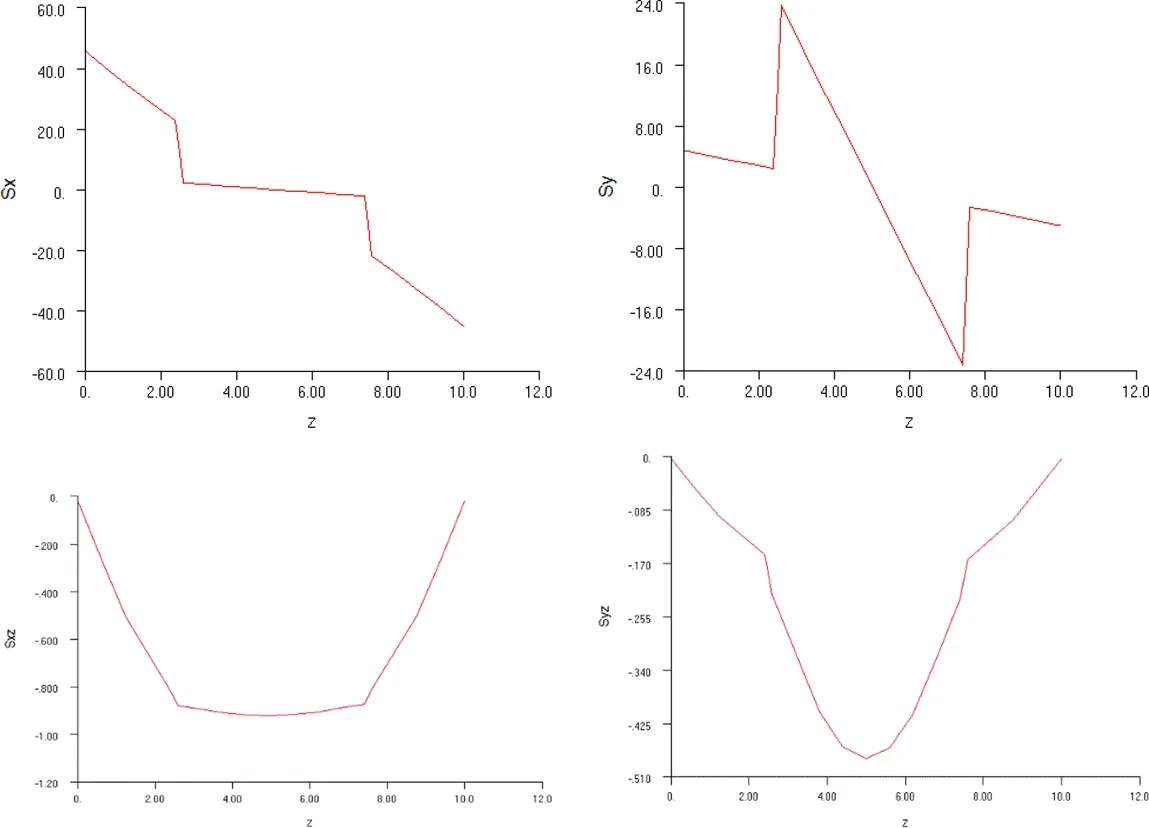
Figure 6:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=45 mm,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=10 mm,for the symmetrical 4-ply thick-section laminated plate(a/h=10),with Nastran.
whereLdenotes the f i ber’s direction andTdenotes the transverse direction.
The laminated plate is simply-supported at each edge.And it is subjected to a uniform lateral loadq=1 psi.
We solve this problem using a uniform 10×10 mesh with DPH32 elements.Computed in-plane and out-of-plane stresses by present DPH32 elements and Nastran are shown in Figs.7–8.It is observed that the present DPH32 solutions agree well with the Nastran solutions.Because of the necessity of meshing each of the 50 layers of laminae for Nastran,it takes about 2.5 hours of computational time and about 1.5 million DOFs in Nastran.However,the present DPH32 only requires 1364 nodes and about 20 seconds of computational time.
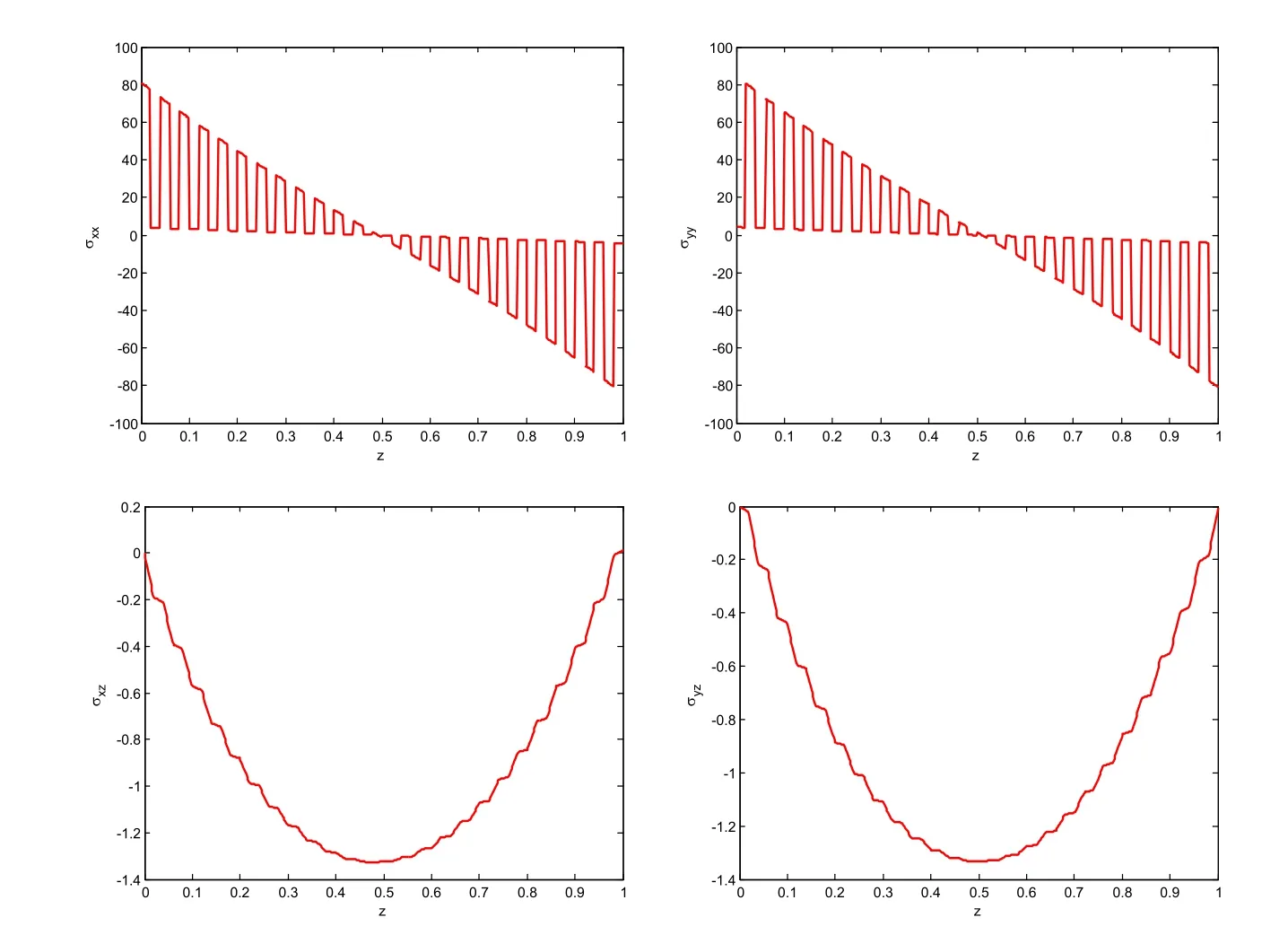
Figure 7:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=4.5 inches,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=1 inch,for the unsymmetrical 50-ply thick-section laminated plate(a/h=10),with DPH32.
