Elasticity and Thermodynamic Properties of EuS Related to Phase Transition
Qiang Liu,Feng Peng
College of Physics and Electronic Information,Luoyang Normal University,Luoyang 471022,China
Elasticity and Thermodynamic Properties of EuS Related to Phase Transition
Qiang Liu,Feng Peng?
College of Physics and Electronic Information,Luoyang Normal University,Luoyang 471022,China
First-principles calculations of the crystal structures,phase transition,and elastic properties of EuS have been carried out with the plane-wave pseudopotential density functional theory method.The calculated values are in very good agreement with experimental data as well as some of the existing model calculations.The dependence of the elastic constants, the aggregate elastic modulus,and the elastic anisotropy on pressure have been investigated. Moreover,the variation of the Poisson’s ratio,Debye temperature,and the compressional and shear elastic wave velocities with pressure have been investigated for the f i rst time.Through the quasi-harmonic Debye model,the thermal expansions,heat capacities,Grneisen parameters and Debye temperatures dependence on the temperature and pressure are obtained in the pressure range from 0 GPa to 60 GPa and temperature range from 0 K to 800 K.
EuS,First-principles,Pressure effect,Thermodynamic properties
I.INTRODUCTION
Rare-earth compounds attract considerable experimental and theoretical attention due to their interesting optical,magnetic and electronic properties[1-4]. Especially,europium chalcogenides have received renewed attention because of their technological importance[5-7]and their potential applications in spintronic and spin f i ltering devices[8].Horne et al.used the ab initio self-interaction corrected(SIC)method to discuss the electronic structure of the Eu chalcogenides and pnictides in both the divalent and trivalent states [8].Kunes and Pickett used the full potential linearized augmented planes waves(FP-LAPW)method to study the effective exchange parameters and the corresponding ordering temperatures of the(ferro)magnetic insulating Eu chalcogenides under ambient and elevated pressure conditions[9].Goncharenko et al.studied magnetic interactions of Eu chalcogenides using neutron dif f raction at very high pressures[10].The calculation of the band-structure and the structural stability of the high-pressure phases of Eu chalcogenides have been investigated by Singh et al.using the tight-binding linear muffin-tin orbital method within the atomic sphere approximation(ASA)[11,12].Svane et al.gave the light of pressure-induced valence transitions in rare earth chalcogenides[13].Recently,Rached et al.studied elastic properties of Eu chalcogenides using the fullpotential linear muffin-tin orbital(FP-LMTO)method [14].Temmerman et al.gave a review of pressure induced valence transitions in f-electron systems of Eu chalcogenides calculated with the self-interaction corrected local spin density(SIC-LSD)approximation[15]. Among the europium chalcogenides compounds very little information is available for EuS.In this work,we studied the elastic and the thermodynamic properties of EuS under pressure considering the phase transition. The high pressure phase transition and elastic properties of EuS from B1(NaCl)to B2(CsCl)are investigated in detail.All calculations are performed based on the plane-wave pseudopotential density-function theory (DFT).
II.CALCULATED DETAILS AND THEORY
A.Calculated details
Vanderbilt-type non-local ultrasoft pseudopotentials (USPP)[16]are employed to describe the electron-ion interactions.The effects of exchange-correlation interaction are treated with the generalized gradient approximation(GGA)of Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof(PBE) [17]considering the spin polarized.In the structure calculation,a plane wave basis set with energy cut-of f680.00 eV is used.Pseudo-atomic calculations are performed for S3s23p4and Eu4f75s25p66s2.For the Brillouin-zone sampling,the 12×12×12 Monkhorst-Pack mesh[18]is adopted.The self-consistent convergence of the total energy is 10-7eV/atom and the maximum force on the atom is 10-4eV/?A.All the total energy electronic structure calculations are implemented through the CASTEP code[19].

TABLE I The lattice parameter a,bulk moduli B(in GPa), and the elastic constants cij(in GPa)at 0 K and 0 GPa for EuS.
