Treating Alzheimer’s disease with Yizhijiannao granules by regulating expression of multiple proteins in temporal lobe
Hong Zhu, Liuyang Luo, Sihang Hu, Keli Dong, Guangcheng Li, Ting Zhang
1 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan Province, China
2 Department of Emergency, Bao-an District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China
Treating Alzheimer’s disease with Yizhijiannao granules by regulating expression of multiple proteins in temporal lobe
Hong Zhu1, Liuyang Luo2, Sihang Hu1, Keli Dong1, Guangcheng Li1, Ting Zhang1
1 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan Province, China
2 Department of Emergency, Bao-an District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China
Yizhijiannao granules have been shown to improve cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease patients. The present study sought to explore the mechanisms involved in the cognitive enhancing effects of Yizhijiannao granule. Senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice with learning and memory disorders were intragastrically treated with Yizhijiannao granule for 8 weeks. Mice intragastrically treated with double distilled water for 8 weeks were considered as the control group. 2D gel electrophoresis was used to isolate total protein from the temporal lobe of senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice, and differential protein spots were obtained by mass spectrometry. Thirty-seven differential protein spots were found in the temporal lobe area of both groups. Ten protein spots were identi fi ed: high mobility group box 1, dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1, neuroglobin, hemoglobin beta adult major chain, peroxiredoxin-6, co fi lin-1, fl otillin 1, peptidylprolyl isomerase A, voltage-dependent anion channel-2 and chaperonin containing TCP1, and subunit 2. Among other functions, these proteins are separately involved in the regulation of amyloid beta production, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, regulation of tau phosphorylation, and regulation of neuronal apoptosis. Our results revealed that Yizhijiannao granule can regulate the expression of various proteins in the temporal lobe of senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice, and may be therapeutically bene fi cial for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
nerve regeneration; traditional Chinese medicine; neurodegeneration; Alzheimer’s disease; Yizhijiannao granule; mass spectrometry; cognition; neural regeneration
Funding: This study was supported by Startup Fund for 125 Scholars of Third Xiangya Hospital; and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, No. 07JJ5017.
Zhu H, Luo LY, Hu SH, Dong KL, Li GC, Zhang T. Treating Alzheimer’s disease with Yizhijiannao granules by regulating expression of multiple proteins in temporal lobe. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(13):1283-1287.
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease is a complex disease that is associated with many dysfunctional processes (Huang and Mucke, 2012; Reiman, 2014). Modern medicines that target speci fi c dysfunctional processes will have limited effect in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. However, therapeutic methods and drugs that have broad-spectrum applications will provide greater outcomes (Huang and Mucke, 2012; Reiman, 2014). Traditional Chinese medicines, which are natural drugs with multiple components and functions, may be possible candidates for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
More and more evidence has shown that the temporal lobe plays an important role in Alzheimer’s disease (Scheff and Price, 1993; Frisoni et al., 2010; Oosterman et al., 2012). Postmortem ultrastructural examination of the temporal lobe in Alzheimer’s disease patients has revealed signi fi cant synapse loss. In addition, atrophy of medial temporal structures has been considered to be a valid diagnostic marker at the mild cognitive impairment stage. Temporal lobe atrophy was closely related to lower executive function, general cognitive function, and episodic memory performance in Alzheimer’s disease.
The senescence accelerate mouse prone 8 is a typical senile mouse model with learning and memory impairments (Wang et al., 2014). The brains of the senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 have some neuropathologic characteristics such as hyperphosphorylation of tau, and the overproduction of amyloid precursor protein and amyloid-beta protein, which are similar to those seen in Alzheimer’s disease. Other characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease shared by senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice include increased oxidative damage, decreased choline acetyltransferase activity, and increased alpha synuclein. With respect to the behavioral and histopathological signatures of Alzheimer’s disease, senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice are currently considered to be an ideal model of Alzheimer’s disease (Morley et al., 2012).