A different plate with a very-high aspect ratio is also considered in this subsection.The same material properties,the same 50-ply([0/90]25)laminate,and the same boundary conditions and loads are adopted.However,the laminated plate has an aspect ratio of 1000 witha=b=1000 inches andh=1 inch.We also solve this problem with 10×10 DPH32 elements.The computed stresses by present method and by CEH8 elements[Dong,El-Gizawy,Juhany and Atluri(2014b)]are shown in Figs.9–10.Very good agreement is observed.This demonstrates that the present method can deal with the problems of both thick and thin plates,without having to resorting to theories of plates and shells.
3.2 Free vibration analysis
3.2.1Modal analysis of a thick-section 10-ply[0/90]5laminated square plate
The free vibration of a thick-section 10-ply([0°/90°]5)laminated plate is analyzed in this subsection.The plate is square witha=b=100 mm,and the thickness ish=10 mm.The material properties are the same as those in the first example.Four different boundary conditions(BCs)are enforced.They are SSSS(simply supported at each edge),CFFF(clamped atx=0 and free atx=a,y=0,b),CSCS(clamped atx=0,aand simply supported aty=0,b)and CSFS(clamped atx=0,free atx=a,and simply supported aty=0,b).
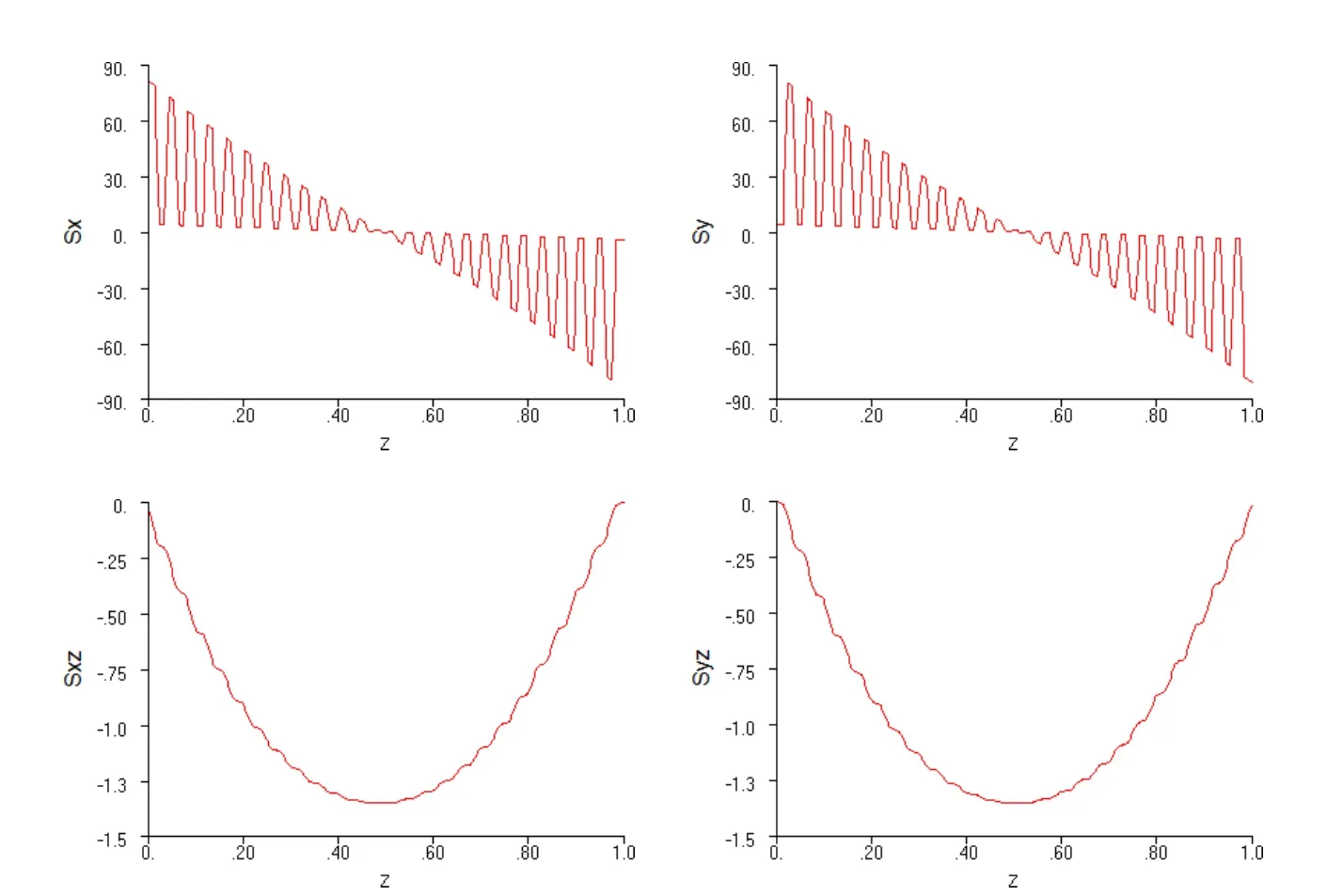
Figure 8:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=4.5 inches,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=1 inch,for the unsymmetrical 50-ply thick-section laminated plate(a/h=10),with Nastran,see[Dong,El-Gizawy,Juhany and Atluri(2014b)].
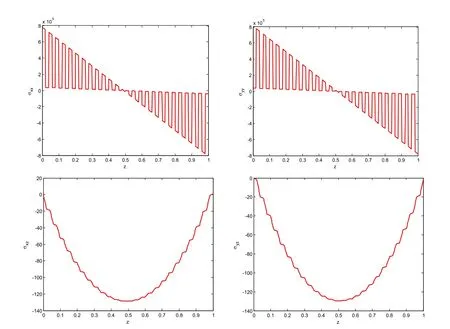
Figure 9:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=450 inches,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=100 inches,for the thin-section laminated plate(a/h=1000),with DPH32.
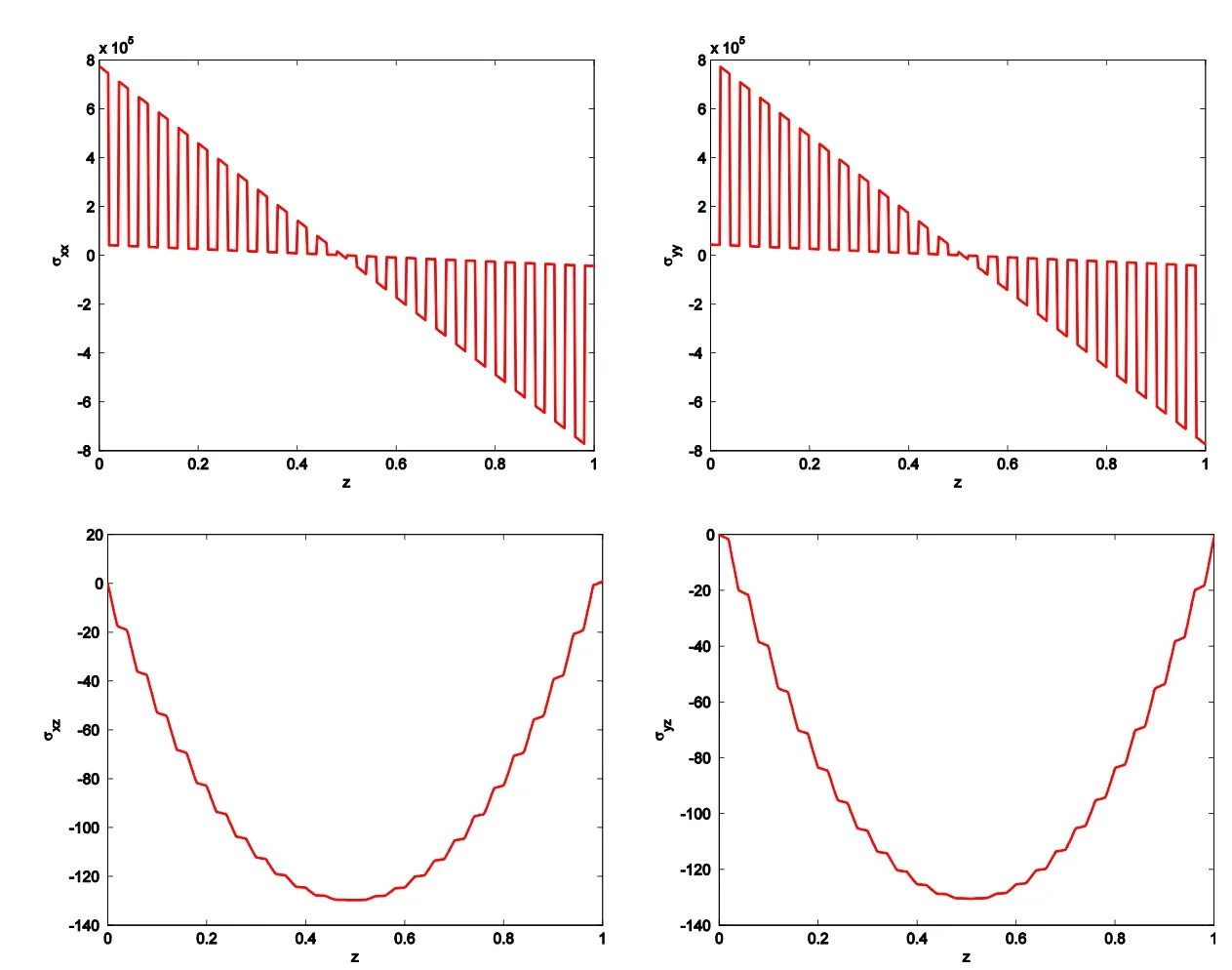
Figure 10:Computed σxx,σyyat x=y=450 inches,and computed σxz,σyzat x=y=100 inches,for the thin-section laminated plate(a/h=1000),with CEH8.