B.Structure property
The energy-volume(E-V)curve can be obtained by f i tting the calculated E-Vresults to the Birch-Murnaghan EOS[20]:
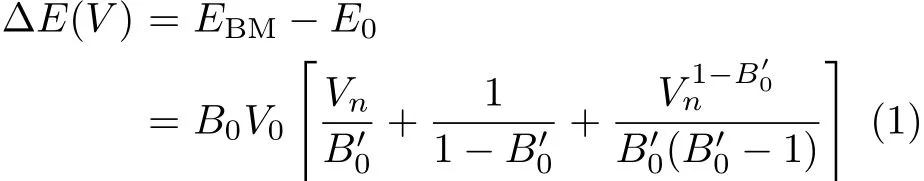
where E0is the equilibrium energy.Pressure P vs.the normalized volume Vnis obtained through the following equation:
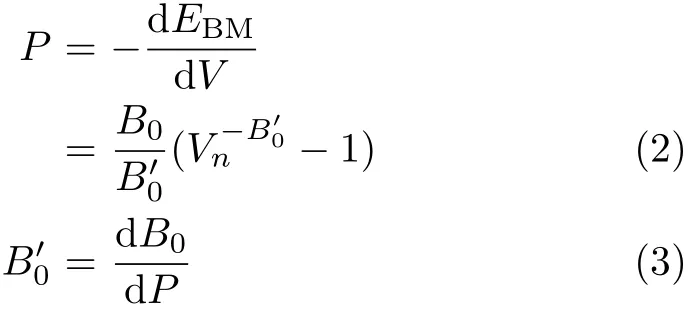
here B00and B0are the pressure derivative of the bulk modulus and zero pressure bulk modulus,respectively.
To calculate the total energy EBMand the corresponding volume V for both phases,a series of different lattice parameters a are taken to obtain the total energy over a wide volume range from 0.6V0to 1.2V0,where V0is the zero pressure equilibrium primitive cell volume. Through these calculations,we can obtain the equilibrium a(Table I).It is found that a and B are in good agreement with experimental data[7,12]and other theoretical results[8,13,20,21],respectively.The ratio V/V0as a function of the applied pressure together with the experimental result is plotted in Fig.1.Our obtained data are consistent well with the experiment[7, 12].
The estimation of the zero-temperature transition pressure between B1 and B2 structures of EuS can be obtained from the usual condition of equal enthalpies, in other words,P,at which enthalpy H=E+PV of both

FIG.1 Variations of the normalized volume V/V0with the applied pressure P for EuS.
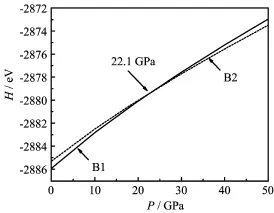
FIG.2 Enthalpy H as a function of pressure P for EuS.
phases is the same.Figure 2 shows the enthalpy as a function of the pressure for EuS.It indicates that the transition pressure from B1 to B2 is about 22.1 GPa. The datum agrees well with the experimental value of 21.5 GPa from Jayaraman et al.[7]and the calculated result of 21.1 GPa from Singh et al.[13].But it is lower than the value of 27 GPa from Rached et al.[14].