Yizhijiannao granule is a cipher prescription that has beenused for treating senile dementia for more than 13 years in our hospital. Previous studies have shown that Yizhijiannao granule can enhance cognitive performance in Alzheimer’s disease patients and Alzheimer’s disease-model mice (Yang et al., 2005; Yang and Dong, 2013). Further studies revealed that Yizhijiannao granule may exert its therapeutic effect by inhibiting neural cell apoptosis, reducing tau phosphorylation and relieving neuroinflammation (Yang et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2009). In addition, Yizhijiannao granule can inhibit early beta-amyloid (25-35)-induced PC12 cell apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2012) . Taken together, these studies suggest that the bene fi cial effect of Yizhijiannao granule involves multiple targets and pathways. Therefore, we aimed to identify target-proteins of Yizhijiannao granule that were particularly related to the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
In the present study, senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice were administered Yizhijiannao granule, and differential protein expression in the temporal lobe was identi fi ed to elucidate the multi-targeted effects of Yizhijiannao granule in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Twenty 6-month-old male senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice were obtained from the Experimental Animal Center, First Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Tianjin, China; license No. 0003740). Mice were housed in separate cages under conditions free of speci fi c pathogens at 21 ± 3°C with a relative humidity of 55-58%, exposed to a daily 12-hour light/dark cycle. Mice were given free access to food and water. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Central South University, China.
Yizhijiannaogranule preparation
Yizhijiannao granule was composed of seven commonly used herbs: Herba Epimedii, Herba Cynomorii, Radix Notoginseng, Radix Acanthopanacis Senticosi, Radix Dipsaci, Semen Platycladi, Hirudo. These herbs were mixed in the ratio of 3:3:2:2:2:2:1 (dry weight). The raw herbs for Yizhijiannao granule were purchased from the Dispensary of traditional Chinese medicine, Xiangya Third Hospital of Central South University, China. All of the herbs are regionally famous drugs and were authenticated by the herbalists of Xiangya Third Hospital. Yizhijiannao granule was extracted as previously described by Hangzhou Dekang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd (Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province, China) (Zhang et al., 2012). Yizhijiannao granule was dissolved in distilled water for administration to mice. The dose of administration used in this study was based on our previous study (Yang et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2009).
Experimental groups
A total of 20 adult male senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice were equally and randomly divided into two groups: (1) treatment group, intragastrically administrated Yizhijiannao granule 1 mL/d for 8 weeks; (2) control group: intragastrically administrated the same volume of double distilled water for 8 weeks. No death or infection occurred in both groups. All 20 mice were included in the fi nal analysis without deletion.
Sample collection of brain tissue
Eight weeks following treatment, all mice were decapitated. Brain tissues were quickly segregated from the temporal lobe at near-freezing temperature, and each tissue was stored in Eppendorf tubes at -80°C in liquid nitrogen.
Total protein extraction and concentration determinationEach tissue (50 mg in average wet weight) was homogenized with 400 μL lysis solution, comprising 2 mmol/L thiourea, 7 mmol/L Urea, 100 mmol/L dithiothreitol, 5 mmol/L phenylmethyl sulfonyl fl uoride, 4% (v/v) 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate, 0.5 mmol/L ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 40 mmol/L Tris, 2% (v/v) NP-40, 1% (v/v) Triton X-100, and 2% pharmalyte). After incubation at 37°C for 1 hour, the homogenate was then centrifuged at 12,000 r/min for 1 hour to obtain the supernatant. The protein concentration of the supernatant was determined using the 2D Quant Kit (Amersham Bioscience, Buckinghamshire, UK.
2D gel electrophoresis
2D gel electrophoresis was performed according to a previous method (Gorg et al., 1995), in a horizontal electrophoresis system, IPGphorTMfor the fi rst-dimensional isoelectric focusing on IPG strips (24 cm long, linear gradient 3-10). In the second dimension of 2D-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, proteins with similar isoelectric points were further separated according to their molecular weight on a sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel.
Staining and computer analysis of the 2D gel
According to the previous blue silver staining method (Gorg et al., 2000), the gels were stained using Coomassie blue-G250. The Coomassie blue-stained gels were then scanned with an Image scanner (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and analyzed by LabScan software to get the gel image. The gel image was then analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively using PD Quest software (Bio-Rad). Only spots showing a difference in the integrated intensity larger than twofold between the control group and the treated group were further studied.