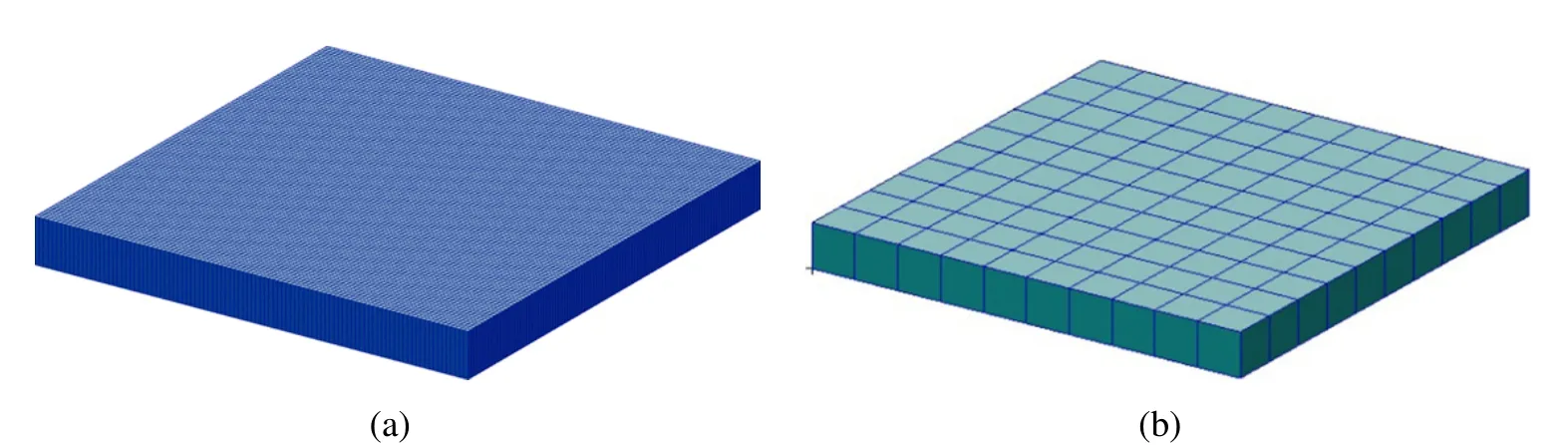
Figure 11:Finite element model for the 10-ply laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nastran with 400,000 elements and(b)present DPH32 with 100 elements.
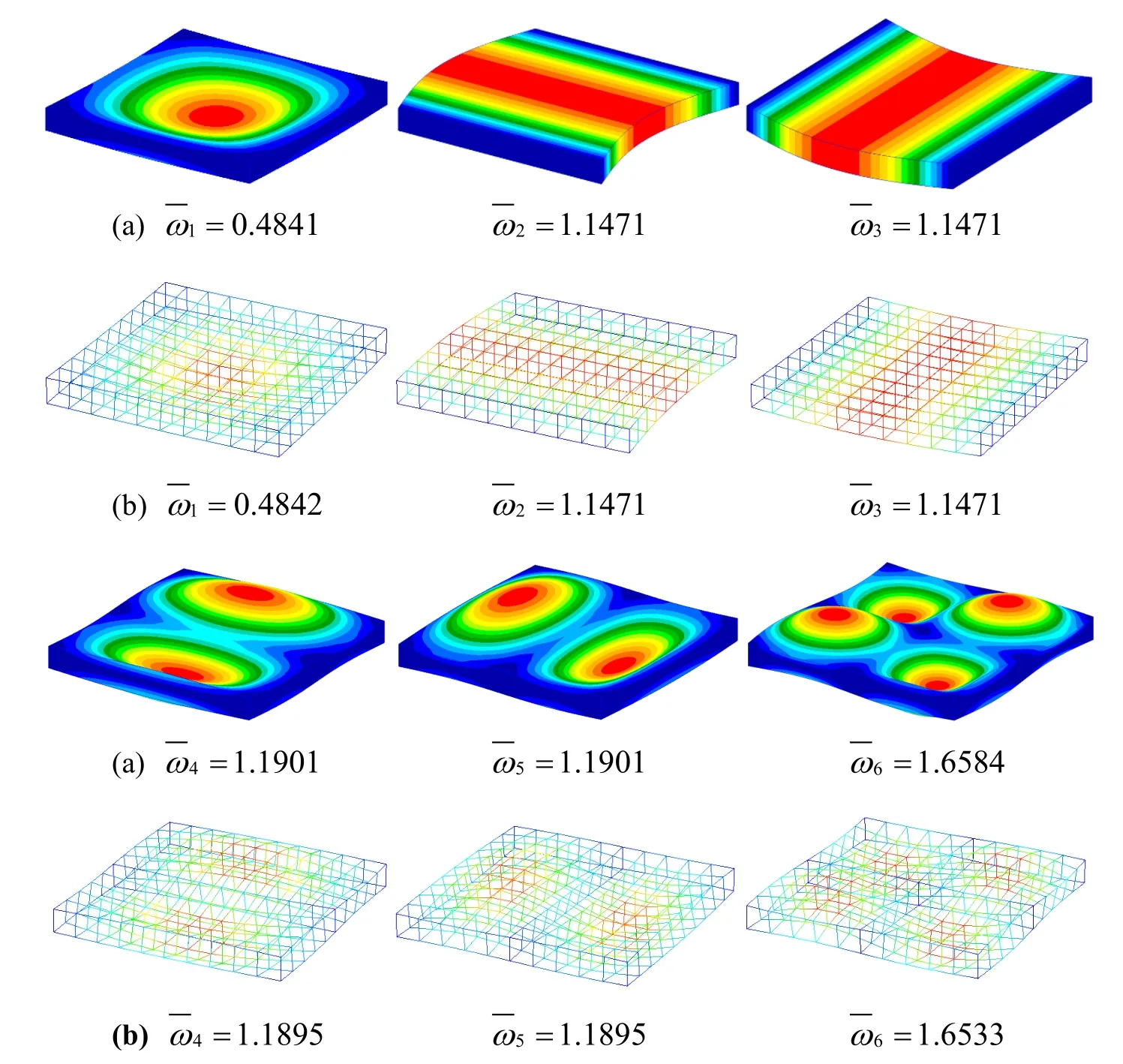
Figure 12:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a SSSS square laminated plate by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
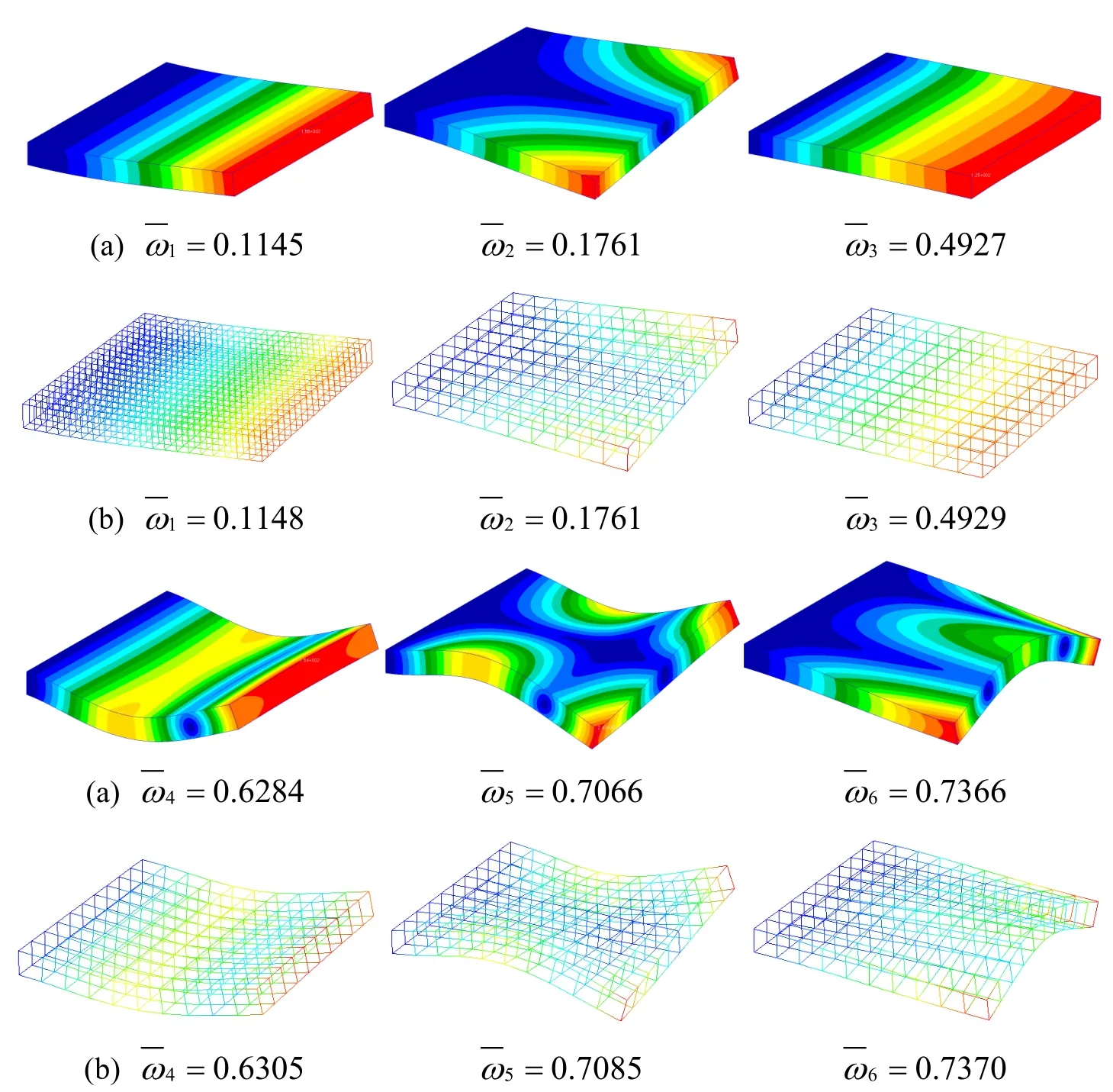
Figure 13:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CFFF Square laminated plate by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
We solve these problems using a uniform 10×10 mesh with DPH32 elements,as well as using Nastran.Comparison between the meshes of the DPH32 model and the Nastran model is given in Fig 11.The non-dimensional frequenciesused for comparison of numerical results.The first six mode shapes,for each case,are depicted in Figs.12–15 in which the correspondent nondimensional frequency is reported below each mode shape within the reference Nastran solution.Very good agreement is observed for all the computations,and