C.Elasticity
To calculate the elastic constants under hydrostatic pressures,the non-volume conserving strains are adopted because this method is consistent with our calculated elastic constants using the stress-strain coefficients,which are appropriate for the calculation of the elastic wave velocities.The elastic constants cijkl, with respect to the fi nite strain variables are de fi ned as [22-24]:
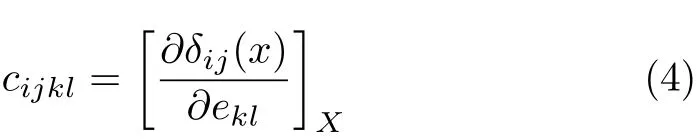
where cijkldenotes the second-order derivatives with respect to the inf i nitesimal strain(Eulerian),and δ is the f i nite strain variable.For EuS(B1 or B2),there are three independent elastic constants,i.e.c11,c12,and c44.In our calculations,for all strains,δ=±0.0018, ±0.003,and±0.0006 are taken to calculate the total energies E for the strained crystal structure,respectively. To make comparison with experimental results under hydrostatic pressure,the elastic constants Cijmust be transformed into the observable cijdef i ned with respect to the f i nite strain variables[23-25].Cijis transformed into cijin the case of hydrostatic pressure P as follows:

From the independent elastic constants above,the theoretical polycrystalline elastic modulus can be obtained. There are two approximation methods to calculate the polycrystalline modulus,namely the Voigt method[26] and the Reuss method[27].The Voigt GVand Reuss GRshear moduli are given by
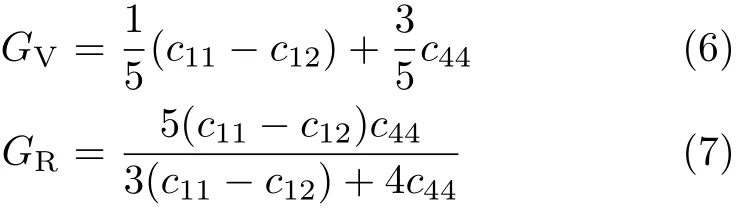
The shear modulus G and bulk modulus B can be estimated by

The polycrystalline Young’s modulus E,anisotropy factor A,and the Poisson’s ratio σ are then calculated by
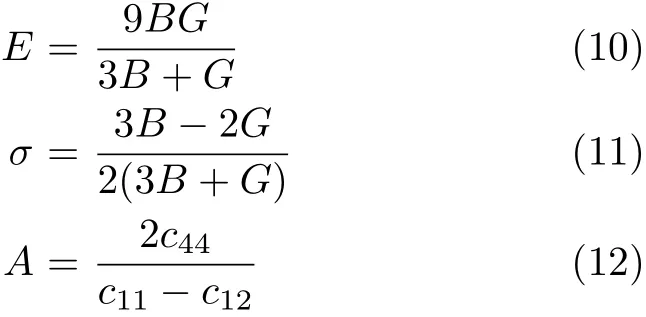
The elastic Debye temperature Θ can be estimated from the average sound velocity vm,by the following equation [28]
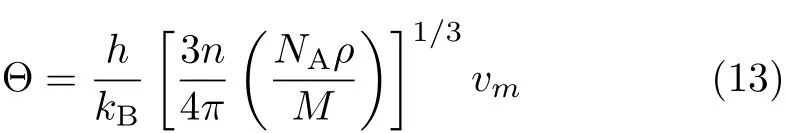
where h is Planck constant,kBis Boltzmann constant, NAis Avogadro number,n is the number of atoms in the molecule,M is the molecular weight,and ρ is the density.vmis approximately calculated from
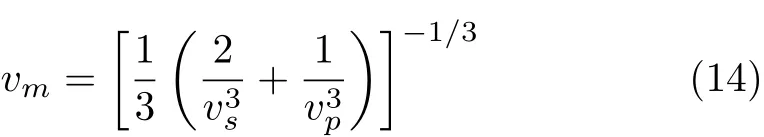
where vpand vsare the compressional and shear wave velocities,respectively,which can be obtained from Navier’s equation[29]
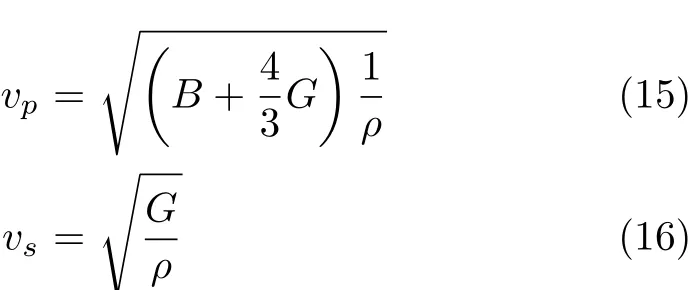
III.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A.Elasticity
Our calculated cijof the EuS for two phases at zero pressure and zero temperature are listed in Table I.Our result is consistent with the data from Shapira et al. [21],but is inconsistent with the value from Rached et al.[14].In Table II,we present the pressure dependence on the cij,B,and G of EuS at di ff erent pressures. It is shown that c11varies substantially under applied pressure compared with the variations in c12and c44. c11represents elasticity in length.A longitudinal strain produces a change in c11.c12and c44are related to the elasticity in shape,which is a shear constant.A transverse strain causes a change in shape without a change in volume.Therefore,c12and c44are less sensitive to pressure as compared with c11.Moreover,B is sensitive to press as compared with G.