Mass spectrometric analysis
The protein spots of interest were cut off the 2D gels and enzymatically degraded with modi fi ed trypsin in accordance with a previous method (Hubbard, 2006). The spots were then analyzed using the MALDI-TOF-MS (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to get the peptide mass fi ngerprint. The peptide mass fingerprint data were submitted to the MASCOT software (http://www. Matrix-science.com/cgi/ search_form.pl?FORMVER=2&SEARCH=PMF) search engine to identify the proteins.
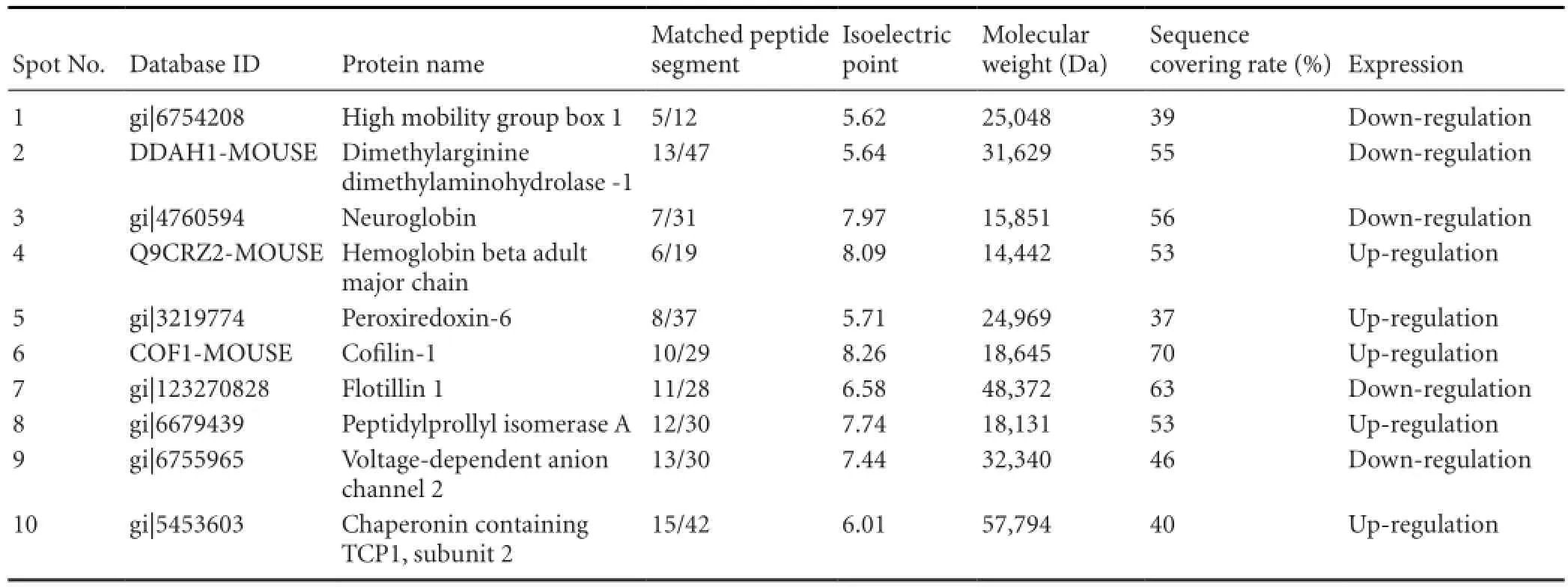
Table 1 Differential protein spots identi fi ed in mass spectrometry protein sequence database
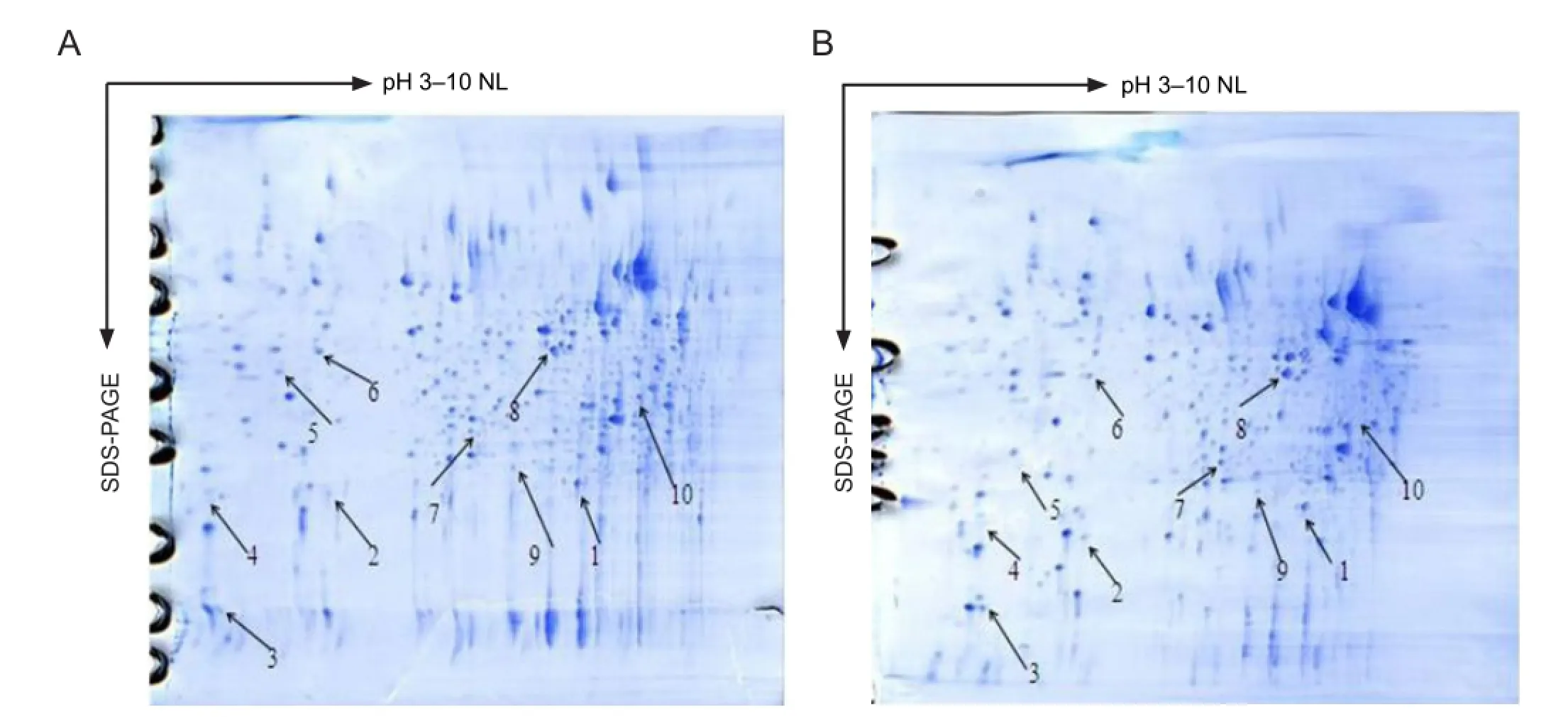
Figure 1 Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis maps in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 from the treatment group and the control group.
Figure 2 Database search results of No. 10 protein spot.
Results
Temporal 2D gel electrophoresis maps and differential protein spot identi fi cation
To ensure maximal reproducibility of the 2D gel electrophoresis experiment, we compared three samples from the treatment group and three samples from the control group in the studied brain regions. We obtained three 2D gel electrophoresis maps in each group. Approximately 900 spots per gel were detected using the PD Quest software. For the mass spectrometric analysis of the spots on the 2D gel electrophoresis maps, a threshold minimum of a two-fold up- or down-regulation in the integrated intensity between the control group and the treatment group was used to exclude proteins that differed in integrated intensity owing to small variationsoccurring randomly during the experimental process. Finally, 10 differentially expressed protein spots were identified, of which 5 protein spots were up-regulated and 5 protein spots were down-regulated (Figure 1). The database search result of protein No. 10 is shown inFigure 2. The differentially expressed protein spots identi fi ed are listed inTable 1.
Discussion
Although the fi rst presentation of Alzheimer’s disease dates back to 1906, the pathogenic mechanisms of the disease remain inadequately understood and fragmentary, some of which are in a state of serious controversy. Thus, we tend to deem that Alzheimer’s disease is a complex disease consisting of multipathogenic mechanisms that have multifactorial involvement. In our present study, the identified proteins could be assigned to several categories related to amyloid beta production, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, cell apoptosis, and tau phosphorylation.