the difference of the frequency parameters does not exceed 0.57%for the worst case.In the meantime,the present DPH32 elements require about 200 times less computational time as compared to Nastran.
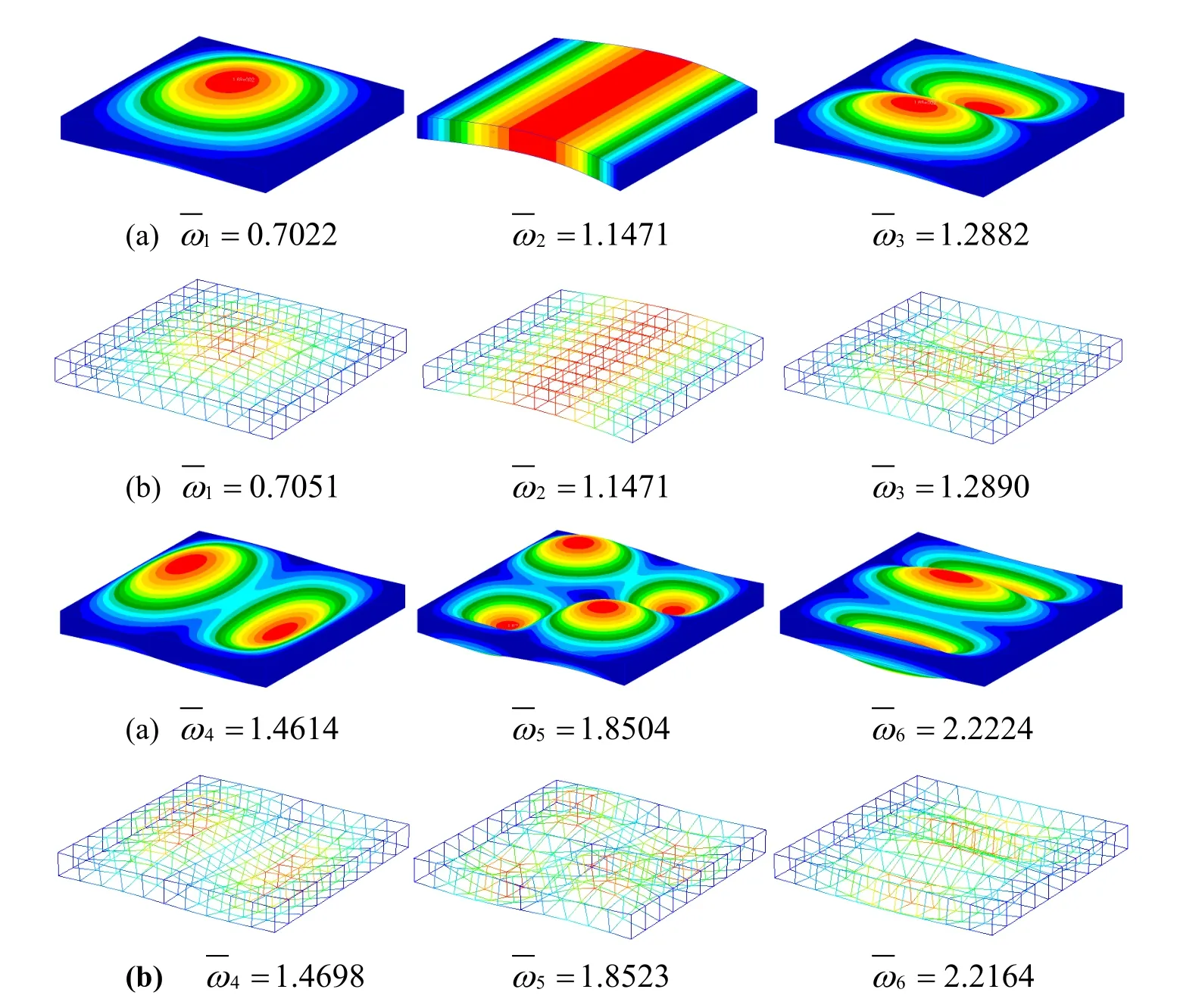
Figure 14:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CSCS Square laminated plate by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
3.2.2Modal analysis a thick-section 10-ply[0/90]5laminated shell
In this subsection,we consider a thick-section 10-ply([0°/90°]5)laminated shell.Each layer of the laminate is composed of the same Graphite-Epoxy T300/934 material whose material parameters are given in the first example.The depth and thickness of the cylindrical shell area=100 mm andh=10 mm respectively.The arc length of the shell is 100 mm and its corresponding angular span is π/3.We investigate four different boundary conditions which are SSSS(simply supported at each edge),CFFF(clamped atx=0 and free atx=a,y=0,b),CSCS(clamped atx=0,aand simply supported aty=0,b)and CSFS(clamped atx=0,free atx=a,and simply supported aty=0,b).