As it is known,the elastic constants determine the response of the crystal to external forces.They play an important part in determining the strength of the material.The single crystal shear moduli for the{100} plane along the[010]direction and for the{110}plane along the[110]direction are simply given by
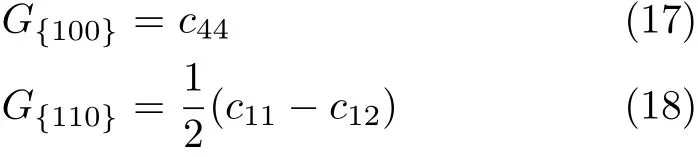
They are listed in Table II together with Young’s modulus E and Eh100i,σ and A under applied pressures.
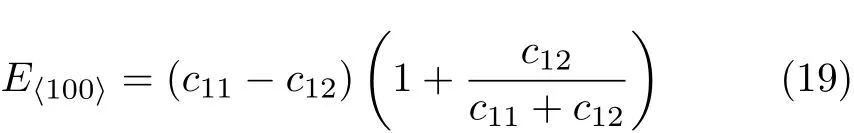
For B1 phase,G{100}are always lower than G{110}from 0 GPa to 20 GPa,indicating that it is harder to shear on the{110}plane along the[110]direction than on the{100}plane along the[010]direction;for B2 phase, the result is contrary.G represents the resistance to plastic deformation,while B represents the resistance to fracture[30].B/G of polycrystalline phases is considered.A high(low)B/G value is associated with ductility(brittleness).The critical value which separates ductile and brittle materials is about 1.75.It is interesting to try to understand the microscopic originof this empirical parameter.For both two phases,when P>10 GPa,the calculated values of the B/G(>1.75) increase with pressures,which means that pressure can improve ductility.
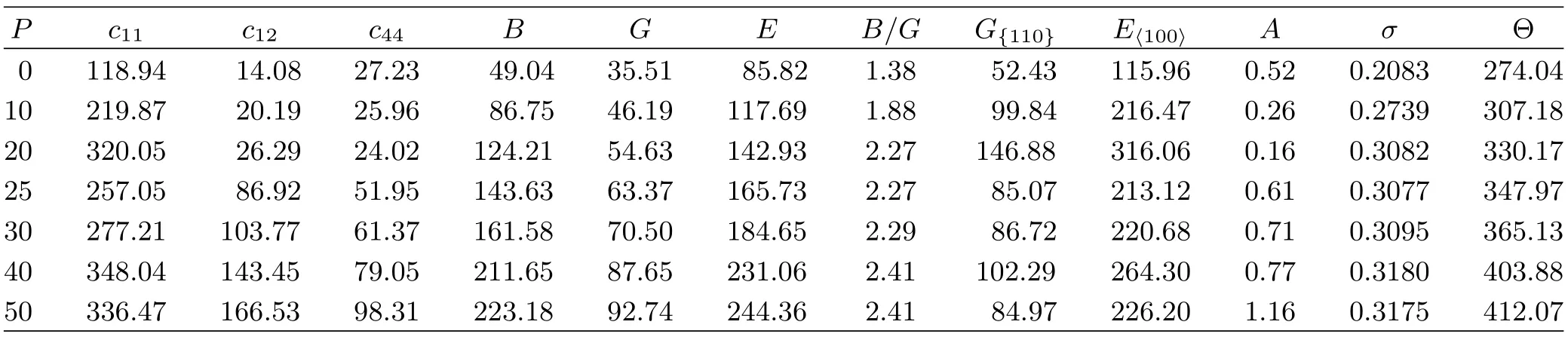
TABLE II The calculated elastic constants cij(in GPa),and aggregate elastic moduli(B,G,E,in GPa),the quotient of bulk to shear modulus B/G,the elastic anisotropic parameter,the Poisson’s ratio σ,the Debye temperature Θ(in K)of the EuS under pressure P(in GPa)at zero temperature.
