A feasible strategy for focal cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury: remote ischemic postconditioning
Qiang Liu, Shengnian Zhou Yaodong Wang, Fang Qi, Yuan Song, Siwei Long
1 Department of Neurology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Brain Science Research Institute of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
2 Department of Neurology, Third Af fi liated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
3 Department of Neurosurgery, Third Af fi liated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
A feasible strategy for focal cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury: remote ischemic postconditioning
Qiang Liu1,2, Shengnian Zhou1, Yaodong Wang3, Fang Qi2, Yuan Song2, Siwei Long2
1 Department of Neurology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Brain Science Research Institute of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
2 Department of Neurology, Third Af fi liated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
3 Department of Neurosurgery, Third Af fi liated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning Province, China
It is difficult to control the degree of ischemic postconditioning in the brain and other ischemia-sensitive organs. Remote ischemic postconditioning could protect some ischemia-sensitive organs through measures on terminal organs. In this study, a focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury model was established using three cycles of remote ischemic postconditioning, each cycle consisted of 10-minute occlusion of the femoral artery and 10-minute opening. The results showed that, remote ischemic postconditioning signi fi cantly decreased the percentage of the infarct area and attenuated brain edema. In addition, in fl ammatory nuclear factor-κB expression was signi fi cantly lower, while anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 expression was signi fi cantly elevated in the cerebral cortex on the ischemic side. Our fi ndings indicate that remote ischemic postconditioning attenuates focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, and that the neuroprotective mechanism is mediated by an anti-apoptotic effect and reduction of the in fl ammatory response.
nerve regeneration; remote ischemic postconditioning; focal cerebral ischemia; neuroprotection; apoptosis; inflammation; brain injury; nuclear factor-κB; Bcl-2; neural regeneration
Funding:This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation (Joint Fund) of Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 2013022021.
Liu Q, Zhou SN, Wang YD, Qi F, Song Y, Long SW. A feasible strategy for focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: remote ischemic postconditioning. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(15):1460-1463.
Introduction
In 1986, Murry et al. (1986) introduced the concept of“ischemic preconditioning”, which then gradually developed into a treatment strategy for cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. However, the application of ischemic preconditioning has been greatly restricted due to the dif fi culty in predicting cerebral ischemic diseases. In 2003, Zhao et al. (2003) proposed the concept of ischemia postconditioning, in which they believed that giving short-term ischemic stimulation at the early stage following ischemia and reperfusion, may produce adaptability of the organism in response to ischemia, and accordingly prevent the organism from severe damage caused by long-term ischemia. However, it remains a problem to regulate the degree of ischemic postconditioning in the ischemia and hypoxia-sensitive organs and tissues, such as the brain. Remote ischemia postconditioning (RIP) cannot only be performed following ischemia, but also protects ischemia-sensitive organs through measures on the non-critical remote organs (Ren et al., 2011). RIP is a kind of endogenous protective measure, which can trigger an endogenous protective effect, enhance ischemic tolerance in the brain, and ultimately reduce nervous system damage following ischemia-reperfusion (Pignataro et al., 2013). This study aimed to explore the neuroprotective effects of RIP in rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Fifty clean male 10-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 220-280 g, were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Dalian Medical University of China (license No. SCXK (Liao) 2008-0002). All rats were maintained and fed at 22-25°C, 56-70% humidity, for a week to adapt to the experimental conditions. Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University in China. Rats were allowed free access to water, but were fasted prior to experimentation. After feeding, rats were randomly divided into sham group (n= 10), model group (n= 20) and RIP group (n= 20).
Establishment of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model
Excepting the sham group, the cerebral ischemia/reperfusion model was established in rats from the model and RIP groups,viaocclusion of the middle cerebral artery using the modi fi ed suture method as previously described (Longa et al., 1989). Rats were weighed and anesthetized with 4% (v/v) en fl urane combined with 30% (v/v) O2and 70% (v/v) N2O. The anesthesia effect was maintained using 2% (v/v) en fl urane com-bined with 30% (v/v) O2and 70% (v/v) N2O during surgery. A midline incision was cut along the neck, followed by separation of the right common carotid artery, internal carotid artery and external carotid artery. A 0.4 mm nylon fi lament was inserted into the internal carotid arteryviathe external carotid artery until it reached 2.0 cm lateral to the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery and external carotid artery. 2 hours later, the nylon thread was removed and ischemia was terminated to avoid the reperfusion of blood fl ow. Intraoperative blood fl ow in the brain was monitored with a laser Doppler (AD Instruments, Sydney, Australia) to verify the occlusion. Sham-operated rats were anesthetized, exposing the right common carotid artery, internal carotid artery and external carotid artery.