We solve these problems using a uniform 10×10 mesh with DPH32 elements,as well as using Nastran.Comparison between the meshes by present DPH32 ele-ments and by Nastran is given in Fig 16.Computed non-dimensional frequencies and corresponding mode shapes by DPH32 and Nastran are given in Figs.17–20 respectively.Very good agreement is observed for all the results,and the difference of the non-dimensional frequencies does not exceed 0.60%for the worst case.
3.3 Transient dynamic response of laminated plates
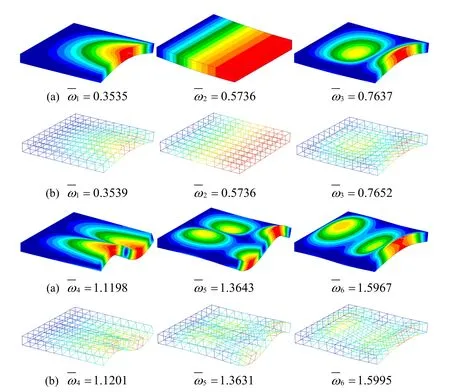
Figure 15:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CSFS Square laminated plate by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
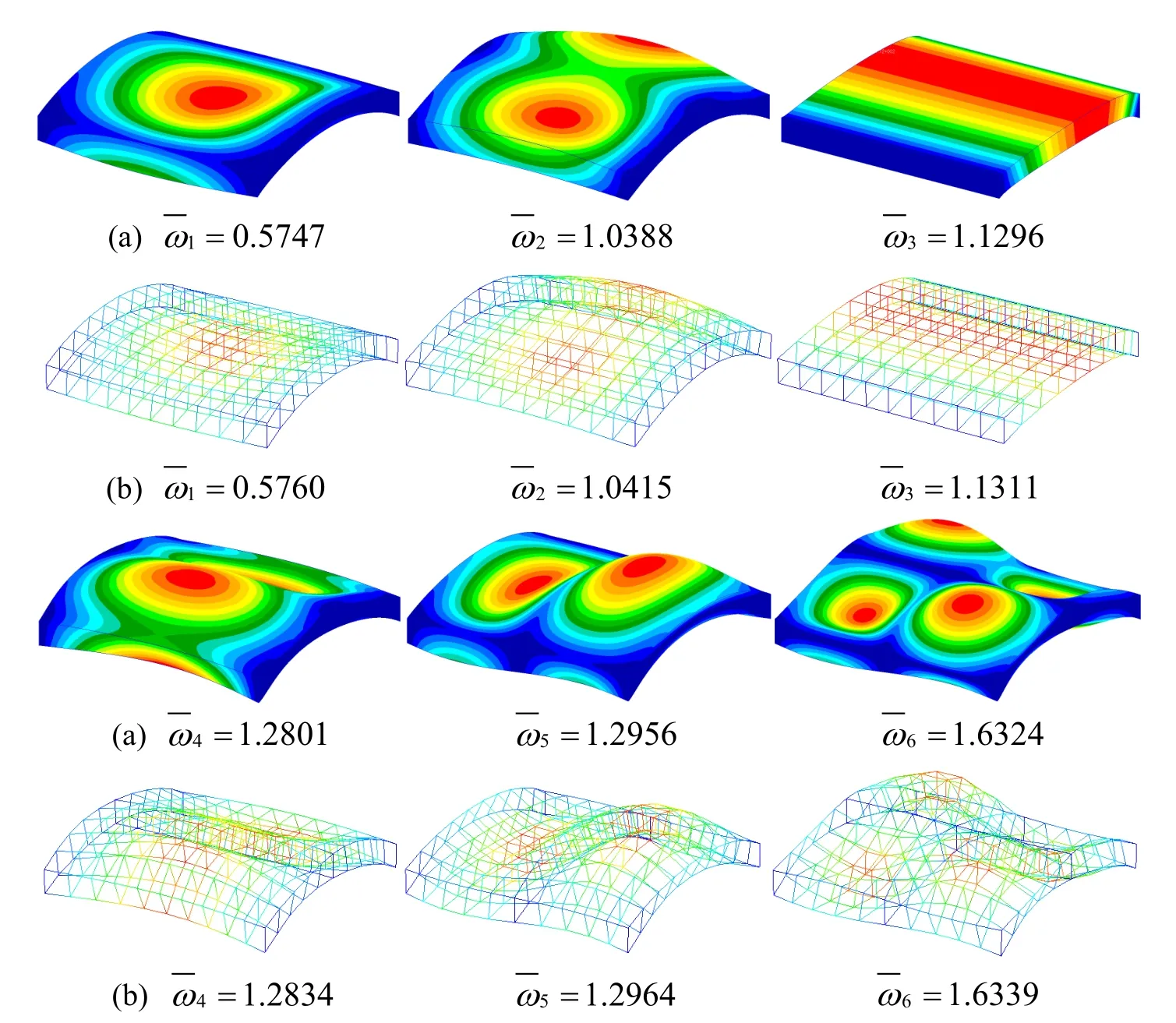
Figure 17:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a SSSS laminated shell by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
In this section,we study the transient dynamic responses of a simply-supported symmetrical 4-ply([0/90]s)laminated square plate subjected to a uniform pressure(step load)of magnitude 1kPa at timet=0.The geometry and material properties are same as the f i rst example.The same DPH32 FEM model with a uniform 10×10 mesh is also used to compute the global nodal force vector,mass matrix and stiffness matrix.Newmark beta method is used to evaluate the time-domain numerical integration.Direct transient response by Nastran is also used to obtain the results of displacements,velocities and stresses in each element.The vertical displacements and normal stresses by DPH32 elements and by Nastran are presented in Fig.21–22.It is clearly shown that the results obtained by the present method are in good agreement with numerical results using Nastran.In the meantime,small global matrices derived from the present method significantly improve the computational efficiency.