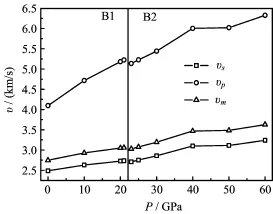
FIG.3 The calculated elastic velocities v vs.pressure P at 0 K.
The Young’s modulus E and Poisson’s ratio σ are important for technological and engineering applications. E is def i ned as the ratio from stress to strain,and is used to provide a measure of the stif f ness of the solid, i.e.,the larger the value of E,the stiffer the material is.v provides more information about the characteristics of the bonding forces than any of the other elastic constants.The v=0.25 and 0.5 are the lower limit and upper limit for central force solids,respectively.In our case,v increases with the applied pressure for both phases(Table II).The obtained v values are very close to the value of 0.30 which indicates that the interatomic forces in the EuS are central forces.
The elastic anisotropy of crystals has an important implication in engineering science since it is highly correlated with the possibility to induce microcracks in the materials[31].The anisotropy factor was evaluated to provide insight on the elastic anisotropy of the EuS.For a completely isotropic material,the A factor takes the value of 1,while values smaller or greater than unity measure the degree of elastic anisotropy.In the wide range of applied pressure,the obtained anisotropy factors are listed in Table II.One can f i nd that the B1-EuS exhibits low elastic anisotropy at zero pressure and the degree of the anisotropy increases with pressure;for B2-EuS,the degree of the anisotropy decreases with pressure.
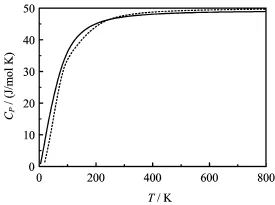
FIG.4 The calculated heat capacity CPof B1 structure of EuS vs.temperature T at ambient pressure P.The dashed line data are from phonon dispersion,and the solid line data are from quasi-harmonic Debye model.
The obtained compressional,shear and average wave velocities are illustrated in Fig.3.It is shown that the vs,vp,and vmincrease gradually with pressure.However,vpis more sensitive to pressure than vsand vm.
B.Thermodynamic properties
Through the quasi-harmonic Debye model,the thermodynamic properties of EuS are obtained.The calculated details can be seen in our recent works[32-35]. To test the validity of quasi-harmonic Debye model,we calculated the phonon dispersion of B1-EuS by the linear response method and obtained the thermodynamic properties from the phonon dispersion.Figure 4 shows that heat capacities curves of B1-EuS vs.temperature from different methods f i t very well.So,the quasiharmonic Debye model is valid in this work.
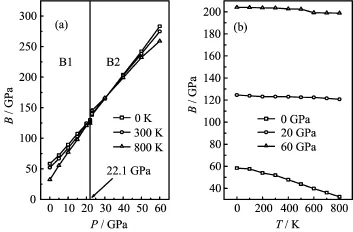
FIG.5 Pressure P(a)and temperature T(b)dependence of the isothermal bulk modulus B for EuS.

FIG.6 Temperature T dependence of the heat capacity CPfor EuS.