RIP intervention
At 8 and 24 hours after modeling, 10 rats in the RIP group were selected for isolation and exposure of the bilateral femoral arteries. The obtained femoral artery was occluded for 10 minutes and then opened for 10 minutes for a total of 3 cycles. In the sham and model groups, the femoral artery was only exposed.
Assessment of neurological score
At 24 hours after modeling, neurological behavior of rats was assessed according to the methods of Longa et al. (1989). 0 point: neurological symptoms are not obvious; 1 point: the left anterior paw cannot fully extend; 2 points: rats rotate to the left side; 3 points: rats slump to the left when walking; 4 points: rats cannot walk independently and lose consciousness; 5 points: rats die from subarachnoid hemorrhage accompanied by infarction. Rats scoring more than 1 point were regarded successful models. Animals that died of pulmonary insuf fi ciency and suffocation were excluded from the study.
Triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining of cerebral infarction
At 8 and 24 hours post ischemia-reperfusion, rats were intraperitoneally anesthetized with 5 mL 3.6% (w/v) chloral hydrate, and perfused with 250 mL ice-cold saline. The brain tissue was harvested and sliced into continuous coronal sections. Sections were incubated in 2% (w/v) TTC solution (Amresco Inc., Radnor, Pennsylvania, USA) at 37°C in the dark for 30 minutes. Normal brain tissue was stained red by TTC, while necrotic tissue remained unstained. Normal tissue and necrotic tissue were separated and weighed to calculate the percentage of brain infarct. Infarct ratio (%) = weight of infarct tissue/(normal tissue weight + infarct tissue weight) × 100%.
Measurements of brain water content
At 8 and 24 hours post ischemia-reperfusion, the water content in the brain was measured, which re fl ected the degree of brain edema. Rats were euthanized 24 hours after modeling, brain tissue was isolated, the left and right hemispheres were separated and the wet weight was measured immediately. Tissue was baked at 110°C for 24 hours, then the dried weight was measured. Brain water content (%) = (wet weight - dry weight)/wet weight × 100%.
Western blot analysis for detection of nuclear factor (NF)-κB and Bcl-2 expression in the ischemic cerebral cortex of rats
Three rats in each group were killed by decapitation at 8 and 24 hours after modeling and the cerebral cortex on the ischemic side was harvested. Tissue was lysed on ice for 30 minutes, homogenated, treated with ultrasound (20 kHz, 30 seconds × 3), and centrifugated at 13,000 r/min for 15 minutes. The supernatant was transferred to a new EP tube. Protein concentration was detected using the NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scienti fi c Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) and the samples were stored at -20°C for further use. Protein samples were isolated on 10% (w/v) SDS-polyacrylamide gels and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membrane. After blocking with 5% (w/v) skim milk at room temperature for 1 hour, protein samples were incubated with rabbit anti-rat NF-κB or Bcl-2 antibody (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) at 4°C overnight, rinsed with Tris-buffer saline with Tween-20 (TBST) three times, followed by incubation with goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:1,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) at room temperature for 1.5 hours, and TBST washing. Protein absorbance was determined using the LAS4000mini chemiluminescence imager (GE, Fair fi eld, CT, USA).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 19.0 Software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Data were expressed as mean ± SD. One-way analysis of variance and the least significant difference test were used for comparison. AP< 0.05 indicated statistical signi fi cance.
Results
RIP had no impact on the neurological function of rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
Sham-operated rats showed no neurological deficit symptoms. In the model group, rats exhibited varying degrees of neurological de fi cit symptoms, such as leforelimb fl exion and left-prone walking paths. RIP had no impact on the neurological function scores in rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (P> 0.05;Figure 1).
RIP alleviated cerebral infarction in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
TTC staining revealed that rat brain tissue from the sham group stained red, no infarction was found; in the model group, the rat brain tissue was obviously swollen, ischemic tissue became white, and the infarct area was very large, involving the cortex, basal ganglia and hippocampus. The infarction was more apparent at 24 hours post-occlusion, but the infarction ratio was similar to that at 8 hours post-occlusion (P> 0.05); the infarction area was reduced following RIP (P< 0.05,vs. model group;Figure 2).