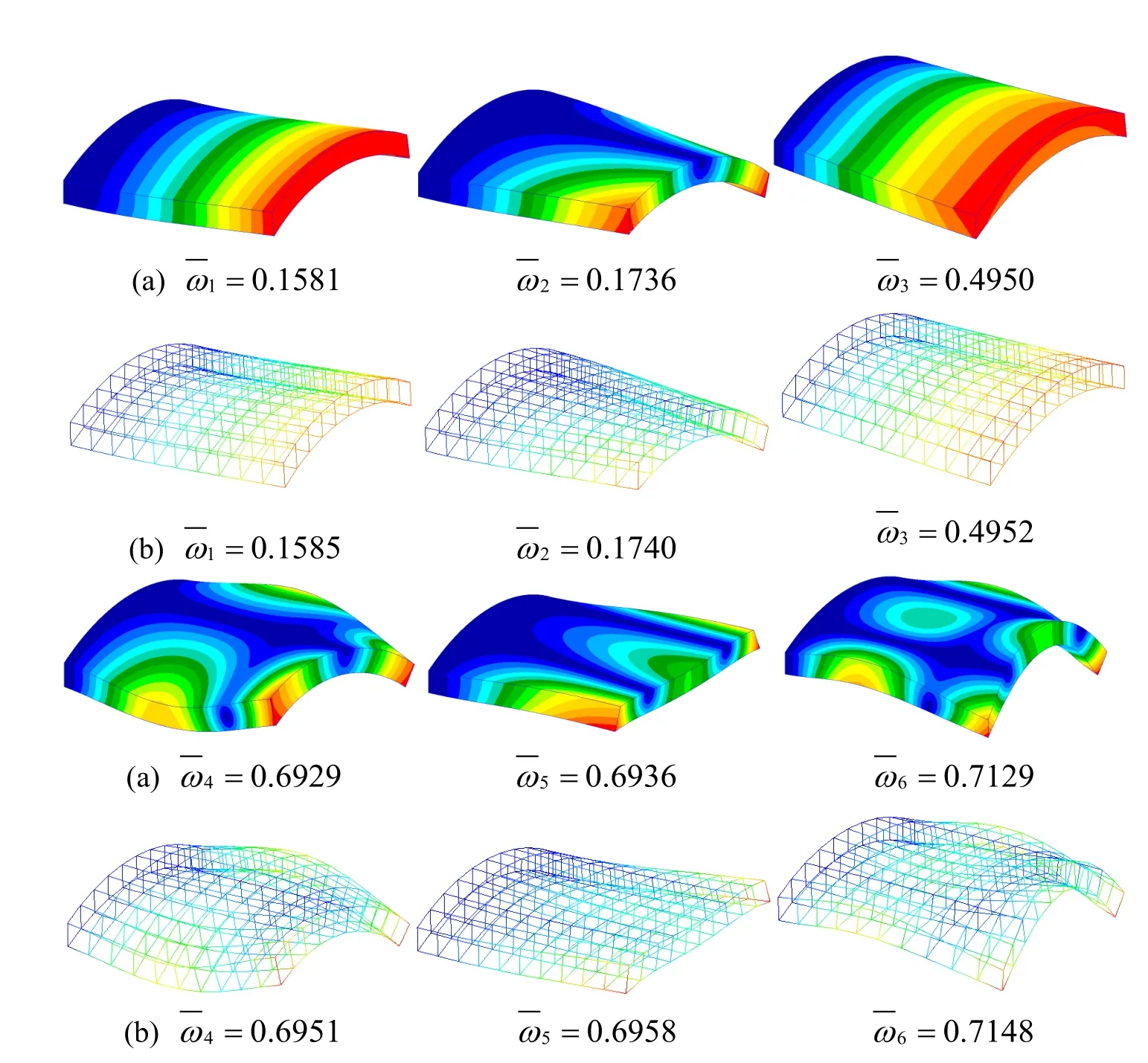
Figure 18:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CFFF laminated shell by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
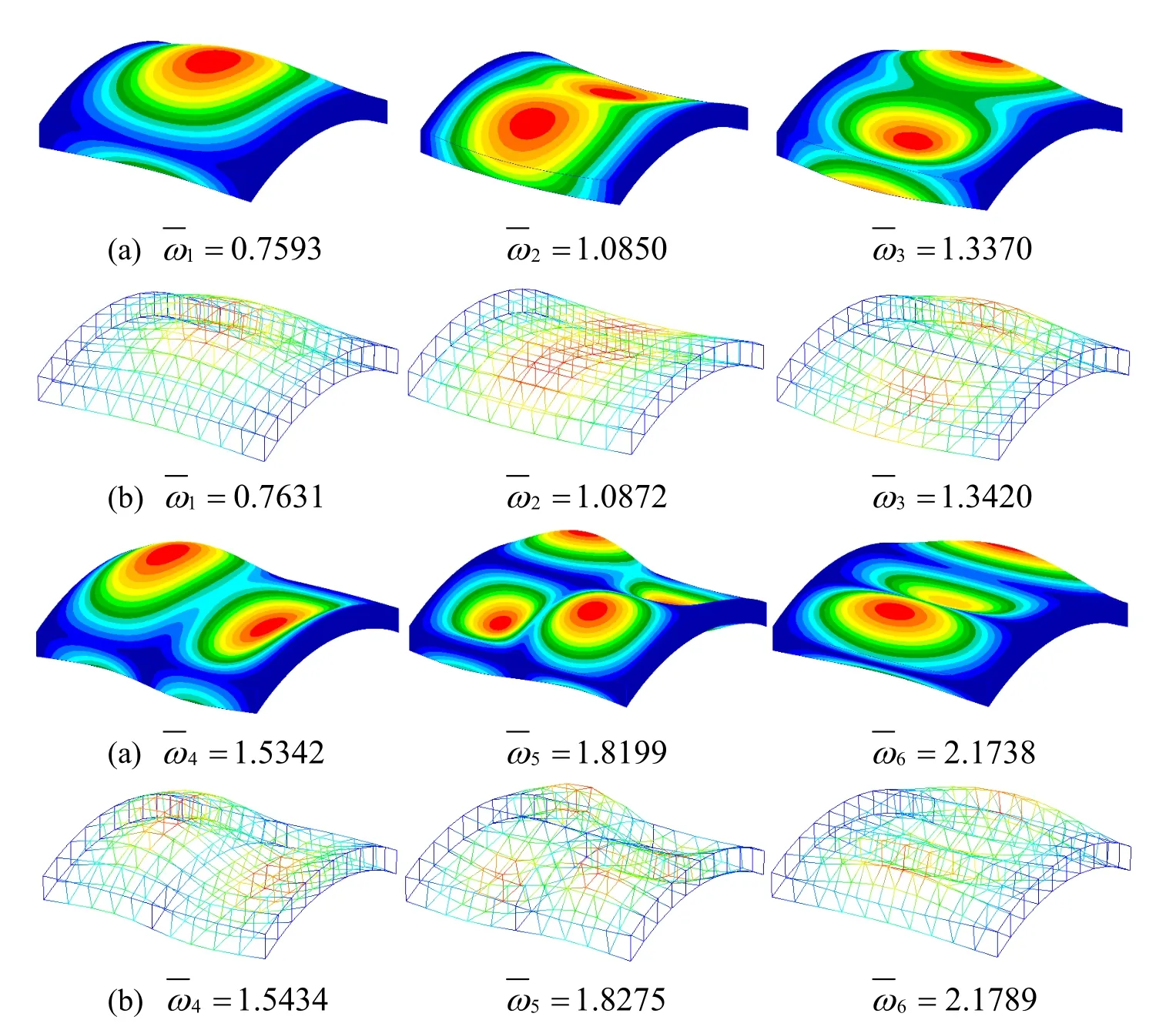
Figure 19:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CSCS laminated shell by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
We also consider the same laminated plate subjected to a time-dependent sinusoidal pressure shown in Fig.23.The problem is solved by present DPH32 elements and by Nastran separately.The vertical displacements and normal stresses computed by DPH32 elements and by Nastran are presented in Fig.24–25.Very good agreement is also observed.
4 Conclusion
In this paper,a very simple displacement-based hexahedral 32-node element(denoted as DPH32),with over-integration in the thickness direction,is developed for static and dynamic analysis of laminated composite plates and shells.In contrast to the many thousands of papers which are higher-order or layer-wise theories of plates and shells,the present method saves the trouble of developing specif i c theories of plates and shells,but simply use the 32-node 3D solid element which is already mature in most FEM packages.Over-integration is used to evaluate the stiffness matrices of laminated structures with an arbitrary number of laminae when only one element is used in the thickness direction,without increasing the number of degrees of freedom.A stress-recovery approach is used to compute the distribu-tion of transverse stresses by considering the equations of 3D elasticity.Comprehensive numerical results are presented for various laminated plates and shells with different boundary conditions.It is clearly shown that the proposed methodology can accurately and efficiently predict the static and dynamical behaviors of laminated composite plates and shells in a very simple manner,with very economical computational time as well as analysis time.