Figure 5 presents the relation of the isothermal bulk modulus as a function of temperature T up to 800 K at P=0,30,and 60 GPa,respectively.At lower pressures, the isothermal bulk modulus is nearly a constant when T<200 K,but it drops remarkably when T>200 K, which are in accordance with the relationships between the ratio V/V0and T as shown in Fig.1.It demonstrates that dramatic volume variation leads to the rapid decreases in the isothermal bulk modulus.One can f i nd that the effect of T on the isothermal bulk modulus is less important than that of P on it.
The calculated heat capacity CPat constant pressure and heat capacity CVat constant volume with T at different P are shown in Fig.6.There is little difference between CPand CVat low temperatures.However,at high temperature,the CVapproaches to a constant,CPincreases monotonously with the increment of the temperature.The values follow the Debye model at low temperature(CV(T)-T3)and the classical behavior(CV(T)-3R for mono-atomic solids)is found at sufficiently high temperatures,obeying Dulong and Petit’s Rule.From Fig.6,one can also see that the heat capacity increases with the temperatures at the same pressure and decreases with the pressures at the same temperature,and the inf l uences of the temperature on the heat capacity are much more significant than that of the pressure on it.

FIG.7VariationoftheDebyetemperatureΘand Gr¨uneisen parameter γ with pressure P.
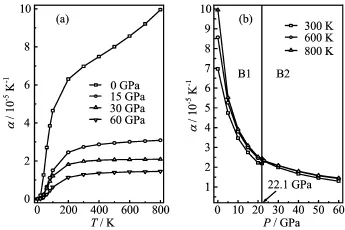
FIG.8 Temperature T(a)and pressure P(b)dependence of the thermal expansion coefficient α for EuS.
The Debye temperature Θ is a fundamental parameter of a material which is link to many physical properties such as speci fic heat,elastic constants,and melting point[36].The Debye temperature and the Gru¨neisen parameter at various temperatures and di ff erent pressures are presented in Fig.7.Our calculated Debye temperature at T=0 K is 278.51 J/(mol K),which is in agreement with the results of 274.04 J/(mol K) from Eq.(12)and 276 J/(mol K)from Ref.[21]and 280 J/(mol K)from Ref.[37].From Fig.7,one can fi nd:(i)When the temperature keeps constant,the Debye temperature increases almost linearly with applied pressures;while the Gru¨neisen parameter decreases smoothly with pressures.(ii)When the pressure keeps constant,the Debye temperature decreases with the increasing temperatures;while the Gru¨neisen parameter increases with the increasing temperatures.In virtue of the fact that the e ff ect of increasing pressure on the material is the same as decreasing temperature of the material.(iii)The Debye temperature at the temperature of 800 K is lower than that at 300 K,which shows that the vibration frequency of the particles in EuS changes with the pressures and the temperatures.
The thermal expansion coefficient α with T and P for EuS is presented in Fig.8.From Fig.8(a),α increaseswith T3at low temperature and gradually approaches a linear increase at high temperatures and then the increasing trend becomes gentler.The effects of pressure on α are very small at low temperatures;the effects are increasingly obvious as the temperature increases. As P increases,α decreases rapidly and the effects of T become less and less pronounced,resulting in linear high-temperature behaviour.It is noteworthy that the high-temperature dependence of α is not linear at low pressures(0 GPa);this is an indication of the inadequacy of the quasi-harmonic approximation at high temperature and low pressure.It can be found that α converges to a constant value at high temperature and pressure.However,from Fig.8(b),as the pressure increases,α decreases almost exponentially,and the higher the temperature is,the faster α decreases. It shows that the effect of temperature is much greater than that of pressure on α.