RIP alleviated brain edema in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
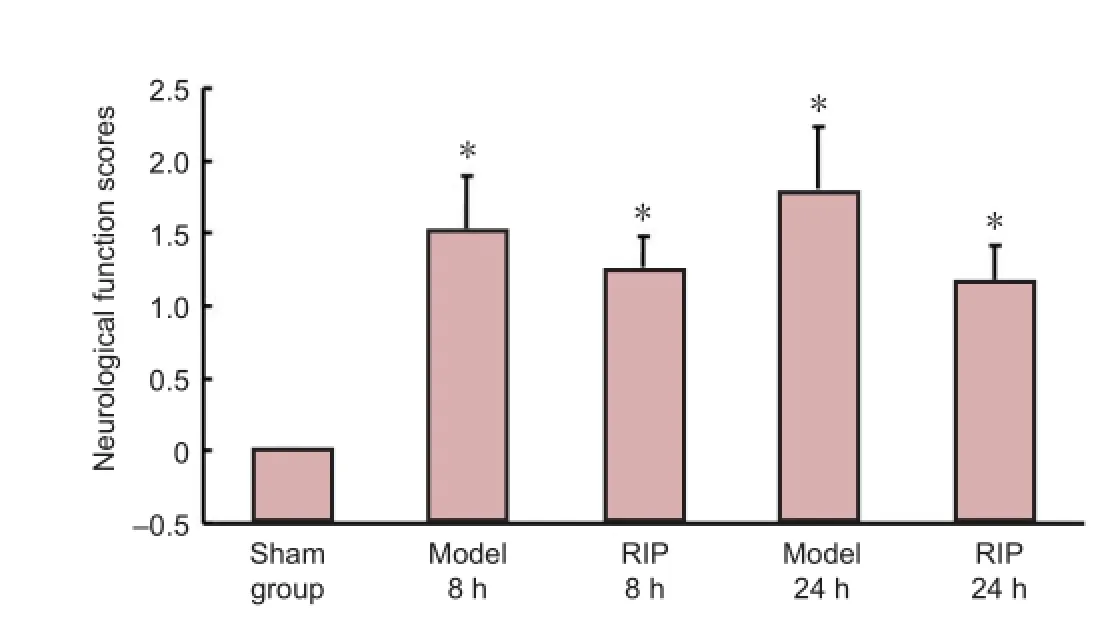
Figure 1 Effect of remote ischemic postconditioning (RIP) on neurological function scores in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
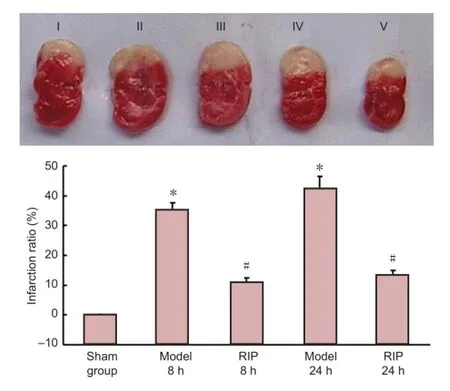
Figure 2 Effect of remote ischemic postconditioning (RIP) on the infarction ratio in rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (TTC staining).
Compared with the sham group, brain water content in rats from the model group were signi fi cantly increased (P< 0.05), but were signi fi cantly decreased in the RIP group at 8 and 24 hours aer occlusion (P<0.05;Figure 3).
Effect of RIP on in fl ammatory factor NF-κB and anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 in the ischemic cerebral cortex of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injured rats
Western blot analysis results showed that the expression level of NF-κB in the model group was significantly higher (P< 0.01), while the expression level of Bcl-2 was signi fi cantly lower (P< 0.01) compared with the sham group. At 8 and 24hours following RIP, NF-κB expression levels decreased signi fi cantly (P< 0.01), while Bcl-2 expression was signi fi cantly elevated (P< 0.01;Figure 4) compared with the model group.