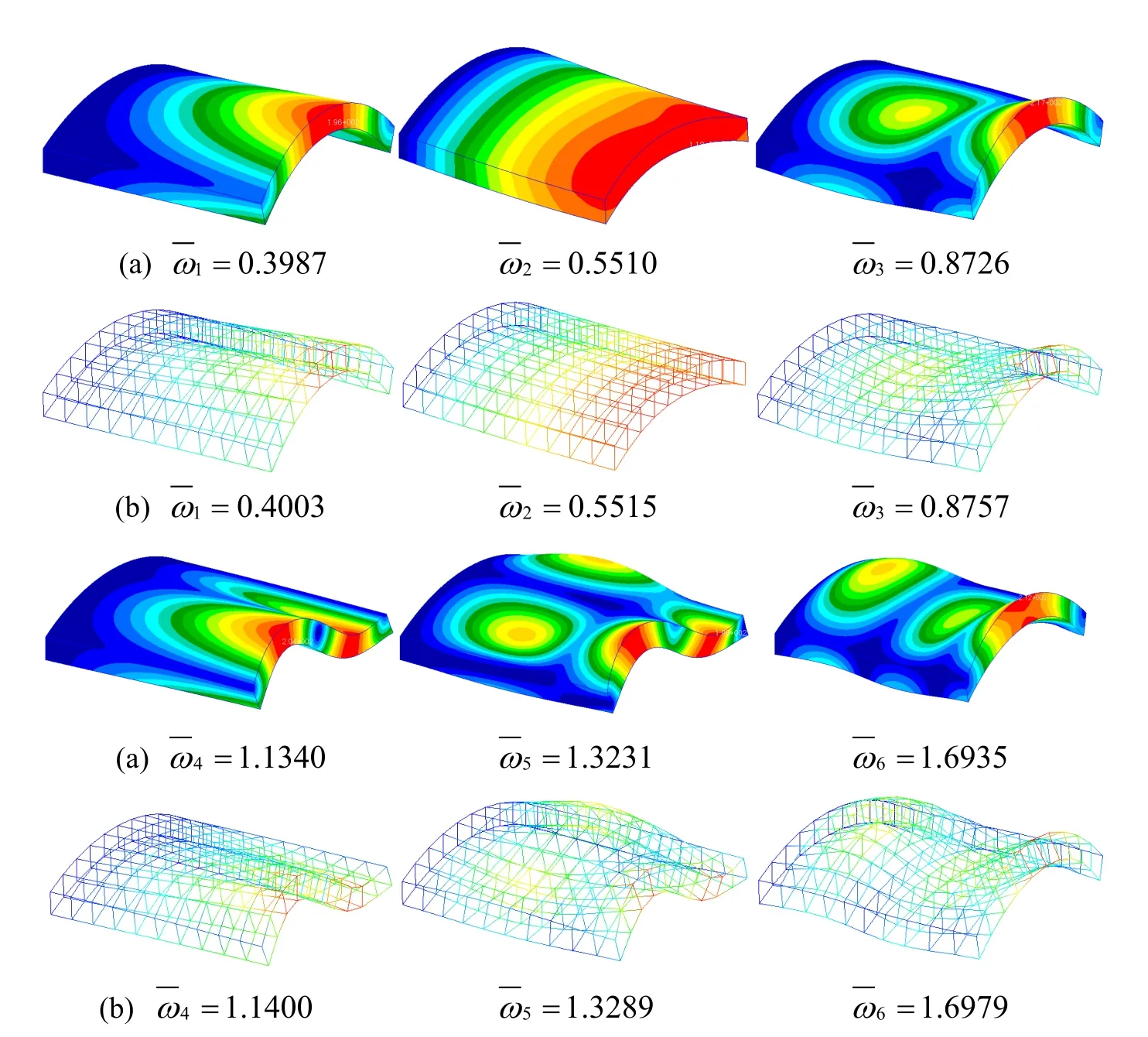
Figure 20:First six non-dimensional frequency parameters and their corresponding mode shapes of a CSFS laminated shell by(a)Nastran and(b)present DPH32 elements.
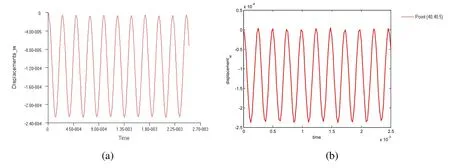
Figure 21:Vertical displacement response of the laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nas-tran and(b)the present DPH32 elements.
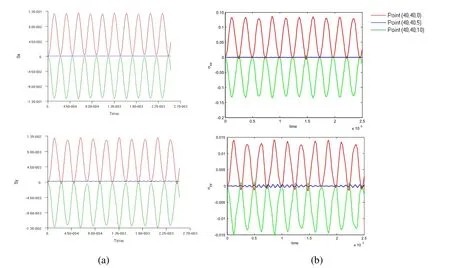
Figure 22:Normal stress response of the laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nastran and(b)the present DPH32 elements.
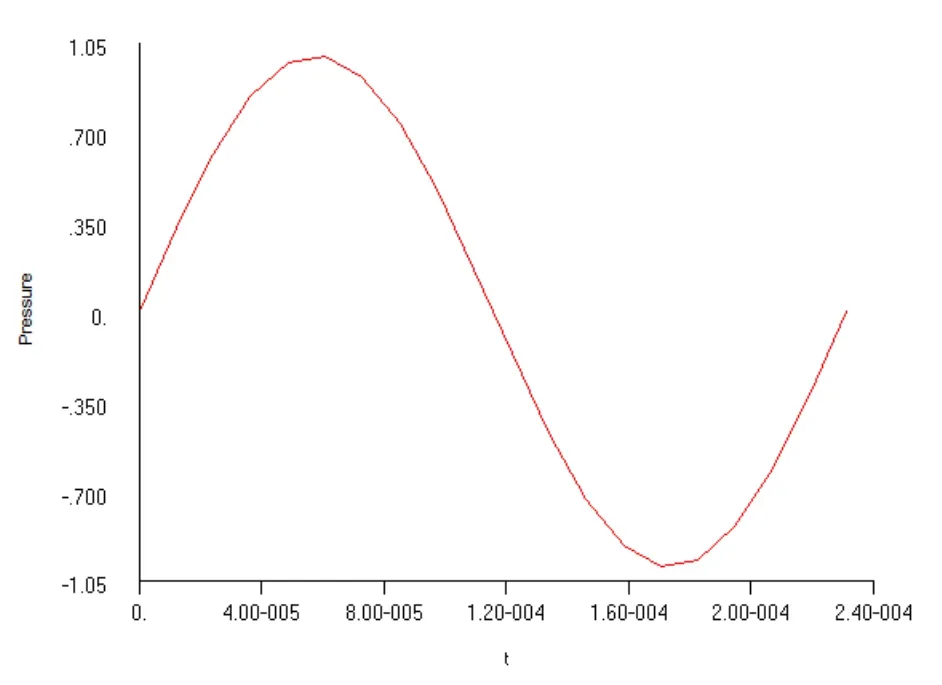
Figure 23:The applied time-dependent sinusoidal pressure
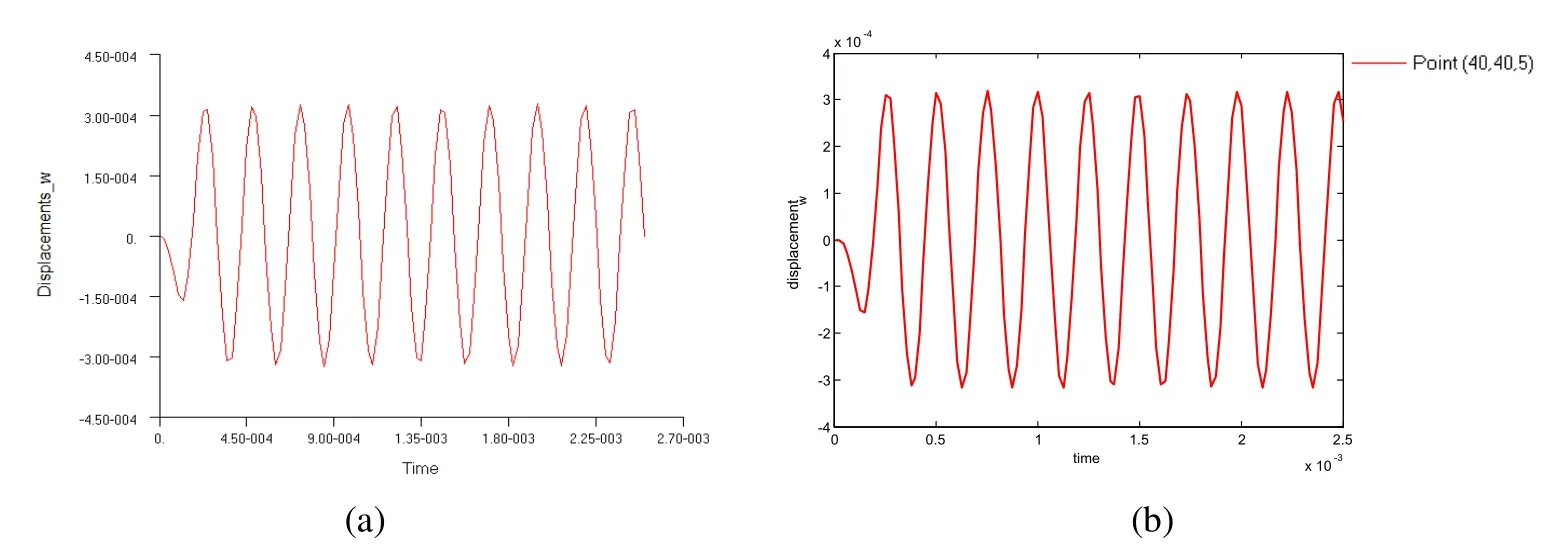
Figure 24:Vertical displacement response of the laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nas-tran and(b)the present DPH32 elements.