IV.CONCLUSION
The structural properties and phase transition and elastic constants of EuS at high pressure are computed by the ultrasoft pseudopotentials within the generalized gradient approximation in the frame of density functional theory.We carry out total energy calculations over a wide range of volume from 0.6V0to 1.2V0,and obtain the equilibrium ratio of the normalized volume V/V0for a given volume.The obtained pressure dependence on the normalized volume is in excellent agreement with the experimental result.
The aggregate elastic modulus(B,G,E),Poisson’s ratio and the shear anisotropic factor A of EuS at high pressure from 0 GPa to 60 GPa considering phase transition are also calculated.An analysis of the calculated parameters reveals the anisotropy in EuS.When P>10 GPa,the calculated values of the B/G(>1.75) increase with pressure,which indicates that pressure can improve ductility.The obtained Poisson’s ratios are very close to the value of 0.30,which means that the interatomic forces in the EuS are central forces.The compressional and shear wave velocities,and the Debye temperature are successfully obtained.The experimental values of the sound velocity,Poisson ratio,and Debye temperature under high pressure are not available for comparison yet,but considering the case of Refs.[38, 39],our predicted data should be credible.
The other thermodynamic properties are predicted using the quasi-harmonic Debye model.It is found that the high temperature leads to a smaller adiabatic bulk modulus,a smaller Debye temperature,a larger Gr¨uneisen parameter,a larger heat capacity,and a bigger thermal expansion coefficient at constant pressure. But the high pressure gives birth to a lager isothermal bulk modulus,a larger Debye temperature,a smaller Gr¨uneisen parameter,a smaller heat capacity,and a smaller thermal expansion coefficient at constant temperature.The thermal expansion coefficient and heat capacity at constant volume are shown to converge to a nearly constant value at high pressures and temperatures.
V.ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.40804034 and No.11304141),the Natural Science Foundation of the Education Department of Henan Province of China (No.2011B140014),the Program for the Science and Technology Department of Henan Province of China (No.112102310641),and the Program for Innovative Research Team(in Science and Technology)in University of Henan Province(No.13IRTSTHN020).
[1]F.J.Ried,L.K.Matsan,J.F.Miller,and R.C.Maines, J.Phys.Chem.Solids 25,969(1964).
[2]R.Didchenko and F.P.Gortsema,J.Phys.Chem. Solids 24,863(1963).
[3]R.Akimoto,M.Kobayashi,and T.Suzuki,J.Phys. Soc.Jpn.62,1490(1993).
[4]I.N.Goncharenko and I.Mirebeau,Europhys.Lett.37, 633(1997).
[5]C.J.M.Rooymans,Solid State Commun.3,421 (1965).
[6]A.Chatterjee,A.K.Singh,and A.Jayaraman,Phys. Rev.B 6,2285(1972).
[7]A.Jayaraman,A.K.Singh,A.Chatterjee,and S.U. Devi,Phys.Rev.B 9,2513(1974).
[8]M.Horne,P.Strange,W.M.Temmerman,Z.Szotek, A.Svane,and H.Winter,J.Phys.:Condens.Matter 16,5061(2004).
[9]J.Kunes and W.E.Pickett,Physica B 359,205(2005).
[10]I.N.Goncharenko and I.Mirebeau,Phys.Rev.Lett. 80,1082(1998).
[11]D.Singh,M.Rajagopalan,and A.K.Bandyopadhyay, Solid State Commun.112,39(1999).
[12]D.Singh,M.Rajagopalan,M.Husain,and A.K. Bandyopadhyay,Solid State Commun.115,323(2000).
[13]A.Svane,P.Strange,W.M.Temmerman,Z.Szotek, H.Winter,and L.Petit,Phys.Stat.Sol.(b)223,105 (2001).
[14]D.Rached,M.Ameri,M.Rabah,R.Khenata,A. Bouhemadou,N.Benkhettou,and M.D.el Hannani, Phys.Stat.Sol.(b)244,1988(2007).
[15]W.M.Temmerman,A.Svane,L.Petit,M.L¨uders,P. Strange,and Z.Szotek,Phase Trans.80,415(2007).