One of the pathologic hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is the extracellular aberrant accumulation of amyloid beta in senile plaques. Recently, it was shown that lipid rafts played an important role in the amyloidogenic processing of the amyloid precursor protein; lipid rafts could function as platforms for amyloid beta production (Vetrivel and Thinakaran, 2010). The identified protein flotillin-1 has been used as a biochemical marker of lipid rafts in neural tissue (Girardot et al., 2003; Kokubo et al., 2003), and its expression is increased in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease subjects and increases in parallel to increasing stages of amyloid beta deposition (Kania et al., 2012). In our study, fl otillin-1 was down-regulated in the treatment group, thus affording fewer platforms for amyloid beta production. Therefore, it is tempting to speculate that Yizhijiannao granule may derive therapeutic effect by decreasing amyloid beta production in a platform-dismantling mechanism, which may be a new direction for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. However, further research is needed.
Numerous studies on Alzheimer’s disease during the past decade have consistently confirmed the involvement of oxidative stress in disease pathogenesis (Padurariu et al., 2013; Kosenko et al., 2014). Recently, more and more evidence shows that neuroglobin may act as an intracellular reactive oxidative species and a reactive nitrogen species scavenger to play a role in neuron protection (Jin et al., 2008; Li et al., 2008). Being a reactive oxidative species scavenger, it could attenuate amyloid beta neurotoxicity in vitro, the transgenic Alzheimer phenotype in vivo, and protect PC12 cells against amyloid beta-induced cell injury (Khan et al., 2007; Liu and Chan, 2014). Taken together, these evidences indicate that increasing neuroglobin expression may have a therapeutic effect in Alzheimer’s disease. With neuroglobin up-regulated, our research shows that Yizhijiannao granule may use the antioxidant properties of neuroglobin to obtain a therapeutic effect.
There is a consensus that chronic in fl ammatory processes are involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (Liu and Chan, 2014; Serpente et al., 2014). When glial cells are activated, they release proin fl ammatory factors to initiate the neuroinflammatory process. High mobility group box 1, a mediator of acute and chronic in fl ammatory diseases (Asavarut et al., 2013), was previously reported to be signi fi cantly upregulated in Alzheimer’s disease brains and colocalize with senile plaques (Takata et al., 2003). Based on the above research, we may assume that high mobility group box 1 probably plays a role in the chronic in fl ammatory process in Alzheimer’s disease brains as a proin fl ammatory factor. In our study, Yizhijiannao granule may down-regulate high mobility group box 1 to accomplish an anti-in fl ammatory effect.
Another major pathologic characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease is the accumulation of intra-cellular neuro fi brillary tangles, which contains paired helical filaments composed of the microtubule-associated protein tau. Peptidyl-prolyl-cis-trans isomerase A (PPIase A, pin1) was shown to be involved in tauopathies in Alzheimer’s disease, and the levels of soluble pin1 are decreased in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients (Lu et al., 1999a, b). Pin1 can bind to phosphorylated tau at Thr-231, dephosphorylating the phosphorylated tau and facilitating conformational changes (Kimura et al., 2013), thereby restoring its biological function of binding microtubules and enhancing microtubule assembly. The decrease of pin1 in brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients may break the balanced phosphorylation state of tau proteins, leading to tau hyperphosphorylation and neuro fi brillary tangle formation. In view of the evidence presented above, we presume that pin1 could protect against tau hyperphosphorylation and thus inhibit the formation of neuro fi brillary tangles. In our study, pin1 was up-regulated in the treated group, so Yizhijiannao granule may play a part in the regulation of tau phosphorylation to produce a therapeutic effect.
Voltage-dependent anion channel is considered to be a global regulator, or governor, of mitochondrial function (Lemasters and Holmuhamedov, 2006; Colombini, 2012), participating in many cellular processes, especially in cell apoptosis (Shoshan-Barmatz et al., 2010). Voltage-dependent anion channel-2, up-regulated in our study, was reported to be capable of inhibiting BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis, with cells deficient in voltage-dependent anion channel-2 exhibiting enhanced BAK oligomerization and being more susceptible to apoptotic death (Cheng et al., 2003). Conversely, overexpression of voltage-dependent anion channel-2 selectively prevented BAK activation and inhibited the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway (Cheng et al., 2003). Therefore, voltage-dependent anion channel-2 may facilitate a neuroprotective function in Alzheimer’s disease based on its anti-apoptotic property. By up-regulating voltage-dependent anion channel-2, Yizhijiannao granule may be involved in this anti-apoptotic process.