Figure 3 Effect of remote ischemic postconditioning (RIP) on brain water content in rats with focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
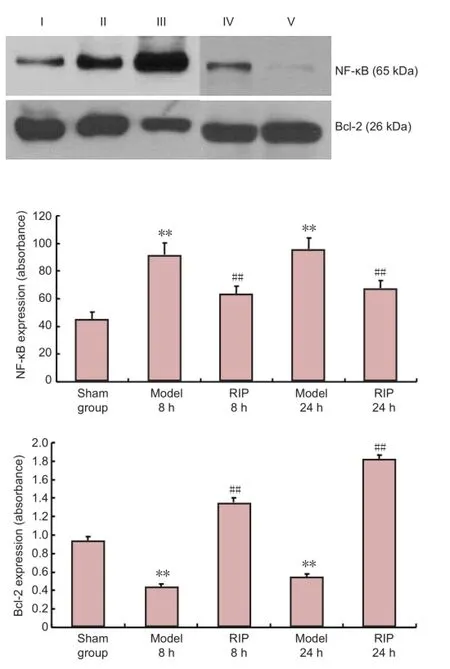
Figure 4 Effect of remote ischemic postconditioning (RIP) on nuclear factor (NF)-κB and Bcl-2 expression in the ischemic cerebral cortex of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats (western blot assay).
Discussion
Growing evidence from existing studies has shown that RIP following ischemia, reperfusion can reduce infarct volume and alleviate reperfusion injury, with the underlying mechanism involving brain edema, the blood-brain barrier, and regulation of nerve cell apoptosis (Zhao et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2010; Geng et al., 2012). Li et al. (2006) adopted, for the fi rst time, remote ischemic preconditioning for the treatment of ischemia/reperfusion injury, and found that it effectively protected the myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ren et al. (2009) further demonstrated that RIP reduced infarct volume, significantly improved neurological function, and protected brain function in a rat model of left artery permanent occlusion. Ischemic postconditioning was shown to prevent cerebral ischemic injury in various animal experiments. This evidence highlights the potential contribution of RIP in the clinical treatment of stroke. Scholars have already investigated ischemia/reperfusion injury in human cases through non-invasive occlusion of the femoral artery (Loukogeorgakis et al., 2007). Ischemic tolerance is a very strong endogenous protective measure. Ischemic tolerance produced by ischemic preconditioning and remote ischemic preconditioning contributes to the protection of ischemic organs, in which a variety of signaling pathways or protein kinases are involved (Shimohata et al., 2007a, b; Scartabelli et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2009; Tsubota et al., 2010; Xie et al., 2013).
NF-κB is a recently discovered transcription factor that is closely related to ischemic brain injury (Gabriel et al., 1999). Increasing evidence indicates that the activation of NF-κB is a key player in the in fl ammatory response. Many studies have found that NF-κB is activated in nerve cells, brain vascular endothelial cells and glial cells during ischemia (Villoslada and Genain, 2004). Rehni et al. (2009) demonstrated that the neuroprotective effect of RIP against ischemia/reperfusion injury was largely dependent on the activation of the NF-κB pathway. Similarly, the results of the present study showed that NF-κB expression levels were signi fi cantly elevated in the brain tissue of middle cerebral artery occlusion rats, and RIP e ff ectively reduced the levels of NF-κB.is evidence indicates that NF-κB is a critical target for the neuroprotective e ff ect of RIP. Meanwhile, the process of focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is accompanied by apoptosis (Fisher and Schaebitz, 2000; Sugawara et al., 2004). Our findings showed that anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression in brain tissue was signi fi cantly decreased aer ischemic injury, suggesting that a large amount of cells become apoptotic during the cerebral infarction process. Moreover, RIP increased Bcl-2 expression and reduced infarct volume.
In summary, RIP can reduce infarct volume, and its neuroprotective e ff ect is achieved through the inhibition of NF-κB expression and an increase in Bcl-2 expression.
Fisher M, Schaebitz W (2000) An overview of acute stroke therapy: past, present, and future. Arch Intern Med 160:3196-3206.
Gabriel Cl, Justicia C, Camins A, Planas AM (1999) Activation of nuclear factor-κB in the rat brain after transient focal ischemia. Mol Brain Res 65:61-69.
Geng X, Ren C, Wang T, Fu P, Luo Y, Liu X, Yan F, Ling F, Jia J, Du H, Ji X, Ding Y (2012) E ff ect of remote ischemic postconditioning on an intracerebral hemorrhage stroke model in rats. Neurol Res 34:143-148.