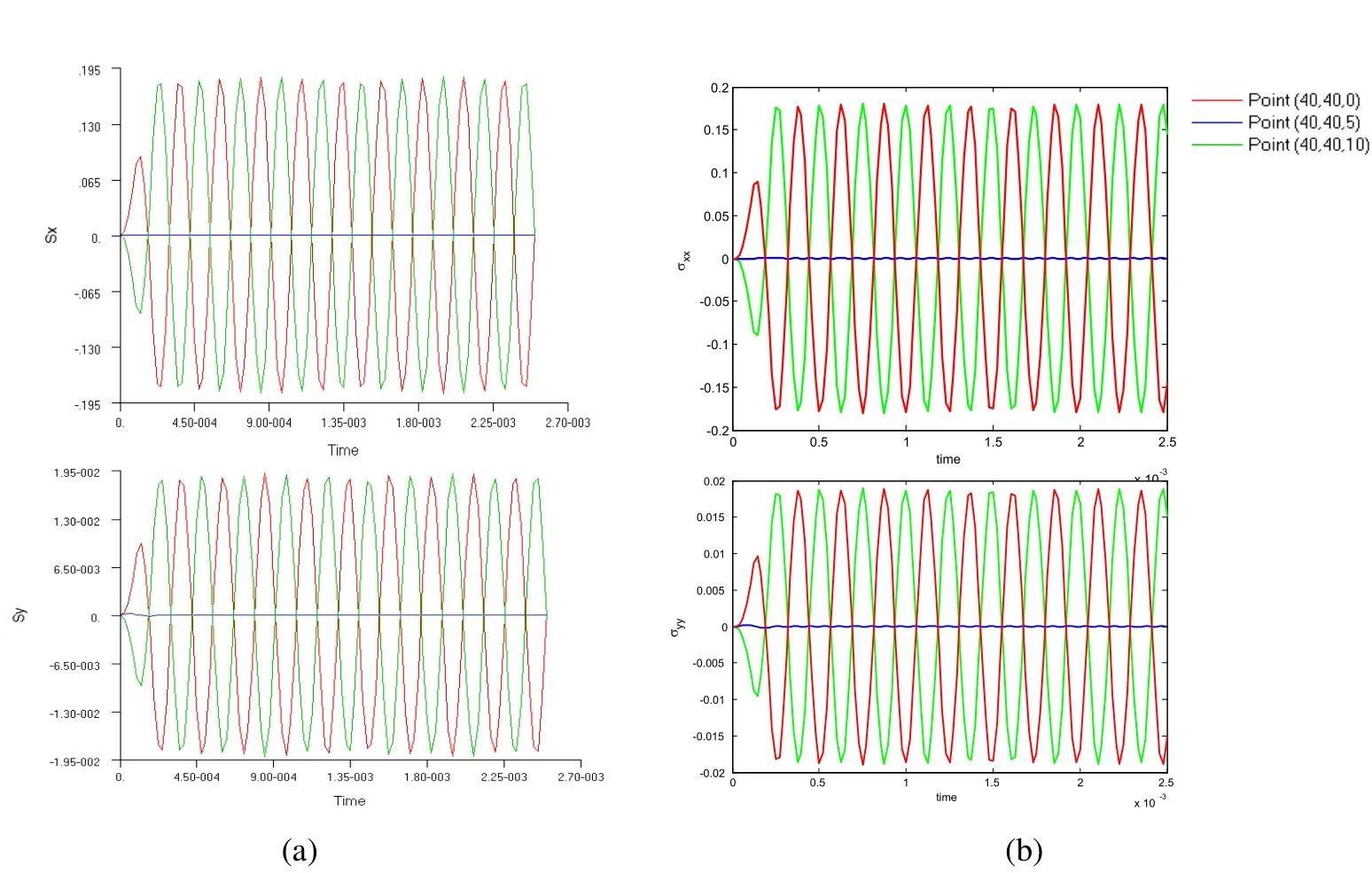
Figure 25:Normal stress response of the laminated plate(a/h=10)by(a)Nastran and(b)the present DPH32 elements.
Acknowledgement: This research is supported by the Mechanics Section,Vehicle Technology Division,of the US Army Research Labs.The first author acknowledges the financial support by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China(863 Program,grant No.2012AA112201).The support of National Natural Science Foundation of China(grant No.11502069)and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province(grant No.BK20140838)is also thankfully acknowledged.
Atluri,S.N.(2005):Methods of Computer Modeling in Engineering and the Sciences,Tech Science Press.
Di Sciuva,M.(1985):Development of an anisotropic,multilayered,sheardeformable rectangular plate element.Computers&structures,vol.21(4),pp.789-796.
Carrera,E.(2003):Historical review of zig-zag theories for multilayered plates and shells.Applied Mechanics Reviews,vol.56,issue 3,pp.287-308.
Dong,L.;Alotaibi,A.;Mohiuddine,S.A.;Atluri,S.N.(2014a):Computational methods in engineering:a variety of primal&mixed methods,with global&local interpolations,for well-posed or ill-Posed BCs.CMES:Computer Modeling in Engineering&Sciences,vol.99,no.1,pp.1-85.
Dong,L.;El-Gizawy,A.S.;Juhany,K.A.;Atluri,S.N.(2014b):A simple locking-alleviated 4-node mixed-collocation f i nite element with over-integration,for homogeneous or functionally-graded or thick-section laminated composite beams.CMC:Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.40,issue 1,pp.49-77.
Dong,L.;El-Gizawy,A.S.;Juhany,K.A.;Atluri,S.N.(2014c):A simple locking-alleviated 3D 8-Node mixed-collocationC0f i nite element with overintegration,for functionally-graded and laminated thick-section plates and shells,with&without z-pins.CMC:Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.41,issue 3,pp.163-192.
Lo,K.H.;Christensen,R.M.;Wu,E.M.(1977):A high-order theory of plate deformation—part 2:laminated plates.Journal of Applied Mechanics,vol.44,issue 4,pp.669-676.
Mindlin,R.D.(1951):Inf l uence of rotatory inertia and shear on flexural motions of isotropic,elastic plates.Journal of Applied Mechanics,vol.18,pp.31-38.
Pandya,B.N.;Kant,T.(1988):Finite element analysis of laminated composite plates using a higher-order displacement model.Composites Science and Technology,vol.32,pp.137-155.
Ray,R.M.;Dong,L.;Atluri,S.N.(2015):Simple Efficient Smart Finite Elements for the Analysis of Smart Composite Beams.CMC:Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.47,issue 2,pp.65-99.
Reddy,J.N.(1984):A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates.Journal of Applied Mechanics,vol.51,issue 4,pp.745-752.
Reddy,J.N.;Robbins,D.H.(1994):Theories and computational models for composite laminates.Applied Mechanics Reviews,vol.47,issue 6,pp.147-169.
Reddy,J.N.(2004):Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells:theory and analysis,CRC press.
Reissner,E.(1945):The effect of transverse shear deformation on the bending of elastic plates.Journal of Applied Mechanics,vol.12,pp.69-77.
Timoshenko,S.;Woinowsky-Krieger,S.(1959):Theory of Plates and Shells.McGraw hill,New York.
Toledano,A.;Murakami,H.(1987):A composite plate theory for arbitrary laminate configurations.Journal of applied mechanics,vol.54(1),pp.181-189.
1School of Aeronautic Science and Engineering,Beihang University,China
2Taizhou Polytechnic College,China
3Corresponding Author,Email:dong.leiting@gmail.com
4Department of Mechanical Engineering,Texas Tech University,USA
 Computers Materials&Continua2015年8期
Computers Materials&Continua2015年8期
- Computers Materials&Continua的其它文章
- Research on damage distribution and permeability distribution of coal seam with slotted borehole
- Identification of Damaged Teeth in Gears using Wavelet Transform Applied to the Angular Vibration Signal
- Evaluating Water Vapor Permeance Measurement Techniques for Highly Permeable Membranes