[16]D.Vanderbilt,Phys.Rev.B 41,7892(1990).
[17]J.P.Perdew,K.Burke,and M.Ernzerhof,Phys.Rev. Lett.77,3865(1996).
[18]H.J.Monkhorst and J.D.Pack,Phys.Rev.B 13,5188 (1976).
[19]M.D.Segall,P.J.D.Lindan,M.J.Probert,C.J. Pickard,P.J.Hasnip,S.J.Clark,and M.C.Payne,J. Phys.:Condens.Matter 14,2717(2002).
[20]A.Svane,G.Santi,Z.Szotek,W.M.Temmerman,P. Strange,M.Horne,G.Vaitheeswaran,V.Kanchana,L. Petit,and H.Winter,Phys.Stat.Sol.(b)241,3185 (2004).
[21]Y.Shapira and T.B.Reed,Conf.Proc.5,837(1971).
[22]J.Wang,J.Li,S.Yip,S.Phillpot,and D.Wolf,Phys. Rev.B 52,12627(1995).
[23]D.C.Wallace,Thermodynamics of Crystals,New York: John Wiley&Sons,20(1972).
[24]B.B.Karki,G.J.Ackland,and J.Crain,J.Phys.: Condens.Matter 9,8579(1997).
[25]T.H.K.Barron and M.L.Klein,Proc.Phys.Soc.85, 523(1965).
[26]K.Tsubouchi and N.Mikoshiba,IEEE.Trans.Sonics Ultrason.Su-32,634(1985).
[27]A.Reuss,Z.Angew.Math.Mech.9,49(1929).
[28]G.V.Sin’ko and N.A.Smirnov,J.Phys.:Condens. Matter 14,6989(2002).
[29]O.L.Anderson,J.Phys.Chem.Solids 24,909(1963). [30]S.F.Pugh,Philos.Mag.45,823(1954).
[31]V.Tvergaard and J.W.Hutchinson,J.Am.Ceram. Soc.71,157(1988).
[32]F.Peng,Q.Liu,H.Z.Fu,and X.D.Yang,Solid State Commun.149,56(2009).
[33]F.Peng,H.Z.Fu,and X.D.Yang,Solid State Commun.145,91(2008).
[34]F.Peng,Y.Han,H.Z.Fu,and X.Cheng,Phys.Stat. Sol.(b)245,2743(2008).
[35]F.Peng,H.Z.Fu,and X.D.Yang,Phys.B 403,2851 (2008).
[36]P.Ravindran,L.Fast,P.A.Korzhavyi,B.Johansson,J.Wills,and O.Eriksson,J.Appl.Phys.84,4891 (1998).
[37]E.M.Dudnik,G.V.Lashkarev,Y.B.Paderno,and V. A.Obolonchik,Inorg.Mater.2,833(1966).
[38]T.Iitaka and T.Ebisuzaki,Phys.Rev.B 64,012103 (2001).
[39]O.G¨ulseren and R.E.Cohen,Phys.Rev.B 65,064103 (2002).
ceived on March 16,2014;Accepted on May 8,2014)
?Author to whom correspondence should be addressed.E-mail:pengfengscu@gmail.com,Tel.:+86-379-62960015,FAX:+86-379-65526093
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS2014年4期
CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS2014年4期
- CHINESE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS的其它文章
- Exchange Bias Effect in Phase Separated La0.33Pr0.34Ca0.33MnO3Thin Films
- Corrosion Study on Tantalum in Anhydrous Ethanol
- Kinetics Study on O2Adsorption and OHadDesorption at Pt(111),Its Implication to Oxygen Reduction Reaction Kinetics
- Phase Transition Behaviour of VO2Nanorods
- Effect of Molybdenum Doping on Oxygen Permeation Properties and Chemical Stability of SrCo0.8Fe0.2O3-δ
- Preparation of TiO2/Bi2O3Microf i bers and Their Photocatalytic Activity