Li CM, Zhang XH, Ma XJ, Luo M (2006) Limb ischemic postconditioning protects myocardium from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Scand Cardiovasc J 40:312-317.
Liu L, Ran K, Chang Y (2010) E ff ect of iso fl urane delayed preconditioning on the expression of Bcl-2 and caspase-3 in myocardium during ischemia reperfusion in rabbits. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 35:346-350.
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84-91.
Loukogeorgakis SP, Williams R, Panagiotidou AT, Kolvekar SK, Donald A, Cole TJ, Yellon DM, Dean fi eld JE, MacAllister RJ (2007) Transient limb ischemia induces remote preconditioning and remote postconditioning in humans by a K(ATP)-channel dependent mechanism. Circulation 116:1386-1395.
Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124-1136.
Pignataro G, Cuomo O, Vinciguerra A, Sirabella R, Esposito E, Boscia F, Di Renzo G, Annunziato L (2013) NCX as a key player in the neuroprotection exerted by ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Adv Exp Med Biol 961:223-240.
Rehni AK, Bhateja P, Singh N (2009) Diethyl dithiocarbamic acid, a possible nuclear factor kappa B inhibitor, attenuates ischemic postconditioning-induced attenuation of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Can J Physiol Pharm 87:63-68.
Ren C, Yan Z, Wei D, Gao X, Chen X, Zhao H (2009) Limb remote ischemic postconditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1288:88-94.
Ren C, Gao M, Dornbos D, Ding Y, Zeng X, Luo Y, Ji X (2011) Remote ischemic post-conditioning reduced brain damage in experimental ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Res 33:514-519.
Scartabelli T, Gerace E, Landucci E, Moroni F, Pellegrini-Giampietro DE (2008) Neuroprotection by group I mGlu receptors in a rat hippocampal slice model of cerebral ischemia is associated with the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway: a novel postconditioning strategy? Neuropharmacology 55:509-516.
Shimohata T, Zhao H, Steinberg GK (2007a) Epsilon PKC may contribute to the protective e ff ect of hypothermia in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. Stroke 38:375-380.
Shimohata T, Zhao H, Sung JH, Sun G, Mochly-Rosen D, Steinberg GK (2007b) Suppression of [delta]PKC activation aer focal cerebral ischemia contributes to the protective e ff ect of hypothermia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1463-1475.
Sugawara T, Fujimura M, Noshita N, Kim GW, Saito A, Hayashi T, Narasimhan P, Maier CM, Chan PH (2004) Neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. NeuroRx 1:17-25.
Tsubota H, Marui A, Esaki J, Bir SC, Ikeda T, Sakata R (2010) Remote postconditioning may attenuate ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the murine hindlimb through adenosine receptor activation. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 40:804-809.
Villoslada P, Genain CP (2004) Role of nerve growth factor and other trophic factors in brain in fl ammation. Prog Brain Res 146:403-414.
Wang HY, Wang GL, Yu YH, Wang Y (2009) The role of phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt pathway in propofol-induced postconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res 1297:177-184.
Xie R, Wang P, Ji X, Zhao H (2013) Ischemic post-conditioning facilitates brain recovery aer stroke by promoting Akt/mTOR activity in nude rats. J Neurochem 127:723-732.
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2006) Interrupting reperfusion as a stroke therapy: ischemic postconditioning reduces infarct size aer focal ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1114-1121.
Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, Kerendi F, Wang NP, Guyton RA, Vinten-Johansen J (2003) Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H579-588.
Copyedited by Diuakarla S, Norman C, Yu J, Yang Y, Li CH, Song LP, Zhao M
Shengnian Zhou, M.D., Department of Neurology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Brain Science Research Institute of Shandong University, No. 107 Wenhuaxi Road, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China, zhoushengnian126@126.com.
10.4103/1673-5374.139463
http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2014-07-04
- 中國神經再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Changes in cortical activation patterns accompanying somatosensory recovery in a stroke patient: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study
- Changes in brain activation in stroke patients after mental practice and physical exercise: a functional MRI study
- Integration of animal behaviors under stresses with different time courses
- Pretreatment with Danhong injection protects the brain against ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Neuroprotective effect of pretreatment with ganoderma lucidum in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat hippocampus
- Optimal therapeutic dose and time window of picroside II in cerebral ischemic injury