Proteomics has been considered to be a useful tool to analyze protein changes in complex diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there are also some shortcomings for this analytical tool that should be taken into consideration; the main problem is that proteomics cannot isolate all the low-abundance proteins, some of which may own strong bioactivities and play important roles in Alzheimer’s disease onset andtreatment. Therefore, further research is needed to verify the results of proteomics studies. Collectively, in the present study, we have identi fi ed some proteins which could be potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Yizhijiannao granule could induce a remedial effect on Alzheimer’s disease owing to its targeting of multiple pathways, which include reducing amyloid beta production, anti-oxidant, anti-in fl ammatory and anti-apoptotic properties, and dephosphorylation of tau proteins.
Acknowledgments:We thank Xing XW from Central Laboratory of Third Xiangya Hospital, China for guidelines in proteomics.
Author contributions:Zhu H designed this study, analyzed data and wrote the draft of the manuscript. Luo LY and Hu SH were responsible for data integration. Li GC authorized the manuscript and guided the study. Dong KL provided technical suggestions. Zhang T was in charge of animal preparations. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Con fl icts of interest:None declared.
Asavarut P, Zhao H, Gu J, Ma D (2013) The role of HMGB1 in in fl ammation-mediated organ injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan 51:28-33.
Cheng EH, Sheiko TV, Fisher JK, Craigen WJ, Korsmeyer SJ (2003) VDAC2 inhibits BAK activation and mitochondrial apoptosis. Science 301:513-517.
Colombini M (2012) VDAC structure, selectivity, and dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:1457-1465.
Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Jack CRJ, Scheltens P, Thompson PM (2010) The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:67-77.
Girardot N, Allinquant B, Langui D, Laquerriere A, Dubois B, Hauw JJ, Duyckaerts C (2003) Accumulation of fl otillin-1 in tangle-bearing neurones of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29:451-461.
Gorg A, Boguth G, Obermaier C, Posch A, Weiss W (1995) Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with immobilized pH gradients in the fi rst dimension (IPG-Dalt): the state of the art and the controversy of vertical versus horizontal systems. Electrophoresis 16:1079-1086.
Gorg A, Obermaier C, Boguth G, Harder A, Scheibe B, Wildgruber R, Weiss W (2000) The current state of two-dimensional electrophoresis with immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis 21:1037-1053.
Huang Y, Mucke L (2012) Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 148:1204-1222.
Hubbard MJ (2006) Hierarchical protein identifications and assignments. J Proteome Res 5:733.
Jin K, Mao XO, Xie L, Khan AA, Greenberg DA (2008) Neuroglobin protects against nitric oxide toxicity. Neurosci Lett 430:135-137.
Kania E, Pajak B, Gajkowska B, Orzechowski A (2012) Lipid rafts in Alzheimer’s disease. Postepy Biochem 58:209-216.
Khan AA, Mao XO, Banwait S, Jin K, Greenberg DA (2007) Neuroglobin attenuates beta-amyloid neurotoxicity in vitro and transgenic Alzheimer phenotype in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:19114-19119.
Kimura T, Tsutsumi K, Taoka M, Saito T, Masuda-Suzukake M, Ishiguro K, Plattner F, Uchida T, Isobe T, Hasegawa M, Hisanaga S (2013) Isomerase Pin1 stimulates dephosphorylation of tau protein at cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk5)-dependent Alzheimer phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem 288:7968-7977.
Kokubo H, Helms JB, Ohno-Iwashita Y, Shimada Y, Horikoshi Y, Yamaguchi H (2003) Ultrastructural localization of fl otillin-1 to cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains, rafts, in rat brain tissue. Brain Res 965:83-90.
Kosenko EA, Solomadin IN, Tikhonova LA, Reddy VP, Aliev G, Kaminsky YG (2014) Pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease: role of oxidative stress, amyloid-beta peptides, systemic ammonia and erythrocyte energy metabolism. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 13:112-119.
Lemasters JJ, Holmuhamedov E (2006) Voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) as mitochondrial governator--thinking outside the box. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762:181-190.
Li RC, Morris MW, Lee SK, Pouranfar F, Wang Y, Gozal D (2008) Neuroglobin protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress. Brain Res 1190:159-166.
Liu L, Chan C (2014) The role of in fl ammasome in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev 15C:6-15.
Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Lu KP (1999a) Function of WW domains as phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-binding modules. Science 283:1325-1328.
Lu PJ, Wulf G, Zhou XZ, Davies P, Lu KP (1999b) The prolyl isomerase Pin1 restores the function of Alzheimer-associated phosphorylated tau protein. Nature 399:784-788.
Morley JE, Farr SA, Kumar VB, Armbrecht HJ (2012) The SAMP8 mouse: a model to develop therapeutic interventions for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 18:1123-1130.
Oosterman JM, Oosterveld S, Rikkert MG, Claassen JA, Kessels RP (2012) Medial temporal lobe atrophy relates to executive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Int Psychogeriatr 24:1474-1482.
Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Lefter R, Serban IL, Stefanescu C, Chirita R (2013) The oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatr Danub 25:401-409.
Reiman EM (2014) Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: advances in 2013. Lancet Neurol 13:3-5.
Scheff SW, Price DA (1993) Synapse loss in the temporal lobe in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 33:190-199.
Serpente M, Bonsi R, Scarpini E, Galimberti D (2014) Innate immune system and in fl ammation in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathogenesis to treatment. Neuroimmunomodulat 21:79-87.
Shoshan-Barmatz V, De Pinto V, Zweckstetter M, Raviv Z, Keinan N, Arbel N (2010) VDAC, a multi-functional mitochondrial protein regulating cell life and death. Mol Aspects Med 31:227-285.
Takata K, Kitamura Y, Kakimura J, Shibagaki K, Tsuchiya D, Taniguchi T, Smith MA, Perry G, Shimohama S (2003) Role of high mobility group protein-1 (HMG1) in amyloid-beta homeostasis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:699-703.
Vetrivel KS, Thinakaran G (2010) Membrane rafts in Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid production. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:860-867.
Wang H, Dong K, Li G (2009) Effect of yizhi jiannao granules on the expression of Pin1 and HMGB1mRNA in the hippocampus of SAMP8 mice. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban 34:63-66.
Wang H, Lian K, Han B, Wang Y, Kuo SH, Geng Y, Qiang J, Sun M, Wang M (2014) Age-related alterations in the metabolic profile in the hippocampus of the senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8: a spontaneous Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Alzheimers Dis 39:841-848.
Yang P, Dong K (2013) A Study of clinical observation on patients of Alzheimer Disease Treated by YizhiJiannao-Granule. Xin Zhong Yi 45:56-58.
Yang P, Dong K, Zeng W (2005) Influences of traditional medicine Yizhijiannao keli on behavior of SAMP8. Zhongguo Xingwei Yixue Kexue 14:601-602.
Yang P, Dong K, Zeng W (2006) Effect of yizhi jiannao granule on the behavior and neuron apoptosis in SAMP/8 mice. Zhongnan Daxue Xuebao: Yixue Ban 31:56-59.
Zhang T, Zhang Z, Dong K (2012) Yizhijiannao Granule and a combination of its effective monomers,icariin and Panax notoginseng saponins,inhibit early PC12 cell apoptosis induced by beta-amyloid(25-35). Neural Regen Res 7:1845-1850.
Copyedited by Diwakarla S, Pack M, Wang J, Qiu Y, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
10.4103/1673-5374.137575
Guangcheng Li, Ph.D., Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South
University, Changsha 410013, Hunan Province, China, yellingu@163.com.
http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2014-05-20
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Changes in motor function in the unaffected hand of stroke patients should not be ignored
- Targeted thrombolysis strategies for neuroprotective effect
- Selective verbal memory impairment due to left fornical crus injury in a patient with intraventricular hemorrhage
- Morphological changes of gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons in the rat preoptic area across puberty
- Role of Notch-1 signaling pathway in PC12 cell apoptosis induced by amyloid beta-peptide (25-35)
- Autophagy activation aggravates neuronal injury in the hippocampus of vascular dementia rats

